好家伙,
1.使用场景
现在来,来想一下,作为一个使用Vue的开发者,假设现在我们要使用created(),我们会如何使用
1.1. .vue文件中使用
{{ message }}
1.2. Vue实例中使用
<head>Vue created() example head>id="app">{{ message }}
1.3. 混入
Vue.Mixin({ //全局
created:function a(){
console.log('a----1')
}
})
那么如果我这样去定义
是否会报错呢?
答案是不会
对于created()钩子函数,在每个Vue实例创建时,会依次执行全局混入函数中定义的created()方法和实例本身定义的created()方法。
当Vue实例被创建时,它会先执行全局混入函数的对应生命周期钩子函数,然后再执行实例本身的生命周期钩子函数。
因此,在你的代码中,全局混入函数中的created()会在实例的created()之前执行,且会按照它们在全局混入函数中的定义顺序执行。
这样的设计允许开发者在多个地方定义相同的生命周期钩子函数,以实现不同的功能扩展和逻辑处理。
同时,由于生命周期钩子函数的执行顺序已经确定,开发者可以根据需要合理安排代码逻辑
最后,也说明,created()定义的方法被合并处理了,所以我们要把这个"合并"实现
2.项目上下文
老样子,先看看项目更新了哪些东西
代码已开源https://github.com/Fattiger4399/analytic-vue.git

2.1.Vue入口文件index.js中

添加全局方法
2.2. global-api/index.js
import { mergeOptions } from "../utils/index"
export function initGlobApi(Vue) {
//源码
//Vue.options ={created:[a,b,c],watch:{a,b}}
Vue.options ={}
Vue.Mixin = function (mixin) { // {}
//源码
//{created:[a,b,c],watch:[a,b]}
//对象的合并
console.log(999)
this.options = mergeOptions(this.options,mixin)
console.log(Vue.options,"||this is vue.options")
}
}
此处涉及我们的核心方法mergeOptions
这方法要实现一个怎么样的效果?
Vue.Mixin({ //全局
created: function a() {
console.log('a----1')
}
})
Vue.Mixin({ //全局
created: function b() {
console.log('b----2')
}
})
let vm = new Vue({
el: '#app', //编译模板
// data: {
// },
data() {
// console.log(this)
return {
msg: 'hello',
a: {
b: 99
},
list: [1, 2, 3],
arr: [{
a: 1
}]
}
},
created() {
console.log(555)
}
})
将上述所有与created()有关的方法
最后合并到一个对象当中去

