-
基于Docker_Nginx+LVS+Flask+MySQL的高可用Web集群
文章目录
一.项目介绍
1.拓扑图

2.详细介绍
项目名称:基于Docker_Nginx+LVS+Flask+MySQL的高可用Web集群
项目环境:centos7.9,docker24.0.5,mysql5.7.30,nginx1.25.2,mysqlrouter8.0.21,keepalived 1.3.5,ansible 2.9.27等
项目描述:模拟一个可扩展、高可用性的企业级 Web 应用架构,集成了多个关键组件以支持大规模的 Web 服务。采用了现代化的docker容器化技术、lvs七层负载均衡、keepalived高可用机制、nginx动静分离及反向代理、 uWSGI和Flask动态Web服务器、MySQL半同步复制、prometheus监控和ansible自动化部署,以确保系统的可靠性、性能和可维护性。
项目步骤:
1.规划IP配置ansible服务器并建立免密通道,一键安装好软件环境
2.部署lvs四层负载均衡主从服务器并配置keepalived双vip实现高可用,使用docker配置nginx静态双web服务器启用反向代理实现动静分离
3.配置flask双动态web服务器并且使用rsync+sersync同步工具部署NFS主从服务器实现动静web界面的数据同源
4.配置MySQL服务器,安装半同步相关的插件,开启gtid功能,启动主从复制服务,web服务器上使用mysqlrouter中间件实现MySQL的读写分离
5.搭建DNS域名服务器,配置一个域名对应2个vip,实现基于DNS的负载均衡,访问同一URL解析出双vip地址
6.使用ab和sysbench对整个MySQL集群的性能进行压力测试,安装部署prometheus实现监控,grafana出图了解系统性能的瓶颈并调优
项目心得:
1.一定要规划好整个集群的架构,脚本要提前准备好,多注意防火墙和selinux的问题
2.体验了lvs和nginx负载均衡的区别,领会了docker部署容器的好处
3.对MySQL的集群和高可用有了深入的理解,对自动化批量部署和监控有了更加多的应用和理解
4.keepalived的配置需要更加细心,对keepalievd的脑裂和vip漂移现象也有了更加深刻的体会和分析
5.认识到了系统性能资源的重要性,对压力测试下整个集群的瓶颈有了一个整体概念二.前期准备
1.项目环境
centos7.9,docker24.0.5,mysql5.7.30,nginx1.25.2,mysqlrouter8.0.21,keepalived 1.3.5,ansible 2.9.27等
2.IP划分
准备15台centos7.9的虚拟机,并且分配IP地址:
序号 主机名 IP 01 DNS服务器 192.168.98.144 02 lvs1 192.168.98.143 03 lvs2 192.168.98.138 04 nginx1 192.168.98.136 05 nginx2 192.168.98.149 06 web1 192.168.98.150 07 web2 192.168.98.146 08 master 192.168.98.131 09 slave1 192.168.98.142 10 slave2 192.168.98.140 11 NFS1 192.168.98.151 12 NFS2 192.168.98.152 13 ansible 192.168.98.147 14 监控服务器 192.168.98.148 15 sysbench压力测试机 192.168.98.145 三. 项目步骤
1.ansible部署软件环境
配置好ansible服务器并建立免密通道,一键安装MySQL、nginx、keepalived、mysqlroute、node_exporters、dns等软件
1.1 安装ansible环境
[root@ansible ~]# yum install epel-release -y [root@ansible ~]# yum install ansible -y- 1
- 2
#修改配置文件 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts [lvs] 192.168.98.143 192.168.98.138 [nginx] 192.168.98.136 192.168.98.149 [web] 192.168.98.150 192.168.98.146 [nfs] 192.168.98.151 192.168.98.152 [mysql] 192.168.98.131 192.168.98.142 192.168.98.140 [dns] 192.168.98.144- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
1.2 建立免密通道
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-keygen -t rsa [root@localhost ~]# cd .ssh [root@localhost .ssh]# ls id_rsa id_rsa.pub known_hosts [root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-copy-id -i id_rsa.pub root@192.168.98.143 [root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-copy-id -i id_rsa.pub root@192.168.98.138 [root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-copy-id -i id_rsa.pub root@192.168.98.136 [root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-copy-id -i id_rsa.pub root@192.168.98.149 [root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-copy-id -i id_rsa.pub root@192.168.98.150 [root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-copy-id -i id_rsa.pub root@192.168.98.146 [root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-copy-id -i id_rsa.pub root@192.168.98.151 [root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-copy-id -i id_rsa.pub root@192.168.98.152 [root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-copy-id -i id_rsa.pub root@192.168.98.131 [root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-copy-id -i id_rsa.pub root@192.168.98.142 [root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-copy-id -i id_rsa.pub root@192.168.98.140 [root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-copy-id -i id_rsa.pub root@192.168.98.144- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
1.3 ansible批量部署软件
1.3.1 在ansible机器上面创建脚本
[root@localhost ~]#vim onekey_install_mysql.sh- 1
#!/bin/bash #解决软件的依赖关系 yum install cmake ncurses-devel gcc gcc-c++ vim lsof bzip2 openssl-devel ncurses-compat-libs net-tools -y #下载安装包到家目录下(由于文件较大请自行下载) cd ~ #curl -O https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/file/?id=519542 #解压mysql二进制安装包 tar xf mysql-5.7.43-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz #移动mysql解压后的文件到/usr/local下改名叫mysql mv mysql-5.7.43-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 /usr/local/mysql #新建组和用户 mysql groupadd mysql #mysql这个用户的shell 是/bin/false 属于mysql组 useradd -r -g mysql -s /bin/false mysql #关闭firewalld防火墙服务,并且设置开机不要启动 service firewalld stop systemctl disable firewalld #临时关闭selinux setenforce 0 #永久关闭selinux sed -i '/^SELINUX=/ s/enforcing/disabled/' /etc/selinux/config #新建存放数据的目录 mkdir /data/mysql -p #修改/data/mysql目录的权限归mysql用户和mysql组所有,这样mysql用户可以对这个文件夹进行读写了 chown mysql:mysql /data/mysql/ #只是允许mysql这个用户和mysql组可以访问,其他人都不能访问 chmod 750 /data/mysql/ #进入/usr/local/mysql/bin目录 cd /usr/local/mysql/bin/ #初始化mysql ./mysqld --initialize --user=mysql --basedir=/usr/local/mysql/ --datadir=/data/mysql &>passwd.txt #让mysql支持ssl方式登录的设置 ./mysql_ssl_rsa_setup --datadir=/data/mysql/ #获得临时密码 