-
SPPNet:金字塔网络
SPP结构是由提出ResNet的何大神在论文《Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition》中提出的,主要就是可以解决CNN输入需要固定尺寸的问题,而且在分类和目标检测中都可以得到比较好的效果SPPNet解决的问题
- 所有的CNN的输入都是必须固定尺寸。所以输出的图像都需要做预处理,或者是crop(裁剪,这样会丢失信息),或者是warp(扭曲,改变了空间属性),都会导致准确率下降
- 卷积层逻辑上就是一个移动窗口的动作,理论上是对尺寸没要求的,任意尺寸都可以。那么CNN的固定尺寸在哪里呢?是在后面的全连接层上,全联接层的输出和输入都是固定的,所以输入全连接层的featrue map必须是固定尺寸的。
- 还可以用于多尺寸训练,可以把一些图做一些变换之后直接进行训练。可以降低过拟合的风险。
- 在目标检测领域,比RCNN速度快得多,因为RCNN中每张图像的每个候选框都需要通过卷积层,2000个候选框就非常慢了。而SPPNet的CNN只对图像处理一次,是RCNN速度的24-102倍。
- 使用SPP结构后,整个流程结构变成:

SPPNet结构
SPP的结构其实是在之前就已经提出来了,就是分不同的尺寸对图进行特征提取的过程:
《The pyramid match kernel: Discriminative classification with sets of image features》
《Beyond bags of features: Spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories》等论文都提到了。SPP结构实际上是对更古老的一种特征提取与分类方法:词袋模型(BoW- Bag of Word)的改进。
Bag-of-Words
BoW模型最初应用于文本处理领域,用来对文档进行分类和识别。在应用BoW模型来表述图像时,图像被看作是文档,而图像中的关键特征被看作为“单词”,其应用于图像分类时主要包括三个步骤:
第一步:利用SIFT算法(或者某种其他的特征提取方法)从不同类别的图像中提取视觉词汇向量,这些向量代表的是图像中局部不变的特征点(类似卷积层提取卷积特征,之前的传统算法一般是通过颜色或者纹理等特征进行特征提取);
第二步:将所有特征点向量集合到一块,利用K-Means算法合并词义相近的视觉词汇,构造一个包含K个词汇的单词表,起到一个聚类的作用。比如说1000特特征向量,聚类之后就是20个类,这个类就可以理解为词汇表了;

