-
数据结构——【堆】
一、堆的相关概念
1.1、堆的概念
1、堆在逻辑上是一颗完全二叉树(类似于一颗满二叉树只缺了右下角)。
2、堆的实现利用的是数组,我们通常会利用动态数组来存放元素,这样可以快速拓容也不会很浪费空间,我们是将这颗完全二叉树用层序遍历的方式储存在数组里的。
3、堆有两种分别是大根堆和小根堆 。
1.2、堆的分类
1.2.1、大根堆
大根堆就是整个完全二叉树,任意一个根节点的值都比左右子树的值大
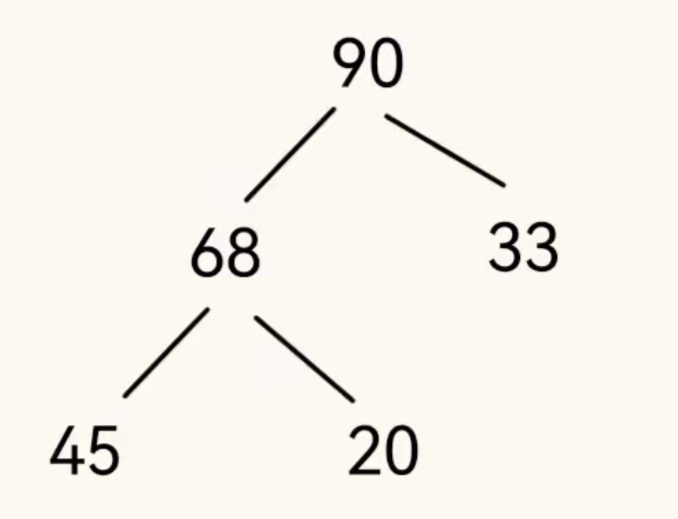
这就是一个大根堆,所有根节点的值永远比左右子树的大,那么就可以看出,整棵树的根节点,他的值是整个堆中最大的。同时我们也发现没有直接父子关系的节点他们的值没有完全地关系,就像第二层的33和第三层的45以及20,没有规定第三层的元素值必须小于第二层,只要满足根节点比自己左右子树节点的值大即可。
1.2.3、小根堆
小根堆表示整个完全二叉树,任意一个根节点的值都比左右子树的值小。
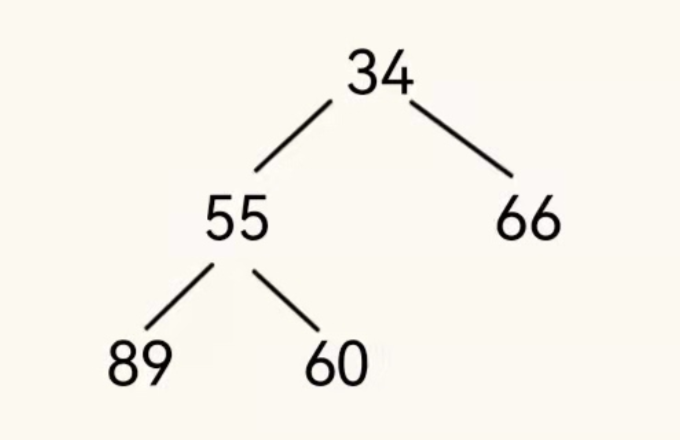
以上就是一个简单地小根堆它的定义与大根堆相似,只是跟节点的值小于自己的左右节点的值,同时小根堆的层与层之间没有直接关系的节点的值也没有必然的大小关系。
1.3、堆的结构
堆的逻辑结构是一颗完全二叉树
堆的物理结构是一个数组
我们可以用左右孩子节点和父节点,来表示所有的节点。
leftchild = parent * 2 + 1;
rightchild = parent * 2 + 2;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;(child可以是左孩子,也可以是右孩子)
如下图:是一个大根堆,父节点的值都大于子节点的值。
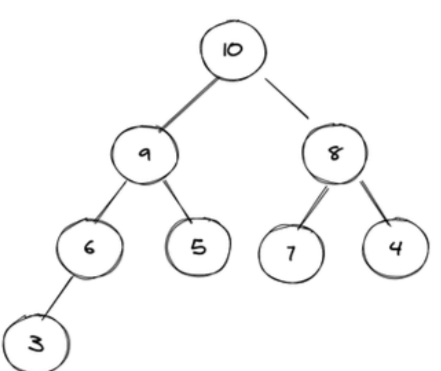
在数组中存储的是:
10 9 8 6 5 7 4 3 二、堆的实现
2.1、堆的功能
我们是以顺序表的形式实现的堆,其中基本的操作和顺序表的操作是大致一样的。
下面是我们要实现的堆的一些基础功能
- #pragma once
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- typedef int HPDataType;
- typedef struct Heap
- {
- HPDataType* a;
- int size;
- int capacity;
- }Heap;
- //堆的初始化
- void HeapInit(Heap* hp);
- // 堆的构建
- void HeapCreate(Heap* hp, HPDataType* a, int n);
- // 堆的销毁
- void HeapDestory(Heap* hp);
- // 堆的插入
- void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HPDataType x);
- // 堆的删除
- void HeapPop(Heap* hp);
- // 取堆顶的数据
- HPDataType HeapTop(Heap* hp);
- // 堆的数据个数
- int HeapSize(Heap* hp);
- // 堆的判空
- int HeapEmpty(Heap* hp);
- //打印堆
- void HeapPrint(Heap* hp);
- //交换函数
- void Swap(HPDataType* p1, HPDataType* p2);
2.2、堆函数的实现
- #include"Heap.h"
- //初始堆
- void HeapInit(Heap* hp)
- {
- assert(hp);
- hp->a = NULL;
- hp->size = 0;
- hp->capacity = 0;
- }
- // 堆的销毁
- void HeapDestory(Heap* hp)
- {
- assert(hp);
- free(hp->a);
- hp->a = NULL;
- hp->size = hp->capacity = 0;
- }
- //交换函数
- void Swap(HPDataType* p1, HPDataType* p2)
- {
- HPDataType temp = *p1;
- *p1 = *p2;
- *p2 = temp;
- }
- //向上调整(前面的是堆)
- void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child)
- {
- int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
