-
在自定义数据集上实现OpenAI CLIP
在2021年1月,OpenAI宣布了两个新模型:DALL-E和CLIP,它们都是以某种方式连接文本和图像的多模态模型。CLIP全称是Contrastive Language–Image Pre-training,一种基于对比文本-图像对的预训练方法。为什么要介绍CLIP呢?因为现在大火得Stable Diffusion 并不是单一模型,而是多个模型组成。其中会用到一个 Text encoder 将用户的文本输入进行编码,这个 text encoder 就是 CLIP 模型中 text encoder
CLIP模型在训练时,可以给它一个输入句子,并提取最相关的图像来配合它。CLIP学习了一个完整的句子和它所描述的图像之间的关系。也就是说它是在完整的句子上训练的,而不是像“汽车”、“狗”等离散的分类,这一点对于应用至关重要。当训练完整的短语时,模型可以学习更多的东西,并识别照片和文本之间的模式。他们还证明,当在相当大的照片和与之相对应的句子数据集上进行训练时,该模型是可以作为分类器的。CLIP在发布的时候能在无任何微调的情况下(zero-shot ),在 ImageNet 数据集上的分类表现超 ResNets-50 微调后的效果,也就是说他是非常有用的。

所以在本文中,我们将使用PyTorch中从头开始实现CLIP模型,以便我们对CLIP有一个更好的理解
这里就需要用到2个库:timm和transformers,我们先导入代码
import os import cv2 import gc import numpy as np import pandas as pd import itertools from tqdm.autonotebook import tqdm import albumentations as A import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import torch from torch import nn import torch.nn.functional as F import timm from transformers import DistilBertModel, DistilBertConfig, DistilBertTokenizer- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
下一步就是预处理数据和通用配置config。config是一个普通的python文件,我们将所有的超参数放在里面,如果使用Jupyter Notebook的情况下,它是一个在Notebook开头定义的类。
class CFG: debug = False image_path = "../input/flickr-image-dataset/flickr30k_images/flickr30k_images" captions_path = "." batch_size = 32 num_workers = 4 head_lr = 1e-3 image_encoder_lr = 1e-4 text_encoder_lr = 1e-5 weight_decay = 1e-3 patience = 1 factor = 0.8 epochs = 2 device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") model_name = 'resnet50' image_embedding = 2048 text_encoder_model = "distilbert-base-uncased" text_embedding = 768 text_tokenizer = "distilbert-base-uncased" max_length = 200 pretrained = True # for both image encoder and text encoder trainable = True # for both image encoder and text encoder temperature = 1.0 # image size size = 224 # for projection head; used for both image and text encoders num_projection_layers = 1 projection_dim = 256 dropout = 0.1- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
还有一些我们自定义指标的辅助类
class AvgMeter: def __init__(self, name="Metric"): self.name = name self.reset() def reset(self): self.avg, self.sum, self.count = [0] * 3 def update(self, val, count=1): self.count += count self.sum += val * count self.avg = self.sum / self.count def __repr__(self): text = f"{self.name}: {self.avg:.4f}" return text def get_lr(optimizer): for param_group in optimizer.param_groups: return param_group["lr"]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
我们的目标是描述图像和句子。所以数据集必须同时返回句子和图像。所以需要使用DistilBERT标记器对句子(标题)进行标记,然后将标记id (input_ids)和注意掩码提供给DistilBERT。DistilBERT比BERT 模型要小,但是模型的结果都差不多,所以我们选择使用它。
下一步就是使用HuggingFace tokenizer进行标记化。在__init__中获得的tokenizer对象,将在模型运行时加载。标题被填充并截断到预定的最大长度。在加载相关图像之前,我们将在**getitem**中加载一个编码的标题,这是一个带有键input_ids和attention_mask的字典,并对其进行转换和扩充(如果有的话)。然后把它变成一个张量,并以“image”作为键存储在字典中。最后我们将标题的原始文本与关键字“标题”一起输入字典。
class CLIPDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset): def __init__(self, image_filenames, captions, tokenizer, transforms): """ image_filenames and cpations must have the same length; so, if there are multiple captions for each image, the image_filenames must have repetitive file names """ self.image_filenames = image_filenames self.captions = list(captions) self.encoded_captions = tokenizer( list(captions), padding=True, truncation=True, max_length=CFG.max_length ) self.transforms = transforms def __getitem__(self, idx): item = { key: torch.tensor(values[idx]) for key, values in self.encoded_captions.items() } image = cv2.imread(f"{CFG.image_path}/{self.image_filenames[idx]}") image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) image = self.transforms(image=image)['image'] item['image'] = torch.tensor(image).permute(2, 0, 1).float() item['caption'] = self.captions[idx] return item def __len__(self): return len(self.captions) def get_transforms(mode="train"): if mode == "train": return A.Compose( [ A.Resize(CFG.size, CFG.size, always_apply=True), A.Normalize(max_pixel_value=255.0, always_apply=True), ] ) else: return A.Compose( [ A.Resize(CFG.size, CFG.size, always_apply=True), A.Normalize(max_pixel_value=255.0, always_apply=True), ] )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
图像和文本编码器:我们将使用ResNet50作为图像编码器。
class ImageEncoder(nn.Module): """ Encode images to a fixed size vector """ def __init__( self, model_name=CFG.model_name, pretrained=CFG.pretrained, trainable=CFG.trainable ): super().__init__() self.model = timm.create_model( model_name, pretrained, num_classes=0, global_pool="avg" ) for p in self.model.parameters(): p.requires_grad = trainable def forward(self, x): return self.model(x)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
使用DistilBERT作为文本编码器。使用CLS令牌的最终表示来获得句子的整个表示。
class TextEncoder(nn.Module): def __init__(self, model_name=CFG.text_encoder_model, pretrained=CFG.pretrained, trainable=CFG.trainable): super().__init__() if pretrained: self.model = DistilBertModel.from_pretrained(model_name) else: self.model = DistilBertModel(config=DistilBertConfig()) for p in self.model.parameters(): p.requires_grad = trainable # we are using the CLS token hidden representation as the sentence's embedding self.target_token_idx = 0 def forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask): output = self.model(input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask) last_hidden_state = output.last_hidden_state return last_hidden_state[:, self.target_token_idx, :]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
上面的代码已经将图像和文本编码为固定大小的向量(图像2048,文本768),我们需要图像和文本具有相似的尺寸,以便能够比较它们,所以我们把2048维和768维向量投影到256维(projection_dim),只有维度相同我们才能比较它们。
class ProjectionHead(nn.Module): def __init__( self, embedding_dim, projection_dim=CFG.projection_dim, dropout=CFG.dropout ): super().__init__() self.projection = nn.Linear(embedding_dim, projection_dim) self.gelu = nn.GELU() self.fc = nn.Linear(projection_dim, projection_dim) self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout) self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(projection_dim) def forward(self, x): projected = self.projection(x) x = self.gelu(projected) x = self.fc(x) x = self.dropout(x) x = x + projected x = self.layer_norm(x) return x- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
所以最后我们的CLIP模型就是这样:
class CLIPModel(nn.Module): def __init__( self, temperature=CFG.temperature, image_embedding=CFG.image_embedding, text_embedding=CFG.text_embedding, ): super().__init__() self.image_encoder = ImageEncoder() self.text_encoder = TextEncoder() self.image_projection = ProjectionHead(embedding_dim=image_embedding) self.text_projection = ProjectionHead(embedding_dim=text_embedding) self.temperature = temperature def forward(self, batch): # Getting Image and Text Features image_features = self.image_encoder(batch["image"]) text_features = self.text_encoder( input_ids=batch["input_ids"], attention_mask=batch["attention_mask"] ) # Getting Image and Text Embeddings (with same dimension) image_embeddings = self.image_projection(image_features) text_embeddings = self.text_projection(text_features) # Calculating