-
【PyQT5教程】-02-UI组件
1.按钮
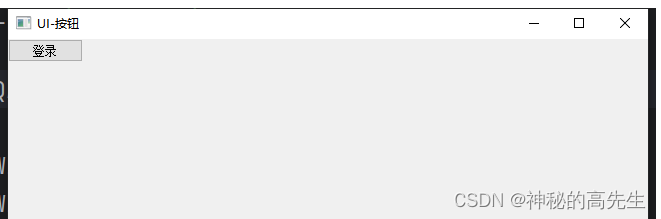
QtWidgets模块提供了多种按钮类,让你可以轻松地创建各种类型的按钮1.1 QPushButton(普通按钮)
QPushButton是PyQt5中最常见的按钮类型之一,用于触发动作或执行操作。通过信号与槽机制,你可以将按钮的点击事件与特定的函数或操作关联起来。import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication,QWidget,QPushButton if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) w1 = QWidget() w1.setWindowTitle("UI-按钮") # 创建一个普通按钮 btn1 = QPushButton("登录") # 将按钮添加到父级中 btn1.setParent(w1) w1.show() app.exec_()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
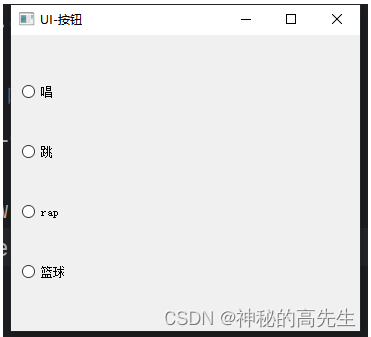
1.2 QRadioButton(单选按钮)
QRadioButton用于在一组选项中进行单选,用户只能选择其中一个选项。import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QRadioButton, QButtonGroup, QVBoxLayout if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) w1 = QWidget() w1.setWindowTitle("UI-按钮") # 1. 创建一个布局容器 layout = QVBoxLayout() # 2. 创建一个按钮组(单选时使用) radioBtnGroup = QButtonGroup() # 3. 创建4个单选按钮 btn1 = QRadioButton("唱") btn2 = QRadioButton("跳") btn3 = QRadioButton("rap") btn4 = QRadioButton("篮球") # 4. 将4个按钮添加到按钮组中 radioBtnGroup.addButton(btn1) radioBtnGroup.addButton(btn2) radioBtnGroup.addButton(btn3) radioBtnGroup.addButton(btn4) # 5. 将每个按钮添加到布局容器中 layout.addWidget(btn1) layout.addWidget(btn2) layout.addWidget(btn3) layout.addWidget(btn4) # 6. 窗口组件设置画布 w1.setLayout(layout) w1.show() app.exec_()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
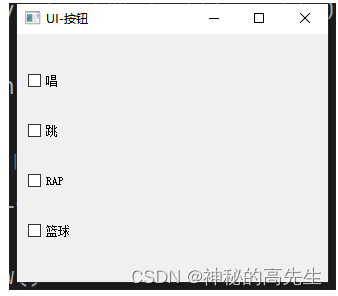
1.3 QCheckBox(复选框)
