-
单链表和双链表

单链表和双链表
单链表:只有一个指向下一节点的指针 --> 单向读取
双链表:既有指向下一节点的指针,也有指向上一节点的指针,可以通过此向前查找

单链表和双链表的反转:逆序
整个链表逆序、部分链表逆序
是否需要返回值
链表的反转需要换头(整个链表逆序)的操作,则需要返回值(需要一个Node类型的返回值,存储换头之后的head值)
单链表的逆序及部分链表的逆序

注:当head为整个链表的头结点时,pre初始值为null,next指针反转之后head头节点指向pre,也就是null
- package linkedlist;
- public class SingleLinkedList {
- class Node {
- public int value;
- public Node next;
- public Node(int data) {
- this.value = data;
- }
- }
- //单链表的反转
- //单链表的反转只需要将指针的方向反转,在逆序整个链表的时候,用head遍历链表的所有结点,使得每个指针由后一结点指向前一结点
- public static Node reverseList(Node head) {//head传入时是链表的头结点,在循环中为当前结点
- Node pre = null;//处理的结点的前一个结点
- Node next = null;//处理的结点的后一个结点
- while (head != null) {
- next = head.next;//head的后一个结点
- head.next = pre;//反转指针
- pre = head;
- head = next;
- }
- return pre;//出循环时head==null,pre为整个链表的最后一个结点,也就是链表反转之后的头
- }
- //部分单链表的反转
- //这里说部分反转应当是不需要返回值的,但是取的不同的start和end数值,可能会导致链表的头改变,需要返回值,因此返回
- public static Node reverselistPart(Node head, int start, int end) {//head为当前结点,starthe end为起始位置
- Node startNode = null;
- Node endNode = null;
- int length = 0;//因为链表与数组不同,不能够直到当前结点在整个链表之间的位置,需要计数
- Node pre = head;
- //遍历整个链表,此时pre指的是当前结点
- while (pre != null) {//获得整个链表的长度
- length++;
- //找到startNode节点的前一个结点
- if (length == start - 1) {
- startNode = pre;
- }
- //找到endNode节点的后一个节点
- if (length == end + 1) {
- endNode = pre;
- }
- pre = pre.next;//遍历,避免死循环
- }
- //判断所给的start和end是否合理
- if (start < 1 || end > length || start >= end) {
- return head;//不合理的数视为不对链表进行逆序
- } else if (startNode == null) {//start==1,反转的部分包含头结点
- pre = head;
- } else {
- pre = startNode.next;
- }
- //反转startNode和后一个结点
- //pre为开始结点的下一个结点,headNode为pre结点的下一个结点
- Node headNode = pre.next;
- pre.next = startNode;//next指针由pre指向startNode,实现指针的反转
- Node next = null;
- //反转从startNode后一个结点到endNode的前一个结点中所有的结点
- while (headNode != endNode) {//链表的反转
- next = headNode.next;
- headNode.next = pre;
- pre = headNode;
- headNode = next;
- }
- // if (startNode != null) {
- // startNode.next = pre;
- // return headNode;
- // }
- return pre;
- }
- }
双链表的逆序
双链表的逆序和单链表相同,但是需要反转pre和next两个指针
- package linkedlist;
- class DoubleNode {
- public DoubleNode(int data) {
- this.value = data;
- }
- public int value;
- public DoubleNode next;
- public DoubleNode pre;
- public static DoubleNode reverseList(DoubleNode head) {
- DoubleNode pre = null;
- DoubleNode next = null;
- while (head != null) {
- next = head.next;
- head.next = pre;
- head.pre = next;
- pre = head;
- head = next;
- }
- return pre;
- }
- }
打印两个有序链表的公共部分