- while (child > 0)
- {
- //小堆
- if (a[child] < a[parent])
- {
- Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
- child = parent;
- parent = (parent - 1) / 2;
- }
- else
- {
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- //打印堆
- void HeapPrint(Heap* hp)
- {
- assert(hp);
- for (size_t i = 0; i < hp->size; i++)
- {
- printf("%d ",hp->a[i]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- // 堆的插入
- void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HPDataType x)
- {
- assert(hp);
- if (hp->size == hp->capacity)
- {
- int newcapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : hp->capacity * 2;
- HPDataType* tem = (HPDataType*)realloc(hp->a,sizeof(HPDataType)*newcapacity);
- if (tem == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc fail");
- exit(-1);
- }
- hp->a = tem;
- hp->capacity = newcapacity;
- }
- hp->a[hp->size] = x;
- hp->size++;
- AdjustUp(hp->a, hp->size - 1);
- }
- //向下调整(大堆或者小堆)
- void AdjustDown(HPDataType* a, int n, int parent)
- {
- int child = parent * 2 + 1;
- while (child < n)
- {
- //小堆
- if (child + 1 < n && a[child+1] < a[child]) //找到两个孩子节点较小的值
- {
- child++;
- }
- //建小堆
- if (a[child]<a[parent])
- {
- Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
- parent = child;
- child = parent * 2 + 1;
- }
- else
- {
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- // 堆顶元素的删除
- void HeapPop(Heap* hp)
- {
- assert(hp);
- assert(hp->size>0);
- Swap(&hp->a[0], &hp->a[hp->size-1]);
- --hp->size;
- AdjustDown(hp->a, hp->size, 0); //大堆
- }
- // 堆的构建
- void HeapCreate(Heap* hp, HPDataType* a, int n)
- {
- assert(hp);
- assert(a);
- hp->a = (HPDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HPDataType) * n);
- if (hp->a == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc fail");
- exit(-1);
- }
- hp->size = n;
- hp->capacity = n;
- memcpy(hp->a, a,sizeof(HPDataType) * n);
- //建堆
- for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
- {
- AdjustUp(hp->a, i);
- }
- }
- // 取堆顶的数据
- HPDataType HeapTop(Heap* hp)
- {
- assert(hp);
- assert(hp->size > 0);
- return hp->a[0];
- }
- // 堆的判空
