-
多线程与高并发——并发编程(6)
文章目录
六、并发集合
1 ConcurrentHashMap
1.1 存储结构
ConcurrentHashMap 是线程安全的 HashMap,在 JDK1.8 中是以 CAS + synchronized 实现的线程安全。
- CAS:在没有 hash 冲突时(Node 要放在数组上时)
- synchronized:在出现 hash 冲突时(Node 存放的位置已经有数据了)
- 存储结构:数组+链表+红黑树
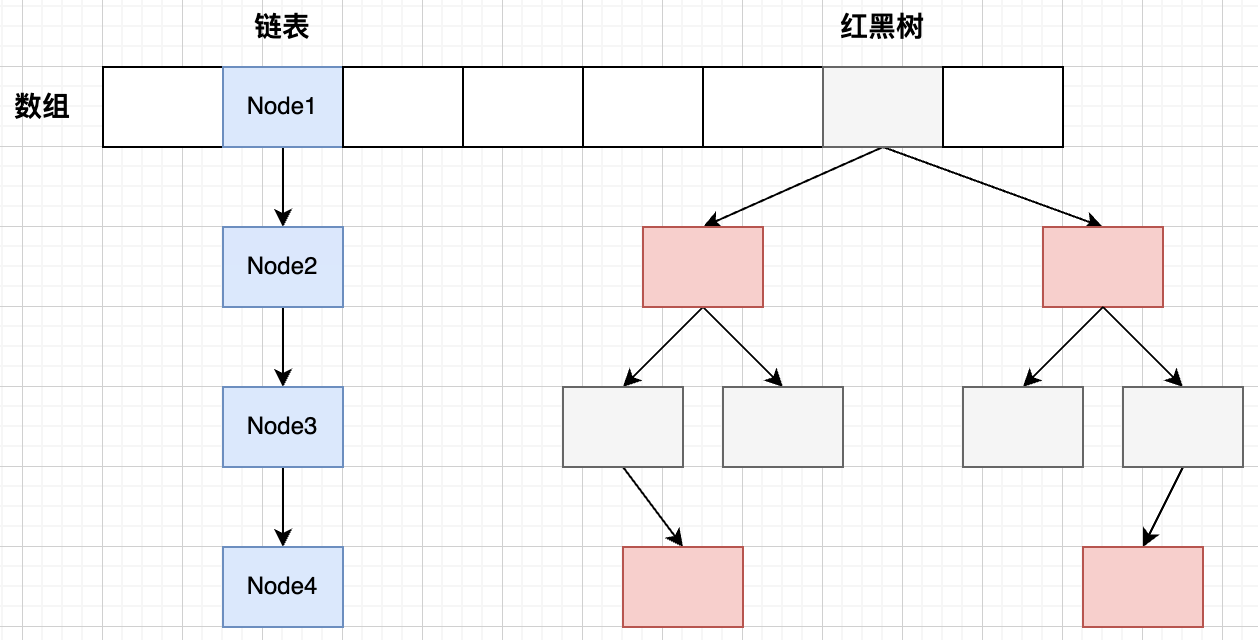
1.2 存储操作
1.2.1 put方法
public V put(K key, V value) { // 在调用put方法时,会调用putVal方法,第三个参数默认传递false // 在调用putIfAbsent时,会调用putVal方法,第三个参数传递true // false: 代表key一致时,直接覆盖数据 // true: 代表key一致时,什么都不做,key不存在正常添加(类似Redis的setnx) return putVal(key, value, false); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
1.2.2 putVal方法-散列算法
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { // ConcurrentHashMap不允许key或者value出现为null的值,跟HashMap的区别 if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); // 根据key的hashCode计算出一个hash值,后期得出当前key-value要存储在哪个数组索引位置 int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); int binCount = 0; // 一个标识,在后面有用 // ...省略大量代码 } // 计算当前Node的hash值的方法 static final int spread(int h) { // 将key的hashCode值的高低16位进行^运算,最终又与HASH_BITS进行了&运算 // 将高位的hash也参与到计算索引位置的运算当中,尽可能将数据打散 // 为什么HashMap、ConcurrentHashMap,都要求数组长度为2^n // HASH_BITS让hash值的最高位符号位肯定为0,代表当前hash值默认情况下一定是正数,因为hash值为负数时,有特殊的含义 // static final int MOVED = -1; // 代表当前hash位置的数据正在扩容 // static final int TREEBIN = -2; // 代表当前hash位置下挂载的是一个红黑树 // static final int RESERVED = -3; // 预留当前索引位置 return (h ^ (h >>> 16)) & HASH_BITS; // 计算数组放到哪个索引位置的方法 (f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash) // n:是数组的长度 } 运算方式 00000000 00000000 00000000 00001111 - 15 (n - 1) & ( ( 00001101 00001101 00101111 10001111 - h ^ 00000000 00000000 00001101 00001101 - h >>> 16 ) & 01111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 - HASH_BITS )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
1.2.3 putVal方法-添加数据到数组&初始化数组
- 添加数据到数组:CAS
- 初始化数组:DCL + CAS
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { // 省略部分代码... // 将Map的数组赋值给tab,死循环 for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { // n: 数组长度;i: 当前Node需要存放的索引位置 // f: 当前数组i索引位置的Node对象;fn: 当前数组i索引位置上数据的hash值 Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; // 判断当前数组是否还没有初始化 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) tab = initTable(); // 将数组进行初始化 // 基于 (n - 1) & hash 计算出当前Node需要存放在哪个索引位置 // 基于tabAt获取到i位置的数据 else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) { // 现在数组的i位置上没有数据,基于CAS的方式将数据存在i位置上 if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null))) break; // 如果成功,执行break跳出循环,插入数据成功 } // 判断当前位置数据是否正在扩容 else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); // 让当前插入数据的线程协助扩容 // 省略部分代码... } addCount(1L, binCount); return null; } // 初始化数组方法 private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() { Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc; // 再次判断数组没有初始化,并且完成tab的赋值 while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) { // sizeCtl:是数组在初始化和扩容操作时的一个控制变量。 // -1: 代表当前数组正在初始化; // 小于-1: 低16位代表当前数组正在扩容的线程个数(如果1个线程扩容,值为-2,如果2个线程扩容,值为-3); // 0: 代表数组还没初始化; // 大于0: 代表当前数组的扩容阈值,或者是当前数组的初始化大小 // 将sizeCtl赋值给sc变量,并判断是否小于0 if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0) Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin // 可以尝试初始化数组,线程会以CAS的方式,将sizeCtl修改为-1,代表当前线程可以初始化数组 else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) { try { // 尝试初始化 // 再次判断当前数组是否已经初始化完毕 if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) { // 开始初始化: 如果sizeCtl > 0,就初始化sizeCtl长度的数组;如果sizeCtl == 0,就初始化默认的长度16 int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY; // 初始化数组 Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n]; // 将初始化的数组nt,赋值给tab和table table = tab = nt; // sc赋值为了数组长度 - 数组长度 右移 2位 16 - 4 = 12,将sc赋值为下次扩容的阈值 sc = n - (n >>> 2); } } finally { // 将赋值好的sc,设置给sizeCtl sizeCtl = sc; } break; } } return tab; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
1.2.4 putVal方法-添加数据到链表
- 添加数据到链表:利用 synchronized 基于当前索引位置的Node,作为锁对象
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { // 省略部分代码... int binCount = 0; for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { // n: 数组长度;i: 当前Node需要存放的索引位置 // f: 当前数组i索引位置的Node对象;fn: 当前数组i索引位置上数据的hash值 Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; // 省略部分代码... else { V oldVal = null; // 声明变量为oldVal synchronized (f) { // 基于当前索引位置的Node,作为锁对象 // 判断当前位置的数据还是之前的f么……(避免并发操作的安全问题) if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { if (fh >= 0) { // 再次判断hash值是否大于0(不是树) // binCount设置为1(在链表情况下,记录链表长度的一个标识) binCount = 1; // 死循环,每循环一次,对binCount for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) { K ek; // 当前i索引位置的数据,是否和当前put的key的hash值一致 if (e.hash == hash && // 如果当前i索引位置数据的key和put的key == 返回为true // 或者equals相等 ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) { // key一致,可能需要覆盖数据,当前i索引位置数据的value赋值给oldVal oldVal = e.val; // 如果传入的是false,代表key一致,覆盖value;如果传入的是true,代表key一致,什么都不做 if (!onlyIfAbsent) e.val = value; // 覆盖value break; } Node<K,V> pred = e; // 拿到当前指定的Node对象 // 将e指向下一个Node对象,如果next指向的是一个null,可以挂在当前Node下面 if ((e = e.next) == null) { // 将hash,key,value封装为Node对象,挂在pred的next上 pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null); break; } } } // 省略部分代码... } } if (binCount != 0) { if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD) // binCount是否大于8(链表长度是否 >= 8) // 尝试转为红黑树或者扩容 // 基于treeifyBin方法和上面的if判断,可以得知链表想要转为红黑树,必须保证数组长度大于等于64,并且链表长度大于等于8 // 如果数组长度没有达到64的话,会首先将数组扩容 treeifyBin(tab, i); if (oldVal != null) // 如果出现了数据覆盖的情况,返回之前的值 return oldVal; break; } } } // 省略部分代码... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
为什么链表长度为8转换为红黑树,不是能其他数值嘛?
因为泊松分布
