-
Optuna学习博客
介绍
Optuna就是一个能够进行调整超参数的框架,它能够将自动调整超参数以及能够将超参数优化过程可视化,方便保存,分析。可拓展性较强,减枝的优点。
剪枝操作会根据当前中间结果判断是否还需要进行下去。optuna的优化程序具体有三个组成部分。
- objective,负责定义优化函数以及按照制定超参数的数值范围
- trial,对应着objective的执行(包括参数以及执行过程)
- study,负责管理优化,确定优化方式,实验总次数,时间等结果的实例(对象)
我们一般在objective函数中放置我们所需要优化的函数(确定优化目标)
下列以文档中给出的例子为参考。(主要针对不同模型的参数进行设置,所以在objective里面设置即可)如果有其他的需求可以参考官方文档。使用案例
机器学习调整参数+优化历史进行可视化
import optuna import sklearn from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor from sklearn.datasets import load_digits # Define an objective function to be minimized. def objective(trial): # Invoke suggest methods of a Trial object to generate hyperparameters. # 确定优化模型的名称/种类 regressor_name = trial.suggest_categorical('classifier', ['SVR', 'RandomForest']) if regressor_name == 'SVR': # 放置参数 svr_c = trial.suggest_loguniform('svr_c', 1e-10, 1e10, log=True) regressor_obj = sklearn.svm.SVR(C=svr_c) else: rf_max_depth = trial.suggest_int('rf_max_depth', 2, 32) regressor_obj = RandomForestRegressor(max_depth=rf_max_depth) X, y = load_digits(return_X_y=True) X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0) regressor_obj.fit(X_train, y_train) y_pred = regressor_obj.predict(X_val) error = sklearn.metrics.mean_squared_error(y_val, y_pred) # An objective value linked with the Trial object. return error # Create a new study. study = optuna.create_study(study_name='svm_test_optuna', direction='minimize') # 这里可以选择迭代的次数n_trials # Invoke optimization of the objective function. study.optimize(objective, n_trials=10) # 在这一步的时候需要运用pip install -U plotly>=4.0.0去安装plotly这个库进行每个trial的可视化 # 可视化的时候需要用下列的表达式去判断 print(optuna.visualization.is_available()) fig = optuna.visualization.plot_optimization_history(study) fig.show() print(study.best_params) # 最优参数 print(study.best_value) # 最优的loss/优化目标数值- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
返回的结果如下所示。
True
{‘classifier’: ‘SVR’, ‘svr_c’: 10748891.080318237}
0.5439382462559595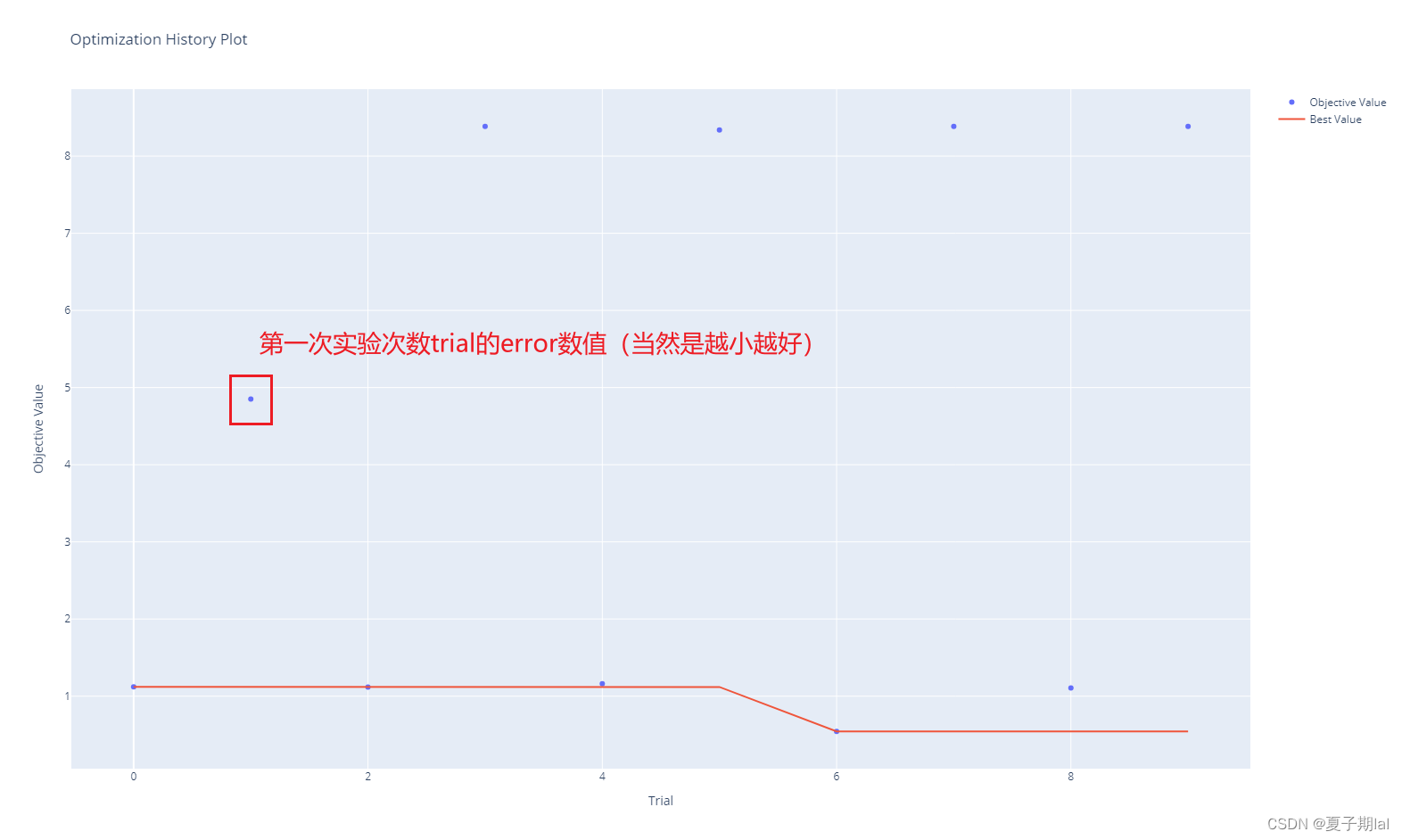
绘制各 trail单次实验次数的学习曲线(MLP模型为例子)
import optuna from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from sklearn.datasets import load_iris from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from optuna.visualization import plot_intermediate_values import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader # 加载Iris数据集 iris = load_iris() X, y = iris.data, iris.target X = X.astype(float) y = y.astype(int) # 划分训练集和验证集 X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42) # 定义自定义数据集类 class CustomDataset(Dataset): def __init__(self, data, target): self.data = data self.target = target def __len__(self): return len(self.data) def __getitem__(self, idx): x = self.data[idx] y = self.target[idx] return x, y # 单层MLP class mlp_model(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size): super(mlp_model, self).