-
C++核心编程--类篇
C++核心编程
1.内存分区模型
C++程序在执行时,将内存大方向分为4个区域
意义:不同区域存放数据,赋予不同的生命周期,更能灵活编程
- 代码区:存放函数体的二进制代码,由操作系统进行管理的
- 全局区:存放全局变量和静态变量以及常量
- 栈区:由编译器自动分配释放,存放函数的参数值,局部变量等
- 堆区:由程序员分配和释放,若程序员不释放,程序结束时由操作系统回收
1.1、程序运行前
代码区:- 存放CPU执行的
机器指令 - 代码区是共享的,共享的目的是为了频繁被执行的程序
- 代码区是只读的,防止程序以外地修改它的指令
全局区全局变量和静态变量存放在此- 全局区包含了
常量区 - 该区域数据在程序结束后操作系统自动释放
1.2、程序运行后
栈区:不要返回局部变量地址,栈区开辟的数据会被编译器自动释放
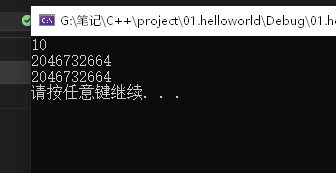
#includeusing namespace std; int* func() { int a = 10; //局部变量 return &a; //返回局部变量的值 } int main() { int* p = func(); cout << *p << endl; //编译器会自动保存一次正确的值 cout << *p << endl; cout << *p << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
堆区:- 由我们自己开辟内存,我们不结束程序,不会释放
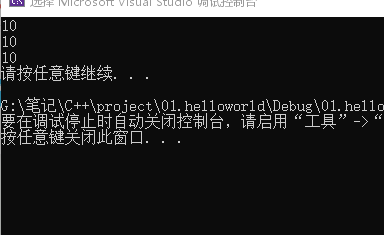
#includeusing namespace std; int* fun() { //new关键字,可以将数据开辟到堆区 int * a = new int(10); return a; } int main() { int * p = fun(); cout << *p << endl; cout << *p << endl; cout << *p << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
1.3、new关键字
在堆区中开辟数据,可以使用
new关键字利用new创建的数据,会返回该数据对应的类型的指针
语法:
new 数据类型- 开辟数据后可以手动释放,利用
delete
#includeusing namespace std; int* fun() { //new关键字,可以将数据开辟到堆区 int * a = new int(10); return a; } int main() { int * p = fun(); cout << *p << endl; cout << *p << endl; //释放数据 delete p; cout << *p << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
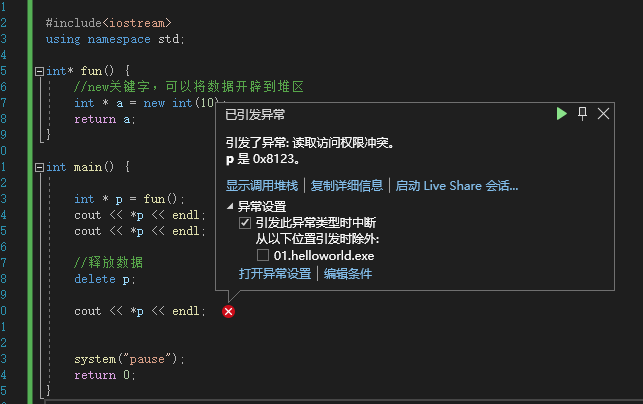
这里只会输出打印俩个P数据

- 数组同理
语法
int * arr = new int[10];
delete [] arrvoid fun() { //new关键字,可以将数据开辟到堆区 //int * a = new int(10); //return a; int* arr = new int[10]; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { arr[i] = i + 100; } for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout << arr[i] << endl; } //删除数组 delete [] arr; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
2、引用
作用:给变量起别名
语法:
数据类型 &别名 = 原名注意:一旦初始化,不可以更改,不能再次修改别名指向另一个
本质:引用的本质在C++内部实现是个指针常量
#includeusing namespace std; int main() { int a = 10; //给a取个别名b int &b = a; cout << b << endl; //利用别名修改a的值 b = 100; cout << b << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
2.1、引用做函数参数
作用:函数传参时,可以利用引用的技术让形参修饰实参优秀:可以简化指针修改实参//交换 void swap01(int& a, int& b) { int temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } #includeusing namespace std; int main() { int a = 10; int b = 20; swap01(a, b); cout << "交换后A:" << a << endl; cout << "交换后B:" << b << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
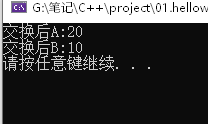
2.2、引用做函数返回值
作用:作为返回值存在注意:不要返回局部变量引用用法:函数调用作为左值(左边的值)- 返回局部变量情况(错误)
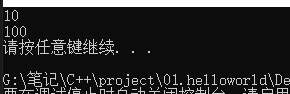