The main disadvantage of per-bin locks is that other update * operations on other nodes in a bin list protected by the same * lock can stall, for example when user equals() or mapping * functions take a long time. However, statistically, under * random hash codes, this is not a common problem. Ideally, the * frequency of nodes in bins follows a Poisson distribution * (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Poisson_distribution) with a * parameter of about 0.5 on average, given the resizing threshold * of 0.75, although with a large variance because of resizing * granularity. Ignoring variance, the expected occurrences of * list size k are (exp(-0.5) * pow(0.5, k) / factorial(k)). The * first values are: * * 0: 0.60653066 * 1: 0.30326533 * 2: 0.07581633 * 3: 0.01263606 * 4: 0.00157952 * 5: 0.00015795 * 6: 0.00001316 * 7: 0.00000094 * 8: 0.00000006 * more: less than 1 in ten million- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
1.3 扩容操作
1.3.1 treeifyBin方法触发扩容
// 在链表长度大于等于8时,尝试将链表转为红黑树 private final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int index) { Node<K,V> b; int n, sc; // 数组不能为空 if (tab != null) { // 数组的长度n,是否小于64 if ((n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) // 如果数组长度小于64,不能将链表转为红黑树,先尝试扩容操作 tryPresize(n << 1); // 省略部分代码…… } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
1.3.2 tryPresize方法-针对putAll的初始化操作
// size是将之前的数组长度 左移 1位得到的结果 private final void tryPresize(int size) { // 如果扩容的长度达到了最大值,就使用最大值,否则需要保证数组的长度为2的n次幂 // 这块的操作,是为了初始化操作准备的,因为调用putAll方法时,也会触发tryPresize方法 // 如果刚刚new的ConcurrentHashMap直接调用了putAll方法的话,会通过tryPresize方法进行初始化 int c = (size >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor(size + (size >>> 1) + 1); // 这些代码和initTable一模一样 int sc; // 将sizeCtl的值赋值给sc,并判断是否大于0,这里代表没有初始化操作,也没有扩容操作 while ((sc = sizeCtl) >= 0) { // 将ConcurrentHashMap的table赋值给tab,并声明数组长度n Node<K,V>[] tab = table; int n; // 数组是否需要初始化 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) { // 进来执行初始化 // sc是初始化长度,初始化长度如果比计算出来的c要大的话,直接使用sc,如果没有sc大,说明sc无法容纳下putAll中传入的map,使用更大的数组长度 n = (sc > c) ? sc : c; // 设置sizeCtl为-1,代表初始化操作 if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) { try { // 再次判断数组的引用有没有变化 if (table == tab) { // 初始化数组 Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n]; // 数组赋值 table = nt; // 计算扩容阈值 sc = n - (n >>> 2); } } finally { // 最终赋值给sizeCtl sizeCtl = sc; } } } // 如果计算出来的长度c小于等于c,或者数组长度大于等于最大长度,直接退出循环结束方法 else if (c <= sc || n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) break; // 省略部分代码... } } // 将c这个长度设置到最近的2的n次幂的值, 15 -> 16 17 -> 32 // c == size + (size >>> 1) + 1 // size = 17 00000000 00000000 00000000 00010001 + 00000000 00000000 00000000 00001000 + 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001 // c = 26 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011010 private static final int tableSizeFor(int c) { // c = 26 // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011001 int n = c - 1; // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011001 // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00001100 // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011101 n |= n >>> 1; // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011101 // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000111 // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011111 n |= n >>> 2; // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011111 // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001 // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011111 n |= n >>> 4; // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011111 // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011111 n |= n >>> 8; // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011111 n |= n >>> 16; // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00100000 return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
1.3.3 tryPreSize方法-计算扩容戳&查看BUG
private final void tryPresize(int size) { // n:数组长度 while ((sc = sizeCtl) >= 0) { // 省略部分代码… // 判断当前的tab是否和table一致 else if (tab == table) { // 计算扩容标识戳,根据当前数组的长度计算一个16位的扩容戳 // 第一个作用是为了保证后面的sizeCtl赋值时,保证sizeCtl为小于-1的负数 // 第二个作用用来记录当前是从什么长度开始扩容的 int rs = resizeStamp(n); // BUG --- sc < 0,永远进不去 if (sc < 0) { // 如果sc小于0,代表有线程正在扩容 // 省略部分代码……协助扩容的代码(进不来~~~~) } // 代表没有线程正在扩容,我是第一个扩容的。 else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, (rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2)) // 省略部分代码……第一个扩容的线程…… } } } // 计算扩容标识戳 // 32 = 00000000 00000000 00000000 00100000 // Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(32) = 26 // 1 << (RESIZE_STAMP_BITS - 1) // 00000000 00000000 10000000 00000000 // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00011010 // 00000000 00000000 10000000 00011010 static final int resizeStamp(int n) { return Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(n) | (1 << (RESIZE_STAMP_BITS - 1)); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
1.3.4 tryPreSize方法-对sizeCtl的修改&条件判断的BUG
private final void tryPresize(int size) { // sc默认为sizeCtl while ((sc = sizeCtl) >= 0) { else if (tab == table) { // rs: 扩容戳 00000000 00000000 10000000 00011010 int rs = resizeStamp(n); if (sc < 0) { // 说明有线程正在扩容,过来帮助扩容 Node<K,V>[] nt; // 依然有BUG // 当前线程扩容时,老数组长度是否和我当前线程扩容时的老数组长度一致 // 00000000 00000000 10000000 00011010 if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs // 10000000 00011010 00000000 00000010 // 00000000 00000000 10000000 00011010 // 这两个判断都是有问题的,核心问题就应该先将rs左移16位,再追加当前值 // 判断当前扩容是否已经即将结束 || sc == rs + 1 // sc == rs << 16 + 1 BUG // 判断当前扩容的线程是否达到了最大限度 || sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS // sc == rs << 16 + MAX_RESIZERS BUG // 扩容已经结束了 || (nt = nextTable) == null // 记录迁移的索引位置,从高位往低位迁移,也代表扩容即将结束 || transferIndex <= 0) break; // 如果线程需要协助扩容,首先就是对sizeCtl进行+1操作,代表当前要进来一个线程协助扩容 if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1)) // 上面的判断没进去的话,nt就代表新数组 transfer(tab, nt); } // 是第一个来扩容的线程 // 基于CAS将sizeCtl修改为 10000000 00011010 00000000 00000010 // 将扩容戳左移16位之后,符号位是1,就代码这个值为负数,低16位在表示当前正在扩容的线程有多少个 // 为什么低位值为2时,代表有一个线程正在扩容 // 每一个线程扩容完毕后,会对低16位进行-1操作,当最后一个线程扩容完毕后,减1的结果还是-1,当值为-1时,要对老数组进行一波扫描,查看是否有遗漏的数据没有迁移到新数组 else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2)) // 调用transfer方法,并且将第二个参数设置为null,就代表是第一次来扩容! transfer(tab, null); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
