-
数据结构:线性表(栈的实现)
1. 栈(Stack)
1.1 栈的概念
- 栈(Stack)是只允许在一端进行插入或删除操作的线性表.首先栈是一种线性表,但限定这种线性表只能在某一端进行插入和删除操作.
- 进行数据插入和删除操作的一端叫栈顶,另一端称为栈底.
- 栈中的元素遵循后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶.
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈,出数据也在栈顶.1.2 栈的结构
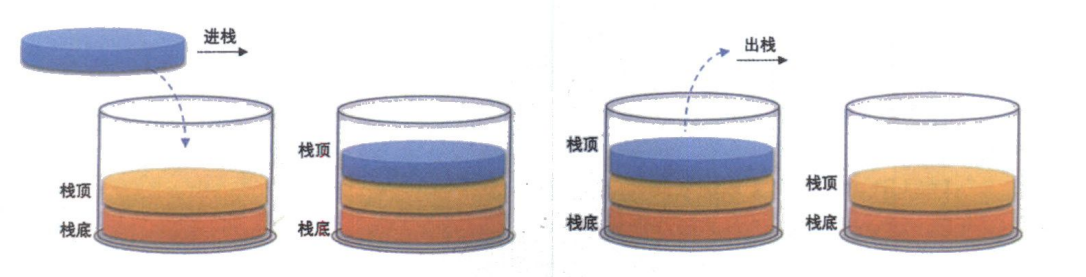
栈的元素,遵循后进先出原则
栈采用什么逻辑结构呢?
通常栈可以用链表和数组实现.
当然我们调用的时候不需要知道,使用的是什么方法实现.链表栈
通过在表前端插入来实现 push ,通过删除表前端元素实现 pop.
可以使用之前实现的单链表来实现栈,单链表实现详见.只用注意,栈只有插入删除操作,需要头删和头插.虽然操作都是花费常数时间,但是对
malloc和free的调用是十分昂贵的.数组栈
更为流行的是使用数组来实现栈.虽然数组的大小需要提前说明或者临时开辟,但是,在典型的应用程序中,栈元素的实际个数一般不会太大,使用数组是更加高效的方法.
总结:
- 推荐使用数组结构实现栈
- 若使用链表实现栈
用尾做栈顶,尾删尾插,要设计成双向链表
用头做栈顶,头删头插,要设计成单链表
2. 栈的定义
一般来说,使用动态栈而非静态栈,需要扩容的时候,可以进行适当扩容,增加了程序的适用性.
动态栈实现的数据结构
typedef int STDataType; typedef struct Stack { STDataType* a; //指向栈空间 int top; //栈顶 int capacity; //容量 }Stack;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
接口函数
// 初始化栈 void StackInit(Stack* ps); // 入栈 void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data); // 出栈 void StackPop(Stack* ps); // 获取栈顶元素 STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps); // 获取栈中有效元素个数 int StackSize(Stack* ps); // 检测栈是否为空, 如果为空返回非零结果, 如果不为空返回 0 int StackEmpty(Stack* ps); // 销毁栈 void StackDestroy(Stack* ps);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
3. 栈的实现
3.1 初始化栈 (StackInit)
// 初始化栈 void StackInit(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); ps->a = NULL; ps->top = 0; ps->capacity = 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 和创建顺序表的操作是一致的,通过结构体指针
ps修改主函数中的结构体的成员变量,将ps指向的数组指针指向NULL,同时将容量capacity和栈顶元素top置为 0.