the Loss logits = (text_embeddings @ image_embeddings.T) / self.temperature images_similarity = image_embeddings @ image_embeddings.T texts_similarity = text_embeddings @ text_embeddings.T targets = F.softmax( (images_similarity + texts_similarity) / 2 * self.temperature, dim=-1 ) texts_loss = cross_entropy(logits, targets, reduction='none') images_loss = cross_entropy(logits.T, targets.T, reduction='none') loss = (images_loss + texts_loss) / 2.0 # shape: (batch_size) return loss.mean() #这里还加了一个交叉熵函数 def cross_entropy(preds, targets, reduction='none'): log_softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1) loss = (-targets * log_softmax(preds)).sum(1) if reduction == "none": return loss elif reduction == "mean": return loss.mean()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
这里需要说明下,CLIP使用 symmetric cross entropy 作为损失函数,可以降低噪音影响,提高模型鲁棒性,我们这里为了简单只是用cross entropy 。
我们可以进行测试:
# A simple Example batch_size = 4 dim = 256 embeddings = torch.randn(batch_size, dim) out = embeddings @ embeddings.T print(F.softmax(out, dim=-1))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
下一步就是训练了,有一些函数可以帮助我们加载训练和验证的dataloader
def make_train_valid_dfs(): dataframe = pd.read_csv(f"{CFG.captions_path}/captions.csv") max_id = dataframe["id"].max() + 1 if not CFG.debug else 100 image_ids = np.arange(0, max_id) np.random.seed(42) valid_ids = np.random.choice( image_ids, size=int(0.2 * len(image_ids)), replace=False ) train_ids = [id_ for id_ in image_ids if id_ not in valid_ids] train_dataframe = dataframe[dataframe["id"].isin(train_ids)].reset_index(drop=True) valid_dataframe = dataframe[dataframe["id"].isin(valid_ids)].reset_index(drop=True) return train_dataframe, valid_dataframe def build_loaders(dataframe, tokenizer, mode): transforms = get_transforms(mode=mode) dataset = CLIPDataset( dataframe["image"].values, dataframe["caption"].values, tokenizer=tokenizer, transforms=transforms, ) dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader( dataset, batch_size=CFG.batch_size, num_workers=CFG.num_workers, shuffle=True if mode == "train" else False, ) return dataloader- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
然后就是训练和评估
def train_epoch(model, train_loader, optimizer, lr_scheduler, step): loss_meter = AvgMeter() tqdm_object = tqdm(train_loader, total=len(train_loader)) for batch in tqdm_object: batch = {k: v.to(CFG.device) for k, v in batch.items() if k != "caption"} loss = model(batch) optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() optimizer.step() if step == "batch": lr_scheduler.step() count = batch["image"].size(0) loss_meter.update(loss.item(), count) tqdm_object.set_postfix(train_loss=loss_meter.avg, lr=get_lr(optimizer)) return loss_meter def valid_epoch(model, valid_loader): loss_meter = AvgMeter() tqdm_object = tqdm(valid_loader, total=len(valid_loader)) for batch in tqdm_object: batch = {k: v.to(CFG.device) for k, v in batch.items() if k != "caption"} loss = model(batch) count = batch["image"].size(0) loss_meter.update(loss.item(), count) tqdm_object.set_postfix(valid_loss=loss_meter.avg) return loss_meter- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
最后整合起来就是全部流程
