-
谷粒商城----缓存与分布式锁
1、缓存使用
为了系统性能的提升,我们一般都会将部分数据放入缓存中,加速访问。而 db 承担数据落盘工作。
哪些数据适合放入缓存?
即时性、数据一致性要求不高的
访问量大且更新频率不高的数据(读多,写少)举例:电商类应用,商品分类,商品列表等适合缓存并加一个失效时间(根据数据更新频率来定),后台如果发布一个商品,买家需要 5 分钟才能看到新的商品一般还是可以接受的
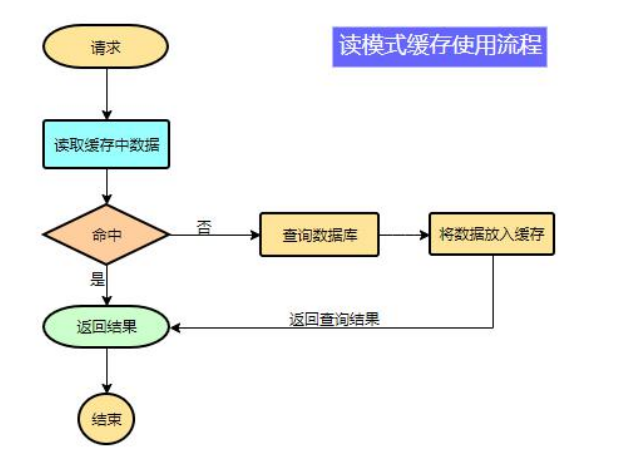
data = cache.load(id);//从缓存加载数据 If(data == null){ data = db.load(id);//从数据库加载数据 cache.put(id,data);//保存到 cache 中 } return data;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
🚩注意:在开发中,凡是放入缓存中的数据我们都应该
指定过期时间,使其可以在系统即使没有主动更新数据也能自动触发数据加载进缓存的流程。避免业务崩溃导致的数据永久不一致问题。2、springboot整合redis(StringRedisTemplate)
@Autowired StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate; @Test public void testStringRedisTemplate(){ ValueOperations<String, String> ops = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue(); ops.set("hello","world_"+ UUID.randomUUID().toString()); String hello = ops.get("hello"); System.out.println(hello); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
3、缓存使用-改造三级分类业务

缓存穿透,缓存击穿,缓存雪崩

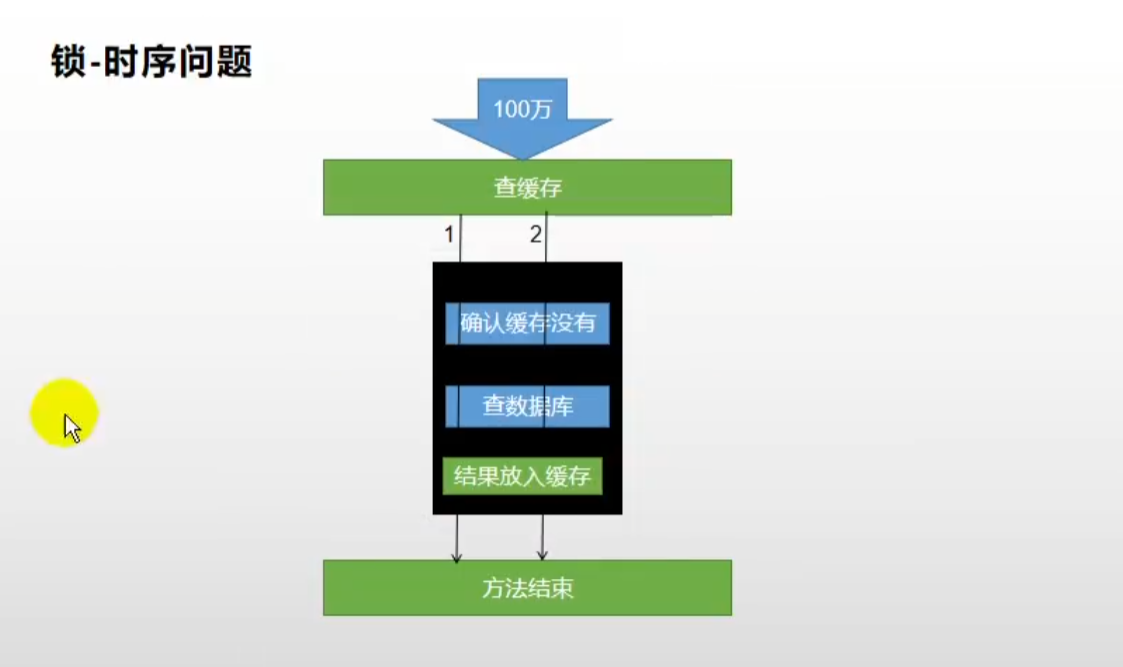
4、分布式锁setnx

🚩优化一:过期时间(解决不释放锁导致死锁问题)
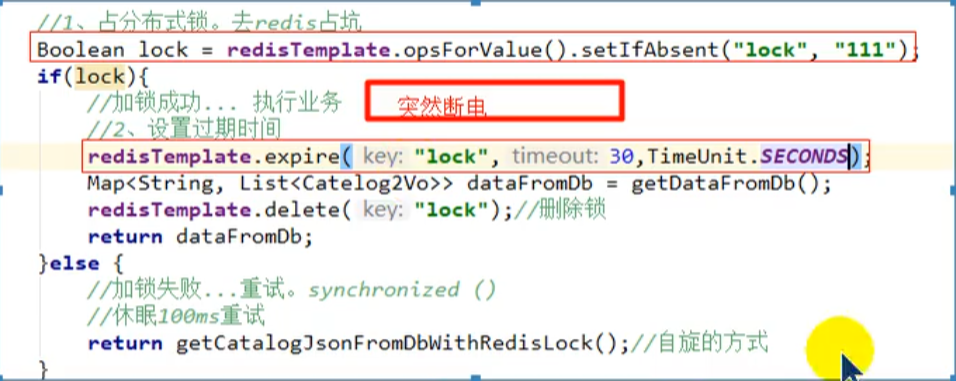
🚩优化二:过期时间和加锁同步setex+nx(解决加锁原子性问题)

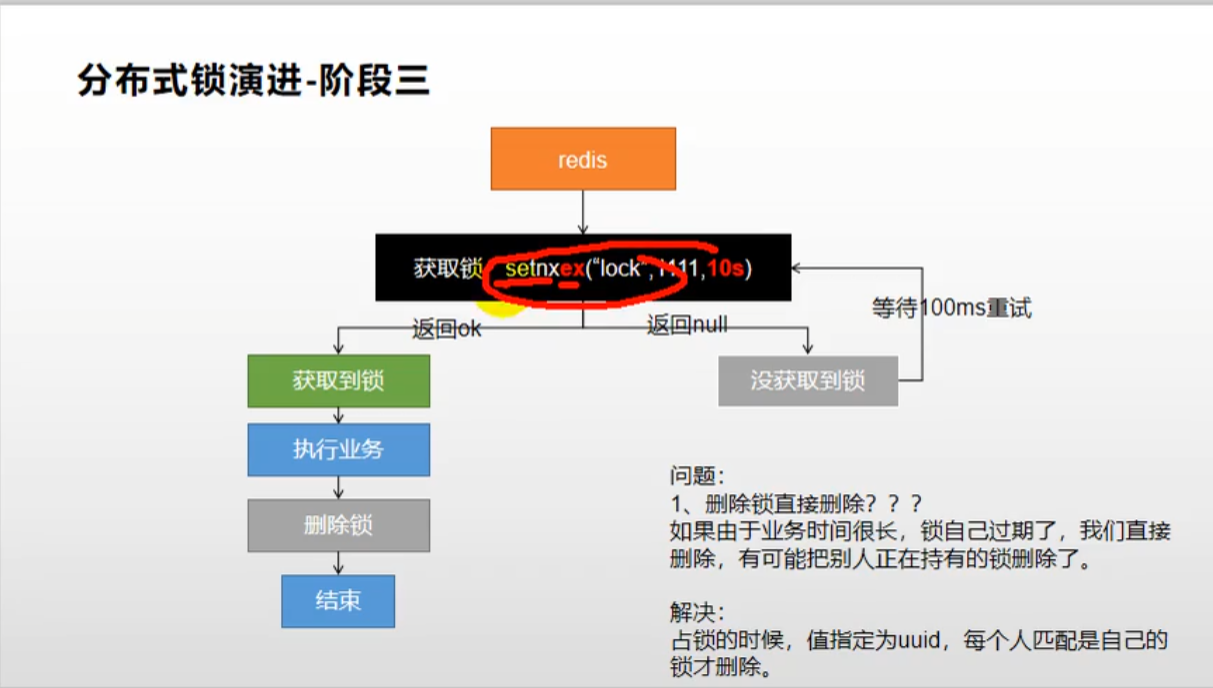
🚩优化三:redis+lua脚本解决删锁原子性问题
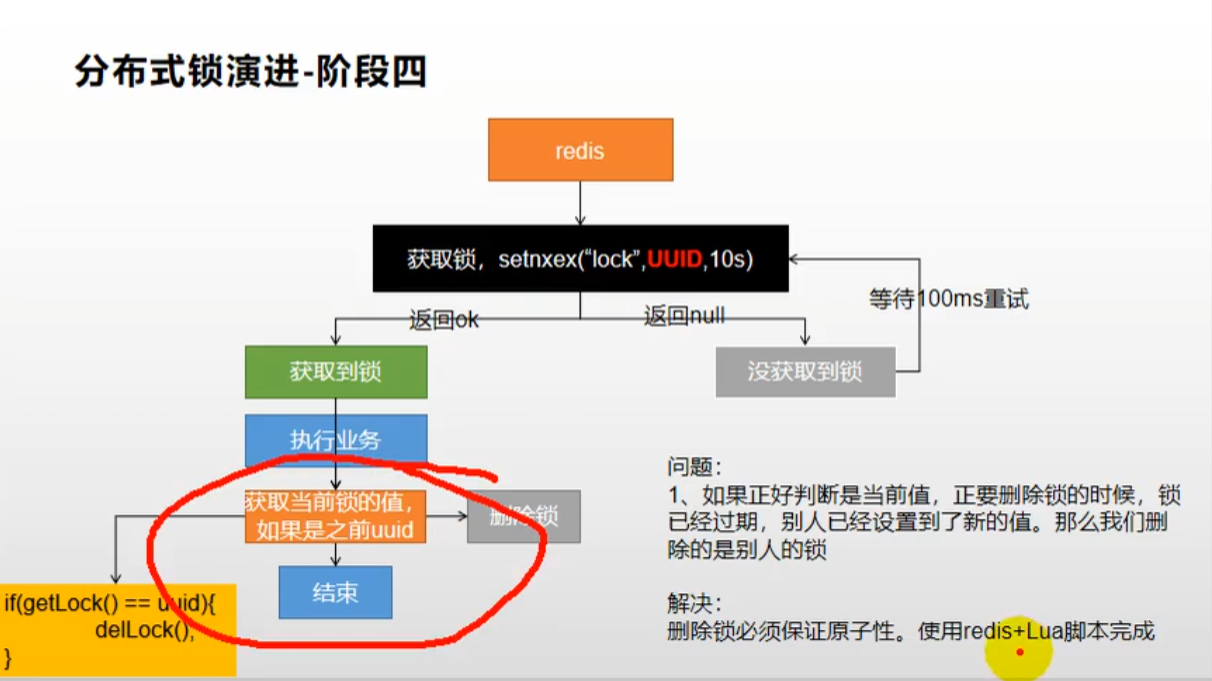
/** * 分布式锁 * lua脚本 * @return */ public Map<String, List<Catelog2Vo>> getCatelogJsonFromDBWithRedisLock() { // 1.