-
Python项目实战:基于2D或3D的区域增长算法
一、简介
1.1、算法详解
区域生长是一种图像分割方法,通过相邻像素之间的相似性进而合并成一个独立区域。
算法步骤:
(1)初始化:手动选择一个种子像素点(或多个种子点)作为起始点,将其标记为一个(或多个)独立的连通区域。
(2)生长准则:通常是基于像素的灰度强度、颜色、纹理等属性的相似性。如果相邻像素满足生长准则,它们将被合并到当前区域。
(3)生长过程:从种子点开始,按照生长准则不断地检查并合并相邻像素,直到不能再生长为止(使用递归、队列或堆栈等数据结构来实现)。
(4)标记和分类:在生长过程中,标记每一个像素属于哪个连通区域。
(5)终止条件: 可以根据像素的属性、区域的大小、生长次数等来决定何时停止生长。1.2、可调参数
区域生长算法的可调参数(影响着算法的性能和结果)
-
种子点(Seed Point):种子点是区域生长的起始位置。选择合适的种子点对于获取所需的区域非常重要。 -
容忍度(Tolerance):容忍度(即相邻像素的范围)表示两个像素值之间的允许差异范围。容忍度值越大,允许的差异越大,区域生长范围就越广。容忍度值越小,增长的区域越接近种子点的像素值。 -
连接条件(Connectivity):定义了哪些邻域像素被认为是连接的一部分。- 在2D图像中:
- (1)使用
4连接(一个像素的邻域包括上下左右四个像素) - (2)使用
8连接(一个像素的邻域包括上下左右四个像素以及四个对角线方向的像素)
- (1)使用
- 在3D图像中:
- (1)使用
6连接(一个像素的邻域包括其上下左右前后六个相邻像素) - (2)使用
26连接(一个像素的邻域包括其上下左右前后以及八个对角线方向的像素)
- (1)使用
- 在2D图像中:
-
最大连接区域大小(Max Region Size):限制区域生长的大小,以防止无限制地增长。 -
像素相似度度量(Pixel Similarity Metric):决定了像素之间相似性的度量方式。如:灰度强度相似度、颜色相似度、纹理相似度等等。
二、项目实战
2.1、2D图像(4连接 + 8连接):10 x 10
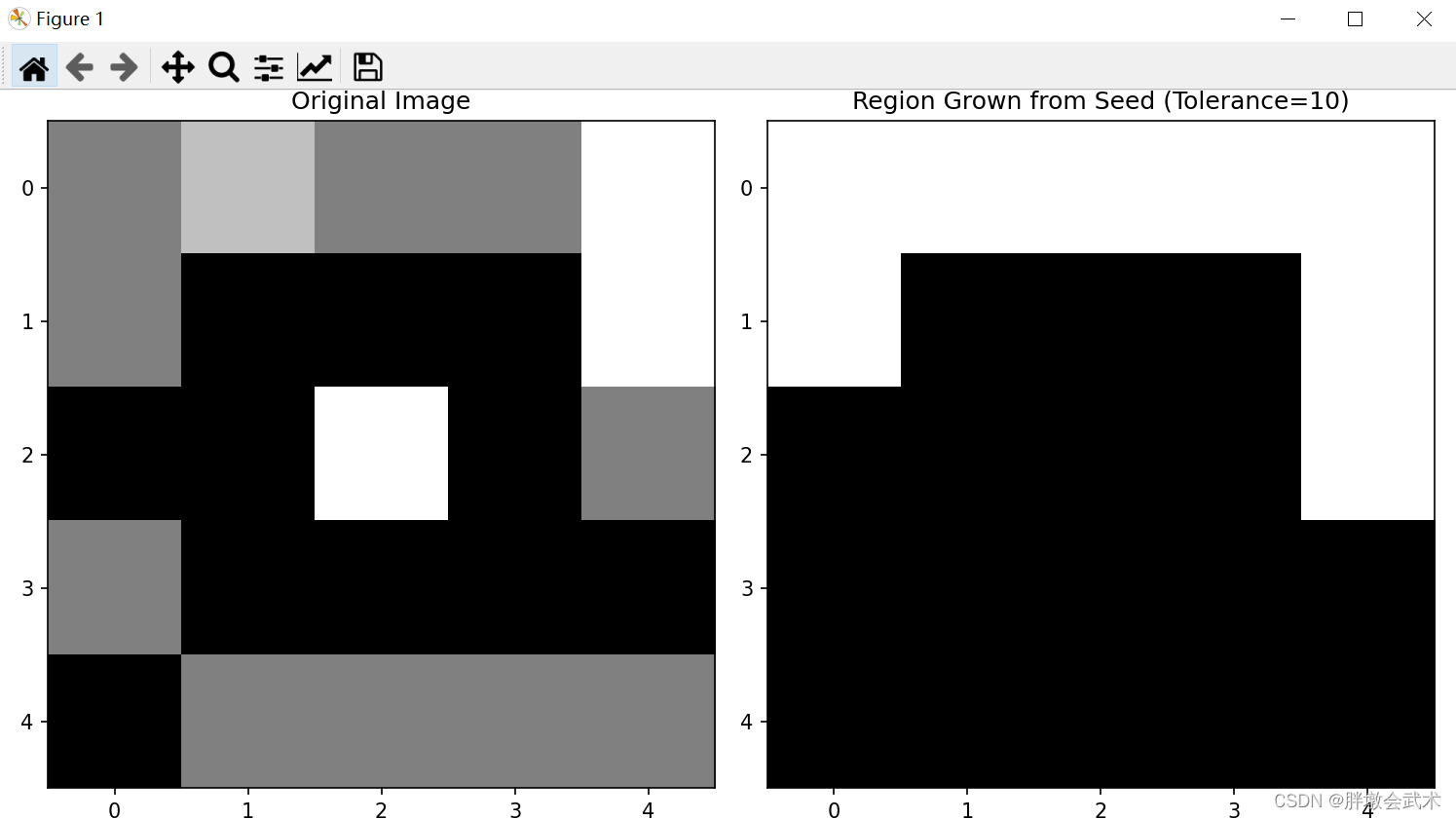
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt """ 区域生长算法:2D图像中的4连接条件 + 8连接条件 """ def region_growing_4connect(image, seed, tolerance=1, max_region_size=None): """在2D图像中,4连接条件""" region = np.zeros_like(image, dtype=bool) height, width = image.shape stack = [(seed[0], seed[1])] while stack: y, x = stack.pop() if not (0 <= x < width and 0 <= y < height): continue if region[y, x]: continue if max_region_size is not None and np.sum(region) >= max_region_size: continue ########################################################################### """ 若添加该条件:其会将多个被独立区域完全分割,导致区域生长无法与周边独立区域进行连接。 若取消该条件:则将两个独立区域连接的同时,中间的黑色区域也会同时连接。 备注:当像素值与背景值差异越小则影响越大,反之差异越大则影响越小。 备注:被黑色包围的区域认定为 "独立区域" 备注:区域生长最终结果必定是一个独立的整体 """ if image[y, x] == 0: # 如果当前像素值为0(不连接黑色块),则跳过 continue ########################################################################### if abs(image[seed[0], seed[1]] - image[y, x]) <= tolerance: region[y, x] = 1 stack.extend([(y - 1, x), (y + 1, x), (y, x - 1), (y, x + 1)]) return region def region_growing_8connect(image, seed, tolerance=1, max_region_size=None): """在2D图像中,8连接条件""" region = np.zeros_like(image, dtype=bool) height, width = image.shape stack = [(seed[0], seed[1])] while stack: y, x = stack.pop() if not (0 <= x < width and 0 <= y < height): continue if region[y, x]: continue if max_region_size is not None and np.sum(region) >= max_region_size: continue ########################################################################### """ 若添加该条件:其会将多个被独立区域完全分割,导致区域生长无法与周边独立区域进行连接。 若取消该条件:则将两个独立区域连接的同时,中间的黑色区域也会同时连接。 备注:当像素值与背景值差异越小则影响越大,反之差异越大则影响越小。 备注:被黑色包围的区域认定为 "独立区域" 备注:区域生长最终结果必定是一个独立的整体 """ if image[y, x] == 0: # 如果当前像素值为0(不连接黑色块),则跳过 continue ########################################################################### if abs(image[seed[0], seed[1]] - image[y, x]) <= tolerance: region[y, x] = 1 stack.extend([(y - 1, x), (y + 1, x), (y, x - 1), (y, x + 1), (y - 1, x - 1), (y - 1, x + 1), (y + 1, x - 1), (y + 1, x + 1)]) return region if __name__ == "__main__": # (1)灰度图像数据 image = np.array([[2, 3, 2, 2, 4], [2, 0, 0, 0, 4], [0, 0, 4, 0, 2], [2, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 2, 2, 2, 2]]) # (2)选择种子点并执行区域生长 seed_point = (0, 0) # 选择3D种子点 tolerance_value = 2 # 设置容忍度,即相邻像素的范围 max_region_size = 25 # 设置最大区域大小 connect_condition = 4 # 设置连接条件 result_region = region_growing_4connect(image, seed_point, tolerance=tolerance_value, max_region_size=max_region_size) # (3)可视化显示3D原始图像和区域生长的结果(按像素值进行可视化) plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5)) plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) plt.imshow(image, cmap='gray', origin='upper') plt.title('Original Image') plt.subplot(1, 2, 2) plt.imshow(result_region, cmap='gray', origin='upper') plt.title(f'Region Grown from Seed (Tolerance={tolerance_value})') plt.tight_layout() plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
2.2、2D图像(4连接 + 8连接):100 x 100
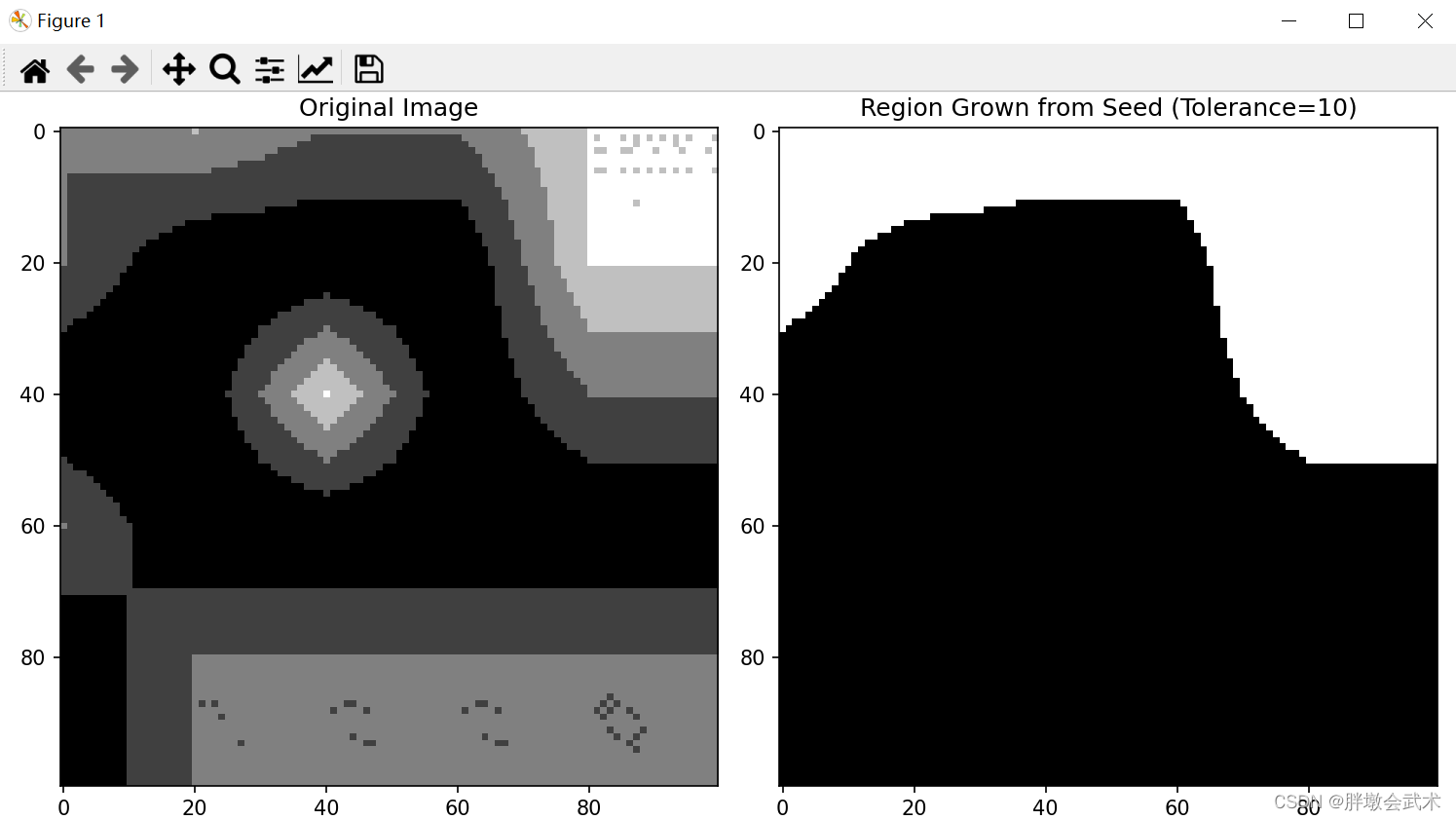
