-
LeetCode //C - 637. Average of Levels in Binary Tree
637. Average of Levels in Binary Tree
Given the root of a binary tree, return the average value of the nodes on each level in the form of an array. Answers within 1 0 − 5 10^{-5} 10−5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
Example 1:
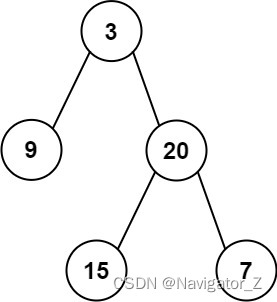
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [3.00000,14.50000,11.00000]
Explanation: The average value of nodes on level 0 is 3, on level 1 is 14.5, and on level 2 is 11.
Hence return [3, 14.5, 11].Example 2:
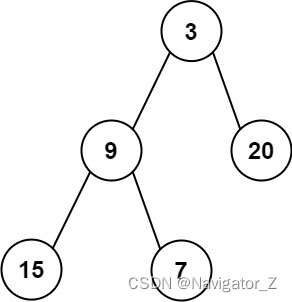
Input: root = [3,9,20,15,7]
Output: [3.00000,14.50000,11.00000]Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [ 1 , 1 0 4 1, 10^4 1,104].
- − 2 31 < = N o d e . v a l < = 2 31 − 1 -2^{31} <= Node.val <= 2^{31} - 1 −231<=Node.val<=231−1
From: LeetCode
Link: 637. Average of Levels in Binary Tree
Solution:
Ideas:
-
Initialize a queue to store nodes at the current level.
-
Add the root node to the queue.
-
While there are nodes in the queue:
a. Record the number of nodes at the current level (i.e., the size of the queue).b. Initialize two variables: sum for the sum of node values at the current level, and count for the number of nodes.
c. For each node at the current level:
- i. Dequeue the node.
- ii. Add its value to sum.
- iii. Enqueue its left child and right child (if they exist).
- iv. Increment count.
d. Compute the average for the current level by dividing sum by count. Add this average to the result list.
-
Return the result list.
Code:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ /** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ double* averageOfLevels(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){ // Edge case: if the tree is empty if (!root) { *returnSize = 0; return NULL; } struct TreeNode** queue = (struct TreeNode**)malloc(10000 * sizeof(struct TreeNode*)); double* result = (double*)malloc(10000 * sizeof(double)); int front = 0, rear = 0, levelCount, resultIndex = 0; double sum; queue[rear++] = root; // enqueue root while (front < rear) { levelCount = rear - front; // nodes at current level sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < levelCount; i++) { struct TreeNode* currentNode = queue[front++]; sum += currentNode->val; if (currentNode->left) queue[rear++] = currentNode->left; if (currentNode->right) queue[rear++] = currentNode->right; } result[resultIndex++] = sum / levelCount; } *returnSize = resultIndex; free(queue); return result; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
-
相关阅读:
Haproxy负载均衡集群
Kubernetes kafka系列 | k8s部署kafka+zookeepe集群
python-3.列表简介
四十九、openlayers官网示例Immediate Rendering (Geographic)——在地图上绘制星空动画效果
怎么把flac转换成mp3格式?
vue3 echarts实现k线
Allegro如何给铜皮导弧操作详解
【maven】idea中基于maven-webapp骨架创建的web.xml问题
期货开户中常见问题汇总
51nod 22.7暑假冲刺联训CSP-J 第一场II D题
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/navicheung/article/details/132894322