占分布式锁 设置这个锁10秒自动删除 [原子操作] String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString(); Boolean lock = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent("lock", uuid, 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS); if (lock) { // 2.设置过期时间加锁成功 获取数据释放锁 [分布式下必须是Lua脚本删锁,不然会因为业务处理时间、网络延迟等等引起数据还没返回锁过期或者返回的过程中过期 然后把别人的锁删了] Map<String, List<Catelog2Vo>> data; try { data = getDataFromDB(); } finally { // stringRedisTemplate.delete("lock"); String lockValue = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("lock"); // 删除也必须是原子操作 Lua脚本操作 删除成功返回1 否则返回0 String script = "if redis.call('get',KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then return redis.call('del',KEYS[1]) else return 0 end"; // 原子删锁 stringRedisTemplate.execute(new DefaultRedisScript<>(script, Long.class), Arrays.asList("lock"), uuid); } return data; } else { // 重试加锁 try { // 登上两百毫秒 Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return getCatelogJsonFromDBWithRedisLock(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
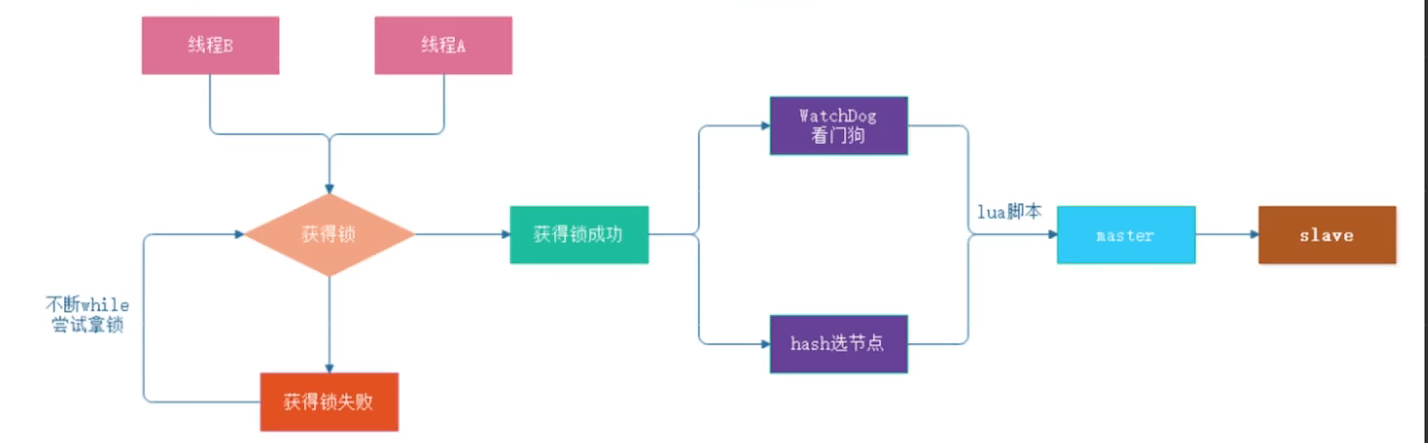
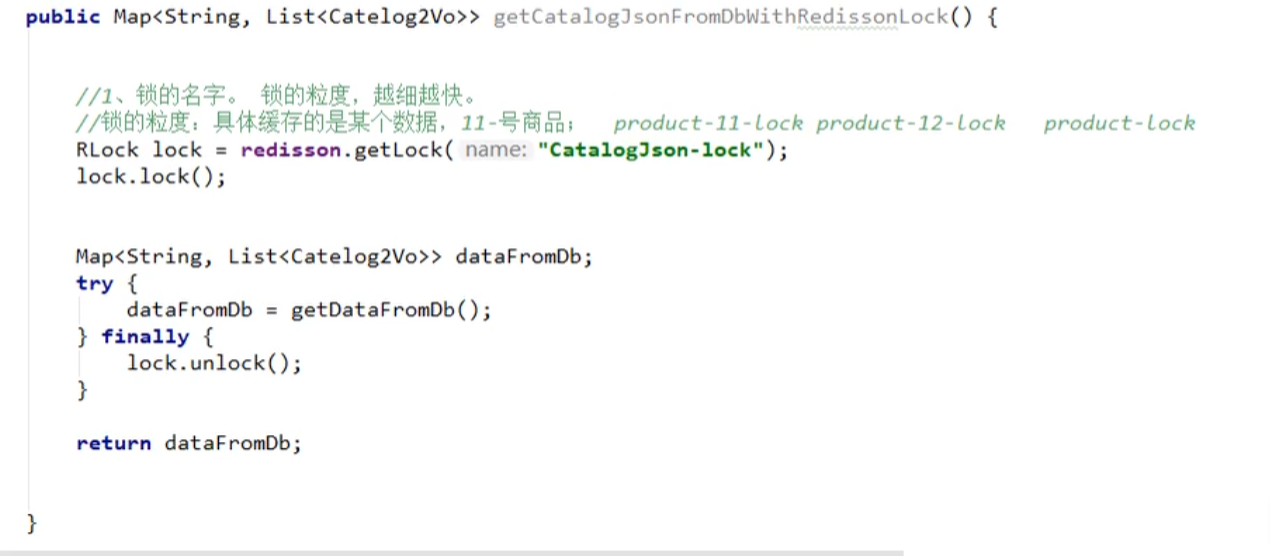
5、redisson分布式锁
@ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/index/hello") public String hello() { RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("my-lock"); // 阻塞式等待 lock.lock(); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } return "hello"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
