-
从 LinkedHashMap 源码到手撕 LRU 缓存
大家好,我是 方圆。最近在刷 LeetCode 上LRU缓存的题目,发现答案中有 LinkedHashMap 和自己定义双向链表的两种解法,但是我对 LinkedHashMap 相关源码并不清楚,所以准备学习和记录一下。如果大家想要找刷题路线的话,可以参考 Github: LeetCode。
LRU(Least Recently Used),即最近最少使用,是一种常用的页面置换算法,选择最近最久未使用的页面予以淘汰。
1. LinkedHashMap 源码
LinkedHashMap 继承了 HashMap,并使用双向链表对所有的 entry 进行管理,使得这些节点能够按照 插入顺序 或 访问(access)顺序 来排列,并且节点的添加和移除 时间复杂度为 O(1)。
顺序的模式通过字段
accessOrder来定义,为 false 时表示插入顺序,否则为访问顺序。LinkedHashMap 中能够定义顺序模式的构造方法如下:public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean accessOrder) { super(initialCapacity, loadFactor); this.accessOrder = accessOrder; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
需要注意的是,按照插入顺序排列的 LinkedHashMap,如果 将其中已有的 key 再重新插入到 map 中,则它的节点顺序不会受到影响,我们来具体看一下源码:
LinkedHashMap 调用
put方法时会执行 HashMap 中的putVal方法,关键的代码部分如下:final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { // ... else { // ... // map 中已经存在了这个 key if (e != null) { V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; // 重点关注这里 afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } // ... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
当 map 中已有该 key 时,会执行上述逻辑,注意其中的
afterNodeAccess方法,它是定义在 HashMap 中的钩子方法,LinkedHashMap 对该方法做了实现,如下:// 将 节点 移动到末尾 void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last; // 需要满足是访问顺序排列和当前节点不是尾节点的条件 if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) { // p 为当前节点,b 为 p 的前驱节点,a 为 p 的后继节点 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p = (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after; // p 作为新的尾节点,after 指针为 null p.after = null; // 处理 p 的前驱节点 b,为空的话后继节点为新的头节点 if (b == null) head = a; else // 否则 b 的 after 指针指向 p 的后继节点 a b.after = a; // 处理 p 的后继节点 a,不为空的话 a 的前驱节点为 b if (a != null) a.before = b; else // 这个 else 条件与当前节点 p 不是尾节点的条件相悖,理论上 a 节点不为空 last = b; // 空链表会进入到这里,将第一插入的 p 节点作为头节点 if (last == null) head = p; else { // p 节点作为新的尾节点,那么它的前驱节点是原尾节点 last p.before = last; // 原尾节点 last 的后继节点为 p last.after = p; } // tail 尾节点指针指向 p tail = p; ++modCount; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
我们可以发现在判断条件
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e)中,插入顺序accessOrder为 false,不会执行任何逻辑,所以重新插入已有的 key 不改变节点的顺序。当accessOrder为 true 时,即为访问顺序时,会将该节点移动到尾节点处。LRU 算法需要通过访问顺序来实现,所以我们需要指定 accessOrder 为 True。如果需要指定 LRU 缓存的容量(超过容量将最老的节点移除),我们需要关注
afterNodeInsertion方法,它也是定义在 HashMap 中的钩子方法,调用时机在第一次插入节点时,关键代码如下,它在 HashMap 的putVal方法中:final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { // ... // 新节点第一次插入 afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
我们来关注下 LinkedHashMap 中对此方法的实现:
// 头节点是最旧的,将头节点进行移除 void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> first; // evict 为 true,且头节点不为空,removeEldestEntry 为 true 时将节点进行移除 if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) { K key = first.key; removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
removeEldestEntry方法我们需要点进去看看:protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) { return false; }- 1
- 2
- 3
我们可以发现,该方法默认情况下为 False,所以插入节点是不会对节点进行移除的。而LRU算法需要将缓存维持在固定大小,那么我们需要对该方法进行重写,比如要保持容量大小始终在100:
private static final int MAX_ENTRIES = 100; protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) { return size() > MAX_ENTRIES; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
