-
【力扣周赛】第 113 场双周赛(贪心&异或性质&换根DP)
竞赛链接
https://leetcode.cn/contest/biweekly-contest-113/
Q1:8039. 使数组成为递增数组的最少右移次数
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-right-shifts-to-sort-the-array/
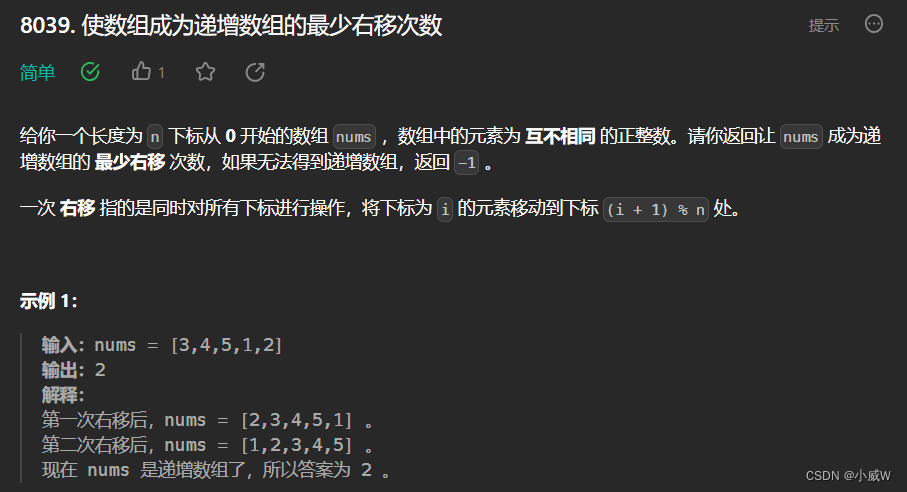
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 100
1 <= nums[i] <= 100
nums 中的整数互不相同。竞赛时代码——枚举答案
因为数据范围很小,所以可以从小到大枚举可能的答案。
class Solution { public int minimumRightShifts(List<Integer> nums) { int n = nums.size(); // a 是排好序之后的数组,作为标准答案 int[] a = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) a[i] = nums.get(i); Arrays.sort(a); // 枚举答案,即枚举右移次数 for (int x = 0; x < n; ++x) { boolean f = true; // 检查这个答案下每一位是否移动后相等 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (nums.get(i) != a[(i + x) % n]) { f = false; break; } } if (f) return x; } return -1; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
Q2:2856. 删除数对后的最小数组长度
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-array-length-after-pair-removals/
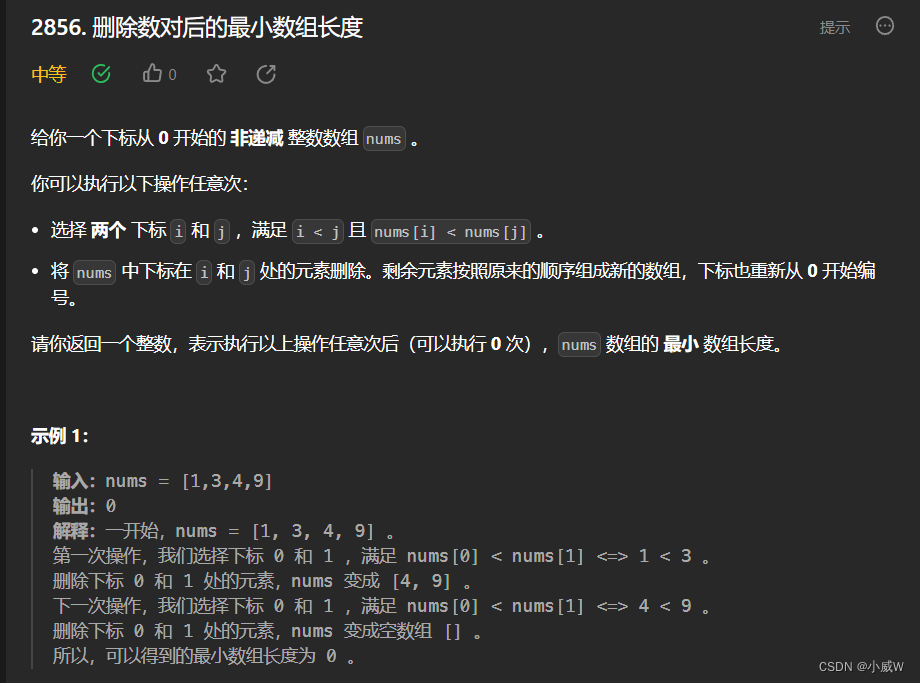
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^5
1 <= nums[i] <= 10^9
nums 是 非递减 数组。竞赛时代码——贪心+优先队列
首先贪心地想,能匹配就匹配。
但是对于样例 [2, 3, 5, 4] 来说,2 和 3 匹配之后,5 和 4就不能匹配了。
所以在 2 和 3 匹配之后,当枚举到 5 时,可以使用 5 替换掉 3,重新将 3 放入待匹配队列中。具体算法如下:
使用两个优先队列维护已经被枚举过的数值。
pq1 维护等待匹配的较小数字,pq2 维护已经匹配过的较大数字。分情况讨论:
- 当前数字比 pq1 中的数字大时,就将 pq1 中最小的数字删除,两者完成配对,当前数字放入 pq2。
- 当前 pq1 中没有数字,即前面没有元素等待配对时,将当前数字与 pq2 中最小的数字比较,如果 pq2 中的数字较小,就使用当前数字替换 pq2 中的数字与前面配对,同时 pq2 中这个最小的数字就多余了,将其放入 pq1 中等待后序的匹配。
- 当前数字无法处理时,就放入 pq1 等待后面出现更大的数字时删除。