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt """ 区域生长算法:2D图像中的4连接条件 + 8连接条件 """ def region_growing_4connect(image, seed, tolerance=1, max_region_size=None): """在2D图像中,4连接条件""" region = np.zeros_like(image, dtype=bool) height, width = image.shape stack = [(seed[0], seed[1])] while stack: y, x = stack.pop() if not (0 <= x < width and 0 <= y < height): continue if region[y, x]: continue if max_region_size is not None and np.sum(region) >= max_region_size: continue ########################################################################### """ 若添加该条件:其会将多个被独立区域完全分割,导致区域生长无法与周边独立区域进行连接。 若取消该条件:则将两个独立区域连接的同时,中间的黑色区域也会同时连接。 备注:当像素值与背景值差异越小则影响越大,反之差异越大则影响越小。 备注:被黑色包围的区域认定为 "独立区域" 备注:区域生长最终结果必定是一个独立的整体 """ if image[y, x] == 0: # 如果当前像素值为0(不连接黑色块),则跳过 continue ########################################################################### if abs(image[seed[0], seed[1]] - image[y, x]) <= tolerance: region[y, x] = 1 stack.extend([(y - 1, x), (y + 1, x), (y, x - 1), (y, x + 1)]) return region def region_growing_8connect(image, seed, tolerance=1, max_region_size=None): """在2D图像中,8连接条件""" region = np.zeros_like(image, dtype=bool) height, width = image.shape stack = [(seed[0], seed[1])] while stack: y, x = stack.pop() if not (0 <= x < width and 0 <= y < height): continue if region[y, x]: continue if max_region_size is not None and np.sum(region) >= max_region_size: continue ########################################################################### """ 若添加该条件:其会将多个被独立区域完全分割,导致区域生长无法与周边独立区域进行连接。 若取消该条件:则将两个独立区域连接的同时,中间的黑色区域也会同时连接。 备注:当像素值与背景值差异越小则影响越大,反之差异越大则影响越小。 备注:被黑色包围的区域认定为 "独立区域" 备注:区域生长最终结果必定是一个独立的整体 """ if image[y, x] == 0: # 如果当前像素值为0(不连接黑色块),则跳过 continue ########################################################################### if abs(image[seed[0], seed[1]] - image[y, x]) <= tolerance: region[y, x] = 1 stack.extend([(y - 1, x), (y + 1, x), (y, x - 1), (y, x + 1), (y - 1, x - 1), (y - 1, x + 1), (y + 1, x - 1), (y + 1, x + 1)]) return region if __name__ == "__main__": ###################################################################### # (1.1)原始数组大小 original_array = np.array([[2, 3, 2, 2, 4], [2, 0, 0, 0, 4], [0, 0, 4, 0, 2], [2, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 2, 2, 2, 2]]) # (1.2)目标数组大小 target_size = (100, 100) # 目标大小 x_scale = target_size[1] / original_array.shape[1] # 计算x轴方向的缩放因子 y_scale = target_size[0] / original_array.shape[0] # 计算y轴方向的缩放因子 target_array = np.zeros(target_size, dtype=original_array.dtype) # 创建目标数组 # (1.3)使用双线性插值填充目标数组 for y in range(target_size[0]): for x in range(target_size[1]): # 3.1、计算在原始数组中的坐标 original_x = x / x_scale original_y = y / y_scale # 3.2、四个最近的原始数组中的点 x1, y1 = int(original_x), int(original_y) x2, y2 = x1 + 1, y1 + 1 # 3.3、边界检查 x1 = min(max(x1, 0), original_array.shape[1] - 1) x2 = min(max(x2, 0), original_array.shape[1] - 1) y1 = min(max(y1, 0), original_array.shape[0] - 1) y2 = min(max(y2, 0), original_array.shape[0] - 1) # 3.4、双线性插值 fx = original_x - x1 fy = original_y - y1 target_array[y, x] = (1 - fx) * (1 - fy) * original_array[y1, x1] + fx * (1 - fy) * original_array[y1, x2] + \ (1 - fx) * fy * original_array[y2, x1] + fx * fy * original_array[y2, x2] image = target_array ###################################################################### # (2)选择种子点并执行区域生长 seed_point = (0, 0) # 选择3D种子点 tolerance_value = 2 # 设置容忍度,即相邻像素的范围 max_region_size = 10000 # 设置最大区域大小 connect_condition = 4 # 设置连接条件 result_region = region_growing_4connect(image, seed_point, tolerance=tolerance_value, max_region_size=max_region_size) # (3)可视化显示3D原始图像和区域生长的结果(按像素值进行可视化) plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5)) plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) plt.imshow(image, cmap='gray', origin='upper') plt.title('Original Image') plt.subplot(1, 2, 2) plt.imshow(result_region, cmap='gray', origin='upper') plt.title(f'Region Grown from Seed (Tolerance={tolerance_value})') plt.tight_layout() plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
2.3、3D图像(6连接 + 26连接):10 x 10 x 10

import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt """ 区域生长算法:3D图像中的6连接条件 + 26连接条件 """ def region_growing_6connect(image, seed, tolerance=1, max_region_size=None): """在3D图像中,6连接条件""" region = np.zeros_like(image, dtype=bool) depth, height, width = image.shape stack = [(seed[0], seed[1], seed[2])] while stack: z, y, x = stack.pop() if not (0 <= x < width and 0 <= y < height and 0 <= z < depth): continue if region[z, y, x]: continue if max_region_size is not None and np.sum(region) >= max_region_size: continue ########################################################################### """ 若添加该条件:其会将多个被独立区域完全分割,导致区域生长无法与周边独立区域进行连接。 