tem_passwd=$(cat passwd.txt |grep "temporary"|awk '{print $NF}') #$NF表示最后一个字段 # abc=$(命令) 优先执行命令,然后将结果赋值给abc # 修改PATH变量,加入mysql bin目录的路径 #临时修改PATH变量的值 export PATH=/usr/local/mysql/bin/:$PATH #重新启动linux系统后也生效,永久修改 echo "PATH=/usr/local/mysql/bin:$PATH">>/root/.bashrc #复制support-files里的mysql.server文件到/etc/init.d/目录下叫mysqld cp ../support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld #修改/etc/init.d/mysqld脚本文件里的datadir目录的值 sed -i '70c datadir=/data/mysql' /etc/init.d/mysqld #生成/etc/my.cnf配置文件 cat >/etc/my.cnf <<EOF [mysqld_safe] [client] socket=/data/mysql/mysql.sock [mysqld] socket=/data/mysql/mysql.sock port = 3306 open_files_limit = 8192 innodb_buffer_pool_size = 512M character-set-server=utf8 [mysql] auto-rehash prompt=\\u@\\d \\R:\\m mysql> EOF #修改内核的open file的数量 ulimit -n 1000000 #设置开机启动的时候也配置生效 echo "ulimit -n 1000000" >>/etc/rc.local chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local #启动mysqld进程 service mysqld start #将mysqld添加到linux系统里服务管理名单里 /sbin/chkconfig --add mysqld #设置mysqld服务开机启动 /sbin/chkconfig mysqld on #初次修改密码需要使用--connect-expired-password 选项 #-e 后面接的表示是在mysql里需要执行命令 execute 执行 #set password='123456'; 修改root用户的密码为123456 mysql -uroot -p$tem_passwd --connect-expired-password -e "set password='123456';" #检验上一步修改密码是否成功,如果有输出能看到mysql里的数据库,说明成功。 mysql -uroot -p'123456' -e "show databases;"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
[root@localhost ~]# vim onekey_install_docker.sh- 1
#!/bin/bash #安装yum-utils工具包 yum install yum-utils -y #下载docker-ce.repo文件存放在/etc/yum.repos.d yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo #安装docker-ce相关软件 yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin -y #关闭firewalld防火墙服务,并且设置开机不要启动 service firewalld stop systemctl disable firewalld #临时关闭selinux setenforce 0 #永久关闭selinux sed -i '/^SELINUX=/ s/enforcing/disabled/' /etc/selinux/config #启动docker并设计开机启动 systemctl start docker systemctl enable docker- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
1.3.2 在ansible机器上面创建node_exporter脚本,为prometheus在node节点服务器上采集数据
[root@ansible ~]# vim node_exporter.sh- 1
#!/bin/bash #进入root家目录 cd ~ #下载node_exporter源码(由于github无法访问,故省略该步,手动下载) #curl -O https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases/download/v1.6.1/node_exporter-1.6.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz #解压node_exporters源码包 tar xf node_exporter-1.6.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz #改名 mv node_exporter-1.6.1.linux-amd64 /node_exporter cd /node_exporter #修改PATH环境变量 PATH=/node_exporter:$PATH echo "PATH=/node_exporter:$PATH" >>/root/.bashrc #后台运行,监听8090端口 nohup node_exporter --web.listen-address 0.0.0.0:8090 &- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
1.3.3 在ansible机器上面编写playbook批量部署mysql、keepalived、mysqlroute、node_exporters、dns等软件
[root@ansible ~]# vim software_install.yaml- 1
- hosts: lvs remote_user: root tasks: - name: install keepalived #负载均衡器中安装keepalived,实现高可用 yum: name=keepalived state=installed - name: install ipvsadm #负载均衡器中安装lvs管理工具ipvsadm yum: name=ipvsadm state=installed - hosts: nfs web nginx #安装nfs软件 remote_user: root tasks: - name: install nfs yum: name=nfs-utils state=installed - hosts: web nginx #安装docker remote_user: root tasks: - name: copy onekey_install_docker.sh #上传安装docker脚本 copy: src=/root/onekey_install_docker.sh dest=/root/ - name: install docker #执行脚本 script: /root/onekey_install_docker.sh - hosts: mysql #mysql集群 remote_user: root tasks: - name: copy mysql.tar.gz #上传MySQL安装包到mysql主机组 copy: src=/root/mysql-5.7.43-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz dest=/root/ - name: copy mysql.sh #上传脚本到mysql主机组 copy: src=/root/onekey_install_mysql.sh dest=/root/ - name: install mysql #安装MySQL script: /root/onekey_install_mysql.sh - hosts: web #web服务器 remote_user: root tasks: - name: copy file #上传mysqlrouter安装包到服务器 copy: src=/root/mysql-router-community-8.0.23-1.el7.x86_64.rpm dest=/root/ - name: install mysqlrouter #安装mysqlrouter shell: rpm -ivh mysql-router-community-8.0.23-1.el7.x86_64.rpm - hosts: dns #dns服务器 remote_user: root tasks: - name: install dns yum: name=bind.* state=installed - hosts: lvs nginx web nfs mysql #调用本地node_exporter脚本,批量安装部署node_exporter,为prometheus采集数据 remote_user: root tasks: - name: copy file #上传node_exporter安装包到服务器 copy: src=/root/node_exporter-1.6.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz dest=/root/ - name: copy file #上传脚本到服务器 copy: src=/root/node_exporter.sh dest=/root/ - name: install node_exporters #执行脚本 script: /root/node_exporter.sh tags: install_exporter - name: start node_exporters #后台运行node_exporters shell: nohup node_exporter --web.listen-address 0.0.0.0:8090 & tags: start_exporters #打标签,方便后面直接跳转到此处批量启动node_exporters- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
[root@localhost ~]# ansible-playbook software_install.yaml- 1