判断一个链表是否是一个回文结构
1、将链表结构放到栈中,比较栈弹出的顺序是否与原序相同(栈先进后出),全部相同则是回文
O(n)的额外空间
- package linkedlist;
- import java.util.Stack;
- public class IsPalindromic {
- class Node {
- public int value;
- public Node next;
- public Node(int data) {
- this.value = data;
- }
- }
- public static boolean isplindromicbyStack(Node head) {
- Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();//创建栈结构
- Node temp = head;
- while (temp != null) {
- stack.push(temp);//入栈
- temp = temp.next;
- }
- while (head != null){
- if(head.value != stack.pop().value){//出栈,判断前后顺序是否相同
- return false;
- }
- head = head.next;
- }
- return true;
- }
- }
2、优化:降低空间复杂度
O(n/2)的额外空间
将右半部分的链表放到栈中,从链表左侧开始遍历,每遍历一个栈弹出一个,一一进行比较,全部相同则回文
单链表无法获知整个链表有多少数,单指针无法判断此时经历的结点是否是链表结构的一半
快慢指针:快指针一次走2步,慢指针一次走1步;当快指针遍历完整个链表,慢指针走到中点
在实际情况中快慢指针需要根据题目调整代码
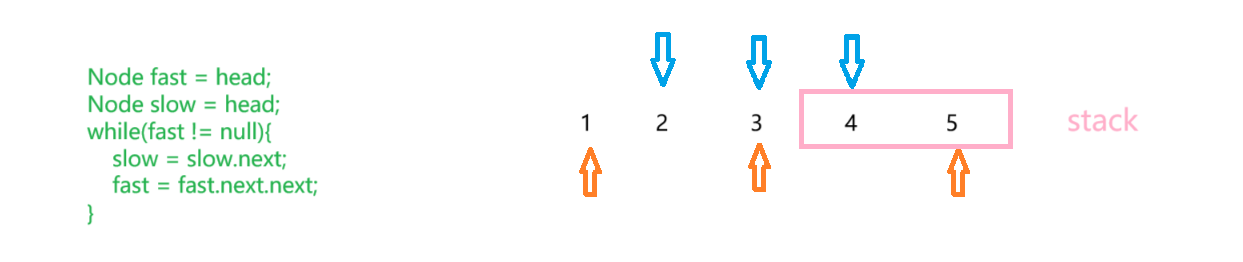
- public static boolean isplindromicbyfastandslowPointer(Node head){
- if(head == null || head.next == null){
- return true;//整个链表为空或是只有一个Node也被视为回文结构
- }
- //快慢指针
- Node slow = head.next;
- Node fast = head;
- //整个链表为偶数时,慢指针位于n/2位置上;奇数时,整个链表位于n/2位置向上取整+1(5 - 4)
- while(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null){
- slow = slow.next;
- fast = fast.next.next;
- }
- //取出后半段入栈
- Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
- while(slow != null){
- stack.push(slow);
- slow = slow.next;
- }
- //将后半段与前半段比较,是否相同
- while(!stack.isEmpty()){
- if(head.value != stack.pop().value){
- return false;
- }
- head = head.next;
- }
- return true;
- }
3、优化:不使用额外的数据结构
O(1)的额外空间
快指针一次走2步,慢指针一次走1步;慢指针走到中间的位置,遍历后面部分的链表逆序;
两个指针,一个从head向后遍历,一个从end向前遍历,直到一个指针指向空
- public static boolean isplindromicbytwoPointer(Node head) {
- if (head == null || head.next == null) {
- return true;//整个链表为空或是只有一个Node也被视为回文结构
- }
- Node slow = head;
- Node fast = head;
- while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
- slow = slow.next;//最后到达中点位置,奇数时中点位置向上取整
- fast = fast.next.next;//最后到达链表最后一位或两位
- }
- fast = slow.next;//从右半部分的起点开始
- slow.next = null;//空出空间便于后半部分逆序
- //后半部分逆序
- Node temp = null;
- while (fast != null) {
- temp = fast.next;
- fast.next = slow;//反转指针
- slow = fast;
- fast = temp;
- }
- temp = slow;//slow为反转部分的最后一个结点,也就是后半部分反转部分的头
- fast = head;//左半部分的头
- boolean res = true;
- //slow表示右半部分,fast表示左半部分
- while (slow != null && fast != null) {
- if (slow.value != fast.value) {
- res = false;
- break;
- }
- slow = slow.next;
- fast = fast.next;
- }
- //将链表反转回去 slow -- fast , temp -- slow , fast -- temp
- slow = temp.next;
- temp.next = null;
- // fast = slow.next;
- // slow.next = null;
- while (slow != null) {
- // while (fast != null)
- fast = slow.next;
- slow.next = temp;
- temp = slow;
- slow = fast;
- // temp = fast.next;
- // fast.next = slow;//反转指针
- // slow = fast;
- // fast = temp;
- }
- return res;
- }
将单链表按某值划分为左边小、中间相等、右边大的形式