__init__() self.linear = nn.Linear(input_size, 1) self.relu = nn.ReLU() def forward(self, x): x = x.float() x = self.relu(x) out = self.linear(x) return out # 定义目标函数 def objective(trial): # 超参数搜索空间 learning_rate = trial.suggest_loguniform('learning_rate', 1e-5, 1e-1) # 创建模型和数据加载器 model = mlp_model(input_size=X_train.shape[1]) criterion = nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss() optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) train_dataset = CustomDataset(X_train, y_train) train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=16, shuffle=True) num_epochs = 50 train_loss = [] for epoch in range(num_epochs): model.train() epoch_loss = 0.0 for batch_x, batch_y in train_loader: optimizer.zero_grad() output = model(batch_x) loss = criterion(output.squeeze(), batch_y.float()) loss.backward() optimizer.step() epoch_loss += loss.item() train_loss.append(epoch_loss / len(train_loader)) trial.report(epoch_loss, epoch) if trial.should_prune(): raise optuna.exceptions.TrialPruned() return train_loss[-1] # 创建Optuna学习实例 study = optuna.create_study(direction='minimize') study.optimize(objective, n_trials=10) # 绘制中间值图 plot_intermediate_values(study).show() #- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
结果如图所示。(呈现交互式结果)

设置优化参数
- suggest_categorical(name, choices) 设置模型的名称或者为种类
- suggest_discrete_uniform(name, low, high, q) 设置离散类型变量的区间以及步长
- suggest_float(name, low, high, *[, step, log]) 设置浮点类型数据的区间和步长
- suggest_int(name, low, high[, step, log]) 设置整形类型数据的区间和步长
- suggest_loguniform(name, low, high) 设置连续类型数据的区间和步长(一般用这个设置学习率)
suggest_uniform(name, low, high) 设置连续类型数据的区间和步长
原文介绍如下所示。
具体可以参考下列链接。有关于设置参数的optuna搜索结果
查看优化参数参数以及结果
主要是通过study的参数查询即可。
- study.best_params(最优的参数)
- best_trial(最优的实验次数)
- best_valye(最优的loss/优化目标的值)
参考资料
或许是东半球最好用的超参数优化框架: Optuna 简介
Optuna: 一个超参数优化框架(官方中文文档)
Optimize Your Optimization(官方网站)
Optuna: 一个超参数优化框架(官方英文文档) -
相关阅读:
对 Python 中 GIL 的一点理解
C++进制转换题
Java下打印直角三角型(另一个方向)
线上展厅设计服务
【leetcode面试经典150题】71. 对称二叉树(C++)
C/C++数据结构——虚虚实实(并查集欧拉路)
计算机视觉项目-文档扫描OCR识别
区别:b、B、KB、M、MB、GB、TB、PB、EB、ZB、YB、BB以及它们之间的关系
Python3,os模块还可以这样玩,自动删除磁盘文件,非必要切勿操作。
空气扬尘远程监控物联网解决方案
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/xiaziqiqi/article/details/132873740