class Solution { public int minLengthAfterRemovals(List<Integer> nums) { int cnt = 0; // 记录删除了几个数字 // pq1记录较小的数字,pq2记录较大的数字 PriorityQueue<Integer> pq1 = new PriorityQueue<>(), pq2 = new PriorityQueue<>(); for (int x: nums) { // 如果当前数字比之前出现的 还没被删除过的数字 大 if (!pq1.isEmpty() && x > pq1.peek()) { cnt += 2; pq1.poll(); pq2.offer(x); } else { if (pq1.isEmpty() && !pq2.isEmpty() && x > pq2.peek()) { // 如果较小的数字没有了 且 当前数字比已经删除的较大的数字大,就替换一下,将之前较大的数字放入较小的数字组中 pq1.offer(pq2.poll()); pq2.offer(x); } else pq1.offer(x); } } return nums.size() - cnt; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
解法2——贪心+二分查找 O ( log N ) O(\log{N}) O(logN)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-array-length-after-pair-removals/solutions/2446146/olog-n-tan-xin-er-fen-cha-zhao-pythonjav-t3qn/
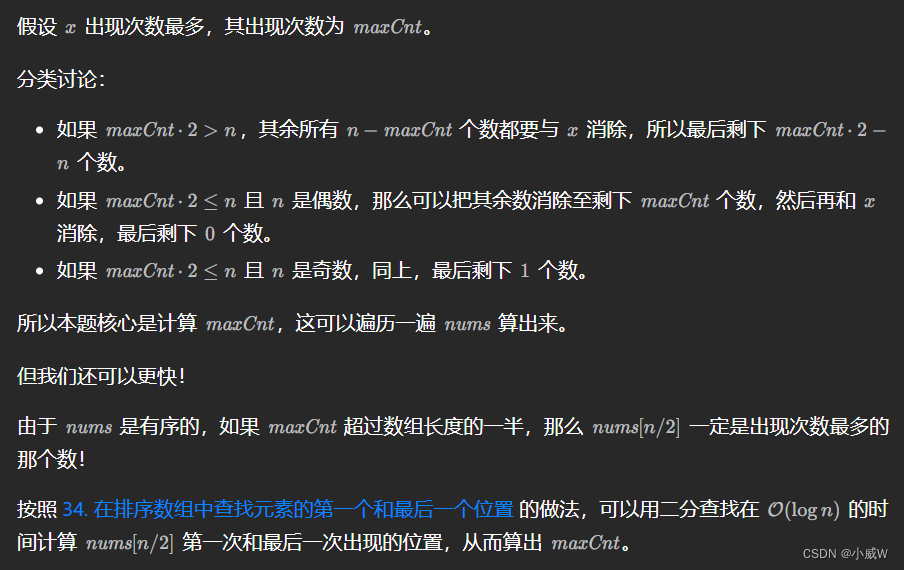
当 m a x C n t ∗ 2 < = n maxCnt * 2 <= n maxCnt∗2<=n 时,最后的结果只和 n 的奇偶性有关。
所以我们只需要考虑 maxCnt 超过半数的情况,此时有序序列 nums 的中间位置元素 x 一定是出现次数最多的元素。
使用二分查找可以找到元素 x 出现的次数。class Solution { public int minLengthAfterRemovals(List<Integer> nums) { int n = nums.size(); int x = nums.get(n / 2); // 只需考虑maxCnt*2>n的情况,其它情况剩下的数字数量只和n有关 int maxCnt = lowerBound(nums, x + 1) - lowerBound(nums, x); return Math.max(maxCnt * 2 - n, n % 2); } // 找nums中最后一个比target小的位置 public int lowerBound(List<Integer> nums, int target) { int l = -1, r = nums.size() - 1; while (l < r) { int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1; if (nums.get(mid) < target) l = mid; else r = mid - 1; } return l; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
Q3:6988. 统计距离为 k 的点对
https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-pairs-of-points-with-distance-k/

提示:
2 <= coordinates.length <= 50000
0 <= xi, yi <= 10^6
0 <= k <= 100竞赛时代码——异或性质+哈希表
可以看到数据范围很怪,是 50000,而 k 的数据范围比较小,是 100。我们可以写一个时间复杂度是 O ( n ∗ k ) O(n * k) O(n∗k) 的算法。
将已经枚举过的 x 和 y 放入哈希表中。
对于一个新的 x 和 y,他要和另外的坐标匹配之和为 k,最多有 k 中可能,即 —— 0 + k, 1 + (k - 1),2 + (k - 2),… ,k + 0。枚举每种情况即可。根据异或的性质,有 x ^ (i ^ x) = i, y ^ ((k - i) & y) = k - i,因此与 坐标 (x, y) 可以匹配的坐标是 (i ^ x, (k - i) ^ y),其中 i 的取值范围是 0 ~ k。
