-
【C++】C++ 引用详解 ⑥ ( 普通变量 / 一级指针 / 二级指针 做函数参数的作用 )
一、普通变量 / 一级指针 / 二级指针 做函数参数的作用
1、普通变量 做函数参数的作用
普通变量 的 作用 : 将 普通变量 传入函数作为参数 ,
- 则可以在 函数 中 , 访问到 该 普通变量 的值 ,
- 但是 无法修改 该普通变量 ;
2、一级指针 做函数参数的作用
一级指针 的 作用 : 将 普通变量 的 一级指针 传入函数作为参数 ,
- 可以在函数中 访问 该 一级指针 指向的 普通变量 , 并且可以 修改 该普通变量 的值 ,
- 但是 该普通变量 所在内存地址 不能被修改 ;
3、二级指针 做函数参数的作用
二级指针 的 作用 : 将 普通变量 的 二级指针 传入函数作为参数 ,
- 可以在 函数中 访问 该 二级指针 指向的 一级指针 , 以及 访问 一级指针 指向的 内存空间中的 普通变量值 , 不仅可以修改普通变量的值 , 还可以重新创建该普通变量 , 修改 该普通变量在内存中的地址 ;
使用 二级指针 作为参数 , 可以实现如下功能 :
- 动态内存管理 : 借助二级指针 , 可以在函数中分配或释放内存 ; 如 : 创建一个动态数组或调整现有数组的大小 , 在函数中需要一个指向指针的指针作为参数 , 以便修改原始指针 ;
void createArray(int **arr, int size) { *arr = malloc(size * sizeof(int)); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 修改指针的值 : 借助二级指针 , 可以在函数中修改指针的值 , 即改变它所指向的地址 ; 如果直接传递 一级指针 , 函数只能修改指针指向内存中的数据 , 指针的指向不会改变 ;
void changePointer(int **ptr) { int new_value = 10; *ptr = &new_value; // 修改指针值 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 传递多维数组 : C 语言中 , 数组名本质上是指向数组第一个元素的指针 , 传递多维数组到函数中通常需要传递一个指向指针的指针 , 即二级指针 ; 借助二级指针 , 函数可以修改原始数组的行指针 ;
void process2DArray(int **array, int rows, int cols) { //... }- 1
- 2
- 3
4、代码示例 - 二级指针 做函数参数的作用
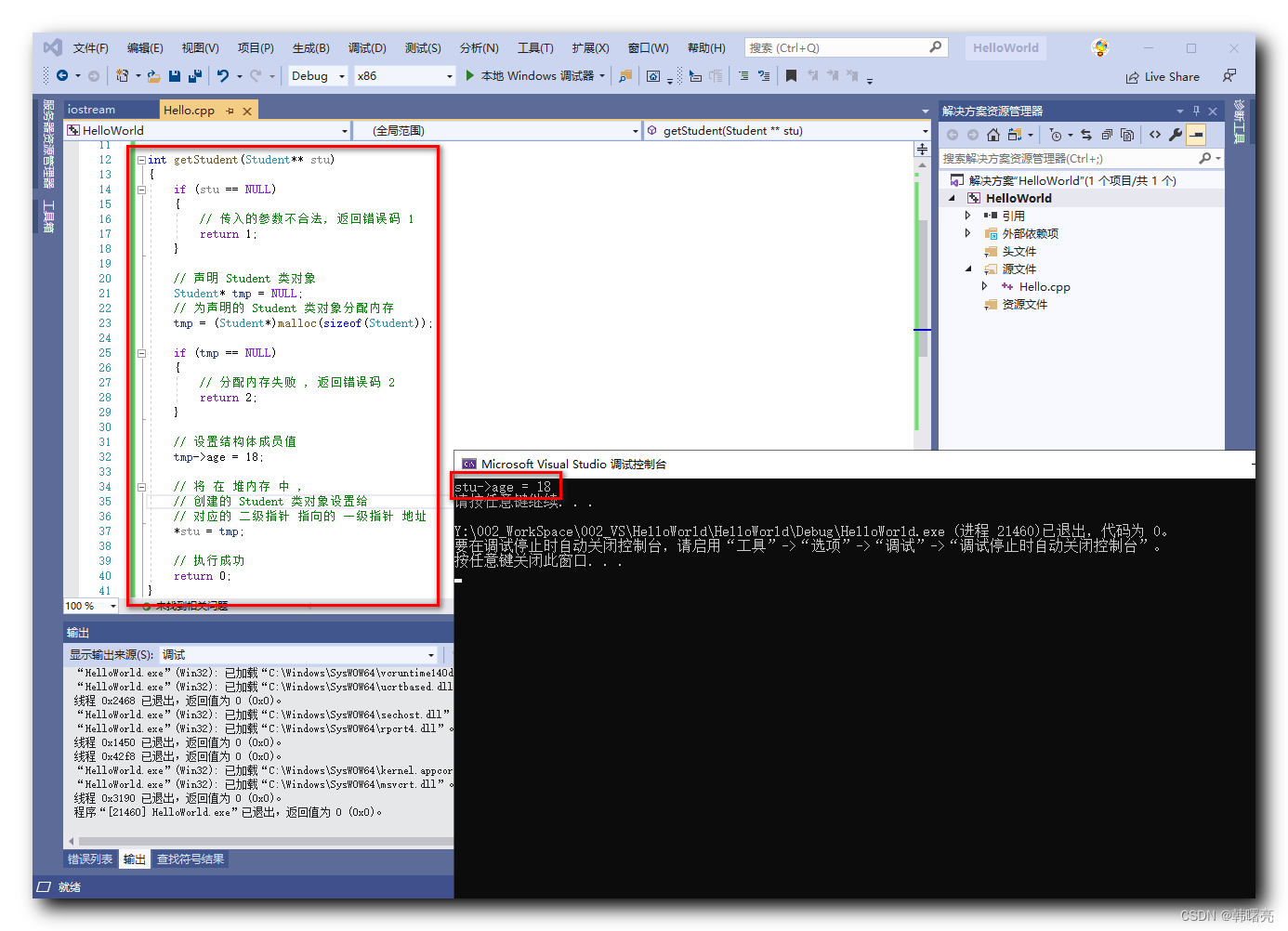
Student 是一个结构体 , C++ 中 结构体 可以当做 类 使用 ;
在 int getStudent(Student** stu) 函数中 , 传入 Student 类的二级指针 , 并在堆内存中创建一个 Student 类 , 赋值给一个临时的一级指针 Student* tmp ;