def main(): train_df, valid_df = make_train_valid_dfs() tokenizer = DistilBertTokenizer.from_pretrained(CFG.text_tokenizer) train_loader = build_loaders(train_df, tokenizer, mode="train") valid_loader = build_loaders(valid_df, tokenizer, mode="valid") model = CLIPModel().to(CFG.device) params = [ {"params": model.image_encoder.parameters(), "lr": CFG.image_encoder_lr}, {"params": model.text_encoder.parameters(), "lr": CFG.text_encoder_lr}, {"params": itertools.chain( model.image_projection.parameters(), model.text_projection.parameters() ), "lr": CFG.head_lr, "weight_decay": CFG.weight_decay} ] optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(params, weight_decay=0.) lr_scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau( optimizer, mode="min", patience=CFG.patience, factor=CFG.factor ) step = "epoch" best_loss = float('inf') for epoch in range(CFG.epochs): print(f"Epoch: {epoch + 1}") model.train() train_loss = train_epoch(model, train_loader, optimizer, lr_scheduler, step) model.eval() with torch.no_grad(): valid_loss = valid_epoch(model, valid_loader) if valid_loss.avg < best_loss: best_loss = valid_loss.avg torch.save(model.state_dict(), "best.pt") print("Saved Best Model!") lr_scheduler.step(valid_loss.avg)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
应用:获取图像嵌入并找到匹配。
我们训练完成后如何实际应用呢?我们需要编写一个函数加载训练后的模型,为其提供验证集中的图像,并返回形状(valid_set_size, 256)和模型本身的image_embeddings。
def get_image_embeddings(valid_df, model_path): tokenizer = DistilBertTokenizer.from_pretrained(CFG.text_tokenizer) valid_loader = build_loaders(valid_df, tokenizer, mode="valid") model = CLIPModel().to(CFG.device) model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=CFG.device)) model.eval() valid_image_embeddings = [] with torch.no_grad(): for batch in tqdm(valid_loader): image_features = model.image_encoder(batch["image"].to(CFG.device)) image_embeddings = model.image_projection(image_features) valid_image_embeddings.append(image_embeddings) return model, torch.cat(valid_image_embeddings) _, valid_df = make_train_valid_dfs() model, image_embeddings = get_image_embeddings(valid_df, "best.pt") def find_matches(model, image_embeddings, query, image_filenames, n=9): tokenizer = DistilBertTokenizer.from_pretrained(CFG.text_tokenizer) encoded_query = tokenizer([query]) batch = { key: torch.tensor(values).to(CFG.device) for key, values in encoded_query.items() } with torch.no_grad(): text_features = model.text_encoder( input_ids=batch["input_ids"], attention_mask=batch["attention_mask"] ) text_embeddings = model.text_projection(text_features) image_embeddings_n = F.normalize(image_embeddings, p=2, dim=-1) text_embeddings_n = F.normalize(text_embeddings, p=2, dim=-1) dot_similarity = text_embeddings_n @ image_embeddings_n.T values, indices = torch.topk(dot_similarity.squeeze(0), n * 5) matches = [image_filenames[idx] for idx in indices[::5]] _, axes = plt.subplots(3, 3, figsize=(10, 10)) for match, ax in zip(matches, axes.flatten()): image = cv2.imread(f"{CFG.image_path}/{match}") image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) ax.imshow(image) ax.axis("off") plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
调用方法如下:
find_matches(model, image_embeddings, query="one dog sitting on the grass", image_filenames=valid_df['image'].values, n=9)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
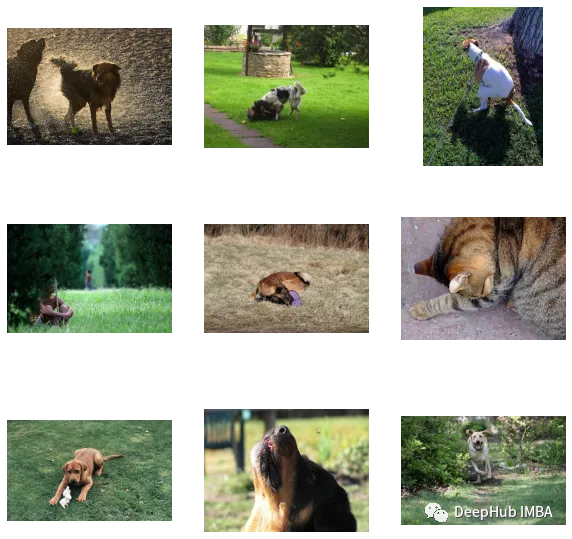
可以看到我们自定义效果还是不错的(但是图里面有个猫,哈)。也就是说CLIP这种方法在小数据集上自定义也是可行的。
以下是本文的代码和数据集:
https://avoid.overfit.cn/post/25295aa8daee45fc8336b2e86a29106a
作者:Jyoti Dabass, Ph.D
-
相关阅读:
【数据结构】——二叉树oj题详解
长春理工大学计算机考研资料汇总
C# +SQL 存储过程 实现系统数据权限审查AOP效果
C语言—位运算符
Javascript V8引擎与Blob对象
【Lua基础 第2章】lua遍历table的方式、运算符、math库、字符串操作方法
【云原生 | Kubernetes篇】自建高可用k8s集群优化
SC7A20(士兰微-加速度传感器)示例
雷达波束高度估计、折射分类、大气波导现象概念
@Component 和 @Bean的区别
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_46510245/article/details/132800715