- int HeapEmpty(Heap* hp)
- {
- assert(hp);
- return hp->size == 0;
- }
- // 堆的数据个数
- int HeapSize(Heap* hp)
- {
- assert(hp);
- return hp->size;
- }
2.3、堆的插入
堆是一个完全二叉树,在插入元素时是在堆的末尾插入的,但是为了把一个元素插入后,使这个堆还是一个堆,我们需要对堆中的数据尽心再次调整。
向上调整
我们插入一个元素是,在进行向上调整,把这个数放到合适的位置。我们来看看代码实现
- void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child)
- {
- int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
- while (child > 0)
- {
- //大堆
- if (a[child] > a[parent])
- {
- Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
- child = parent;
- parent = (parent - 1) / 2;
- }
- else
- {
- break;
- }
- }
- }
下面这张图帮助大家理解
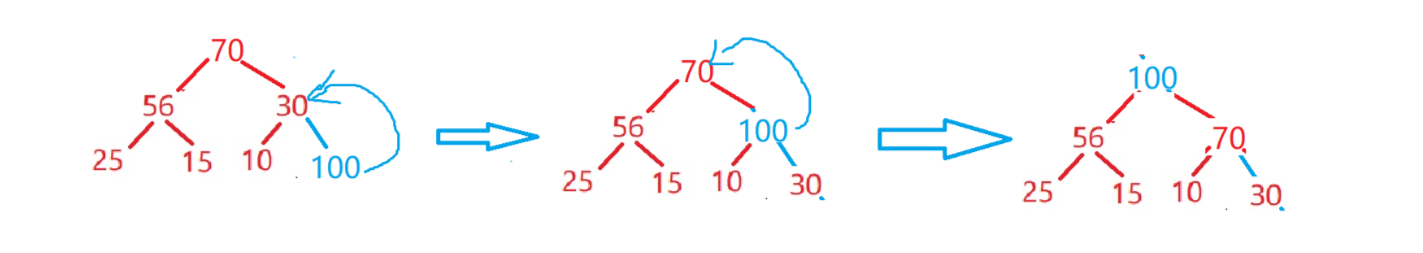
接下来我们来实现堆的插入
我们还是和顺序表一样,相对其扩容情况进行讨论,当hp->size==hp->capacity时,证明没有多余空间了,我们需要增加空间,这里还是使用,realloc函数,将这个数插入进去后,对这个数进行向上调整,使之变成一个新堆。
- void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HPDataType x)
- {
- assert(hp);
- if (hp->size == hp->capacity)
- {
- int newcapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : hp->capacity * 2;
- HPDataType* tem = (HPDataType*)realloc(hp->a,sizeof(HPDataType)*newcapacity);
- if (tem == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc fail");
- exit(-1);
- }
- hp->a = tem;
- hp->capacity = newcapacity;
- }
- hp->a[hp->size] = x;
- hp->size++;
- AdjustUp(hp->a, hp->size - 1);
- }
2.4、堆的删除
向上调整
我们在堆中删除一个元素时删除的时堆顶元素,也就是第一个元素,我们一般会先让第一个元素和最后一个元素交换位置,然后hp->size--;为了让新的数据成为堆,我们将第一个数据向下调整,使之变成一个新堆。
我们来看看向下调整的代码该如何写:
- void AdjustDown(HPDataType* a, int n, int parent)
- {
- int child = parent * 2 + 1;
- while (child < n)
- {
- //小堆
- if (child + 1 < n && a[child+1] > a[child]) //找到两个孩子节点较大的值
- {
- child++;
- }
- //建小堆
- if (a[child]>a[parent])
- {
- Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
- parent = child;
- child = parent * 2 + 1;
- }
- else
- {
- break;
- }
- }
- }
我们来看看这张图跟好的理解向下调整:
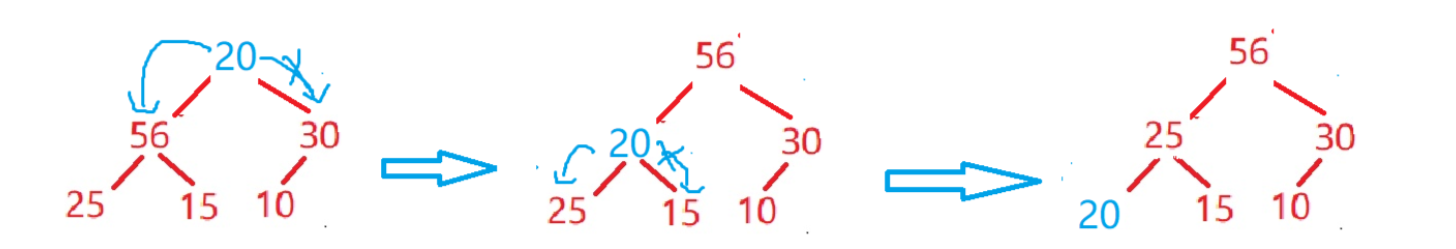
接下来我们来实现堆的删除
我们先考虑一下hp->size的临界问题,用一个断言就可以避免此类问题。
- void HeapPop(Heap* hp)
- {
- assert(hp);
- assert(hp->size>0);
- Swap(&hp->a[0], &hp->a[hp->size-1]);
- --hp->size;
- AdjustDown(hp->a, hp->size, 0); //大堆
- }
三、建堆
给一个数组我们如何把这个数组建成堆呢?