2.部署nginx和lvs主从服务器
部署lvs主从服务器实现四层负载均衡,使用keepalived配置双vip实现高可用,使用docker配置nginx静态双web服务器启用反向代理实现动静分离
2.1 docker配置nginx静态双web服务器从nfs主服务器上那页面数据
1.nginx1、2和nfs1、2都安装好nfs软件
[root@localhost ~]# yum install nfs-utils -y [root@localhost ~]# service nfs restart 关闭防火墙服务并且设置开机不启动 [root@localhost ~]# service firewalld stop [root@localhost ~]# systemctl disable firewalld- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
2.nfs1上面新建共享目录和index.html网页
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /web -p [root@localhost ~]# cd /web [root@localhost web]# echo "welcome to nfs1" >index.html- 1
- 2
- 3
3.设置共享目录
[root@localhost web]# vim /etc/exports [root@localhost web]# cat /etc/exports /web 192.168.98.0/24(rw,no_root_squash,sync) [root@localhost web]# chmod 777 /web 在linux系统里也给其他机器上的用户写的权限- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
共享权限: 是nfs服务器里设置的 /etc/exports rw ro
系统权限: 是在linux系统里设置 chmodno_root_squash 其他机器的root用户连接过来nfs服务的时候,把它当做root用户对待
root_squash 其他机器的root用户连接过来nfs服务的时候把它当做普通的用户对待(nfsnobody)
all_squash 其他机器的所有的用户当做普通的用户对待(nfsnobody)4.刷新nfs或者重新输出共享目录
exportfs的选项
-a 输出所有共享目录
-v 显示输出的共享目录
-r 重新输出所有的共享目录[root@localhost web]# exportfs -rv 重启nfs服务 [root@localhost web]# service nfs restart 重启nfs服务 [root@localhost web]# systemctl enable nfs 设置nfs开机启动- 1
- 2
- 3
5.在2台docker宿主机上创建nginx文件夹,并且配置conf,log和html
#运行一个test用于拷贝文件 [root@localhost ~]# docker run --name nginx-test -p 80:80 -d nginx #创建文件夹 [root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p nginx/conf nginx/logs nginx/html [root@localhost ~]# docker cp nginx-test:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf /root/nginx/conf [root@localhost ~]# docker cp nginx-test:/etc/nginx/conf.d/ /root/nginx/conf #挂载html页面,实现页面同源 [root@localhost ~]# mount 192.168.98.151:/web /root/nginx/html- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
6.在2台docker宿主机上都要启动容器
[root@scdocker test]# docker run -d --name nginx-1 -p 80:80 -v /root/nginx/html:/usr/share/nginx/html -v /root/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf -v /root/nginx/conf/conf.d:/etc/nginx/conf.d -v /root/nginx/logs:/var/log/nginx nginx [root@scdocker test]# docker ps- 1
- 2
7.访问创建的nginx web服务器,打开浏览器去访问
http://192.168.98.136:80/http://192.168.98.149:80/

2.2 使用keepalived搭建双vip双master高可用架构
lvs1上配置
[root@localhost conf]# vim /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf- 1
! Configuration File for keepalived global_defs { notification_email { acassen@firewall.loc failover@firewall.loc sysadmin@firewall.loc } notification_email_from Alexandre.Cassen@firewall.loc smtp_server 192.168.200.1 smtp_connect_timeout 30 router_id LVS_DEVEL vrrp_skip_check_adv_addr #vrrp_strict vrrp_garp_interval 0 vrrp_gna_interval 0 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state MASTER interface ens33 virtual_router_id 88 priority 120 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.98.88 } } vrrp_instance VI_2 { state BACKUP interface ens33 virtual_router_id 99 priority 100 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.98.99 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
[root@localhost conf]# service keepalived restart- 1
lvs2上配置
[root@localhost conf]# vim /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf- 1
! Configuration File for keepalived global_defs { notification_email { acassen@firewall.loc failover@firewall.loc sysadmin@firewall.loc } notification_email_from Alexandre.Cassen@firewall.loc smtp_server 192.168.200.1 smtp_connect_timeout 30 router_id LVS_DEVEL vrrp_skip_check_adv_addr #vrrp_strict vrrp_garp_interval 0 vrrp_gna_interval 0 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state BACKUP interface ens33 virtual_router_id 88 priority 110 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.98.88 } } vrrp_instance VI_2 { state MASTER interface ens33 virtual_router_id 99 priority 120 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.98.99 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
[root@localhost conf]# service keepalived restart- 1

2.2 配置LVS四层负载均衡主从服务器
LVS是Linux Virtual Server的简写,意即Linux虚拟服务器,该实验使用DR模式
-
两台服务器都使用脚本一键实现LVS四层负载均衡
[root@localhost ~]# vim lvs_dr.sh- 1
#!/bin/bash #安装 yum -y install ipvsadm #手动生成/etc/sysconfig/ipvsadm文件 /usr/sbin/ipvsadm --save > /etc/sysconfig/ipvsadm # director 服务器上开启路由转发功能 echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward #清除防火墙规则 iptables -F #关闭firewalld防火墙服务,并且设置开机不要启动 service firewalld stop systemctl disable firewalld #临时关闭selinux setenforce 0 #永久关闭selinux sed -i '/^SELINUX=/ s/enforcing/disabled/' /etc/selinux/config # 清空lvs里的规则 /usr/sbin/ipvsadm -C #添加lvs的虚拟vip规则,此处直接使用keepalived生成的虚拟ip /usr/sbin/ipvsadm -A -t 192.168.98.88:80 -s rr /usr/sbin/ipvsadm -A -t 192.168.98.99:80 -s rr #-g 是指定使用DR模式 -w 指定后端服务器的权重值为1 -r 指定后端的real server -t 是指定vip -a 追加一个规则 append /usr/sbin/ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.98.88:80 -r 192.168.98.136:80 -g -w 1 /usr/sbin/ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.98.88:80 -r 192.168.98.149:80 -g -w 1 /usr/sbin/ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.98.99:80 -r 192.168.98.136:80 -g -w 1 /usr/sbin/ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.98.99:80 -r 192.168.98.149:80 -g -w 1 #保存配置规则 /usr/sbin/ipvsadm -S > /etc/sysconfig/ipvsadm #启动服务 systemctl start ipvsadm- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