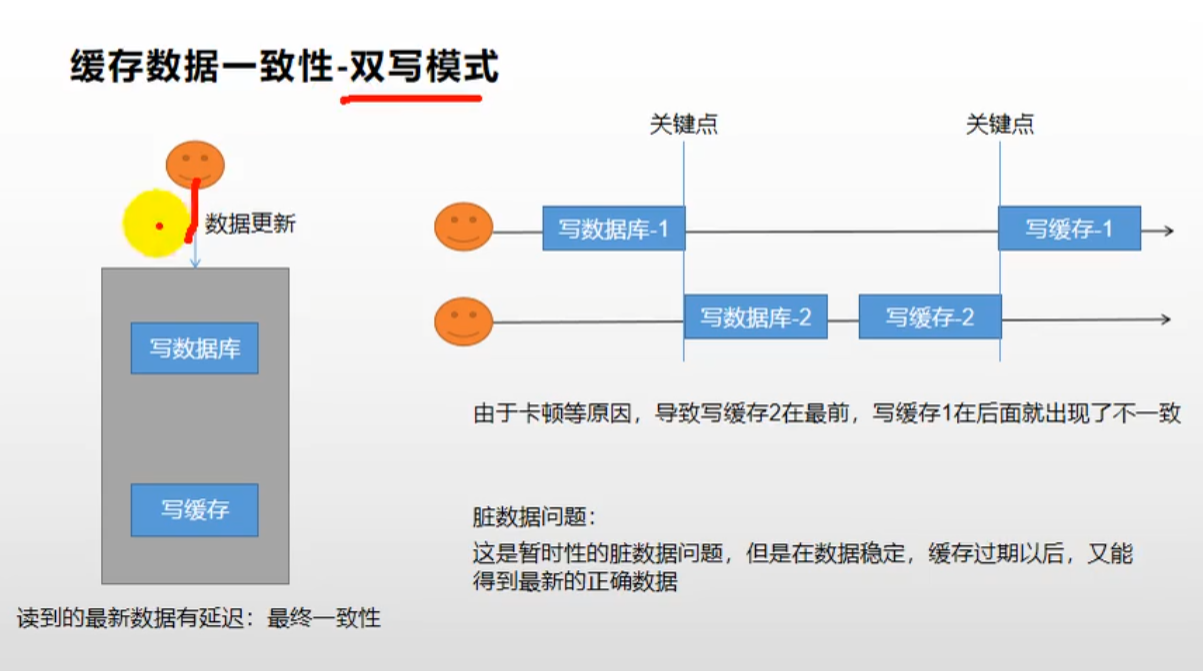
6、双写一致性与延迟双删
双写一致性
🚩双写一致性的解决方案一:可以在修改数据的方法加锁,就是每次只允许一个线程去修改数据库,这样就保证了Mysql和redis数据的一致性
🚩双写一致性的解决方案二:给redis设置过期时间,过期后就会去Mysql查最新的数据,保证最终数据一致
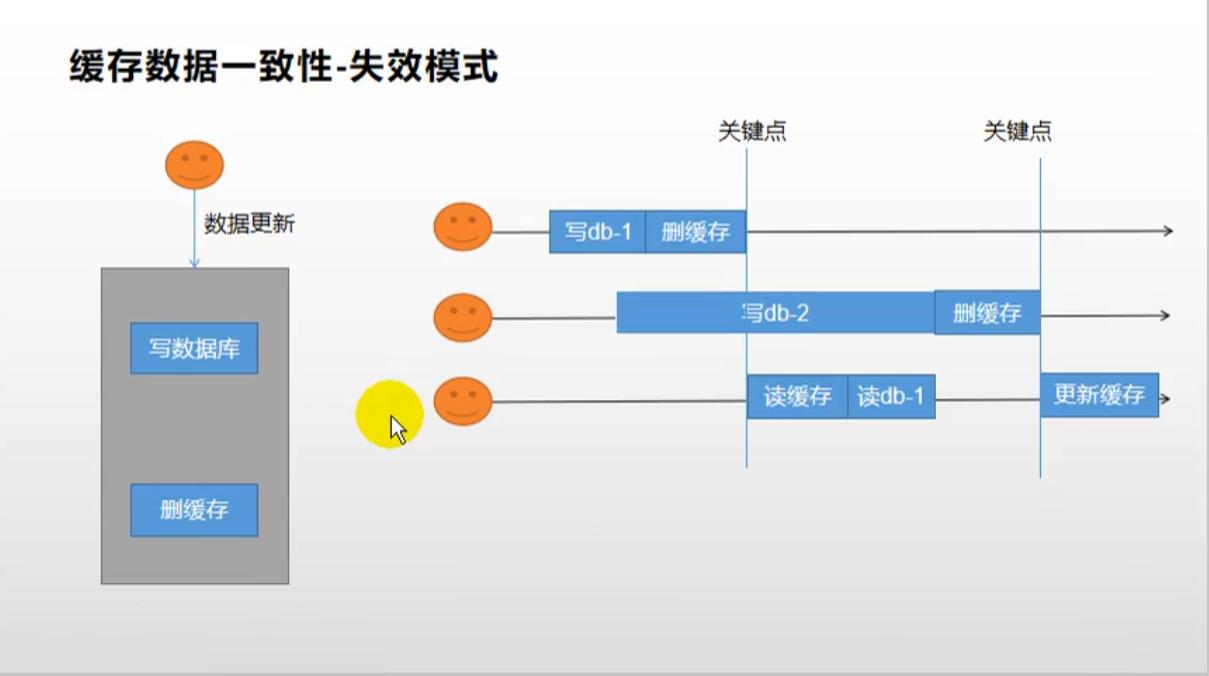
失效模式
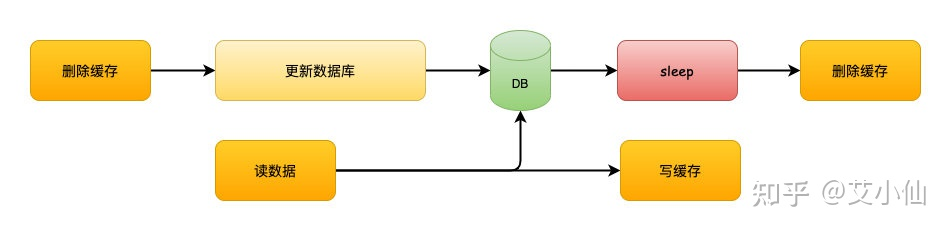
延迟双删
延时双删的方案的思路是,为了避免更新数据库的时候,其他线程从缓存中读取不到数据,就在更新完数据库之后,再sleep一段时间,然后再次删除缓存。
sleep的时间要对业务读写缓存的时间做出评估,sleep时间大于读写缓存的时间即可。
流程如下:
1、线程1删除缓存,然后去更新数据库
2、线程2来读缓存,发现缓存已经被删除,所以直接从数据库中读取,这时候由于线程1还没有更新完成,所以读到的是旧值,然后把旧值写入缓存
3、线程1,根据估算的时间,sleep,由于sleep的时间大于线程2读数据+写缓存的时间,所以缓存被再次删除
4、如果还有其他线程来读取缓存的话,就会再次从数据库中读取到最新值
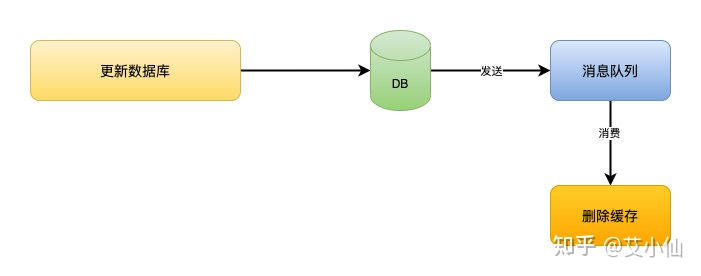
消息队列
这是网上很多文章里都有写过的方案。但是这个方案的缺陷会更明显一点。
