-
在使用SpringBoot时遇到的异常总结(持续更新...)
因为平时在写SpringBoot项目时,总是会遇到各种各样的异常,因此在这里记录一下,以便以后再遇到相同的错误时能够有一个参考异常
MyBatis
java.sql.SQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException: Cannot add or update a child row: a foreign key constraint fails
时间:2023年09月18日
这个错误实际上并不是coding的问题,而是在向数据库中添加数据时出现的问题,更准确地说是外键约束的问题
-
squad表


-
member表

可以看到member表中的字段group_id是一个外键(不考虑user_id这一字段)
但是我在向数据库member表中插入数据时,插入的内容是:

可以发现,向member表插入的数据中groupId=0,但是在squad表中并不存在id=0,所以出现上述异常
还有一个地方:为什么表的名字是squad而不是group/groups,因为group/groups都是mysql的关键字,具体请参考这篇文章:记录使用mybatis-plus时遇到的错误Mybatis-Plus查询语句无故自动加条件
2023年09月18日
正常的查询语句:

在这里,查询语句是:SELECT COUNT(*) AS total FROM stakeholder WHERE deleted = 0 AND (user id = ?)- 1
但是,这次遇到的问题是出现了错误的查询语句,导致没有办法进行正常的查询:
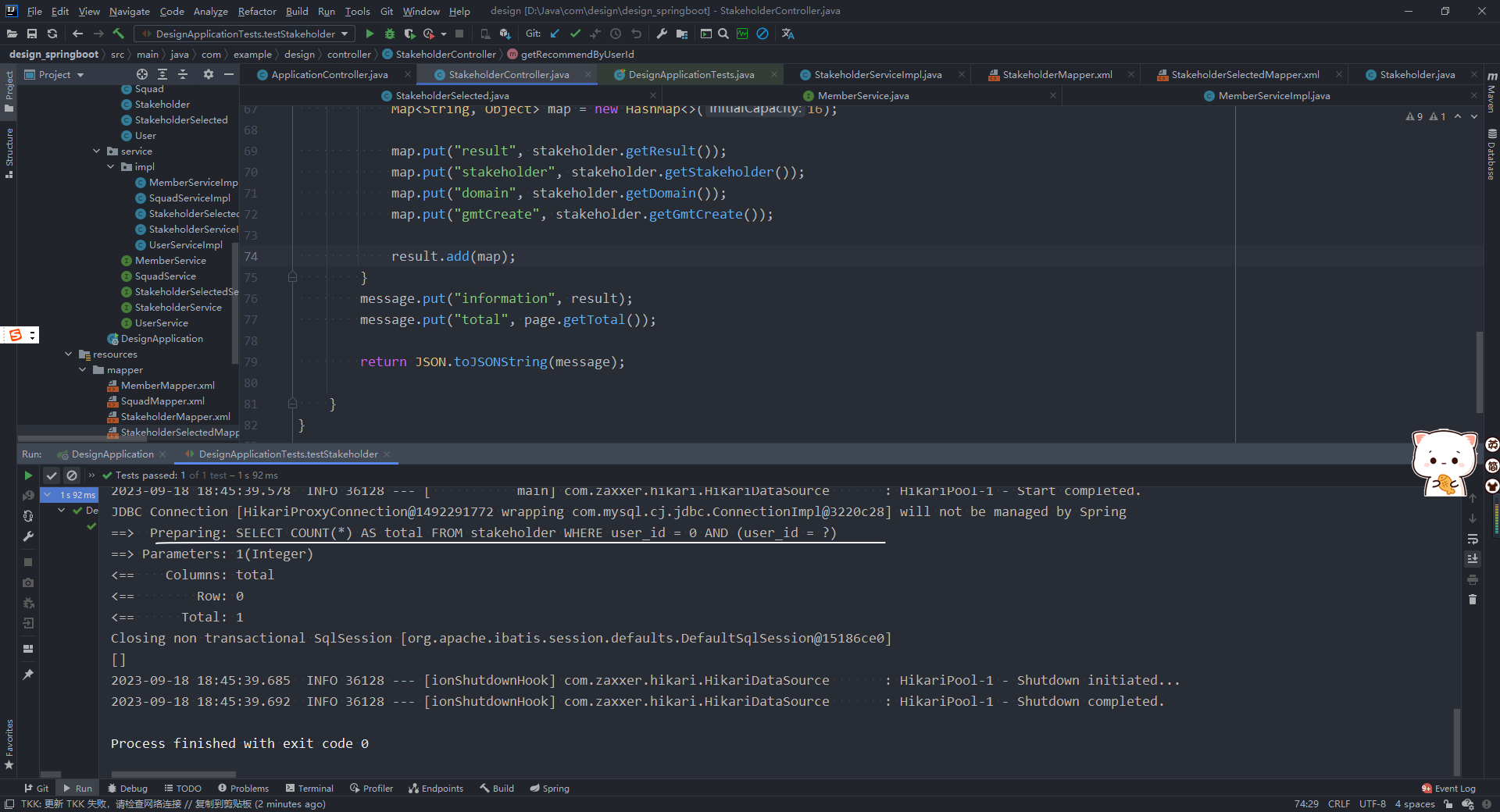
出现了错误的查询语句:SELECT COUNT(*) AS total FROM stakeholder WHERE user_id = 0 AND (user_id = ?)- 1
之所以会出现这样的问题,有两个方面的原因(因为我自己遇到了这两个方面的错误):
- 因为在
DAO实体类中某一个成员属性是这样定义的:private int userId;,问题就在这里,int 类型的默认值为0,此处应该采用 Integer ,封装类,Integer的默认值为 null ,改为Integer后QueryMapper要搜索的其值就不是0了而是null,即对当前数据库中的表进行全查,而不是查0 - 因为我用到了逻辑删除,我自己将逻辑删除的注解
@TableLogic放到了private Integer userId,导致出现了这样的问题
Mybatis No enum constant org.apache.ibatis.type.JdbcType.TEXT
2023年9月22日