-
启动并查看
[root@localhost ~]# bash lvs_dr.sh #查看配置 [root@localhost ~]# ipvsadm -ln- 1
- 2
- 3
-
两台nginx服务器上面操作
由于DR模式只修改mac,不修改ip,故当nginx收到arp包进行解封装的时候,发现是vip地址,这是nginx服务器自己就需要配置一个相同的vip,不然无法进行进行通信
[root@localhost ~]# vim set_vip_arp.sh- 1
#!/bin/bash #在lo接口(loopback)上配置vip /usr/sbin/ifconfig lo:0 192.168.98.88 netmask 255.255.255.255 broadcast 192.168.203.188 up /usr/sbin/ifconfig lo:1 192.168.98.99 netmask 255.255.255.255 broadcast 192.168.203.199 up #添加一条主机路由到192.168.203.188/199 走lo:0接口 /sbin/route add -host 192.168.98.88 dev lo:0 /sbin/route add -host 192.168.98.99 dev lo:1 #调整内核参数,关闭arp响应 echo "1" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/arp_ignore echo "1" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/lo/arp_ignore echo "2" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/arp_announce echo "2" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/lo/arp_announce- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
[root@localhost ~]# bash set_vip_arp.sh #加载并查看关闭arp响应参数 [root@localhost ~]# sysctl -p #重启网卡和docker [root@localhost ~]# service network restart [root@localhost ~]# service docker restart [root@localhost ~]# docker restart nginx-1- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
为了彰显负载均衡的效果,此处nginx2没有使用nfs1进行页面同源

3.配置flask双动态web服务器
配置flask双动态web服务器并且使用rsync+sersync同步工具部署NFS主从服务器实现动静web界面的数据同源
3.1 使用rsync+sersync同步工具部署NFS主从服务器实现动静web界面的数据同源
3.1.1 nfs2备份服务器一键安装rsync服务端软件并且设置开机启动
[root@localhost ~]# vim onekey_install_rsync_nfs2.sh- 1
#!/bin/bash #创建备份目录 mkdir /web #关闭firewalld防火墙服务,并且设置开机不要启动 service firewalld stop systemctl disable firewalld #临时关闭selinux setenforce 0 #永久关闭selinux sed -i '/^SELINUX=/ s/enforcing/disabled/' /etc/selinux/config #安装rsync服务端软件 yum install rsync xinetd -y #设置开机启动 echo '/usr/bin/rsync --daemon --config=/etc/rsyncd.conf' >>/etc/rc.d/rc.local chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local #生成/etc/rsyncd.conf配置文件 cat >/etc/rsyncd.conf <<EOF uid = root gid = root use chroot = yes max connections = 0 log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock secrets file = /etc/rsync.pass motd file = /etc/rsyncd.Motd [back_data] path = /web comment = A directory in which data is stored ignore errors = yes read only = no hosts allow = 192.168.98.151 EOF #创建用户认证文件 cat >/etc/rsync.pass <<EOF nfs2:123456 EOF #设置文件所有者读取、写入权限 chmod 600 /etc/rsyncd.conf chmod 600 /etc/rsync.pass #启动rsync /usr/bin/rsync --daemon --config=/etc/rsyncd.conf #启动xinetd(xinetd是一个提供保姆服务的进程,rsync是它照顾的进程) systemctl start xinetd- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
[root@localhost ~]# bash onekey_install_rsync_nfs1.sh- 1
xinetd是一个提供保姆服务的进程,rsync是它照顾的进程
3.1.2 查看rsync和xinetd监听的进程
[root@localhost ~]# ps aux|grep rsync root 976 0.0 0.0 114852 572 ? Ss 10:19 0:00 /usr/bin/rsync --daemon --config=/etc/rsyncd.conf root 2200 0.0 0.0 112828 976 pts/0 S+ 14:24 0:00 grep --color=auto rsync [root@localhost ~]# ps aux|grep xinetd root 968 0.0 0.0 25044 588 ? Ss 10:19 0:00 /usr/sbin/xinetd -stayalive -pidfile /var/run/xinetd.pid root 2203 0.0 0.0 112828 980 pts/0 S+ 14:25 0:00 grep --color=auto xinetd- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
3.1.3 nfs1服务器一键安装rsync服务端软件并且设置开机启动
[root@localhost ~]# vim onekey_install_rsync_nfs1.sh- 1
#!/bin/bash #关闭firewalld防火墙服务,并且设置开机不要启动 service firewalld stop systemctl disable firewalld #临时关闭selinux setenforce 0 #永久关闭selinux sed -i '/^SELINUX=/ s/enforcing/disabled/' /etc/selinux/config #安装rsync服务端软件 yum install rsync xinetd -y #设置开机启动 echo '/usr/bin/rsync --daemon --config=/etc/rsyncd.conf' >>/etc/rc.d/rc.local chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local #生成/etc/rsyncd.conf配置文件 cat >/etc/rsyncd.conf <<EOF log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock motd file = /etc/rsyncd.Motd [Sync] comment = Sync uid = root gid = root port= 873 EOF #启动xinetd(xinetd是一个提供保姆服务的进程,rsync是它照顾的进程) systemctl start xinetd #创建认证密码文件,该密码应与slave服务器中的/etc/rsync.pass中的密码一致 cat >/etc/passwd.txt <<EOF 123456 EOF #设置文件所有者读取、写入权限 chmod 600 /etc/passwd.txt- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
[root@localhost ~]# bash onekey_install_rsync.sh #测试一下,将web下面的html文件传送过去 [root@localhost ~]# rsync -avH --port=873 --progress --delete /web root@192.168.98.152::back_data --password-file=/etc/passwd.txt- 1