先更新数据库,成功后往消息队列发消息,消费到消息后再删除缓存,借助消息队列的重试机制来实现,达到最终一致性的效果。
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis; public class DelayedDoubleDeleteExample { private static final int DELAY_TIME = 1000; // 延迟双删时间,单位:毫秒 // 模拟数据库 private static String database = "Original Data"; // 模拟缓存 private static Jedis cache = new Jedis("localhost", 6379); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 初始化缓存 cache.set("key", database); // 更新数据 updateDataInDatabase("Updated Data"); Thread.sleep(DELAY_TIME); // 等待延迟双删时间 // 获取数据 String data = getData("key"); System.out.println("Data: " + data); } private static void updateDataInDatabase(String newData) { // 先更新数据库 database = newData; // 再删除缓存 cache.del("key"); System.out.println("Cache deleted"); } private static String getData(String key) { // 先从缓存读取数据 String data = cache.get(key); if (data == null) { // 缓存不存在,从数据库读取最新数据 data = database; // 将数据写入缓存 cache.set(key, data); System.out.println("Cache updated"); } return data; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
7、Cannal
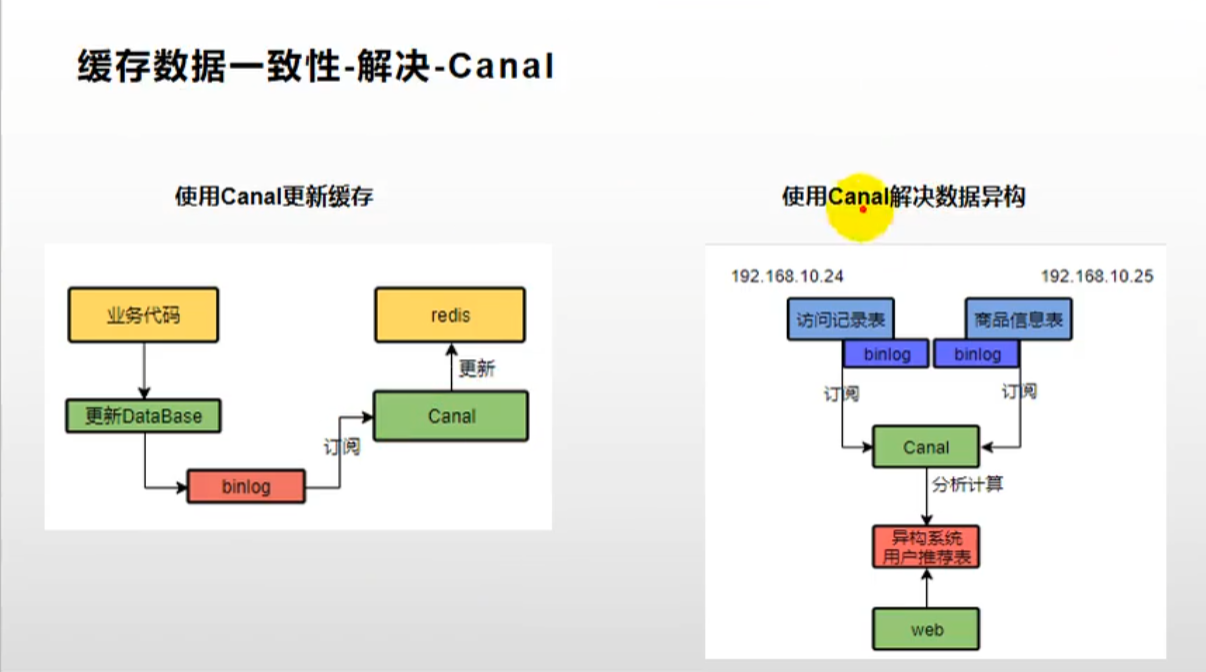
-
相关阅读:
重学前端-js类型
松江辟出长三角G60科创走廊供给侧结构性改革新路
OneNote 教程,如何在 OneNote 中检查拼写?
【C语言】逆置算法
@Retryable和Guava retry
若依集成mybatisplus报错找不到xml
GB28181学习(十六)——基于jrtplib实现tcp被动和主动收流
你要知道的这几个简单的心理学规律
ElasticSearch - 分词器
JavaScript学习笔记——JS基础6
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_57818853/article/details/132741002