int& test02() { int a = 10; return a; } int main() { int& b = test02(); cout << b << endl;//编译器会做一次预存,后面就会出错 cout << b << endl; cout << b << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
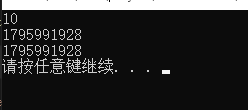
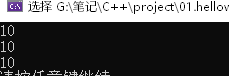
-
正确做法
int & test02() { static int a = 10; //静态变量,存放在全局区 return a; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
2.2、常量引用
用来修饰形参,防止误操作
//用来修饰形参 void printA(const int & a) { //a = 100; 这里就不能修改a cout << "值为:" << a << endl; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
3、函数高级
3.1、函数的默认参数
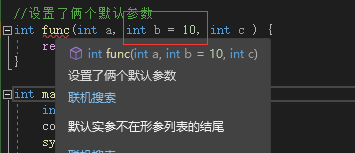
语法: 返回值类型 函数名 (形参 = 默认值){}
//设置了俩个默认参数 int func(int a, int b = 10, int c = 30) { return a + b + c; } int main() { int a = func(10); cout << a << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
注意- 设置默认参数从这个位置
往后的每个参数都必须有默认参数,否则报错 这里的C也必须有默认参数
- 如果函数声明有默认参数,函数实现就不可能有默认参数
声明和实现只能有一个有参数//定义一个函数 //声明 int func2(int a = 10, int b = 10); //实现 int func2(int a = 10, int b = 10) { return a + b; } int main() cout << func2(10, 20) << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
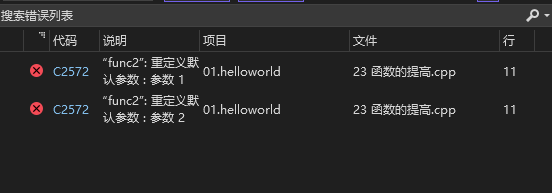
3.2、函数占位参数
语法:返回值类型 函数名 (数据类型){}
void func(int a, int) { cout << "1111" << endl; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 占位参数可以有默认值
void func(int a, int = 10) { cout << "1111" << endl; }- 1
- 2
- 3
3.3、函数重载概述
作用:函数名可以相同,提高复用性
函数重载的满足条件:- 同一作用域下
- 函数名称相同
- 函数参数
类型不同或者个数不同或者顺序不同
注意:函数的返回值不可以作为函数重载的条件#includeusing namespace std; //函数重载 //可以让函数名相同,提高复用性 //以下俩个均在全局作用域下 void func() { cout << "第一个方法" << endl; } //函数参数`类型不同` void func(int a) { cout << "第二个方法" << endl; } int main() { func(); system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22

根据传入的参数不同,可以调用不同的参数的相同名的方法
注意:函数的返回值不可以作为函数重载的条件
3.3.1、函数重载的注意事项
-
引用作为重载条件
-
函数重载碰到函数默认参数
- 引用作为重载条件
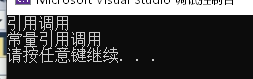
//引用做重载的条件 void func(int& a) { cout << "引用调用" << endl; } void func(const int& a) { cout << "常量引用调用" << endl; } int main() { int a = 10; func(a); //这里的直接插入10会生成一个临时变量赋给const int // int temp = 10; // const int = temp; func(10); system("pause"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 函数重载碰到函数默认参数
//函数重载碰到函数默认参数 void func2(int a, int b = 10) { cout << "方法1" << endl; } void func2(int a) { cout << "方法2" << endl; } int main() { //这里会报错 func2(10); system("pause"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14

4、类和对象
c++面向对象的三大特征:封装、继承、多态
4.1、封装
意义:
- 将属性和行为作为一个整体,表现生活中的事务
- 将属性和行为加以权限控制
- 在设计类的时候,属性和行为写在一起,表现事务