- 2
- 3
3.1.4 数据源nfs1服务器上安装sersync工具,实现自动的实时的同步
(1)一键安装安装sersync工具
[root@localhost ~]# vim onekey_install_sersync.sh- 1
#!/bin/bash cd ~ #修改inotify默认参数(inotify默认内核参数值太小) sysctl -w fs.inotify.max_queued_events="99999999" sysctl -w fs.inotify.max_user_watches="99999999" sysctl -w fs.inotify.max_user_instances="65535" #下载并安装sersync yum install wget -y wget http://down.whsir.com/downloads/sersync2.5.4_64bit_binary_stable_final.tar.gz #解压并改名 tar xf sersync2.5.4_64bit_binary_stable_final.tar.gz mv /root/GNU-Linux-x86 /usr/local/sersync #创建rsync cd /usr/local/sersync/ cp confxml.xml confxml.xml.bak cp confxml.xml data_configxml.xml #data_configxml.xml 是后面需要使用的配置文件 #修改data_configxml.xml配置文件 #修改需要备份的路径为/backup sed -i 's/watch="\/opt\/tongbu"/watch="\/web"/' /usr/local/sersync/data_configxml.xml #修改服务器信息为slave4远程备份服务器 sed -i 's/ip="127.0.0.1" name="tongbu1"/ip="192.168.98.152" name="back_data"/' /usr/local/sersync/data_configxml.xml #开启身份认证,修改密码文件为/etc/passwd.txt sed -i 's/start="false" users="root" passwordfile="\/etc\/rsync.pas"/start="true" users="root" passwordfile="\/etc\/passwd.txt"/' /usr/local/sersync/data_configxml.xml #添加到PATH变量 PATH=/usr/local/sersync/:$PATH echo 'PATH=/usr/local/sersync/:$PATH' >>/root/.bashrc #启动 sersync2 -d -r -o /usr/local/sersync/data_configxml.xml #设计开机启动 echo '/usr/local/sersync/sersync2 -d -r -o /usr/local/sersync/data_configxml.xml' >>/etc/rc.local- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
[root@localhost ~]# bash onekey_install_sersync.sh- 1
-
永久修改参数方法
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf fs.inotify.max_queued_events=99999999 fs.inotify.max_user_watches=99999999 fs.inotify.max_user_instances=65535- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

(2)查看服务,新建文件进行验证
[root@localhost ~]# ps aux|grep sersync [root@localhost ~]# cd /web [root@localhost web]# ls index.html [root@localhost web]# mkdir test [root@localhost web]# ls index.html test #从nfs2中查看 [root@localhost web]# ls index.html test- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
3.2 配置uwsgi+flask双动态web服务器以及nginx动静分离
为什么要使用uwsgi呢?
首先Flask只是是Web框架,并不是Web服务器,它自带的Werkzeug也仅仅用于开发测试环境,生产环境中处理并发的能力太弱,采用uwsgi可以提高并发处理能力。uWSGI负责处理Nginx转发的动态请求,并与我们的Python应用程序沟通,同时将应用程序返回的响应数据传递给Nginx
3.2.1 两台web机器都安装uwsgi和python3环境
#安装python的相关环境 [root@localhost ~]# yum install uwsgi python3 python3-devel -y #使用清华源安装flask和uwsgi模块 [root@localhost ~]# pip3 install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple flask uwsgi- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
3.2.2 两台web机器都配置flask和uwsgi
#创建flask目录并且创建flask的一个接口 [root@localhost ~]# mkdir flask [root@localhost ~]# cd flask [root@localhost flask]# vim app.py from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__) @app.route('/') def hello(): return "Hello, flask1!" if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=8000)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
#创建uwsgi去调用flask的接口 [root@localhost flask]# vim uwsgi.ini [uwsgi] http-socket = 192.168.98.150:8000 #启动地址 chdir = /root/flask #项目地址 wsgi-file = app.py #项目的启动文件 callable = app processes = 2 threads = 10 buffer-size = 32768 master = true daemonize=flaskweb.log #日志文件保存在falskweb.log中 pidfile=uwsgi.pid [root@localhost flask]#uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini #启动 [root@localhost flask]#uwsgi --reload uwsgi.pid #重启- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15

3.3 配置nginx的动态分离和部署flask连接后端MySQL数据库
3.3.1 配置nginx的动态分离,修改nginx的配置文件(已经使用docker映射到宿主机上面/root/nginx/conf/nginx.conf)
注意!一定要注释掉#include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
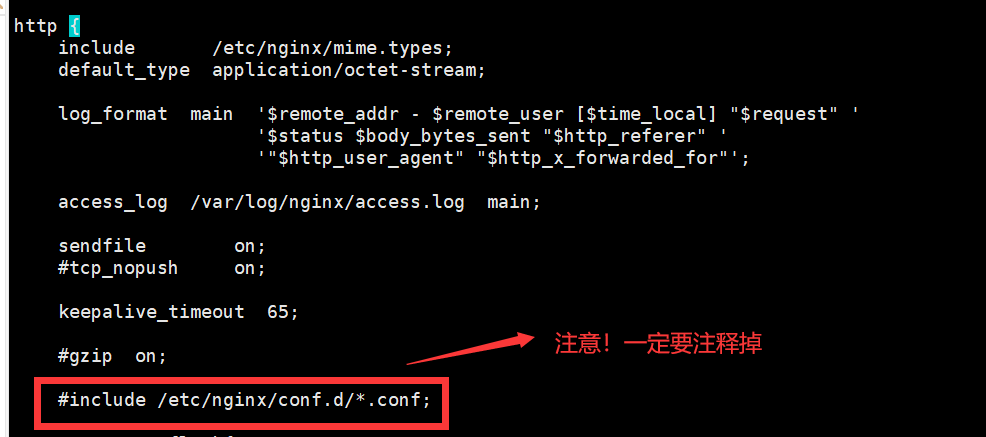
接着在后面加入如下配置文件,实现动静分离
[root@localhost ~]# vim /root/nginx/conf/nginx.conf #include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; upstream flask { server 192.168.98.150:8000; server 192.168.98.146:8000; } server { listen 80; server_name localhost; charset utf-8; #静态资源路由 location ~* .(css|js|html|xhtml|gif|jpg|jpeg|png|ico)$ { root /usr/share/nginx/html; index index.html index.xhtml; } # 动态请求 location / { proxy_pass http://flask; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Scheme $scheme; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
#重新加载配置文件 [root@localhost ~]# docker exec -it nginx-1 nginx -s reload #重启nginx-1也可以重新加载 [root@localhost ~]# docker restart nginx-1- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
3.3.2 部署flask连接后端数据库
#安装数据模块 [root@localhost flask]# pip3 install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple pymysql- 1
- 2
#修改app.py程序 [root@localhost flask]# vim app.py- 1
- 2