第三步:统计单词表中每个单词在图像中出现的次数,从而将图像表示成为一个K维数值向量,相当于做了图像特征向量的直方图统计。

bow缺点是没有位置(空间)信息,因为图片都被完全切割了。Spatial Pyramid Matching是带位置信息的bow。也是spp借鉴的思想之一,都是远古传统机器学习的论文。空间金字塔池化改进了BoW,因为它可以通过在局部空间中pooling来维护空间信息。
SPP的结构与插入的位置
上面提到在经典的CNN网络中,卷积层和池化层对输入的图像或者是特征图是没有尺寸要求的,有尺寸要求的是全连接层。
所以,这个SPP结构就插入到最后的一个卷积+池化层之后,第一个全连接层之前。
论文中使用的是经典的AlexNet网络,所以增加的位置就在 p o o l 5 pool_5 pool5和 f c 6 fc_6 fc6之间。
- SPP由若干个池化层组成的金字塔层,在论文中,池化层都是使用了max-pooling
- 每个金字塔层将图像划分成 n ∗ n n * n n∗n的区域,每个区域单独的做一次池化操作。这样,每个区域可以得到一个向量值,每个金字塔层就可以得到 n ∗ n n * n n∗n个值。
- 假设整个金字塔使用了 5 ∗ 5 5 * 5 5∗5, 3 ∗ 3 3 * 3 3∗3, 1 ∗ 1 1 * 1 1∗1三个层,那么SPP层的输出向量就为25 + 9 + 1 = 35维。
- 从 p o o l 5 pool_5 pool5出来的featrue map的每个channel都需要经过SPP层,假设有k个channel,比如说是64个。那么整个SPP层对特征图的输出向量就为 35 * 64 = 2240维。
- 原文:In each spatial bin, we pool the responses of each filter (throughout this paper we use max pooling). The outputs of the spatial pyramid pooling are kM-dimensional vectors with the number of bins denoted as M (k is the number of filters in the last convolutional layer). The fixed-dimensional vectors are the input to the fully-connected layer。
- spatial bin指的就是每个区域划分出来的一个一个的小格子。
- 位于金字塔顶端的通常为一个1 * 1的bin,也就是直接对整张图像进行池化操作的池化层,可以称作是“global pooling”,作者在文章中提到是说很多算法都会使用到global pooling的方式来提高性能,在SPP里正好以这样一种巧妙的方式进行了集成。Interestingly, the coarsest pyramid level has a single bin that covers the entire image. This is in fact a “global pooling” operation, which is also investigated in several concurrent works. In [31], [32] a global average pooling is used to reduce the model size and also reduce overfitting; in [33], a global average pooling is used on the testing stage after all fc layers to improve accuracy; in [34], a global max pooling is used for weakly supervised object recognition. The global pooling operation corresponds to the traditional Bag-of-Words method。
- 根据上面的描述,FC的输入就是 k ∗ M k * M k∗M, k是通道数,M就是划分的格子的多少,也就是spatial bins。只要这两个确定了,不管是什么样的尺寸图像进来,fc得到的输入就是固定的。即使长宽不一样,也可以报证尺寸统一,因为bins是相同的。
- 每个spatial bin的大小,在论文中也被称作window的大小就是 ⌈ a / n ⌉ \lceil a/n \rceil ⌈a/n⌉,每个window之间的间隔,或者说步长设置为 ⌊ a / n ⌋ \lfloor a/n \rfloor ⌊a/n⌋
目标检测任务
SPP还针对目标检测模型R-CNN做了改进,最主要的改进就是针对R-CNN的速度。
因为R-CNN在经过selective search选出2000个左右的候选框后,每个候选框都要经过AlexNet来做特征提取,这自然非常慢。而SPP的思路是,整张图像作为输入进入CNN,做一次特征提取,在pool5的位置形成featrue map。同时,还是同样采用selective search选出2000个左右的候选框,然后把这个候选框与整张图像的featrue map做一个映射。通过映射得到相应候选框在pool5特征图上的位置,也就是下图中的window,然后这个window进入SPP和后面的全连接层进行计算。这样,相当于一张图像只需要经过一次CNN的卷积运算,自然速度要快得多。

