-
R-Drop: Regularized Dropout for Neural Networks解读
R-Drop: Regularized Dropout for Neural Networks
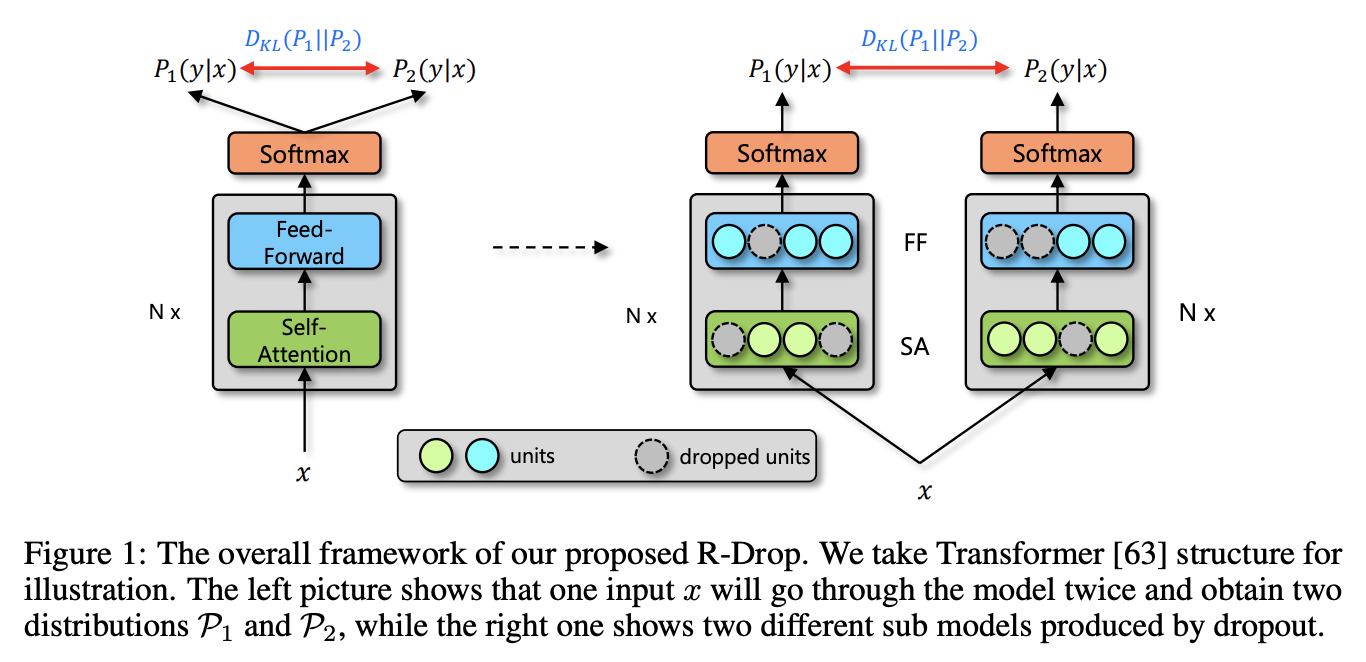
R-Drop的基本思想是:同一个step里面,对于同一个样本,前向传播两次,由于Dropout的存在,会得到两个不同但差异很小的概率分布,通过在原来的交叉熵损失中加入这两个分布的KL散度损失,来共同进行反向传播,参数更新R-Drop刚好是把sub model和完整model之间加了一个bound,如下图:

在下游任务上可以普遍地涨点SimCSE
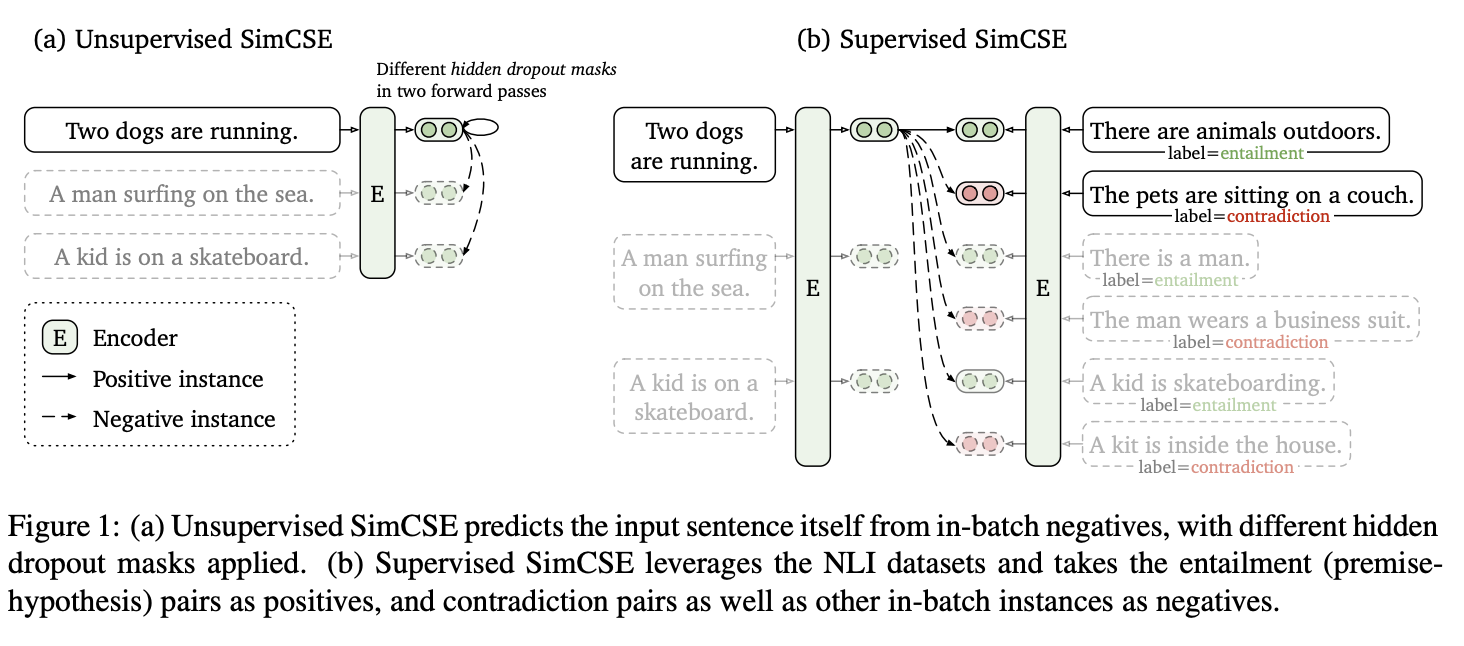
We evaluate SimCSE on standard semantic textual similarity (STS) tasks, and our unsupervised and supervised models using BERTbase achieve an average of 76.3% and 81.6% Spearman’s correlation respectively, a 4.2% and 2.2% improvement compared to the previous best results.部分参考:
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/409523468
- https://www.zhihu.com/zvideo/1528754585883242498
-
相关阅读:
z-library应急办法
机器学习之数据清洗和预处理
PyQt5入门2——添加一个画布并且显示特定的图片
【华为OpenEuler】VirtualBox虚拟机与OpenEuler环境搭建教程
KubeGems容器云平台体验
不同系统下的文件层级符号小结
TestNG与ExtentReport单元测试导出报告文档
JavaScript 进阶03
Python异常使用三大注意事项详解!
旋转矩阵中的易错点
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/taoqick/article/details/132946042