class Solution { public int countPairs(List<List<Integer>> coordinates, int k) { int ans = 0; Map<Integer, Map<Integer, Integer>> cnt = new HashMap<>(); for (List<Integer> c: coordinates) { int x = c.get(0), y = c.get(1); // 枚举 x 和 y 异或取值分配的所有可能。 for (int i = 0; i <= k; ++i) { ans += cnt.getOrDefault(i ^ x, new HashMap<>()).getOrDefault((k - i) ^ y, 0); } // 将当前坐标放入哈希表 if (!cnt.containsKey(x)) cnt.put(x, new HashMap<>()); cnt.get(x).merge(y, 1, Integer::sum); } return ans; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
更多有关
异或的题目可见:异或/XOR部分问题汇总Q4:100041. 可以到达每一个节点的最少边反转次数
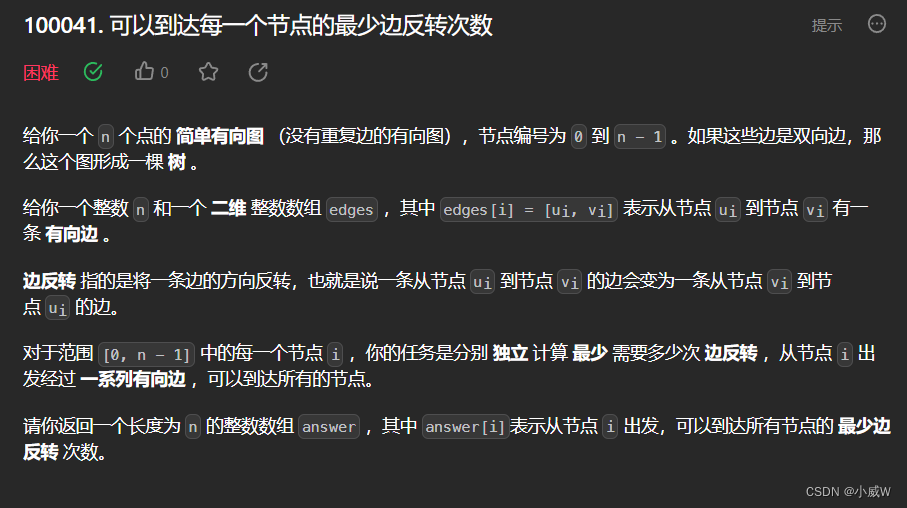
提示:
2 <= n <= 10^5
edges.length == n - 1
edges[i].length == 2
0 <= ui == edges[i][0] < n
0 <= vi == edges[i][1] < n
ui != vi
输入保证如果边是双向边,可以得到一棵树。竞赛时代码——换根DP
第一次 dfs 求各个节点向下需要的反转次数。
第二次 dfs 求答案。class Solution { List<Integer>[] g; Set<Integer>[] t; int n; // 答案,该节点往下传递反转的数量, int[] ans, cnt; public int[] minEdgeReversals(int n, int[][] edges) { this.n = n; ans = new int[n]; cnt = new int[n]; g = new ArrayList[n]; t = new HashSet[n]; Arrays.setAll(g, e -> new ArrayList<>()); Arrays.setAll(t, e -> new HashSet<>()); for (int[] e: edges) { int x = e[0], y = e[1]; g[x].add(y); g[y].add(x); t[x].add(y); } dfs1(0, -1); // 求cnt ans[0] = cnt[0]; dfs2(0, -1); // 求ans return ans; } public void dfs1(int x, int fa) { for (int y: g[x]) { if (y != fa) { dfs1(y, x); // 先求cnt[y] if (!t[x].contains(y)) cnt[x]++; // 如果x不能往y走,就+1 cnt[x] += cnt[y]; } } } public void dfs2(int x, int fa) { for (int y: g[x]) { if (y != fa) { ans[y] = ans[x]; // 两者的差别只取决于x和y之间边的情况 if (t[x].contains(y) && !t[y].contains(x)) ans[y]++; else if (!t[x].contains(y) && t[y].contains(x)) ans[y]--; dfs2(y, x); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