3.核心方法
3.1.utils/index.js
来到我们全篇最核心也是最难的部分
//对象合并 {created:[]}
export const HOOKS =[
"beforeCreated",
"created",
"beforeMount",
"mounted",
"beforeUpdate",
"updated",
"beforeDestory",
"destroyed",
]
// 策略模式
let starts ={}
starts.data =function(parentVal,childVal){
return childVal
} //合并data
starts.computed =function(){} //合并computed
starts.watch =function(){} //合并watch
starts.methods =function(){} //合并methods
//遍历生命周期
HOOKS.forEach(hooks=>{
starts[hooks] = mergeHook
})
function mergeHook(parentVal,childVal){
if(childVal){
if(parentVal){
//把子元素合并进去
return parentVal.concat(childVal)
}else{
return [childVal] //[a]
}
}else{
return parentVal
}
}
export function mergeOptions(parent, child) {
console.log(parent,child,'||this is parent and child in mergeOptions()')
const options ={}
//判断父亲
for(let key in parent){
console.log(key,'||this is key')
mergeField(key)
}
//判断儿子
for(let key in child){
console.log(key,'||this is key')
mergeField(key)
}
function mergeField(key){
//根据key 策略模式
if(starts[key]){ //created {created:[a]}
options[key] =starts[key](parent[key],child[key])
}else{
options[key] = child[key]
}
}
return options
}
这玩意要看懂,必须先把这玩意学了,策略模式
一句话概括策略模式是一种行为型设计模式,它允许在运行时根据不同的情境选择并应用不同的算法或行为(不是条件判断)
挖个坑,后面会补一章策略模式
//对象合并 {created:[]}
export const HOOKS =[
"beforeCreated",
"created",
"beforeMount",
"mounted",
"beforeUpdate",
"updated",
"beforeDestory",
"destroyed",
]
// 策略模式
let starts ={}
starts.data =function(parentVal,childVal){
return childVal
} //合并data
starts.computed =function(){} //合并computed
starts.watch =function(){} //合并watch
starts.methods =function(){} //合并methods
//遍历生命周期
HOOKS.forEach(hooks=>{
starts[hooks] = mergeHook
})
function mergeHook(parentVal,childVal){
if(childVal){
if(parentVal){
//把子元素合并进去
return parentVal.concat(childVal)
}else{
return [childVal] //[a]
}
}else{
return parentVal
}
}
这里定义常量HOOKS包含了一组生命周期钩子的名字
随后创建starts对象,用于存储各个不同属性的不同合并策略
至于mergeHook,这就是个简单的合并方法,不用多解释了
再来看下半部分
export function mergeOptions(parent, child) {
console.log(parent,child,'||this is parent and child in mergeOptions()')
const options ={}
//判断父亲
for(let key in parent){
console.log(key,'||this is key')
mergeField(key)
}
//判断儿子
for(let key in child){
console.log(key,'||this is key')
mergeField(key)
}
function mergeField(key){
//根据key 选择不同策略区处理
if(starts[key]){ //created {created:[a]}
options[key] =starts[key](parent[key],child[key])
}else{
options[key] = child[key]
}
}
return options
}
mergeOptions将父项和子项合并成一个新的对象
这个你真的得亲自上手调试一下
3.2.init.js
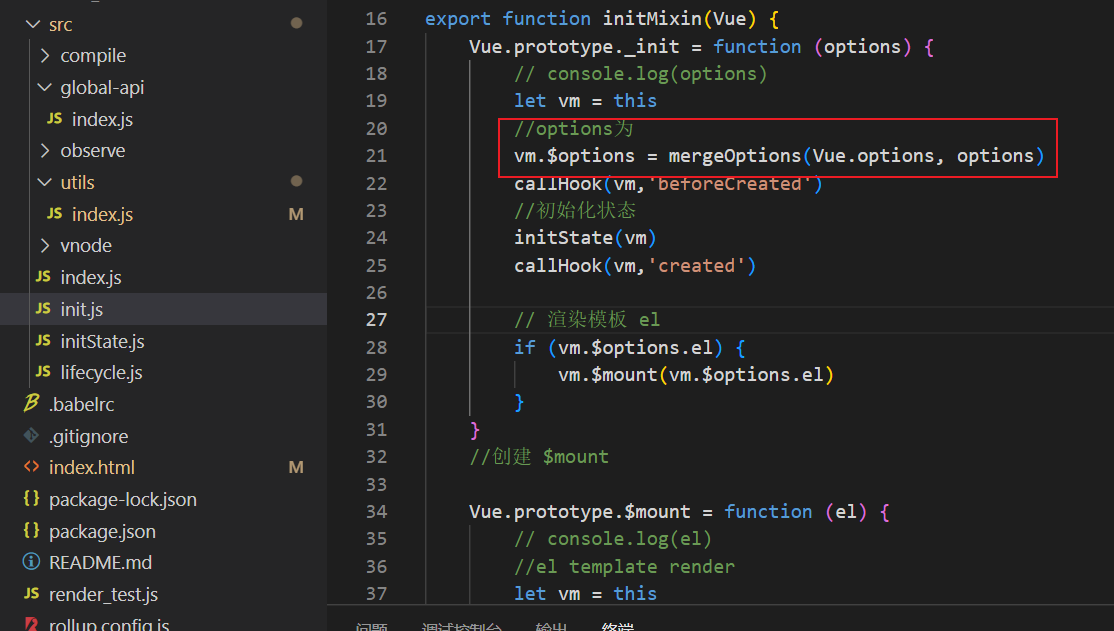
这句就是将在option合并Vue.option中并返回给vm.$options
(option为new Vue时带的参数)
最后,看看效果
将方法都合并到了created中