- 注意,在这里,
top所指向的是栈顶元素后一个空间,此时没有元素,自然就指向了数组的第一个空间
3.2 入栈 (StackPush)
//入栈 void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 //如果容量不够则扩容 if (ps->capacity == ps->top) { int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity; //定义新的容量 STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity); //开辟新的空间 if (tmp == NULL) { perror("malloc error"); exit(-1); } else { ps->a = tmp; ps->capacity = newCapacity; } } //将数据入栈 ps->a[ps->top] = data; ps->top++; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 首先确保
ps合法 - 因为是动态栈,会出现空间不够的情况,在入栈之前首先确保容量充足,如果容量不够,则进行扩容
- 将数据入栈,同时
top++
3.3 出栈 (StackPop)
// 出栈 void StackPop(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 assert(!StackEmpty(ps)); //确保栈不为空 ps->top--; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 确保 ps 合法
- 确保栈不为空
- 直接将
top--即可
3.4 检测栈是否为空 (StackEmpty)
// 检测栈是否为空, 如果为空返回非零结果, 如果不为空返回 0 int StackEmpty(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 if (ps->top > 0) { return 0; } else { return 1; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 确保ps合法
- 如果
top大于0,说明栈不为空,反之则为空
3.5 获取栈顶元素 (StackTop)
// 获取栈顶元素 STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 assert(!StackEmpty(ps)); //确保栈不为空 return ps->a[ps->top - 1]; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 确保ps合法
- 确保栈不为空
- 直接返回
top - 1位置的元素
3.6 获取栈中有效元素个数 (StackSize)
// 获取栈中有效元素个数 int StackSize(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 return ps->top; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 确保ps合法
- 直接将
top返回即可
3.7 销毁栈 (StackDestroy)
// 销毁栈 void StackDestroy(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 free(ps->a); ps->a = NULL; ps->capacity = 0; ps->top = 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 确保ps合法
- 将ps指向的数组空间归还给操作系统,同时将
top和capacity置为0
3.8 完整代码
Stack.h
#pragma once #include#include #include #include typedef int STDataType; typedef struct Stack { STDataType* a; //指向栈空间 int top; //栈顶 int capacity; //容量 }Stack; // 初始化栈 void StackInit(Stack* ps); // 入栈 void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data); // 出栈 void StackPop(Stack* ps); // 获取栈顶元素 STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps); // 获取栈中有效元素个数 int StackSize(Stack* ps); // 检测栈是否为空, 如果为空返回非零结果, 如果不为空返回 0 int StackEmpty(Stack* ps); // 销毁栈 void StackDestroy(Stack* ps); - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
Stack.c
#include "Stack.h" // 初始化栈 void StackInit(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); ps->a = NULL; ps->top = 0; ps->capacity = 0; } //入栈 void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 //如果容量不够则扩容 if (ps->capacity == ps->top) { int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity; //定义新的容量 STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity); //开辟新的空间 if (tmp == NULL) { perror("malloc error"); exit(-1); } else { ps->a = tmp; ps->capacity = newCapacity; } } //将数据入栈 ps->a[ps->top] = data; ps->top++; } // 出栈 void StackPop(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 assert(!StackEmpty(ps)); //确保栈不为空 ps->top--; } // 检测栈是否为空, 如果为空返回非零结果, 如果不为空返回 0 int StackEmpty(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 if (ps->top > 0) { return 0; } else { return 1; } } // 获取栈顶元素 STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 assert(!StackEmpty(ps)); //确保栈不为空 return ps->a[ps->top - 1]; } // 获取栈中有效元素个数 int StackSize(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 return ps->top; } // 销毁栈 void StackDestroy(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 free(ps->a); ps->a = NULL; ps->capacity = 0; ps->top = 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
Test.c
#include "Stack.h" void StackTest1() { Stack st; StackInit(&st); StackPush(&st, 1); printf("%d\n", StackSize(&st)); printf("%d\n", StackTop(&st)); StackPush(&st, 2); printf("%d\n", StackSize(&st)); printf("%d\n", StackTop(&st)); StackPush(&st, 3); printf("%d\n", StackSize(&st)); printf("%d\n", StackTop(&st)); StackPush(&st, 4); printf("%d\n", StackSize(&st)); printf("%d\n", StackTop(&st)); StackPush(&st, 5); printf("%d\n", StackSize(&st)); printf("%d\n", StackTop(&st)); StackPop(&st); printf("%d\n", StackSize(&st)); printf("%d\n", StackTop(&st)); StackPop(&st); printf("%d\n", StackSize(&st)); printf("%d\n", StackTop(&st)); StackPop(&st); printf("%d\n", StackSize(&st)); printf("%d\n", StackTop(&st)); StackPop(&st); printf("%d\n", StackSize(&st)); printf("%d\n", StackTop(&st)); StackPop(&st); printf("%d\n", StackSize(&st)); printf("%d\n", StackTop(&st)); StackPop(&st); } int main(void) { StackTest1(); return 0; } printf("%d\n", StackTop(&st)); StackPop(&st); printf("%d\n", StackSize(&st)); printf("%d\n", StackTop(&st)); StackPop(&st); printf("%d\n", StackSize(&st)); printf("%d\n", StackTop(&st)); StackPop(&st); printf("%d\n", StackSize(&st)); printf("%d\n", StackTop(&st)); StackPop(&st); } int main(void) { StackTest1(); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
-
相关阅读:
Python Pandas Series转换为DataFrame
1.4_14 Axure RP 9 for mac 高保真原型图 - 案例13 【动态面板-滚动条3】双向同步滚动
二进制方式部署consul单机版
Android JetPack~LiveData(二) 数据倒灌问题
Exchangis1.0演讲稿
STM8S芯片问题,批量生产时,板子烧录完程序,放置半个月,1%的板子就开不开机了或者1秒开关机一次,300次内板子必死机
C++之this指针总结(二百二十)
如何从零开始解读产品经理行业分析
【Redis】hash类型-内部编码&使用场景
零基础可以学设计专业吗,怎么学?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Kuzuba/article/details/132685190