总结一下,使用 LinkedHashMap 实现 LRU 缓存需要做两件事:
-
调用特定的构造方法指定
accessOrder为 true,使得每次被访问的节点都改变节点顺序 -
如果需要指定缓存容量的话,需重写
removeEldestEntry方法来保证不超过指定的最大容量
2. 手撕 LRU 缓存
146. LRU 缓存 中等 是 LeetCode 要求手撕 LRU 缓存的题目,大家可以点进去看一下原题,这里我们分别做出两种解法:一种是针对上文所述的 LinkedHashMap 来实现,另一种是借助 HashMap 和我们自己使用双向链表管理 entry 来实现。
LinkedHashMap 法
该方法详细内容在上文中已有具体解释,所以这里不再赘述,直接看代码即可
class LRUCache extends LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> { // 指定缓存的最大容量 private final int capacity; public LRUCache(int capacity) { super(capacity, 0.75F, true); this.capacity = capacity; } public int get(int key) { return super.getOrDefault(key, -1); } public void put(int key, int value) { super.put(key, value); } @Override protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> eldest) { return size() > capacity; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
HashMap 和 双向链表
先上代码,注意其中的注释
class LRUCache { static class ListNode { ListNode left; ListNode right; int key, value; public ListNode(int key, int value) { this.key = key; this.value = value; } } private final HashMap<Integer, ListNode> map; private final ListNode sentinel; private final int capacity; /** * 定义访问过的节点移动到尾节点 */ public LRUCache(int capacity) { this.map = new HashMap<>(capacity); this.capacity = capacity; // 定义单个哨兵节点形成双向循环链表来简化边界条件的判断 ListNode sentinel = new ListNode(-1, -1); this.sentinel = sentinel; sentinel.right = sentinel; sentinel.left = sentinel; } public int get(int key) { if (map.containsKey(key)) { ListNode node = map.get(key); // 将该节点移动到尾节点 refresh(node); return node.value; } else { return -1; } } public void put(int key, int value) { if (map.containsKey(key)) { ListNode node = map.get(key); node.value = value; // 如果已经有这个节点则需要将其移动到尾节点 refresh(node); } else { ListNode node = new ListNode(key, value); // 没有的话先判断容量 if (map.size() == capacity) { // 先移除头节点 ListNode head = sentinel.right; map.remove(head.key); sentinel.right = head.right; head.right.left = sentinel; } // 插入到尾节点 insert(node); // 管理到 map 中 map.put(key, node); } } /** * 移动该节点到尾节点 */ private void refresh(ListNode node) { ListNode pre = node.left, next = node.right; // 处理前驱节点 pre pre.right = next; // 处理后继节点 next next.left = pre; ListNode tail = sentinel.left; // 将当前节点移动到尾节点 tail.right = node; node.left = tail; // 构建双向循环链表 node.right = sentinel; sentinel.left = node; } /** * 添加到尾节点 */ private void insert(ListNode node) { ListNode tail = sentinel.left; // 添加到尾节点 tail.right = node; node.left = tail; // 双向循环链表 node.right = sentinel; sentinel.left = node; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
我们定义了一个
sentinel哨兵节点,并让它形成一个循环的双向链表,我们可以根据该节点轻易获取到头节点(sentinel.right)和尾节点(sentinel.left)。这样做的好处是 简化了边界条件的处理,我们不需要在删除和移动链表节点的时候进行判空。链表图示如下,一个空的链表只由一个哨兵节点构成:
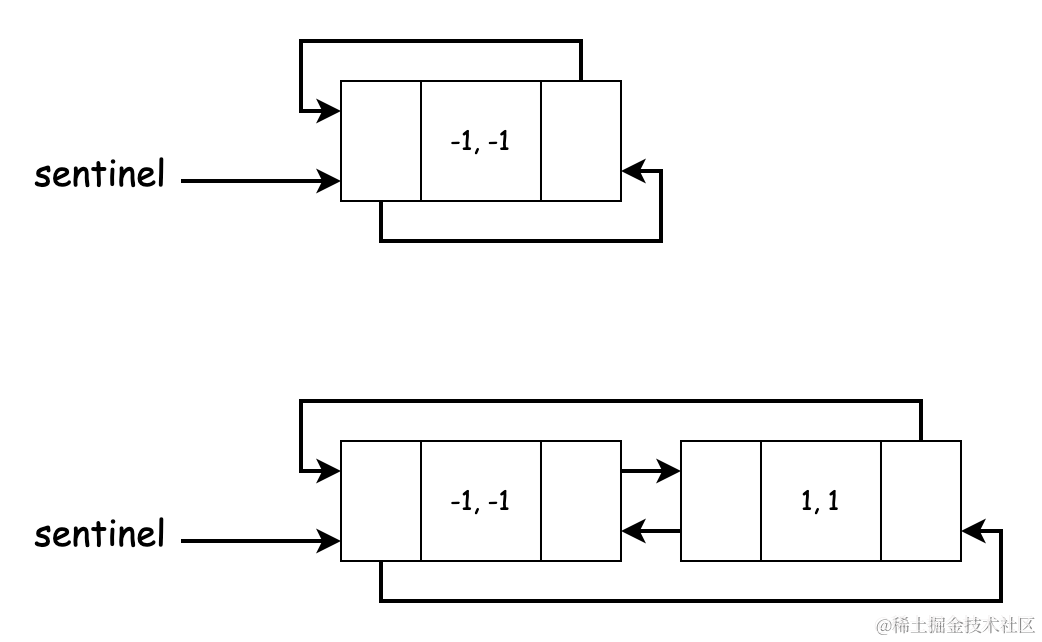
需要注意的是,每次插入新的节点都需要注意维护循环双向链表。
巨人的肩膀
-
《算法导论》第 10.2 章
-
相关阅读:
springboot基础(50):linux安装kafka
前后端交互—Express
linux 安装gitkraken
聊聊什么是分布式事务
YashanDB个人版正式开放下载!参与首批体验官活动赢好礼!
Adobe Illustrator黑洞文字
大数据系统架构师的论文如何写
面试经典-9-跳跃游戏
[unity3D]什么是预制体(Prefab)?如何制作预制体?如何导出预制体?预制体变体是什么?
如何在HarmonyOS应用中集成App Linking服务
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_46225886/article/details/132788136
