-
获取热门电影算法
功能#2:获取热门电影
为我们的“Netflix”项目实现“获取热门电影”功能。
我们将介绍以下内容
描述
解决方案
复杂性措施
时间复杂度
空间复杂度
描述#
现在,我们需要建立一个标准,以便将来自多个国家的顶级电影组合成一个单一的顶级电影列表。为了扩展,内容搜索以分布式方式执行。每个国家/地区的搜索结果在单独的列表中生成。给定列表的每个成员都按受欢迎程度排名,1最受欢迎和受欢迎程度随着排名数字的增加而下降。假设以下标题由提供的 ID 表示:

电影映射到他们的行列
我们将得到n 个列表,这些列表都按受欢迎程度的升序排列。我们必须将这些列表组合成一个列表,该列表将按升序排序,即从最好到最差。请记住,排名对于个别电影是唯一的,一个排名可以在多个列表中。
让我们通过一个插图更好地理解这一点:

将多个评级列表合并为一个
解决方案#
由于我们的任务涉及多个列表,因此您应该将问题分解为多个任务,从一次合并两个列表的问题开始。然后,您应该将前两个列表的结果与第三个列表相结合,依此类推,直到达到最后一个。
让我们讨论一下我们将如何实现这个过程:
-
将第一个列表视为结果,并将其存储在一个变量中。
-
遍历列表的列表,从第二个列表开始,并将其与我们存储的列表组合为结果。结果应该存储在同一个变量中。
-
当组合两个列表时,比如l1和l2,维护一个prev指向虚拟节点的指针。
-
如果 list 的值l1小于或等于 list 的值l2,则将前一个节点连接到l1并递增l1。否则,对 list 执行相同的操作l2。
-
继续重复上述步骤,直到一个列表指向一个nil值。
-
将非零列表连接到合并后的列表并返回。
让我们看看下面解决方案的代码:
package main func merge2SortedLists(l1, l2 *LinkedListNode) *LinkedListNode { dummy := &LinkedListNode{data: -1} prev := dummy for l1 != nil && l2 != nil { if l1.data <= l2.data { prev.next = l1 l1 = l1.next } else { prev.next = l2 l2 = l2.next } prev = prev.next } if l1 == nil { prev.next = l2 } else { prev.next = l1 } return dummy.next } func mergeKSortedLists(lists []*LinkedListNode) *LinkedListNode { if len(lists) > 0 { res := lists[0] for i := 1; i < len(lists); i++ { res = merge2SortedLists(res, lists[i]) } return res } return &LinkedListNode{data: -1} } func main() { a := createLinkedList([]int{11, 41, 51}) b := createLinkedList([]int{21,23,42}) c := createLinkedList([]int{25,56,66,72}) list1 := []*LinkedListNode{a, b, c} display(mergeKSortedLists(list1)) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
package main import ( "fmt" "math/rand" ) type LinkedListNode struct { key int data int next *LinkedListNode arbitrartPointer *LinkedListNode } func createLinkedList(lst []int) *LinkedListNode { var head *LinkedListNode var tail *LinkedListNode for _, x := range lst { newNode := &LinkedListNode{data: x} if head == nil { head = newNode } else { tail.next = newNode } tail = newNode } return head } func insertAtHead(head *LinkedListNode, data int) *LinkedListNode { newNode := &LinkedListNode{data: data} newNode.next = head return newNode } func insertAtTail(head *LinkedListNode, data int) *LinkedListNode { newNode := &LinkedListNode{data: data} if head == nil { return newNode } temp := head for temp.next != nil { temp = temp.next } temp.next = newNode return head } func createRandomList(length int) *LinkedListNode { var listHead *LinkedListNode for i := 0; i < length; i++ { listHead = insertAtHead(listHead, rand.Intn(100)) } return listHead } func toList(head *LinkedListNode) []int { var lst []int temp := head for temp != nil { lst = append(lst, temp.data) temp = temp.next } return lst } func display(head *LinkedListNode) { temp := head for temp != nil { fmt.Printf("%d", temp.data) temp = temp.next if temp != nil { fmt.Printf(", ") } } fmt.Printf("\n") } func mergeAlternating(list1, list2 *LinkedListNode) *LinkedListNode { if list1 == nil { return list2 } if list2 == nil { return list1 } head := list1 for list1.next != nil && list2 != nil { temp := list2 list2 = list2.next temp.next = list1.next list1.next = temp list1 = temp.next } if list1.next == nil { list1.next = list2 } return head } func isEqual(list1, list2 *LinkedListNode) bool { if list1 == list2 { return true } for list1 != nil && list2 != nil { if list1.data != list2.data { return false } list1 = list1.next list2 = list2.next } return (list1 == list2) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
复杂性措施#
时间复杂度#
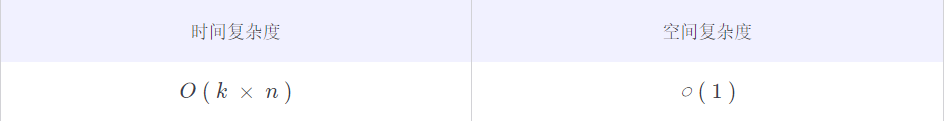
时间复杂度为 O(k \times n)O ( k × n ),其中k是列表的数量,n是单个列表的最大长度。
空间复杂度#
O(1)○ ( 1 ),因为使用了恒定的空间。
-
-
相关阅读:
Hibernate 分页
一个bug引发的对大端小端的深入思考
工业互联网系列白皮书(合集)
排序算法:选择排序(直接选择排序、堆排序)
PWA 应用 Service Worker 缓存的一些可选策略和使用场景
Python高校学生档案管理系统毕业设计源码071528
基于安卓android微信小程序的好物分享系统
golang八股文整理(持续搬运)
private key ssh连接服务器
Composer初次接触
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_50071922/article/details/121651319