若取消该条件:则将两个独立区域连接的同时,中间的黑色区域也会同时连接。 备注:当像素值与背景值差异越小则影响越大,反之差异越大则影响越小。 备注:被黑色包围的区域认定为 "独立区域" 备注:区域生长最终结果必定是一个独立的整体 """ if image[z, y, x] == 0: # 如果当前像素值为0(背景),则跳过 continue ########################################################################### if abs(image[seed[0], seed[1], seed[2]] - image[z, y, x]) <= tolerance: region[z, y, x] = 1 stack.extend([(z - 1, y, x), (z + 1, y, x), (z, y - 1, x), (z, y + 1, x), (z, y, x - 1), (z, y, x + 1)]) return region def region_growing_26connect(image, seed, tolerance=1, max_region_size=None): """在3D图像中,26连接条件""" region = np.zeros_like(image, dtype=bool) depth, height, width = image.shape stack = [(seed[0], seed[1], seed[2])] while stack: z, y, x = stack.pop() if not (0 <= x < width and 0 <= y < height and 0 <= z < depth): continue if region[z, y, x]: continue if max_region_size is not None and np.sum(region) >= max_region_size: continue ########################################################################### """ 若添加该条件:其会将多个被独立区域完全分割,导致区域生长无法与周边独立区域进行连接。 若取消该条件:则将两个独立区域连接的同时,中间的黑色区域也会同时连接。 备注:当像素值与背景值差异越小则影响越大,反之差异越大则影响越小。 备注:被黑色包围的区域认定为 "独立区域" 备注:区域生长最终结果必定是一个独立的整体 """ if image[z, y, x] == 0: # 如果当前像素值为0(背景),则跳过 continue ########################################################################### if abs(image[seed[0], seed[1], seed[2]] - image[z, y, x]) <= tolerance: region[z, y, x] = 1 stack.extend([(z - 1, y, x), (z + 1, y, x), (z, y - 1, x), (z, y + 1, x), (z, y, x - 1), (z, y, x + 1), (z - 1, y - 1, x), (z - 1, y + 1, x), (z + 1, y - 1, x), (z + 1, y + 1, x), (z - 1, y, x - 1), (z - 1, y, x + 1), (z + 1, y, x - 1), (z + 1, y, x + 1), (z, y - 1, x - 1), (z, y - 1, x + 1), (z, y + 1, x - 1), (z, y + 1, x + 1), (z - 1, y - 1, x - 1), (z - 1, y - 1, x + 1), (z - 1, y + 1, x - 1), (z - 1, y + 1, x + 1), (z + 1, y - 1, x - 1), (z + 1, y - 1, x + 1), (z + 1, y + 1, x - 1), (z + 1, y + 1, x + 1)]) return region if __name__ == "__main__": # (1)创建一个典型的3D图像数据 depth, height, width = 10, 10, 10 image3D = np.zeros((depth, height, width), dtype=int) image3D[1:3, 1:3, 1:3] = 1 image3D[2:4, 2:4, 2:4] = 2 image3D[5:8, 5:8, 5:8] = 4 image3D[7:9, 7:9, 7:9] = 6 image3D[7:9, 1:3, 1:3] = 8 # (2)选择种子点并执行区域生长 seed_point = (6, 6, 6) # 选择3D种子点 tolerance_value = 100 # 设置容忍度,即相邻像素的范围 max_region_size = 15 # 设置最大区域大小 connect_condition = 26 # 设置连接条件 result_region = region_growing_26connect(image3D, seed_point, tolerance=tolerance_value, max_region_size=max_region_size) # (3)可视化显示3D原始图像和区域生长的结果(按像素值进行可视化) fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5)) # (3.1)原始3D图像 ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121, projection='3d') x, y, z = np.where(image3D > 0) ax1.scatter(x, y, z, c=image3D[x, y, z], cmap='viridis') # 点状图 ax1.set_title('Original 3D Image') ax1.set_xlim(0, 10) # 设置X轴范围 ax1.set_ylim(0, 10) # 设置Y轴范围 ax1.set_zlim(0, 10) # 设置Z轴范围 # (3.2)区域生长结果,使用第一张图的颜色映射 from matplotlib.colors import Normalize ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122, projection='3d') x, y, z = np.where(result_region) cmap = plt.get_cmap('viridis') norm = Normalize(vmin=np.min(image3D), vmax=np.max(image3D)) ax2.scatter(x, y, z, c=cmap(norm(image3D[x, y, z])), alpha=0.5) # 点状图 ax2.set_title(f'Region Grown from Seed' f'\n [seed_point={seed_point}, Tolerance={tolerance_value}, max_region={max_region_size}, connect={connect_condition}]') ax2.set_xlim(0, 10) # 设置X轴范围 ax2.set_ylim(0, 10) # 设置Y轴范围 ax2.set_zlim(0, 10) # 设置Z轴范围 plt.tight_layout() plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
-
-
相关阅读:
如何让CI/CD同一个阶段的任务先后执行而不是同时执行
基于微服务+Java+Spring Cloud +UniApp +MySql开发的智慧工地源码(物联网、人工智能、AI识别、危大工程)
基于JAVA汽车站车辆运管系统计算机毕业设计源码+数据库+lw文档+系统+部署
GoWeb -- gin框架的入门和使用(2)
Python提取PowerPoint演示文稿表格保存到文本及Excel文件
I2C接口控制器之协议解析
C++中的继承
22年11月-外包-面试题
R语言将多景遥感影像拼接在一起的方法
JSP详解
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/shinuone/article/details/133014004