from flask import Flask import pymysql app = Flask(__name__) # 配置 MySQL 连接信息 db_config = { 'host': '192.168.98.131', 'user': 'read', 'password': '123456', 'db': 'tennis', 'charset': 'utf8mb4', } def connect_db(): return pymysql.connect(**db_config) @app.route('/') def index(): # 在这里执行与数据库的交互操作 connection = connect_db() cursor = connection.cursor() try: cursor.execute("SHOW TABLES") data = cursor.fetchall() return str(data) finally: cursor.close() connection.close() if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=8000)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
[root@localhost flask]# killall uwsgi [root@localhost flask]# uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini #启动 [root@localhost flask]# uwsgi --reload uwsgi.pid #重启- 1
- 2
- 3
在web1和lvs1上面查看效果连接数据库的效果

4.配置基于GTID的半同步主从复制的MySQL集群
配置MySQL服务器,安装半同步相关的插件,开启gtid功能,启动主从复制服务,web服务器上使用mysqlrouter中间件实现MySQL的读写分离
4.1 在master上安装配置半同步的插件,再配置
安装MySQL已经使用playbook部署完成
4.1.1 在master上安装配置半同步的插件,配置半同步复制超时时间,修改配置文件/etc/my.cnf
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -uroot -p'123456' root@(none) 11:08 mysql>install plugin rpl_semi_sync_master SONAME 'semisync_master.so'; root@(none) 11:08 mysql>exit- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/my.cnf 注意!是在添加mysqld下面部分 [mysqld] #二进制日志开启 log_bin server_id = 1 #开启半同步,需要提前安装半同步的插件 rpl_semi_sync_master_enabled=1 rpl_semi_sync_master_timeout=1000 # 1 second #gtid功能 gtid-mode=ON enforce-gtid-consistency=ON [root@sc-master mysql]# service mysqld restart- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
4.1.2 在每台从服务器上配置安装半同步的插件,配置slave配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -uroot -p'123456' root@(none) 11:12 mysql>install plugin rpl_semi_sync_slave SONAME 'semisync_slave.so'; root@(none) 11:12 mysql>set global rpl_semi_sync_slave_enabled = 1; root@(none) 11:13 mysql>exit- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/my.cnf [mysqld] #log bin 二进制日志 log_bin server_id = 2 #注意:每台slave的id都不一样 expire_logs_days = 15 #二进制日志保存15天 #开启半同步,需要提前安装半同步的插件 rpl_semi_sync_slave_enabled=1 #开启gtid功能 gtid-mode=ON enforce-gtid-consistency=ON log_slave_updates=ON [root@sc-slave mysql]# service mysqld restart- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
4.1.3 在master上新建一个授权用户,给slave1和salve2来复制二进制日志
root@(none) 12:06 mysql>grant replication slave on *.* to 'master'@'192.168.98.%' identified by '123456';- 1
4.1.4 在slave上配置master info的信息
在salve1和slave2上配置
#停止 root@(none) 12:06 mysql>stop slave; #清空 root@(none) 12:07 mysql>reset slave all; #配置 root@(none) 12:07 mysql> change master to master_host='192.168.98.131' , master_user='master', master_password='123456', master_port=3306, master_auto_position=1; #开启 root@(none) 12:08 mysql>start slave;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
4.1.5 查看
在slave上查看 root@(none) 12:10 mysql>show slave status\G; 在master上查看 root@(none) 12:11 mysql>show variables like "%semi_sync%"; 在slave上查看 root@(none) 12:11 mysql>show variables like "%semi_sync%";- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
4.1.6 验证GTID的半同步主从复制
在master上面新建或者删除库,slave上面查看有没有实现
4.2 web服务器上部署mysqlrouter中间件实现读写分离
4.2.1 安装部署MySQLrouter(该步骤已经使用playbook部署完成)
- 上传或者去官方网站下载软件
https://dev.mysql.com/get/Downloads/MySQL-Router/mysql-router-community-8.0.23-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
[root@mysql-router-1 ~]# rpm -ivh mysql-router-community-8.0.23-1.el7.x86_64.rpm- 1
4.2.2 两个web服务器同时修改配置文件/etc/mysqlrouter/mysqlrouter.conf
[root@mysql-router-1 mysqlrouter]# vim /etc/mysqlrouter/mysqlrouter.conf [DEFAULT] logging_folder = /var/log/mysqlrouter runtime_folder = /var/run/mysqlrouter config_folder = /etc/mysqlrouter [logger] level = INFO [keepalive] interval = 60 [routing:slave] bind_address = 0.0.0.0:7001 destinations = 192.168.98.131:3306,192.168.98.142:3306 mode = read-only connect_timeout = 1 [routing:master] bind_address = 0.0.0.0:7002 destinations = 192.168.98.131:3306 mode = read-write connect_timeout = 1- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
4.2.3 启动MySQL router服务,监听了7001和7002端口
[root@localhost ~]# service mysqlrouter restart [root@localhost ~]# netstat -anplut|grep mysql tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:7001 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 8084/mysqlrouter tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:7002 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 8084/mysqlrouter- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
4.2.4 在master上创建2个测试账号,一个是读的,一个是写的()
root@(none) 15:34 mysql>grant all on *.* to 'write'@'%' identified by '123456'; root@(none) 15:35 mysql>grant select on *.* to 'read'@'%' identified by '123456';- 1
- 2
由于实现了半同步复制,故需要将slave机器上面的write用户删除
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -uroot -p'123456' root@(none) 22:05 mysql>drop user 'write'@'%';- 1
- 2
4.2.5 在客户端上测试读写分离的效果,使用2个测试账号
#实现读功能 [root@node1 ~]# mysql -h 192.168.98.150 -P 7001 -uread -p'123456' #实现写功能 [root@node1 ~]# mysql -h 192.168.98.146 -P 7002 -uwrite -p'123456'- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