使用额外空间:将单链表的每个结点放到数组中,对数组进行partition操作(左边小、中间相等、右边大)
不使用额外空间:六个变量,分别为小于、等于、大于部分的头和尾
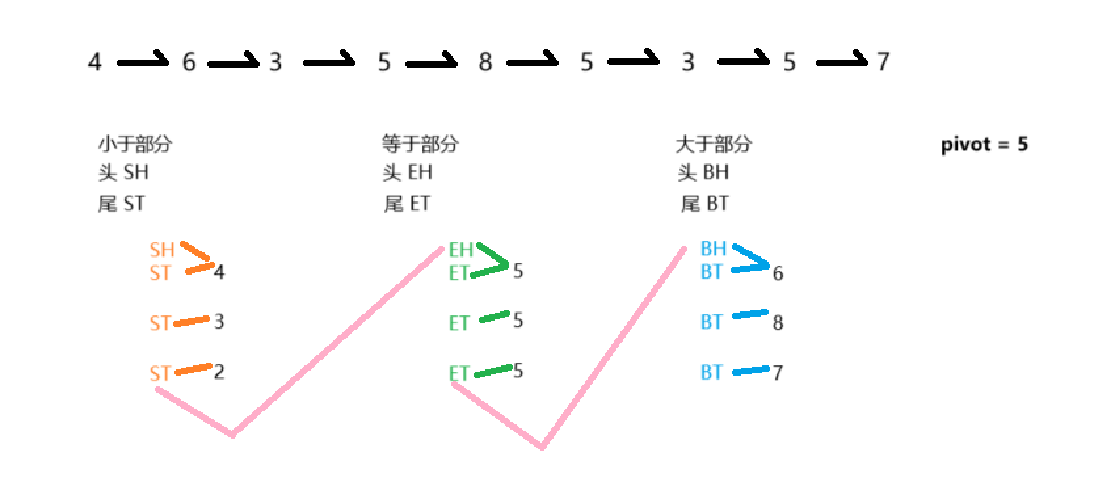
注:三区域串起来的时候需要注意区域是否存在,否则会指向null导致出错
- package linkedlist;
- public class ListPartition {
- class Node {
- public int value;
- public Node next;
- public Node(int data) {
- this.value = data;
- }
- }
- public static Node listPattition(Node head, int pivot) {
- Node SH = null;
- Node ST = null;
- Node EH = null;
- Node ET = null;
- Node BH = null;
- Node BT = null;
- Node temp = null;
- while (head != null) {
- temp = head.next;//存储下一个head
- head.next = null;//消去指针
- if (head.value < pivot) {
- if (SH == null) {
- SH = head;
- ST = head;
- } else {
- ST.next = head;
- ST = head;
- }
- }
- if (head.value == pivot) {
- if (EH == null) {
- EH = head;
- ET = head;
- } else {
- ET.next = head;
- ET = head;
- }
- }
- if (head.value > pivot) {
- if (BH == null) {
- BH = head;
- BT = null;
- } else {
- BT.next = head;
- BT = head;
- }
- }
- head = temp;//再次进行赋值,使得head遍历整个链表
- }
- if (ST != null) {//有小于区域
- if (ET != null) {//有等于区域
- ST.next = EH;
- } else if (BT != null) {//没有等于区域,有大于区域
- ST.next = BH;
- } else {//啥也没有
- ST.next = null;
- }
- }
- if (ET != null) {//有等于区域
- if (BT != null) {//有大于区域
- ET.next = BH;
- } else {//无大于区域
- ET.next = null;
- }
- }
- //最终返回结果
- if(ST != null){
- return SH;
- } else if (ET != null) {
- return EH;
- }else{
- return BH;
- }
- }
- }
复制含有随机指针节点的链表

使用额外空间:哈希表拷贝节点,通过原来的节点1的next指针找到节点2,拷贝后的节点1'对应节点2',由此可知节点1'的next指针指向节点2'。random指针同理。

不使用额外空间:在链表的每个节点后插入其对应拷贝节点,通过节点1的next指针找到拷贝的节点1',节点1的random指针指向节点3,节点3的next指针指向节点3',由此可以拷贝节点1'指向节点3'的random指针
由next指针向下遍历,将每一对的指针都拷贝出,拷贝所有的random指针后抽离出拷贝的链表(画的好丑)

- package linkedlist;
- public class CopyLinkedListWithRand {
- class Node {
- public int value;
- public Node next;
- public Node rand;
- public Node(int data) {
- this.value = data;
- }
- }
- public Node copylistwithRand(Node head) {
- if (head == null) {
- return null;
- }
- Node node1 = head;
- Node node2 = null;
- //1 -> 2
- //1 -> 1' -> 2
- while (node1 != null) {
- node2 = node1.next;
- node1.next = new Node(node1.value);//克隆的新节点
- node1.next.next = node2;
- node1 = node2;
- }
- node1 = head;//重新来过
- //拷贝random指针
- while (node1 != null) {
- if (node1.rand != null) {//节点1的random指针
- node1.next.rand = node1.rand.next;//节点1'的random指针=节点3的next=节点3'
- } else {
- node1.next.rand = null;
- }
- node1 = node1.next.next;
- }
- Node res = head.next;//拷贝出来的链表的头节点
- node1 = head;//再次重新来过
- Node temp = res;
- while(node1 != null){
- node1 = node1.next.next;//跳到第三个,第五个...
- if(node1.next != null) {
- temp.next = node1.next;//第二个指向第四个,第四个指向第六个...
- }else{
- temp.next = null;
- }
- temp = temp.next;//第二个跳第四个,第四个跳第六个...
- }
- return res;//返回拷贝链表的头
- }
- }
-
相关阅读:
【C++】List -- 详解
c++多态
报数模拟(二)
@设计模式-工厂模式
ref实现input自动获取光标并执行多次
think\queue 消息队列
C# 正则表达式判断是否是有效的文件、文件夹路径
酷开科技 | 酷开系统,带你寻觅最爱的影视之旅
2023-11-09 node.js-有意思的项目-记录
技术驱动的数字时代:探索Socks5代理在不同领域的应用
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_73530538/article/details/132661280