当时我在mybatis的xml配置文件中,将jdbcType设置为和数据库保持一致的text类型,结果抛出了上述异常,JDBCType这个枚举类中不存在Text这个类型,那么我们需要查看一下JDBCType的源码:
public enum JDBCType implements SQLType { /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code BIT}. */ BIT(Types.BIT), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code TINYINT}. */ TINYINT(Types.TINYINT), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code SMALLINT}. */ SMALLINT(Types.SMALLINT), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code INTEGER}. */ INTEGER(Types.INTEGER), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code BIGINT}. */ BIGINT(Types.BIGINT), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code FLOAT}. */ FLOAT(Types.FLOAT), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code REAL}. */ REAL(Types.REAL), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code DOUBLE}. */ DOUBLE(Types.DOUBLE), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code NUMERIC}. */ NUMERIC(Types.NUMERIC), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code DECIMAL}. */ DECIMAL(Types.DECIMAL), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code CHAR}. */ CHAR(Types.CHAR), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code VARCHAR}. */ VARCHAR(Types.VARCHAR), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code LONGVARCHAR}. */ LONGVARCHAR(Types.LONGVARCHAR), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code DATE}. */ DATE(Types.DATE), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code TIME}. */ TIME(Types.TIME), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code TIMESTAMP}. */ TIMESTAMP(Types.TIMESTAMP), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code BINARY}. */ BINARY(Types.BINARY), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code VARBINARY}. */ VARBINARY(Types.VARBINARY), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code LONGVARBINARY}. */ LONGVARBINARY(Types.LONGVARBINARY), /** * Identifies the generic SQL value {@code NULL}. */ NULL(Types.NULL), /** * Indicates that the SQL type * is database-specific and gets mapped to a Java object that can be * accessed via the methods getObject and setObject. */ OTHER(Types.OTHER), /** * Indicates that the SQL type * is database-specific and gets mapped to a Java object that can be * accessed via the methods getObject and setObject. */ JAVA_OBJECT(Types.JAVA_OBJECT), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code DISTINCT}. */ DISTINCT(Types.DISTINCT), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code STRUCT}. */ STRUCT(Types.STRUCT), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code ARRAY}. */ ARRAY(Types.ARRAY), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code BLOB}. */ BLOB(Types.BLOB), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code CLOB}. */ CLOB(Types.CLOB), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code REF}. */ REF(Types.REF), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code DATALINK}. */ DATALINK(Types.DATALINK), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code BOOLEAN}. */ BOOLEAN(Types.BOOLEAN), /* JDBC 4.0 Types */ /** * Identifies the SQL type {@code ROWID}. */ ROWID(Types.ROWID), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code NCHAR}. */ NCHAR(Types.NCHAR), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code NVARCHAR}. */ NVARCHAR(Types.NVARCHAR), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code LONGNVARCHAR}. */ LONGNVARCHAR(Types.LONGNVARCHAR), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code NCLOB}. */ NCLOB(Types.NCLOB), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code SQLXML}. */ SQLXML(Types.SQLXML), /* JDBC 4.2 Types */ /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code REF_CURSOR}. */ REF_CURSOR(Types.REF_CURSOR), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code TIME_WITH_TIMEZONE}. */ TIME_WITH_TIMEZONE(Types.TIME_WITH_TIMEZONE), /** * Identifies the generic SQL type {@code TIMESTAMP_WITH_TIMEZONE}. */ TIMESTAMP_WITH_TIMEZONE(Types.TIMESTAMP_WITH_TIMEZONE); /** * The Integer value for the JDBCType. It maps to a value in * {@code Types.java} */ private Integer type; /** * Constructor to specify the data type value from {@code Types) for * this data type. * @param type The value from {@code Types) for this data type */ JDBCType(final Integer type) { this.type = type; } /** *{@inheritDoc } * @return The name of this {@code SQLType}. */ public String getName() { return name(); } /** * Returns the name of the vendor that supports this data type. * @return The name of the vendor for this data type which is * {@literal java.sql} for JDBCType. */ public String getVendor() { return "java.sql"; } /** * Returns the vendor specific type number for the data type. * @return An Integer representing the data type. For {@code JDBCType}, * the value will be the same value as in {@code Types} for the data type. */ public Integer getVendorTypeNumber() { return type; } /** * Returns the {@code JDBCType} that corresponds to the specified * {@code Types} value * @param type {@code Types} value * @return The {@code JDBCType} constant * @throws IllegalArgumentException if this enum type has no constant with * the specified {@code Types} value * @see Types */ public static JDBCType valueOf(int type) { for( JDBCType sqlType : JDBCType.class.getEnumConstants()) { if(type == sqlType.type) return sqlType; } throw new IllegalArgumentException("Type:" + type + " is not a valid " + "Types.java value."); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
因此我们需要在
\中将jdbcType设置为VARCHAR与数据库中Text类型数据进行映射参考文献
1、MyBatis添加数据报错Cannot add or update a child row: a foreign key constraint fails
2、Mybatis-Plus查询语句无故自动加条件 -
-
相关阅读:
JVM栈与堆(一)之栈和栈中单位栈帧
linux luasocket 使用
UE4_定序器控制蓝图对象
PyTorch Lightning - LightningModule 训练逻辑 (training_step) 异常处理 try-except
LeetCode 1.2.题
HTML小游戏3—— 机器人总动员(附完整源码)
浅析ARMv8体系结构:原子操作
【JavaEE初阶】 Callable 接口
redis的锁
【AD-NeRF】音频驱动人脸NeRF
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/julac/article/details/132975236