一些算法细节:
- 四个金字塔层: (1×1, 2×2, 3×3, 6×6, totally 50 bins)
- 训练方法和参数与R-CNN类似,包括正例和反例的选择。We use the ground-truth windows to generate the positive samples. The negative samples are those overlapping a positive window by at most 30% (measured by the intersection-over-union (IoU) ratio). Any negative sample is removed if it overlaps another negative sample by more than 70%
- 每个图像都会将最短边为基础,同比例resize到某个尺寸,也就是首先整图resize到这个尺寸后在作为input输入到CNN中。论文中是提供了五个尺寸:{480, 576, 688, 864, 1200}来做多尺度的训练提升。
- 论文中以ZF-5为baseline。
- 最关键的一点就是怎么把一个候选框映射到特征图上的window,论文中的方式是:S is the product of all previous strides. In our models, S = 16 for ZF-5 on conv5, and S = 12 for Overfeat-5/7 on conv5/7. Given a window in the image domain, we project the left (top) boundary by: x ′ = ⌊ x / S ⌋ + 1 x^{'} = \lfloor x/S \rfloor + 1 x′=⌊x/S⌋+1 and the right (bottom) boundary x ′ = ⌊ x / S ⌋ − 1 x^{'} = \lfloor x/S \rfloor - 1 x′=⌊x/S⌋−1. If the padding is not b p/2c , we need to add a proper offset to x。Y坐标同理。
- 同样,SPP网络针对目标检测任务也做了fine-tuning,具体内容就不贴上来了。
SPPNet的训练方法
原则上,训练SPPNet是可以通过任意尺寸的图像进行训练。但是为了效率起见(GPU和CUDA更适合用固定尺寸进行批量计算,速度更快),论文中是使用了两种尺寸的图像进行训练:180 * 180和224 * 224的两种尺寸。Theoretically, the above network structure can be trained with standard back-propagation [1], regardless of the input image size. But in practice the GPU implementations (such as cuda-convnet [3] and Caffe[35]) are preferably run on fixed input images. Next we describe our training solution that takes advantage of these GPU implementations while still preserving the spatial pyramid pooling behaviors.
论文中也提出了两种训练方法:
- Single-size training
- Multi-size training
Single-size training
- 只使用 224 ∗ 224 224 * 224 224∗224尺寸的crop后的图像进行训练,这里的裁剪是为了做数据类型增强。we first consider a network taking a fixed-size input (224×224) cropped from images.The cropping is for the purpose of data augmentation.
- 预设的金字塔包含三个层的bins :(3×3, 2×2, 1×1)
- p o o l 5 pool_5 pool5出来的尺寸是 13 ∗ 13 13 * 13 13∗13
Multi-size training
- 使用了180 * 180,和224 * 224的两种尺寸进行训练。180 * 180是通过把224 * 224进行resize得到的(同比例缩放)。Rather than crop a smaller 180×180 region, we resize the aforementioned 224×224 region to 180×180. So the regions at both scales differ only in resolution but not in content/layout.
- 因为输入是180 * 180,所以 p o o l 5 pool_5 pool5的输出尺寸是 10 ∗ 10 10 * 10 10∗10。但是上面说了,进入fc的尺寸和bins个数有关,和前面卷积层的输出无关,只是说每个bins的宽高变了而已,做max-pooling又无所谓尺寸。
- 训练方法是每种尺寸的图像都做一些epoch,每种尺寸的epoch轮流训练。To reduce the overhead to switch from one network(e.g., 224) to the other (e.g., 180), we train each full epoch on one network, and then switch to the other one (keeping all weights) for the next full epoch. This is iterated
- 论文中还测试了在 [ 180 , 224 ] [180, 224] [180,224]之间随机分布的 s ∗ s s * s s∗s的尺寸进行训练的结果。Besides the above two-scale implementation, we have also tested a variant using s × s as input where s is randomly and uniformly sampled from [180, 224] at each epoch.
- 固定尺寸只在训练阶段,推理阶段可以是任意尺寸的。
对比实验
何大佬的论文是非常重视对比实验的,和ResNet一样,对比实验非常丰富。
分类任务 ImageNet 2012数据集
- 所有的图像resize到256 * 256的尺寸。然后做crop获得224 * 224的网络输入。
- 裁剪正中间224 * 224大小的图像作为输入。以每个叫做为顶点做224 * 224尺寸的裁剪。
- 为了防止过拟合,采用了水平翻转和颜色修改等操作。
- 在全连接层中使用了Dropout
- 开始为0.01的学习率
在这个数据集的分类任务中,对比了ZF-5,AlexNet(少许修改),OverFeat三个baseline的网络结构及其增加了SPP之后的性能。
三个baseline的结构如下: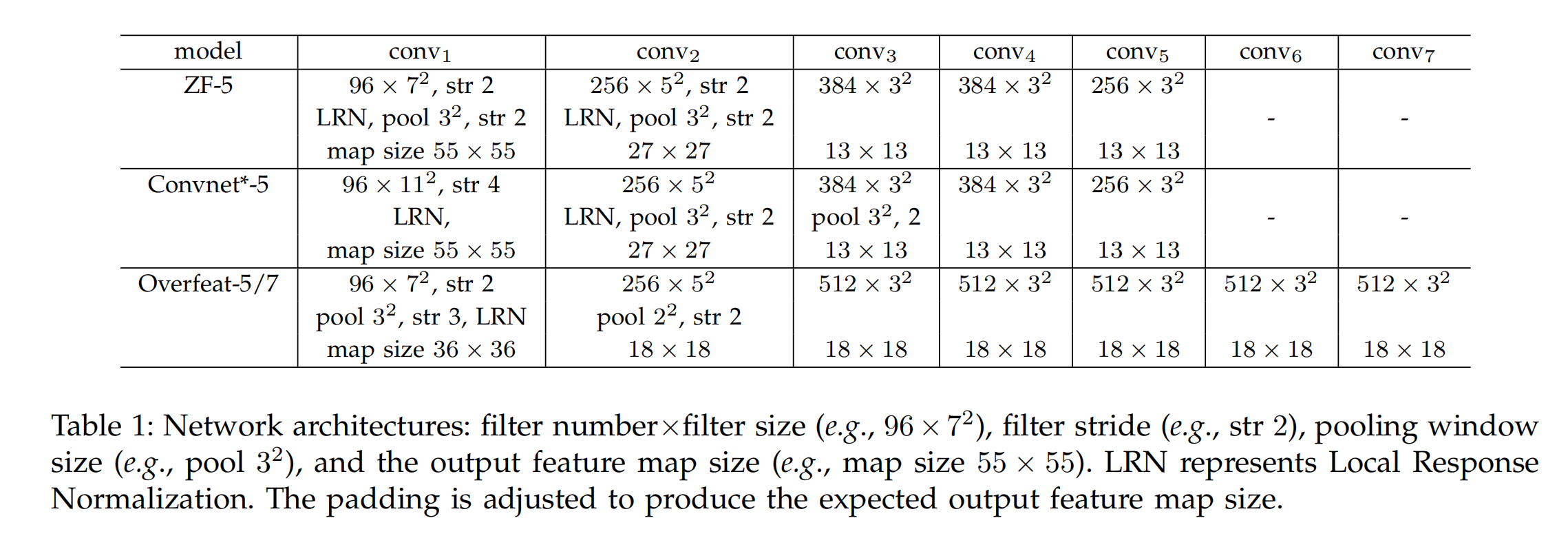
- 几个baseline都是输出了一个6×6大小特征图(通道数没提),然后是两个4096的fc层,最后输出当然是1000个类别,使用的是softmax激活层。In the baseline models, the pooling layer after the last convolutional layer generates 6×6 feature maps, with two 4096-d fc layers and a 1000-way softmax layer following。
- ZF-5训练了70个epoch,其他的都是训练了90个epoch。
- 增加的SPP包含4个金字塔层:{6×6, 3×3, 2×2, 1×1} (totally 50 bins).
结果如下:

-
图中的(a)这一行就是baseline的指标;(b)这一行就是加了SPP结构,但是是使用的上面提到的Single-size training的模型指标;©这一行就是使用了上面提到的Multi-size training方法的模型指标。
-
对于每张测试image都是使用的standard 10-view prediction,就是裁剪十个224 * 224的视野做测试image。
-
对比结论:
- 当然加了SPP的比没有加的要好
- 有趣的事,原来效果越好的,加上SPP的效果就更好,比如说没加SPP的最好的事Overfeat-7,加上SPP后的错误率降低幅度也是最大的。
- 增加了SPP结构不是说在网络中增加了参数所以提高了准确率。论文中在ZF-5上测试了一个{4×4, 3×3, 2×2, 1×1}(totally 30 bins)的SPP结构,增加这个结构后,因为fc的结构从36×256变成了30×256,所以整个网络的参数量(与no-SPP相比)是降低的,但是准确率是有提高的,但是和有50个bin的SPP还是相差一点点。也就是说明了SPP不是单纯的通过提高参数量来提升准确率,而是从结构上就有优势。This network has fewer parameters than its no-SPP counterpart, because its fc6 layer has 30×256-d inputs instead of 36×256-d. The top-1/top-5 errors of this network are 35.06/14.04. This result is similar to the 50-bin pyramid above (34.98/14.14), but considerably better than the no-SPP counterpart (35.99/14.76).
- muti-training全面超越single-train,在每个SPP的模型上都比single-training好,而且是top1和top5的错误率都是。
- 前面提到,论文中除了使用180和224两种尺寸的图像进行训练外,还使用了180-224之间的随机的尺寸进行训练。准确率是:30.06%/10.96%,比两个尺寸的训练结果稍差,但是比单一尺寸的训练要好,这里就说明了多尺度训练的重要性。
- 在这篇论文之前,其他CNN论文基本上都是在testing阶段处理不同尺度的image,不同尺度的image推理出来的score求个平均再做分类,而在训练阶段都是采用统一尺寸的image(通过wrap或者corp统一输入)。SPP是第一个可以用不同尺度的image直接做训练的。
-
全尺寸图像对比,前面进入testing阶段的image都还是经过了corp裁剪操作(10-view),论文还做了全尺寸图像的测试(用全尺寸图做训练),其实是做了resize操作的,只是说在不同分辨率的情况下保留了全图信息。We resize the image so that min(w, h)=256 while maintaining its aspect ratio. The SPP-net is applied on this full image to compute the scores of the full view。
-
对比结果:

- 不管是在哪个模型结构中(ZF-5和Overfeat-7),也不管是single train还是muti-trian,全尺寸的图像,虽然经过了resize,但是结果还是比corp的结果要好,这说明了保留全图信息的重要性。
- 虽然训练数据时正方形的图,但是非正方形的图也可以很好的处理。Even though our network is trained using square images only, it generalizes well to other aspect ratios。
-
对比table2和table3,很容易发现就是说使用muti-train的方法比这个全尺寸训练的方式正确率要高。但是论文还是提出说能直接使用全图做训练还是很有意义的。
- 简单的使用两种全图(原图+翻转图)就可以提升0.2%的正确率。
- 后面两点每太理解是什么意思,初步理解时说可以和其他的特征提取方法可以更好的集成,或者说这个SPP的思路可以用到一些传统方法中去,有兴趣的同学可以去看看原文。
-
对比实验自然不能缺少各种牛逼模型之间的比较:

-
在ImageNet2012的数据集上,SPP达到的最高top-5是在9.08%
-
在ILSRVC 2014竞赛上的结论,比GoogLeNet和VGG还差一点

-
目标检测
Pascal VOC 2007数据集
在VOC 2007数据集上也做了好几个对比实验

- (a)列是没有增加SPP的baseline的指标。(b)列就是增加了对应SPP的指标,能看出这个特征图还是要到fc层往后,SPP才会起到作用。
- 从©列开始,就是采用的full image进行训练的结果。基本都比裁剪的号。还有就是尺寸越大,效果越好,应该就是利用了更多的图像信息。
- 最后的(e)列是将baseline换成了Overfeat,尺寸为364得到了最好的结果。
与R-CNN做的对比实验:

- scale-5就是上面提到的,是使用了5个不同尺寸的图像(resize)进行测试的结果
- 很明显,时间上SPP是R-CNN的N多倍,一个是64倍,一个是24倍。而且准确率并没有降低,还稍微高出了那么一点。
- 然后将R-CNN中的alexnet换成了ZF-5也做了个对比:

最后是一个mAP的大比对:

还有一些其他的比对结果就不一一拿上来了,也就是说SPP主要就是解决了RCNN中的速度问题,而且还保证了mAP精度不下降。
-
相关阅读:
关于手机上的卫星定位
Java面试题之多态
maven的生命周期
流量管制-令牌桶与漏桶
环保主题网页制作作业 保护环境网页设计模板 简单学生网页设计 静态HTML CSS网站制作成品
【牛客 - 剑指offer】JZ8 二叉树的下一个结点 Java实现
基于SSH的高等数学课程网站的设计与开发
TAG YOU‘RE IT
MyBatis-plus+注解形式实现项目与数据库绑定动态更新
gitblit git pycharm 新建版本库及push备忘
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/pcgamer/article/details/132837729