为 tmp 一级指针 指向的 内存空间 设置一个默认数据 , 作为参考 , 这里将 age 成员设置为 18 ;
将 tmp 一级指针 赋值给 参数中的 Student** stu 二级指针 指向的 内存中 , 即 将 该 二级指针 指向 tmp 一级指针 ;
上述操作 在 函数中 , 修改了 二级指针 指向 的一级指针 的值 , 也就是 修改了 一级指针 的地址 , 一级指针 的内存位置 与原来的 一级指针 内存位置 不同 ;
代码示例 :
// 导入标准 io 流头文件 其中定义了 std 命名空间 #include// 导入 std 命名空间 using namespace std; struct Student { char name[64]; int age; }; int getStudent(Student** stu) { if (stu == NULL) { // 传入的参数不合法, 返回错误码 1 return 1; } // 声明 Student 类对象 Student* tmp = NULL; // 为声明的 Student 类对象分配内存 tmp = (Student*)malloc(sizeof(Student)); if (tmp == NULL) { // 分配内存失败 , 返回错误码 2 return 2; } // 设置结构体成员值 tmp->age = 18; // 将 在 堆内存 中 , // 创建的 Student 类对象设置给 // 对应的 二级指针 指向的 一级指针 地址 *stu = tmp; // 执行成功 return 0; } int main() { // 声明 Student 对象 Student* stu = NULL; // 调用函数 将二级指针传入函数 // 在函数内部创建 Student 对象 getStudent(&stu); // 打印结构体成员 printf("stu->age = %d\n", stu->age); // 控制台暂停 system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
执行结果 :
stu->age = 18 请按任意键继续. . .- 1
- 2
-
相关阅读:
python 生成html文件并端口展示
闲置电脑挂机赚钱-Traffmonetizer,支持windows,linux,Android,MacOS多平台
Postman历史版本下载
基于C#实现的小型动物识别推理系统
春秋云镜 CVE-2015-9331
STM32的命名含义
【多目标追踪算法】Deepsort追踪实战
云原生 · Kubernetes - k8s集群搭建(kubeadm)(持续收录报错中)
springBoot--web--favicon规则
嵌入式Qt-实现两个窗口的切换
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/han1202012/article/details/132507923
