-
操作EXCEL计算3万条数据的NDVI并填入
Python操作EXCEL,计算3万条数据的NDVI并填入
问题描述
现在是有构建好了的查找表,不过构建了3万条数据,在excel中手动计算每行的NDVI值太麻烦了,也不会操作。
就试试python吧,毕竟python自动处理大型EXCEL数据很方便
思路
先用pd打开表格,存为dataframe。然后创建一个空的列表用来存入计算好的ndvi。在第一个循环中,计算每行的ndvi,并添加到列表中去。然后打开原来的文件,在第二个循环中,对每一个指定位置逐行写入列表中对应的ndvi值。最后保存文件
源代码
import pandas as pd # 使用python在已存在的excel数据表中的特定位置写入数据 # excel表中的行和列都是从1开始的 import openpyxl as op filePath = r"C:/Users/lenovo/Desktop/lut.xlsx" def readDataFile(readPath): # readPath: 数据文件的地址和文件名 try: if (readPath[-4:] == ".csv"): dfFile = pd.read_csv(readPath, header=0, sep=",") # 间隔符为逗号,首行为标题行 # dfFile = pd.read_csv(filePath, header=None, sep=",") # sep: 间隔符,无标题行 elif (readPath[-4:] == ".xls") or (readPath[-5:] == ".xlsx"): # sheet_name 默认为 0 dfFile = pd.read_excel(readPath,header=0) # 首行为标题行 # dfFile = pd.read_excel(filePath, header=None) # 无标题行 elif (readPath[-4:] == ".dat"): # sep: 间隔符,header:首行是否为标题行 dfFile = pd.read_table(readPath, sep=" ", header=0) # 间隔符为空格,首行为标题行 # dfFile = pd.read_table(filePath,sep=",",header=None) # 间隔符为逗号,无标题行 else: print("不支持的文件格式。") except Exception as e: print("读取数据文件失败:{}".format(str(e))) return return dfFile data=readDataFile('C:/Users/lenovo/Desktop/lut.xlsx') print(data) NIR=data['nir'] R=data['r'] list=[] for i in range(len(data)): ndvi=(NIR[i]-R[i])/(NIR[i]+R[i]) list.append(ndvi) print(list) tableAll = op.load_workbook(filePath) table1 = tableAll['lut'] for i in range(len(list)): table1.cell(i+2, 11, list[i]) tableAll.save(filePath)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
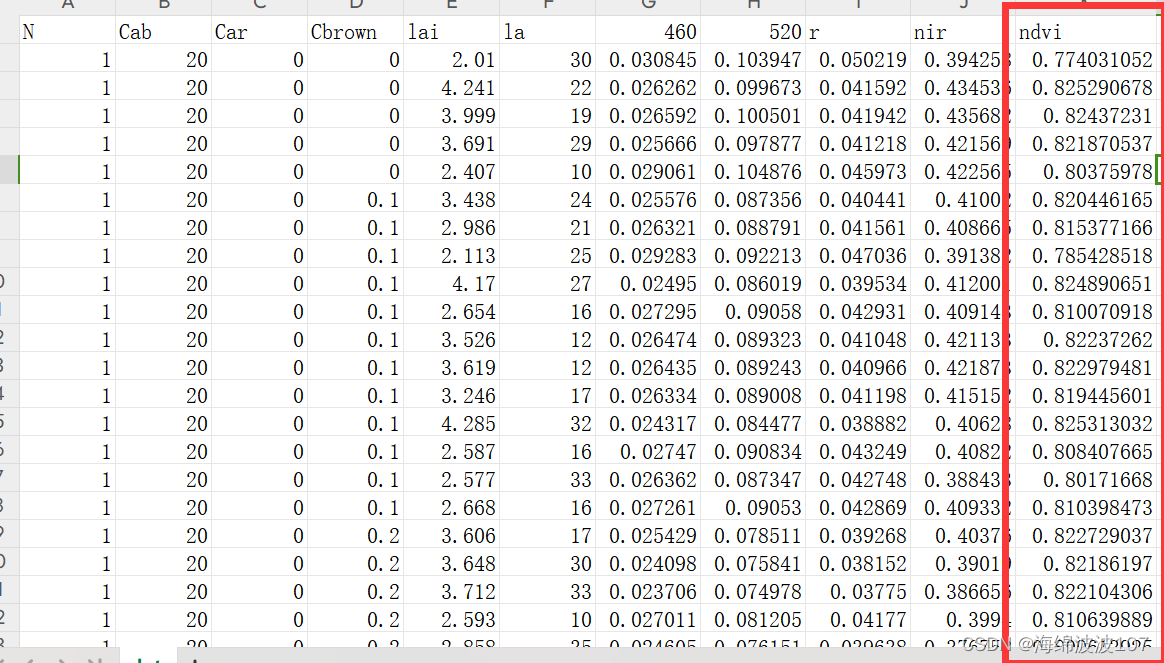
结果
注意
1、把红波段和近红波段的列名从数字改为字符r和nir,因为pd的[‘’]索引方式好像不支持数字。
2、openpyxl库只支持.xlsx格式的数据
3、cell函数行列索引从1开始代码注释
1、tableAll = op.load_workbook(filePath)
使用openpyxl库中的load_workbook()方法来打开指定路径下的工作簿文件,并将其赋值给变量tableAll。其中op是openpyxl库的别名或者导入的模块。
2、table1 = tableAll[‘lut’]
打开工作簿文件的sheet,根据自己的sheet_name来改
3、table1.cell(i+2, 11, list[i])
cell函数第一个元素为指定行,第二个为指定列,最后一个为待写入的数据。注意此时行和列的索引都是从1开始的,与dataframe,len(),range()等等python常见的索引都是从0开始不同。
-
相关阅读:
uniapp——实现电子签名功能——基础积累
肖sir__设计测试用例方法之状态迁移法05_(黑盒测试)
kaptcha-2.3.2.jar
Fast-DDS的代码编译及源码安装-2
Spring Cloud智慧工地源码,利用计算机技术、互联网、物联网、云计算、大数据等新一代信息技术开发,微服务架构
RabbitMQ的RPM包安装和Python读写操作
【HTML/CSS篇】牛客题库练习
经典面试题:为什么 ConcurrentHashMap 的读操作不需要加锁?
牛客 —— 链表中倒数第k个结点(C语言,快慢指针,配图)
INVETA peer-stream 自述文件
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43920838/article/details/133458593
