-
【数据结构练习】链表面试题集锦二
目录
前言:
编程想要学的好,刷题少不了,我们不仅要多刷题,还要刷好题!为此我开启了一个弯道超车必做好题锦集的系列,此为链表面试题第二篇,每篇大约5题左右。该系列会不定期更新,敬请期待!
1.链表分割

代码:
- public class Partition {
- public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
- if(head==null)
- {
- return null;
- }
- ListNode cura1=null;
- ListNode curb1=null;
- ListNode cura2=null;
- ListNode curb2=null;
- ListNode cur=head;
- while (cur!=null){
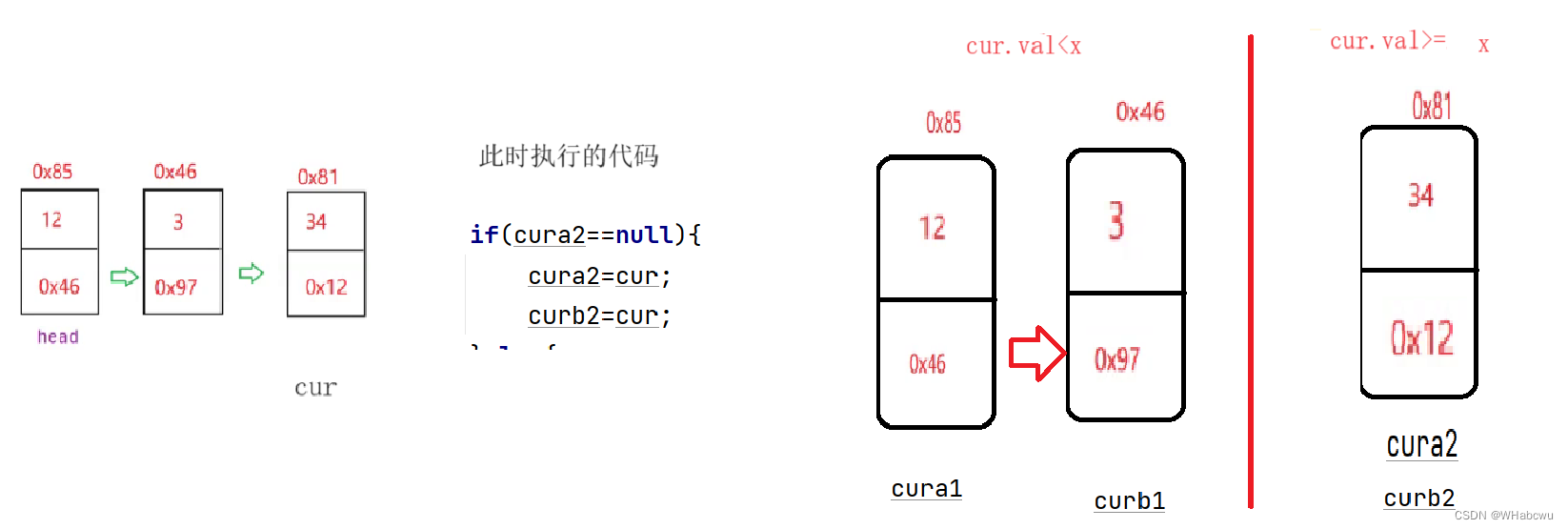
- if(x>cur.val){
- if(cura1==null){
- cura1=cur;
- curb1=cur;
- }else{
- curb1.next=cur;
- curb1=curb1.next;
- }
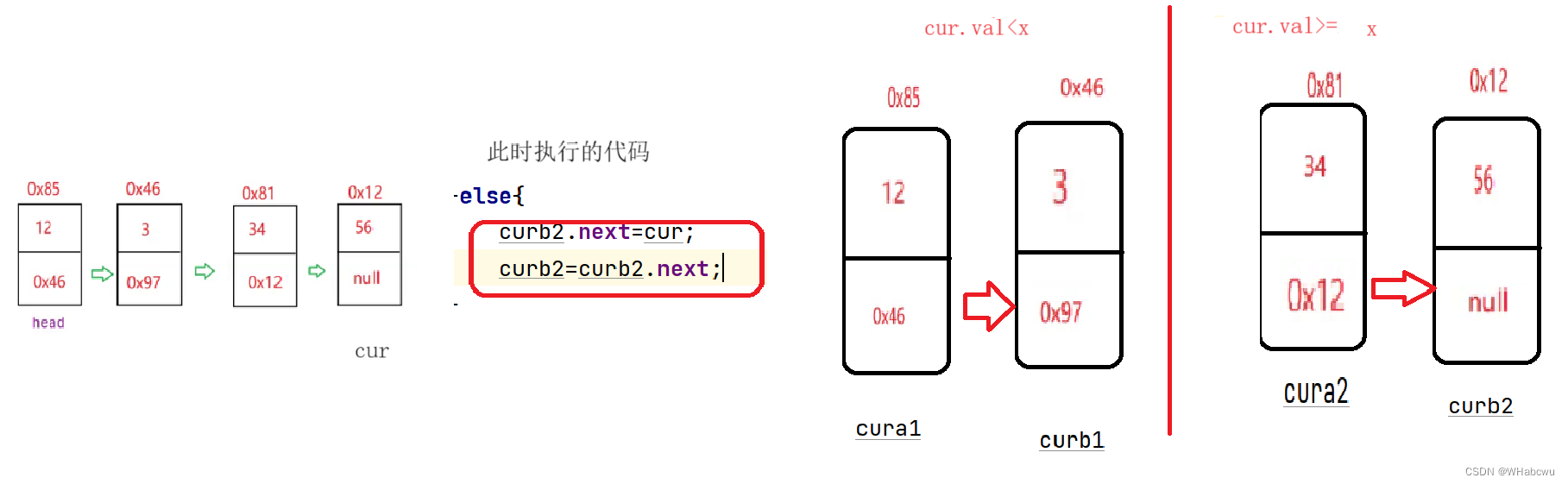
- }else{
- if(cura2==null){
- cura2=cur;
- curb2=cur;
- }else{
- curb2.next=cur;
- curb2=curb2.next;
- }
- }
- cur=cur.next;
- }
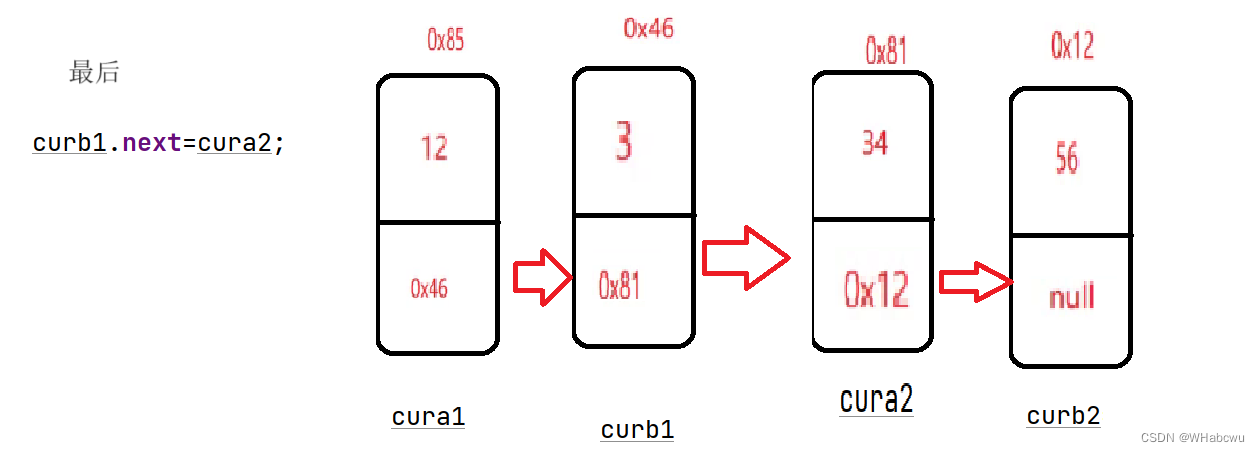
- if(cura1==null){
- return cura2;
- }
- curb1.next=cura2;
- if(curb2!=null){
- curb2.next=null;
- }
- return cura1;
- }
- }
解析:

示例1:
(1)
 (2)
(2)
(3)
(4)

示例2:

示例3:
(1)

(2)

2.相交链表
160. 相交链表
 https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/ 


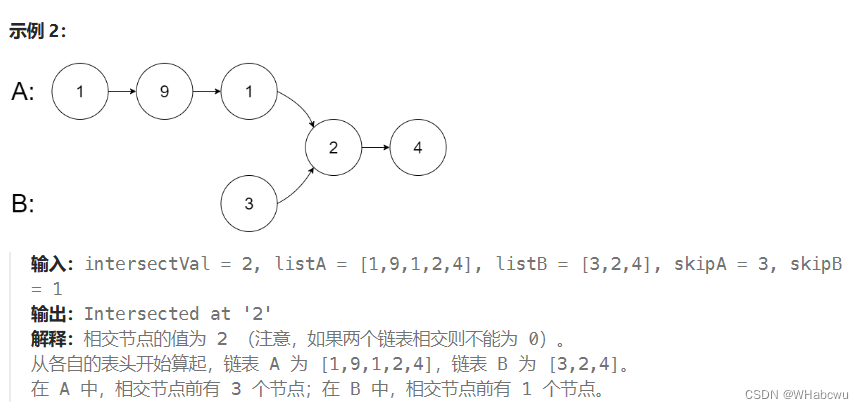


方法1
代码:
- public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
- if (head1==null||head2==null){
- return null;
- }
- int size1=size(head1);
- int size2=size(head2);
- int size=size1-size2;
- //设长链表为head1,短链表为head2
- if(size<0){
- size=-1*size;
- ListNode tmp=head1;
- head1=head2;
- head2=tmp;
- }
- while(size>0){
- size--;
- head1=head1.next;
- }
- while(head1!=head2){
- head1=head1.next;
- head2=head2.next;
- }
- return head1;
- }
- public int size(ListNode head){
- int count=0;
- while(head!=null){
- count++;
- head=head.next;
- }
- return count;
- }
解析:
(1)