一般我们都有两种方法:
3.1、自顶向下(向上调整)
我们来看看代码如何实现
- void HeapCreate(Heap* hp, HPDataType* a, int n)
- {
- assert(hp);
- assert(a);
- hp->a = (HPDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HPDataType) * n);
- if (hp->a == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc fail");
- exit(-1);
- }
- hp->size = n;
- hp->capacity = n;
- memcpy(hp->a, a,sizeof(HPDataType) * n);
- //建堆
- for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
- {
- AdjustUp(hp->a, i);
- }
- }
我们使用错位相减的方式来计算 自顶向下(向上调整)的时间复杂度

时间复杂度:O(nlog(2)^n)
3.2、自低向上(向下调整)
我们来看看代码如何实现
- void HeapCreate(Heap* hp, HPDataType* a, int n)
- {
- assert(hp);
- assert(a);
- hp->a = (HPDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HPDataType) * n);
- if (hp->a == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc fail");
- exit(-1);
- }
- hp->size = n;
- hp->capacity = n;
- memcpy(hp->a, a,sizeof(HPDataType) * n);
- //建堆
- //向下调整算法
- for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
- {
- AdjustDown(arr, n, i);
- }
- }
和自顶向下一样,还是错位相减来计算时间复杂度

时间复杂度:O(n)
四、堆的排序
我们学习堆,有一个很有用的地方,就是可以用堆进行排序,因为我们知道,大堆堆顶元素是数组中最小的,小队堆顶是数组中元素最小的。
当我们需要将一个数组进行从小到大的排序时:
1.将该数组建成一个大堆
2.第一个数和最后一个数交换,然后把交换的那个较大的数不看做堆里面
3.前n-1和数进行向下调整算法,选出大的数放到根节点,再跟倒数第二个交换......
代码如下:
- void HeapSort(int* a,int n)
- {
- int i = 0;
- //这里用向下调整算法来建堆,因为时间复杂度只有O(N)
- for (i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
- {
- AdjustDown(a, n, i);
- }
- int end = n - 1;
- while (end > 0)
- {
- Swap(&a[0], &a[end]);
- AdjustUp(a, end, 0);
- --end;
- }
- }
时间复杂度:O(Nlog(2)^N)
五、topk问题
我们在做一些编程题会遇到一类问题,就是topk问题
topk问题指的有一组很大的数据,我们需要返回它最大(最小)的前K个元素。
这里我们就可以用堆排序很好的解决此类问题。
这里力扣平台有一个练习题,我们一起来看一看
面试题 17.14. 最小K个数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
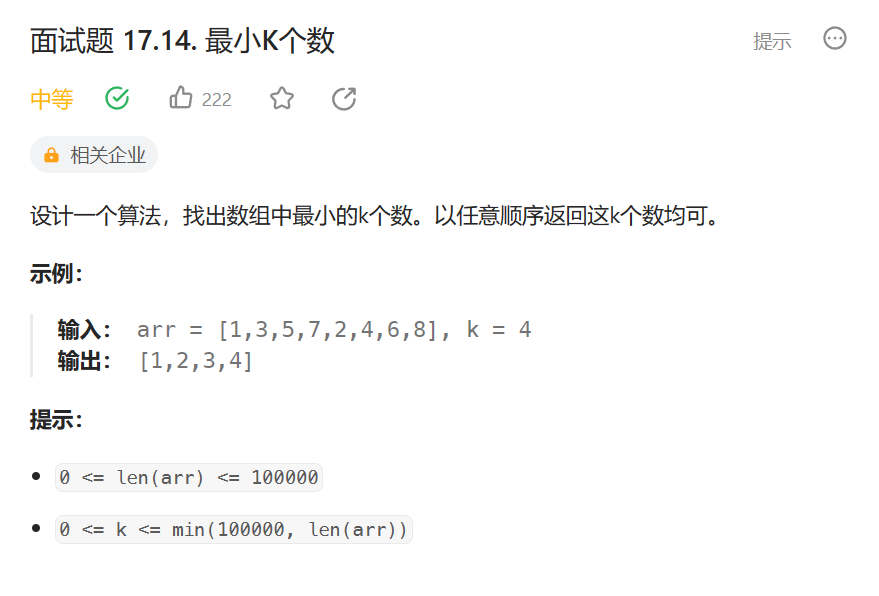
思路:我们先建立一个大堆,先把前K个元素建成一个大堆,然后在将剩下的数和堆顶元素进行比较,如过大于堆顶数据,我们就和堆顶元素进行交换,然后将现在的堆顶元素向下调整,前k个数就是这组数据中最小的前K个数。
我们来看看该如何实现:
- void Swap(int* p1, int* p2)
- {
- int temp = *p1;
- *p1 = *p2;
- *p2 = temp;
- }
- //向下调整
- void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent)
- {
- int child = parent * 2 + 1;
- while (child < n)
- {
- //大堆
- if (child + 1 < n && a[child+1] > a[child]) //找到两个孩子节点较小的值
- {
- child++;
- }
- //建大堆
- if (a[child]>a[parent])
- {
- Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
- parent = child;
- child = parent * 2 + 1;
- }
- else
- {
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- int* smallestK(int* arr, int arrSize, int k, int* returnSize)