语法:class 类名{ 访问权限: 属性 / 行为}#includeusing namespace std; //eg:设计一个圆的类 求圆的周长 //定义常量 const double PI = 3.14; class Cricle { //访问权限 公共的 public: //定义一个半径 int m_r; //获取周长 double CricleZC() { return 2 * PI * m_r; } }; int main() { //实例化 一个对象 Cricle cr; //给对象属性赋值 cr.m_r = 10; / cout << "周长为:" << cr.CricleZC() << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 可利用方法去间接修改属性的值
class Student { //访问权限 public: string name; int St_num; void pr_inf() { cout << "姓名:" << name << '\n' << "学号:" << St_num << endl; } //给姓名赋值 void setName(string nm) { name = nm; } void setSt_num(int num) { St_num = num; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
4.1.1、封装的访问权限
访问权限分为三种:
- public 公共权限
- protected 保护权限
- private 私有权限
-
public 公共权限--------类内可以访问 类外可以访问
-
protected 保护权限--------类内可以访问 类外不可以被访问 (子类可以访问父类的保护内容)
-
private 私有权限--------类内可以访问 类外不可以被访问 (子类不可以访问父类的私有内容)
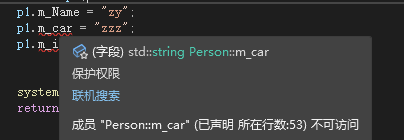
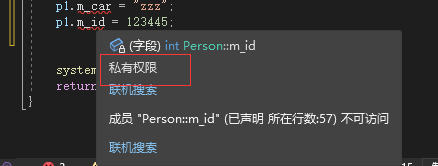
class Person { public: //公共权限 string m_Name; protected: //保护权限 string m_car; private: //私有权限 int m_id; }; int main() { Person p1; p1.m_Name = "zy"; //类内可以访问 类外不可以被访问 //p1.m_car = "zzz"; //p1.m_id = 123445; system("pause"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
4.1.2、struct和class区别
struct和class的
唯一区别:默认访问的权限不同- struct 默认权限为公有
- class 默认权限为私有
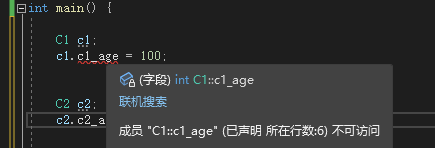
class C1 { int c1_age; }; struct C2 { int c2_age; }; int main() { C1 c1; //报错 //c1.c1_age = 100; C2 c2; c2.c2_age = 100; system("pause"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
4.1.3、成员属性设置为私有
- 将所有成员属性设置为私有,可以自己控制读写
- 对于写权限,我们可以检测数据的有效性
#include#include using namespace std; class Person { public: //定义获取设置名字方法,方便类外部使用 string getName() { return p_name; } void setName(string name) { p_name = name; } //可以根据传入值检测数据的有效性 void setAge(int age) { //检测输入的值 if (age<0||age>=150) { //输入错误设置默认值,并使该方法失效 p_age = 0; cout << "输入的值为错误值" << endl; return; } //如果上面检测不通过,不会执行该条语句 p_age = age; } int getAge() { return p_age; } private: string p_name; int p_age; }; int main() { Person p1; p1.setName("zyy"); p1.setAge(170); string name = p1.getName(); int age = p1.getAge(); cout << "姓名:" << name <<'\n' << "年龄:" << age << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
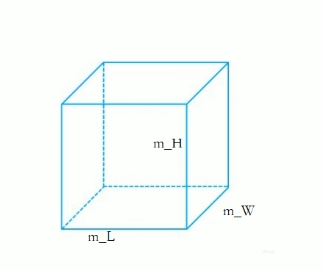
4.1.4、类练习题
- 设计立方体类
- 求出立方体的面积和体积
- 分别用全局函数和成员函数判断俩个立方体是否相等