1.3.5 transfer方法-计算每个线程迁移的长度
// 开始扩容 tab: oldTable private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) { // n: 数组长度 // stride: 每个线程一次性迁移多少数据到新数组 int n = tab.length, stride; // 基于CPU的内核数量来计算,每个线程一次性迁移多少长度的数据最合理 // NCPU = 4 // 举个栗子:数组长度为1024 - 512 - 256 - 128 / 4 = 32 // MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE = 16,为每个线程迁移数据的最小长度 // 根据CPU计算每个线程一次迁移多长的数据到新数组,如果结果大于16,使用计算结果。 如果结果小于16,就使用最小长度16 if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE) stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // 省略部分代码... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
1.3.6 transfer方法-构建新数组&查看标识属性
// 以32长度数组扩容到64位例子 private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) { // 省略部分代码... // n: 老数组长度 32 // stride: 步长 16 // 第一个进来扩容的线程需要把新数组构建出来 if (nextTab == null) { try { // 将原数组长度左移一位,构建新数组长度 Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1]; // 赋值操作 nextTab = nt; } catch (Throwable ex) { // 到这说明已经达到数组长度的最大取值范围 sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 设置sizeCtl后直接结束 return; } // 对成员变量的新数组赋值 nextTable = nextTab; // 迁移数据时,用到的标识,默认值为老数组长度 transferIndex = n; // 32 } // 新数组长度 int nextn = nextTab.length; // 64 // 在老数组迁移完数据后,做的标识 ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab); // 迁移数据时,需要用到的标识 boolean advance = true; boolean finishing = false; // 省略部分代码... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
1.3.7 transfer方法-线程领取迁移任务
// 以32长度扩容到64位为例子 private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) { // 省略部分代码… // n: 32 // stride: 16 int n = tab.length, stride; if (nextTab == null) { // 省略部分代码… nextTable = nextTab; // 新数组 // transferIndex:0 transferIndex = n; } // nextn:64 int nextn = nextTab.length; ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab); // advance:true,代表当前线程需要接收任务,然后再执行迁移;如果为false,代表已经接收完任务 boolean advance = true; boolean finishing = false; // 是否迁移结束 // i = 15 代表当前线程迁移数据的索引值 for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) { Node<K,V> f; int fh; // f = null,fh = 0 while (advance) { // 当前线程要接收任务 // nextIndex = 16,nextBound = 16 int nextIndex, nextBound; // 对i进行--,并且判断当前任务是否处理完毕! if (--i >= bound || finishing) // 第一次进来,这两个判断肯定进不去 advance = false; // 判断transferIndex是否小于等于0,代表没有任务可领取,结束了 // 在线程领取任务会,会对transferIndex进行修改,修改为transferIndex - stride // 在任务都领取完之后,transferIndex肯定是小于等于0的,代表没有迁- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
-
相关阅读:
Docker 安装 MongoDB
【debug】postgres数据存储错乱
无线网络存在的安全问题及现代化解决方案
全网独家首发!Docker顶级教程,简直把所有知识点都涵盖起来了
大学生简单个人静态HTML网页设计作品 HTML+CSS制作我的家乡杭州 DIV布局个人介绍网页模板代码 DW学生个人网站制作成品下载 HTML5期末大作业
自动化防火墙放行目标域名IP
【Oracle】使用 SQL Developer 连接 Oracle 数据库
Java生成Jar包方法
使用Unity制作3D驾驶游戏
GreenPlum6.x之ETL工具
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/yangwei234/article/details/132783814