mysqlrouter通过7001和7002端口实现分流,再通过mysql服务器上面的权限用户(write,read)进行读写分离
5.搭建DNS域名服务器
搭建DNS域名服务器,配置一个域名对应2个vip,实现基于DNS的负载均衡,访问同一URL解析出双vip地址
1.安装软件bind(该软件提供了很多的dns域名查询的命令)->由于playbook已经批量安装过,该处故省略
[root@localhost ~]# yum install bind* -y- 1
2.关闭DNS域名服务器的防火墙服务和selinux
[root@localhost ~]# service firewalld stop [root@localhost ~]#systemctl disable firewalld #临时修改selinux策略 [root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
3.设置named服务开机启动,并且立马启动DNS服务
#设置named服务开机启动 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable named #立马启动named进程 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl start named- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
4.修改dns配置文件,任意ip可以访问本机的53端口,并且允许dns解析
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/named.conf options { listen-on port 53 { any; }; #修改 listen-on-v6 port 53 { any; }; #修改 directory "/var/named"; dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db"; statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt"; memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt"; recursing-file "/var/named/data/named.recursing"; secroots-file "/var/named/data/named.secroots"; allow-query { any; }; #修改 #重启named服务 [root@localhost ~]# service named restart- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
5.编辑dns次要配置文件/etc/named.rfc1912.zones,增加一条主域名记录
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/named.rfc1912.zones zone "liaoobo.com" IN { type master; #类型为主域名 file "liaoobo.com.zone"; #liaoobo.com域名的数据文件,需要去/var/named/下创建 allow-update { none; }; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
[root@localhost ~]# cd /var/named/ [root@localhost named]# cp -a named.localhost liaoobo.com.zone [root@localhost named]# vim liaoobo.com.zone $TTL 1D @ IN SOA @ rname.invalid. ( 0 ; serial 1D ; refresh 1H ; retry 1W ; expire 3H ) ; minimum NS @ A 127.0.0.1 AAAA ::1 www IN A 192.168.98.88 www IN A 192.168.98.99- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
6.测试机器修改dns为DNS服务器的IP:192.168.98.144
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/resolv.conf # Generated by NetworkManager search localdomain nameserver 192.168.98.144- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
注意!dns服务器需要和测试机器需要处于同一网段
为了彰显负载均衡的效果,此处nginx2没有使用nfs1进行页面同源

6.使用ab和sysbench进行压力测试,prometheus和grafana实现监控并出图
使用ab和sysbench对整个MySQL集群的性能(cpu、IO、内存等)进行压力测试,安装部署prometheus实现监控,grafana出图了解系统性能的瓶颈并调优
6.1 安装prometheus server
1.一键源码安装prometheus
源码下载:https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/releases/download/v2.46.0/prometheus-2.46.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
[root@localhost ~]# vim onekey_install_prometheus.sh- 1
#!/bin/bash #创建存放prometheus的目录 mkdir /prom #下载prometheus源码(由于github无法访问,故省略该步,手动下载) #curl -O https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/releases/download/v2.47.0/prometheus-2.47.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz #解压并改名 tar xf ./prometheus-2.47.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz -C /prom mv /prom/prometheus-2.47.0.linux-amd64 /prom/prometheus #添加到PATH变量 PATH=/prom/prometheus:$PATH echo "PATH=/prom/prometheus:$PATH " >>/root/.bashrc #nohub后台执行启动 nohup prometheus --config.file=/prom/prometheus/prometheus.yml & #关闭防火墙 service firewalld stop systemctl disable firewalld- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
2.把prometheus做成一个服务来进行管理
[root@prometheus prometheus]# vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/prometheus.service [Unit] Description=prometheus [Service] ExecStart=/prom/prometheus/prometheus --config.file=/prom/prometheus/prometheus.yml ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID KillMode=process Restart=on-failure [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target #重新加载systemd相关的服务 [root@prometheus prometheus]# systemctl daemon-reload- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
第一次因为是使用nohup 方式启动的prometheus,还是需要使用后kill 的方式杀死第一次启动的进程;后面可以使用service方式管理prometheus了
[root@prometheus prometheus]# ps aux|grep prometheus root 8431 0.2 3.2 782340 61472 pts/0 Sl 11:21 0:01 prometheus --config.file=/prom/prometheus/prometheus.yml root 8650 0.0 0.0 112824 980 pts/0 S+ 11:35 0:00 grep --color=auto prome [root@prometheus prometheus]# kill -9 8431 [root@prometheus prometheus]# service prometheus start- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
3 在node节点服务器上安装exporter程序->已经使用playbook安装完成
6.2 在prometheus server里添加安装了exporter程序的机器