#includeusing namespace std; class Cuboid { public: //获取面积 int getCuboid_are() { //(长×宽+宽×高+长×高)×2 面积公式 return ((m_H * m_L) + (m_H * m_W) + (m_L * m_W) * 2); } //获取体积 int getCuboid_vol() { return m_H * m_L * m_W; } //设置长方体长宽高 void setCuboid_H(int H) { m_H = H; } void setCuboid_L(int L) { m_L = L; } void setCuboid_W(int W) { m_W = W; } //获取长方体的长宽高 int getCuboid_H() { return m_H; } int getCuboid_L() { return m_L; } int getCuboid_W() { return m_W; } //利用成员函数判断是否相等 //这里只传c2 因为类已经存了一个立方体的数下,再更另一个作对比 //谁调用这个函数就传另一个 c1.isEq2(c2); bool isEq2(Cuboid& c2) { if (m_H == c2.getCuboid_H() && m_L == c2.getCuboid_L() && m_W == c2.getCuboid_W()) { return 1; } return 0; } private: //定义长方体的长宽高 int m_H; int m_L; int m_W; }; //全局判断是否相等 传入地址节约内存 bool isEq(Cuboid &c1,Cuboid &c2) { if (c1.getCuboid_H() == c2.getCuboid_H()&&c1.getCuboid_L()==c2.getCuboid_L()&&c1.getCuboid_W() == c2.getCuboid_W()) { return 1; } return 0; } int main() { Cuboid c1,c2; c1.setCuboid_H(10); c1.setCuboid_L(10); c1.setCuboid_W(10); c2.setCuboid_H(10); c2.setCuboid_L(10); c2.setCuboid_W(10); int area = c1.getCuboid_are(); int vol = c1.getCuboid_vol(); cout << "area:" << area << '\n' << "vol:" << vol << endl; //利用全局函数判断是否相等 bool flag = isEq(c1, c2); cout << flag << endl; //利用c1的属性去对比c2 bool flag2 = c1.isEq2(c2); cout << flag2 << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 点和圆的关系
- 设计一个圆形类(Circle),和一个点类(Point),计算点和圆的关系
#includeusing namespace std; class Point { public: //设置X坐标和Y坐标 void setPoint_X(int x) { p_X = x; } void setPoint_Y(int y) { p_Y = y; } //获取X坐标和Y坐标 int getPoint_X() { return p_X; } int getPoint_Y() { return p_Y; } private: //定义X坐标和Y坐标 int p_X; int p_Y; }; class Circle { public: //设置圆心和半径 void setCircle_R(int R) { c_R = R; } void setCircle_XY(int X,int Y) { c_P.setPoint_X(X); c_P.setPoint_Y(Y); } //获取圆心和半径 int getCircle_R() { return c_R; } int getCircle_X() { return c_P.getPoint_X(); } int getCircle_Y() { return c_P.getPoint_Y(); } //判断点和圆的关系 int isEq(Point p) { //获取点到圆心的距离 int distance = (c_P.getPoint_X() - p.getPoint_X()) * (c_P.getPoint_X() - p.getPoint_X()) + (c_P.getPoint_Y() - p.getPoint_Y()) * (c_P.getPoint_Y() - p.getPoint_Y()); int rDistance = c_R * c_R; // 1点在圆上,2点在圆外,3点在内 if (distance == rDistance) { cout << "圆上" << endl; return 1; } else if (distance > rDistance) { cout << "圆外" << endl; return 2; } else { cout << "圆内" << endl; return 3; } } private: //定义半径和圆心 int c_R; //在内中可以让另一个类作为本类中的成员 Point c_P; }; int main() { Circle c1; //设置半径和圆心 c1.setCircle_R(10); c1.setCircle_XY(10, 0); //创建点 Point p; p.setPoint_X(10); p.setPoint_Y(10); int a = c1.isEq(p); cout << a << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
4.1.5、类的拆分
基于上面练习题做一个拆分
- 在头文件中创建一个
.h后缀的头文件
- 在源文件中创建一个
.cpp后缀的源文件
- 在
point.h中只需要成员函数的声明和成员变量的声明。
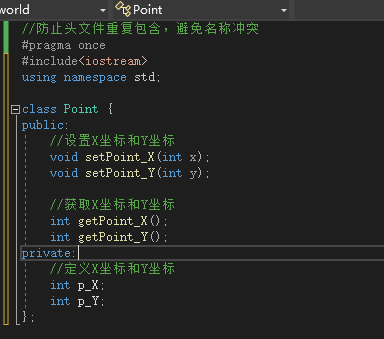