- {
- if(k==0)
- {
- *returnSize=0;
- return NULL;
- }
- int *ret=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*k);
- for(int i=0;i<k;i++)
- {
- ret[i]=arr[i];
- }
- //给前k个元素建大堆
- for(int i=(k-1-1)/2;i>=0;i--)
- {
- AdjustDown(ret, k, i);
- }
- for(int i=k;i<arrSize;i++)
- {
- if(ret[0]>arr[i])
- {
- ret[0]=arr[i];
- AdjustDown(ret,k,0);
- }
- }
- *returnSize=k;
- return ret;
- }
六、大量数据中的topk问题
比如我们现在有100000个数据,我们要找到最大的10个数据,我们需要改怎么实现,还是利用topk解决,我们先将前100个数据建成一个小堆
- //创建一个文件,并且随机生成一些数字
- void CreateDataFile(const char* filename, int N)
- {
- FILE* Fin = fopen(filename, "w");
- if (Fin == NULL)
- {
- perror("fopen fail");
- exit(-1);
- }
- srand(time(0));
- for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
- {
- fprintf(Fin, "%d ", rand() % 10000);
- }
- }
- void PrintTopK(const char* filename, int k)
- {
- assert(filename);
- FILE* fout = fopen(filename, "r");
- if (fout == NULL)
- {
- perror("fopen fail");
- return;
- }
- int* minheap = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * k);
- if (minheap == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc fail");
- return;
- }
- //读前k个数
- for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
- {
- //空格和换行默认是多个值之间的间隔
- fscanf(fout, "%d", &minheap[i]);
- }
- //建k个数的堆
- for (int j = (k - 1 - 1) / 2; j >= 0; j--)
- {
- AdjustDown(minheap, j, k, cmp_down);
- }
- //读取后N-K个
- int x = 0;
- while(fscanf(fout,"%d",&x)!=EOF)
- {
- if (x > minheap[0])
- {
- minheap[0] = x;
- AdjustDown(minheap, 0, k, cmp_down);
- }
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
- {
- printf("%d ", minheap[i]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- free(minheap);
- fclose(fout);
- }
- int main()
- {
- //CreateDataFile("data.txt", 1000000);
- //找前10个最大的数
- PrintTopK("data.txt", 10);
- return 0;
- }
这里只截取了一小部分
我们提前改10个较大的数,验证返回的正确错误。
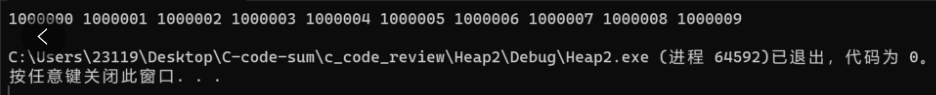
返回的就是我们改的10个大的数字,证明返回正确,而且效率极其的高!
总结:堆的知识就介绍到这里,如有疑问或者质疑,请在评论区发出来,我会尽全力帮大家解决,成长的路上少不了你们的支持,你们的三连是我进步最大的动力,还望大佬们多多支持,一起加油!共勉!
-
相关阅读:
SpringBoot+Vue项目自媒体社区平台
【花雕体验】12 搭建ESP32C3之Arduino开发环境
Python程序化生成三维场景【PyPRT】
自动化测试工具ANSIM,实现4/5/6G核心网产品高效交付
HTML+CSS网页设计期末课程大作业 【茶叶文化网站设计题材】web前端开发技术 web课程设计 网页规划与设计
力扣113题引发的关于DFS和回溯的一点思考
提升技术的13个建议
曲线救国|基于函数计算FC3.0部署AI数字绘画stable-diffusion
Eureka架构篇 - 服务发现
限量版Spring实战笔记与其在收藏里吃灰,不如大家一起学习,欸 大家一起卷!
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_69323023/article/details/132834448