[root@sc-prom prometheus]# vim /prom/prometheus/prometheus.yml scrape_configs: The job name is added as a label `job=<job_name>` to any timeseries scraped from this config. - job_name: "prometheus" static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9090"] #添加下面的配置采集node-liangrui服务器的metrics - job_name: "lvs1" static_configs: - targets: ["192.168.98.143:8090"] - job_name: "lvs2" static_configs: - targets: ["192.168.98.138:8090"] - job_name: "nginx1" static_configs: - targets: ["192.168.98.136:8090"] - job_name: "nginx2" static_configs: - targets: ["192.168.98.149:8090"] - job_name: "web1" static_configs: - targets: ["192.168.98.150:8090"] - job_name: "web2" static_configs: - targets: ["192.168.98.146:8090"] - job_name: "NFS1" static_configs: - targets: ["192.168.98.151:8090"] - job_name: "NFS2" static_configs: - targets: ["192.168.98.152:8090"] - job_name: "master" static_configs: - targets: ["192.168.98.131:8090"] - job_name: "slave1" static_configs: - targets: ["192.168.98.142:8090"] - job_name: "slave2" static_configs: - targets: ["192.168.98.140:8090"] #重启prometheus服务 [root@prometheus prometheus]# service prometheus restart- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55

6.3 grafana部署和安装
6.3.1 先去官方网站下载
wget https://dl.grafana.com/enterprise/release/grafana-enterprise-10.1.1-1.x86_64.rpm- 1
6.3.2 安装
[root@sc-prom grafana]# ls grafana-enterprise-8.4.5-1.x86_64.rpm [root@sc-prom grafana]# yum install grafana-enterprise-10.1.1-1.x86_64.rpm -y- 1
- 2
- 3
6.3.3 启动grafana
[root@sc-prom grafana]# service grafana-server start 设置grafana开机启动 [root@prometheus grafana]# systemctl enable grafana-server 监听的端口号是3000- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
6.3.4 登录,在浏览器里登录
http://192.168.98.148:3000/
默认的用户名和密码是
用户名admin
密码admin
6.4 ab压力测试
ab测试机对web集群和负载均衡器进行压力测试,了解系统性能的瓶颈,对系统性能资源(如内核参数、nginx参数 )进行调优,提升系统性能
[root@localhost ~]# yum install httpd-tools -y- 1
#其中-c表示并发数,-n表示请求数 [root@localhost ~]# ab -c 1000 -n 1000 http://www.liaoobo.com/ Requests per second: 2802.38 [#/sec] (mean) Time per request: 356.839 [ms] (mean) Time per request: 0.357 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests) Transfer rate: 1789.80 [Kbytes/sec] received- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
6.5 sysbench压力测试
sysbench对数据库的读写性能进行测试
1.使用yum安装,使用epel-release源去安装sysbench
[root@nfs-server ~]# yum install epel-release -y [root@nfs-server ~]# yum install sysbench -y- 1
- 2
2.在master数据库里新建sbtest的库和建10个sbtest表
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -h 192.168.98.146 -P 7002 -uwrite -p'123456' write@(none) 12:14 mysql>create database sbtest; [root@localhost ~]# sysbench --mysql-host=192.168.98.146 --mysql-port=7002 --mysql-user=write --mysql-password='123456' /usr/share/sysbench/oltp_common.lua --tables=10 --table_size=10000 prepare- 1
- 2
- 3
3.压力测试
[root@localhost sysbench]# sysbench --threads=4 --time=20 --report-interval=5 --mysql-host=192.168.98.146 --mysql-port=7002 --mysql-user=write --mysql-password='123456' /usr/share/sysbench/oltp_read_write.lua --tables=10 --table_size=100000 run- 1
-
mysql性能测试工具——tpcc
1.下载安装包并解压,然后打开目录进行make
wget http://imysql.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/tpcc-mysql-src.tgz tar xf tpcc-mysql-src.tar cd tpcc-mysql/src make- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
之后会生成两个二进制工具tpcc_load(提供初始化数据的功能)和tpcc_start(进行压力测试)
[root@nfs-server src]# cd .. [root@nfs-server tpcc-mysql]# ls add_fkey_idx.sql drop_cons.sql schema2 tpcc_load count.sql load.sh scripts tpcc_start create_table.sql README src- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
3、初始化数据库
在master服务器上连接到读写分离器上创建tpcc库,需要在测试的服务器上创建tpcc的库
[root@sc-slave ~]# mysqladmin -uwrite -p'123456' -h 192.168.98.146 -P 7002 create tpcc- 1
需要将tpcc的create_table.sql 和add_fkey_idx.sql 远程拷贝到master服务器上
[root@nfs-server tpcc-mysql]# scp create_table.sql add_fkey_idx.sql root@192.168.98.131:/root- 1
然后在master服务器上导入create_table.sql 和add_fkey_idx.sql 文件
mysql -uroot -p'123456' tpcc <create_table.sql mysql -uroot -p'123456' tpcc <add_fkey_idx.sql- 1
- 2
4、加载数据
[root@nfs-server tpcc-mysql]# ./tpcc_load 192.168.98.146:7002 tpcc write Sanchuang1234# 150- 1
5、进行测试
./tpcc_start -h 192.168.98.146 -p 7002 -d tpcc -u write -p 123456 -w 150 -c 12 -r 300 -l 360 -f test0.log -t test1.log - >test0.out- 1
注意:server等信息与步骤4中保持一致
四. 项目总结
1.做项目时遇到的问题
1.脚本执行出错,原因是github无法访问导致脚本执行失败
2.playbook部署mysql服务器时出错,原因是虚拟机内存不够
3.lvs的nat模式出错,需要使用两块网卡,后改用dr模式
3.半同步复制部署不成功,原因是salve服务器上的server_id不能相同
4.keepalived的虚拟ip无法访问时,记得清除防火墙规则
5.DNS配置域名的数据文件和rsync的.conf配置文件出差,原因是不能加注释2.项目心得
1.一定要规划好整个集群的架构,脚本要提前准备好,多注意防火墙和selinux的问题
2.体验了lvs和nginx负载均衡的区别,领会了docker部署容器的好处
3.对MySQL的集群和高可用有了深入的理解,对自动化批量部署和监控有了更加多的应用和理解
4.keepalived的配置需要更加细心,对keepalievd的脑裂和vip漂移现象也有了更加深刻的体会和分析
5.认识到了系统性能资源的重要性,对压力测试下整个集群的瓶颈有了一个整体概念 -
相关阅读:
PICO首届XR开发者挑战赛正式启动,助推行业迈入“VR+MR”新阶段
计算机毕业设计Java程序设计类课程的课堂教学效果评价系统(源码+系统+mysql数据库+lw文档)
LeetCode 周赛 345(2023/05/14)体验一题多解的算法之美
java 实现外观模式
路由事件2
GSAP动画
搜索与图论 ---- 染色法判定二分图
QT C++ AES字符串加密实现
如何將人臉變漂亮(七)
fetch-AJAX
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Bo_B0/article/details/133220666