//防止头文件重复包含,避免名称冲突 #pragma once #includeusing namespace std; class Point { public: //设置X坐标和Y坐标 void setPoint_X(int x); void setPoint_Y(int y); //获取X坐标和Y坐标 int getPoint_X(); int getPoint_Y(); private: //定义X坐标和Y坐标 int p_X; int p_Y; }; - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 在
point.cpp源文件中只需要留住所有函数的实现就可以
注意这里如果直接写会报错需要告诉编译器是哪个作用域下面的函数
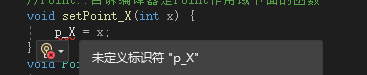
#include "point.h" //设置X坐标和Y坐标 //Point::告诉编译器是Point作用域下面的函数 void Point::setPoint_X(int x) { p_X = x; } void Point::setPoint_Y(int y) { p_Y = y; } //获取X坐标和Y坐标 int Point::getPoint_X() { return p_X; } int Point::getPoint_Y() { return p_Y; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 同理实现Circle的拆分
这里如果涉及到引用其他类需要include引用一下
Circle.h
#pragma once #include#include "point.h" using namespace std; class Circle { public: //设置圆心和半径 void setCircle_R(int R); void setCircle_XY(int X, int Y); //获取圆心和半径 int getCircle_R(); int getCircle_X(); int getCircle_Y(); //判断点和圆的关系 int isEq(Point p); private: //定义半径和圆心 int c_R; //在内中可以让另一个类作为本类中的成员 Point c_P; }; - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
Circle.cpp
#include "Circle.h" //设置圆心和半径 void Circle::setCircle_R(int R) { c_R = R; } void Circle::setCircle_XY(int X, int Y) { c_P.setPoint_X(X); c_P.setPoint_Y(Y); } //获取圆心和半径 int Circle::getCircle_R() { return c_R; } int Circle::getCircle_X() { return c_P.getPoint_X(); } int Circle::getCircle_Y() { return c_P.getPoint_Y(); } //判断点和圆的关系 int Circle::isEq(Point p) { int distance = (c_P.getPoint_X() - p.getPoint_X()) * (c_P.getPoint_X() - p.getPoint_X()) + (c_P.getPoint_Y() - p.getPoint_Y()) * (c_P.getPoint_Y() - p.getPoint_Y()); int rDistance = c_R * c_R; // 1点在圆上,2点在圆外,3点在内 if (distance == rDistance) { cout << "圆上" << endl; return 1; } else if (distance > rDistance) { cout << "圆外" << endl; return 2; } else { cout << "圆内" << endl; return 3; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 在想要用这个源文件中直接引用就可以使用了
#includeusing namespace std; #include "point.h" #include "Circle.h" int main() { Circle c1; //设置半径和圆心 c1.setCircle_R(10); c1.setCircle_XY(10, 0); //创建点 Point p; p.setPoint_X(10); p.setPoint_Y(10); int a = c1.isEq(p); cout << a << endl; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
-
相关阅读:
《web课程设计》 基于HTML+CSS+JavaScript实现中国水墨风的小学学校网站模板(6个网页)
SpringMVC ---- RESTful
javaScript:DOM元素的获取(静态/动态获取)
如何正确部署一个测试环境
List集合&UML图
基于蛙跳算法求解简单调度问题附matlab代码
大二Web课程设计期末考试——基于HTML+CSS+JavaScript+jQuery电商类化妆品购物商城
服务器的环境要求
统一异常处理导致ResponseBodyAdvice失效
添加gitlab runner脚本
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/NITIQ/article/details/132754444