(2)

(3)
 方法2
方法2代码:
- public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
- if (headA == null || headB == null) return null;
- ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB;
- while (pA != pB) {
- pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next;
- pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next;
- }
- return pA;
- }
解析:
pA走过的路径为A链+B链
pB走过的路径为B链+A链
pA和pB走过的长度都相同,都是A链和B链的长度之和,相当于将两条链从尾端对齐,如果相交,则会提前在相交点相遇,如果没有相交点,则会在最后相遇。
3.环形链表
环形链表
 https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/


代码:
- public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
- if(head==null){
- return false;
- }
- ListNode fast = head;
- ListNode slow = head;
- while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
- fast = fast.next.next;
- slow = slow.next;
- if(fast == slow) {
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
解析:
【思路】快慢指针,即慢指针一次走一步,快指针一次走两步,两个指针从链表起始位置开始运行,如果链表 带环则一定会在环中相遇,否则快指针率先走到链表的末尾。当慢指针刚进环时,可能就和快指针相遇了,最差情况下两个指针之间的距离刚好就是环的长度。此时,两个指针每移动一次,之间的距离就缩小一步,不会出现每次刚好是套圈的情况,因此:在慢指针走到一圈之前,快指针肯定是可以追上慢指 针的,即相遇。
扩展问题

小结:
走3步,在2个节点的环中实际上是走了一个周期多一步,当走1步的进入环与 走3步的没有相遇,之后就无法相遇,因为速度相同。
4.环形链表 II
142. 环形链表 II
 https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/
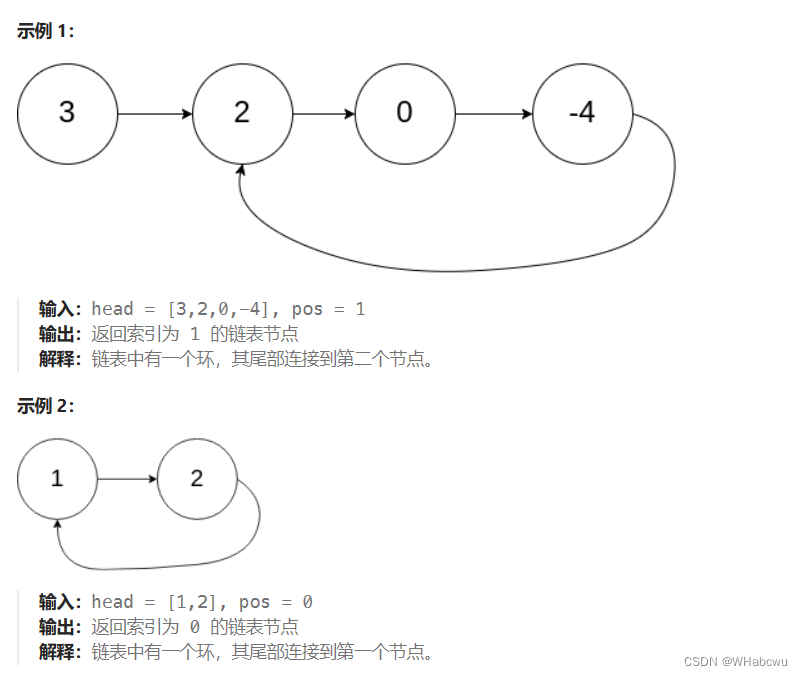
 代码:
代码:- public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
- if(head==null){
- return null;
- }
- ListNode fast = head;
- ListNode slow = head;
- while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
- fast = fast.next.next;
- slow = slow.next;
- if(fast == slow) {
- break;
- }
- }
- if(fast == null || fast.next == null){
- return null;
- }
- slow=head;
- while (slow!=fast){
- fast = fast.next;
- slow = slow.next;
- }
- return slow;
- }
解析:
结论让一个指针从链表起始位置开始遍历链表,同时让一个指针从判环时相遇点的位置开始绕环运行,两个指针 都是每次均走一步,最终肯定会在入口点的位置相遇 。证明:
以上为我个人的小分享,如有问题,欢迎讨论!!!
都看到这了,不如关注一下,给个免费的赞


-
相关阅读:
BIM、建筑机器人、隧道工程施工关键技术
数据可视化之交通可视化
【51单片机】直流电机驱动(PWM)(江科大)
在Windows系统上安装Docker和SteamCMD容器的详细指南有哪些?
计算机网络
【Mybatis】万能的map
【微服务部署】八、HAProxy+Keepalived高可用负载均衡集群配置
Vue.$nextTick的原理是什么-vue面试进阶
填坑之路!SpringBoot导包坑之spring-boot-starter-parent
JVM中的堆的新生代、老年代、永久代
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/WHabc2002/article/details/133144373