更多关于换根DP可见:
【算法】换根DP
【LeetCode每日一题合集】2023.7.10-2023.7.16(dfs & 换根DP)相似题目——2581. 统计可能的树根数目(🐂⭐)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-number-of-possible-root-nodes/

提示:
edges.length == n - 1
2 <= n <= 10^5
1 <= guesses.length <= 10^5
0 <= ai, bi, uj, vj <= n - 1
ai != bi
uj != vj
edges 表示一棵有效的树。
guesses[j] 是树中的一条边。
guesses 是唯一的。
0 <= k <= guesses.lengthclass Solution { List<Integer>[] g; Set<Long> s = new HashSet<Long>(); // 存储各个guess // 节点数目,答案,k,节点0作为根节点猜对的数量 int n, ans, k, cnt0; public int rootCount(int[][] edges, int[][] guesses, int k) { this.n = edges.length + 1; this.k = k; g = new ArrayList[n]; Arrays.setAll(g, e -> new ArrayList<Integer>()); for (int[] edge: edges) { int x = edge[0], y = edge[1]; g[x].add(y); g[y].add(x); } for (int[] guess: guesses) { // 将两个 4 字节数压缩成一个 8 字节数 s.add((long) guess[0] << 32 | guess[1]); } dfs(0, -1); reroot(0, -1, cnt0); return ans; } // 计算 0 为根节点时猜对的次数 public void dfs(int x, int fa) { for (int y: g[x]) { if (y != fa) { if (s.contains((long) x << 32 | y)) ++cnt0; dfs(y, x); } } } // 计算各个节点为根节点时猜对的次数 public void reroot(int x, int fa, int cnt) { if (cnt >= k) ++ans; // 此时已经找到了答案(至少有 k 个,所以是 >= k) for (int y: g[x]) { if (y != fa) { int c = cnt; if (s.contains((long) x << 32 | y)) --c; if (s.contains((long) y << 32 | x)) ++c; reroot(y, x, c); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
成绩记录

靠自己 AK 了!
-
相关阅读:
基于springboot的大学计算机基础网络教学系统
PID控制原理基本介绍(图解)
uni-app, 实现 scroll-view 自动滚动到底部,并控制触发频率
2022小米运维开发笔试1
胆总管结石的危害具体是什么?
51单片机—智能垃圾桶(定时器)
Linux常用命令
AMD发布22.11.1驱动,支持《使命召唤:战区2.0》
vscode package.json文件开头的{总是提升警告
RabbitMQ:消息队列的卓越之选
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43406895/article/details/132928247