-
LeetCode 2251. 花期内花的数目:排序 + 二分
【LetMeFly】2251.花期内花的数目:排序 + 二分
力扣题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-flowers-in-full-bloom/
给你一个下标从 0 开始的二维整数数组
flowers,其中flowers[i] = [starti, endi]表示第i朵花的 花期 从starti到endi(都 包含)。同时给你一个下标从 0 开始大小为n的整数数组persons,persons[i]是第i个人来看花的时间。请你返回一个大小为
n的整数数组answer,其中answer[i]是第i个人到达时在花期内花的 数目 。示例 1:

输入:flowers = [[1,6],[3,7],[9,12],[4,13]], persons = [2,3,7,11] 输出:[1,2,2,2] 解释:上图展示了每朵花的花期时间,和每个人的到达时间。 对每个人,我们返回他们到达时在花期内花的数目。
示例 2:
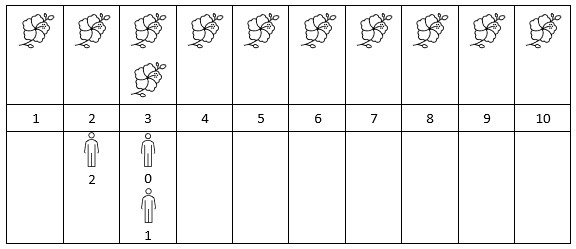
输入:flowers = [[1,10],[3,3]], persons = [3,3,2] 输出:[2,2,1] 解释:上图展示了每朵花的花期时间,和每个人的到达时间。 对每个人,我们返回他们到达时在花期内花的数目。
提示:
1 <= flowers.length <= 5 * 104flowers[i].length == 21 <= starti <= endi <= 1091 <= persons.length <= 5 * 1041 <= persons[i] <= 109
方法一:排序 + 二分
将所有的开花时间放入一个数组并从小到大排序;将所有的闭花时间也放入一个数组并从小到大排序。
对于某个时刻(某一天),当前盛开的花朵的数量为: 开花时间小于等于当前时间的花数 − 闭花小于等于当前时间前一天的花数 开花时间小于等于当前时间的花数 - 闭花小于等于当前时间前一天的花数 开花时间小于等于当前时间的花数−闭花小于等于当前时间前一天的花数。
如何快速得到非降序数组 a a a中 ≤ k \leq k ≤k的元素的个数?二分即可。(C++的upper_bound / Python的bisect_right)
- 时间复杂度 O ( ( n + m ) log n ) O((n + m)\log n) O((n+m)logn),其中 n = l e n ( f l o w e r s ) n = len(flowers) n=len(flowers), m = l e n ( p e o p l e ) m = len(people) m=len(people)
- 空间复杂度 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),力扣返回值不计入算法空间复杂度
AC代码
C++
class Solution { public: vector<int> fullBloomFlowers(vector<vector<int>>& flowers, vector<int>& people) { vector<int> start(flowers.size()), end(flowers.size()), ans(people.size()); for (int i = 0; i < flowers.size(); i++) { start[i] = flowers[i][0]; end[i] = flowers[i][1]; } sort(start.begin(), start.end()); sort(end.begin(), end.end()); for (int i = 0; i < people.size(); i++) { // 到这一天为止的开花总数 - 到这一天的前一天为止的闭花总数 int hanagasaku = upper_bound(start.begin(), start.end(), people[i]) - start.begin(); // 花が咲く(はながさく) int hanagatiru = upper_bound(end.begin(), end.end(), people[i] - 1) - end.begin();// 花が散る(はながちる) ans[i] = hanagasaku - hanagatiru; } return ans; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
Python
真简!
# from typing import List # from bisect import bisect_right class Solution: def fullBloomFlowers(self, flowers: List[List[int]], people: List[int]) -> List[int]: start = sorted([f[0] for f in flowers]) end = sorted([f[1] for f in flowers]) return [bisect_right(start, p) - bisect_right(end, p - 1) for p in people]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
同步发文于CSDN,原创不易,转载经作者同意后请附上原文链接哦~
Tisfy:https://letmefly.blog.csdn.net/article/details/133378624 -
相关阅读:
【无标题】
mybatis 如何实现批量更新呢?
单元测试(unit testing)到底是什么?
Java常用工具环境安装手册(持续更新)
【MATLAB】BiGRU神经网络回归预测算法
测试开发日记:python代码调试神器,工作提效利器
力扣环形链表(1)进阶环形链表(2)及环形链表的约瑟夫问题
双端口USB Type-C控制器 CYPD6227 (CYPD6227-96BZXI)
Word控件Spire.Doc 【图像形状】教程(2) ;在 C#、VB.NET 中从 Word 中提取图像
海螺问问编写shell脚本zabbix监控华为设备微信接入预警
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Tisfy/article/details/133378624
