-
多分类中混淆矩阵的TP,TN,FN,FP计算
关于混淆矩阵,各位可以在这里了解:混淆矩阵细致理解_夏天是冰红茶的博客-CSDN博客
上一篇中我们了解了混淆矩阵,并且进行了类定义,那么在这一节中我们将要对其进行扩展,在多分类中,如何去计算TP,TN,FN,FP。
原理推导
这里以三分类为例,这里来看看TP,TN,FN,FP是怎么分布的。
类别1的标签:
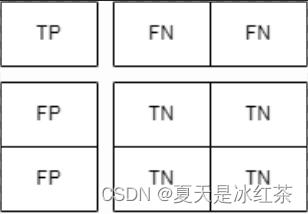
类别2的标签:
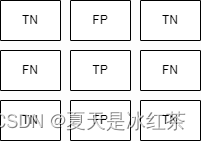
类别3的标签:

这样我们就能知道了混淆矩阵的对角线就是TP
TP = torch.diag(h)假正例(FP)是模型错误地将负类别样本分类为正类别的数量
FP = torch.sum(h, dim=1) - TP假负例(FN)是模型错误地将正类别样本分类为负类别的数量
FN = torch.sum(h, dim=0) - TP最后用总数减去除了 TP 的其他三个元素之和得到 TN
TN = torch.sum(h) - (torch.sum(h, dim=0) + torch.sum(h, dim=1) - TP)逻辑验证
这里借用上一篇的例子,假如我们这个混淆矩阵是这样的:
tensor([[2, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1],
[0, 2, 0]])为了方便讲解,这里我们对其进行一个简单的编号,即0—8:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 torch.sum(h, dim=1) 可得 tensor([2., 2., 2.]) , torch.sum(h, dim=0) 可得 tensor([2., 3., 1.]) 。
- TP: tensor([2., 1., 0.])
- FN: tensor([0., 1., 2.])
- TN: tensor([4., 2., 3.])
- FP: tensor([0., 2., 1.])
我们先来看看TP的构成,对应着矩阵的对角线2,1,0;FP在类别1中占3,6号位,在类别2中占1,7号位,在类别3中占2,5号位,加起来即为0,1,2;TN在类别1中占4,5,7,8号位,在类别2中占边角位,在类别3中占0,1,3,4号位,加起来即为4,2,3;FN在类别1中占1,2号位,在类别2中占3,5号位,在类别3中占6,7号位,加起来即为0,2,1。
补充类定义
- import torch
- import numpy as np
- class ConfusionMatrix(object):
- def __init__(self, num_classes):
- self.num_classes = num_classes
- self.mat = None
- def update(self, t, p):
- n = self.num_classes
- if self.mat is None:
- # 创建混淆矩阵
- self.mat = torch.zeros((n, n), dtype=torch.int64, device=t.device)
- with torch.no_grad():
- # 寻找GT中为目标的像素索引
- k = (t >= 0) & (t < n)
- # 统计像素真实类别t[k]被预测成类别p[k]的个数
- inds = n * t[k].to(torch.int64) + p[k]
- self.mat += torch.bincount(inds, minlength=n**2).reshape(n, n)
- def reset(self):
- if self.mat is not None:
- self.mat.zero_()
- @property
- def ravel(self):
- """
- 计算混淆矩阵的TN, FP, FN, TP
- """
- h = self.mat.float()
- n = self.num_classes
- if n == 2:
- TP, FN, FP, TN = h.flatten()
- return TP, FN, FP, TN
- if n > 2:
- TP = h.diag()
- FN = h.sum(dim=1) - TP
- FP = h.sum(dim=0) - TP
- TN = torch.sum(h) - (torch.sum(h, dim=0) + torch.sum(h, dim=1) - TP)
- return TP, FN, FP, TN
- def compute(self):
- """
- 主要在eval的时候使用,你可以调用ravel获得TN, FP, FN, TP, 进行其他指标的计算
- 计算全局预测准确率(混淆矩阵的对角线为预测正确的个数)
- 计算每个类别的准确率
- 计算每个类别预测与真实目标的iou,IoU = TP / (TP + FP + FN)
- """
- h = self.mat.float()
- acc_global = torch.diag(h).sum() / h.sum()
- acc = torch.diag(h) / h.sum(1)
- iu = torch.diag(h) / (h.sum(1) + h.sum(0) - torch.diag(h))
- return acc_global, acc, iu
- def __str__(self):
- acc_global, acc, iu = self.compute()
- return (
- 'global correct: {:.1f}\n'
- 'average row correct: {}\n'
- 'IoU: {}\n'
- 'mean IoU: {:.1f}').format(
- acc_global.item() * 100,
- ['{:.1f}'.format(i) for i in (acc * 100).tolist()],
- ['{:.1f}'.format(i) for i in (iu * 100).tolist()],
- iu.mean().item() * 100)
我在代码中添加了属性修饰器,以便我们可以直接的进行调用,并且也考虑到了二分类与多分类不同的情况。
性能指标
关于这些指标在网上有很多介绍,这里就不细讲了
- class ModelIndex():
- def __init__(self,TP, FN, FP, TN, e=1e-5):
- self.TN = TN
- self.FP = FP
- self.FN = FN
- self.TP = TP
- self.e = e
- def Precision(self):
- """精确度衡量了正类别预测的准确性"""
- return self.TP / (self.TP + self.FP + self.e)
- def Recall(self):
- """召回率衡量了模型对正类别样本的识别能力"""
- return self.TP / (self.TP + self.FN + self.e)
- def IOU(self):
- """表示模型预测的区域与真实区域之间的重叠程度"""
- return self.TP / (self.TP + self.FP + self.FN + self.e)
- def F1Score(self):
- """F1分数是精确度和召回率的调和平均数"""
- p = self.Precision()
- r = self.Recall()
- return (2*p*r) / (p + r + self.e)
- def Specificity(self):
- """特异性是指模型在负类别样本中的识别能力"""
- return self.TN / (self.TN + self.FP + self.e)
- def Accuracy(self):
- """准确度是模型正确分类的样本数量与总样本数量之比"""
- return (self.TP + self.TN) / (self.TP + self.TN + self.FP + self.FN + self.e)
- def FP_rate(self):
- """False Positive Rate,假阳率是模型将负类别样本错误分类为正类别的比例"""
- return self.FP / (self.FP + self.TN + self.e)
- def FN_rate(self):
- """False Negative Rate,假阴率是模型将正类别样本错误分类为负类别的比例"""
- return self.FN / (self.FN + self.TP + self.e)
- def Qualityfactor(self):
- """品质因子综合考虑了召回率和特异性"""
- r = self.Recall()
- s = self.Specificity()
- return r+s-1
-
相关阅读:
nextcloud安全与设置警告解决办法,关于您的设置有一些警告
使用HTML制作静态网站作业——我的校园运动会(HTML+CSS)
【英语:基础进阶_核心词汇扩充】E2.常见词后缀拓词
BUUCTF:[MRCTF2020]ezmisc
从GPU的内存访问视角对比NHWC和NCHW
数据结构与算法之美学习笔记:29 | 堆的应用:如何快速获取到Top 10最热门的搜索关键词?
郁金香2021年游戏辅助技术(初级班)(中)
诚迈科技董事长王继平出席中国(太原)人工智能大会并发表演讲
DataBinding 进阶用法
「Redis数据结构」哈希表(Dict)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_62919535/article/details/132926719