QCheckBox用于在多个选项中进行多选,用户可以选择多个选项import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QButtonGroup, QVBoxLayout, QCheckBox if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) w1 = QWidget() w1.setWindowTitle("UI-按钮") btnNames = ["唱","跳","RAP","篮球"] btnObjs = [] # 1. 创建一个布局容器 layout = QVBoxLayout() for bt_name in btnNames: # 2. 创建4个多选按钮 temp_btn = QCheckBox(bt_name) # 3. 将每个按钮添加到布局容器中 layout.addWidget(temp_btn) btnObjs.append(temp_btn) # 4. 窗口组件设置画布 w1.setLayout(layout) w1.show() app.exec_()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
注意:多选框不要使用按钮组对象,否则就变为多选框的单选效果
1.4 按钮的事件机制
在pyqt中,事件的调用过程是:
1.定义按钮或元素
2.通过事件名称.connect绑定事件
所以,我们需要定义事件的回调方法,注意,事件回调方法机制就保证事件内容是要返回回调可调用对象,建议在类中定义
1.4.1 用类的方式定义函数
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QButtonGroup, QVBoxLayout, QCheckBox, QPushButton class MyQtWindow(): def __init__(self): self.__initUI() def __initUI(self): app = QApplication(sys.argv) w1 = QWidget() w1.setWindowTitle("UI-按钮") # 创建一个普通按钮 btn1 = QPushButton("登录") # 绑定事件,单点击的时候调用say方法 btn1.clicked.connect(self.say) # 将按钮添加到父级中 btn1.setParent(w1) w1.show() app.exec_() def say(self): print(f"你好") if __name__ == '__main__': window = MyQtWindow()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
1.4.2 回调函数中传递参数
1.使用lambda表达式实现
btn1.clicked.connect(lambda x: self.say("123")) ... def say(self,arg): print(f"你好:{arg}")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
在这个例子中,
lambda函数将创建一个新的函数,该函数接受一个参数x,然后将这个参数和你的参数一起传递给say函数。2.定义辅助函数实现
btn1.clicked.connect(self.fuzhu_say) ... # 辅助函数 def fuzhu_say(self): self.say("参数") def say(self,arg): print(f"你好:{arg}")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
辅助函数传参需要在辅助函数中实现,如果你需要传递关键字参数,那么使用辅助函数可能是更好的选择
1.5 控制元素的位置和大小
对应元素使用:setGeometry(p_x,p_y,w,h) 函数
# 创建一个普通按钮 btn1 = QPushButton("登录") btn1.setGeometry(300,300,300,50)- 1
- 2
- 3
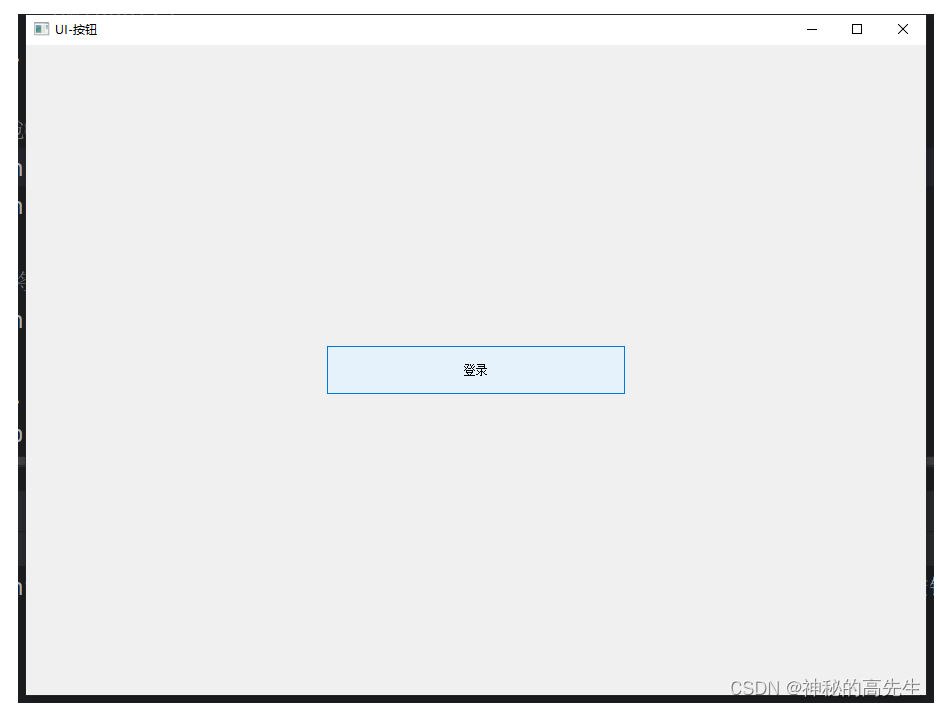
btn1.setGeometry(300,300,300,50)是一个在编程中设置图形界面元素(例如按钮)的位置和大小的语句。具体来说,这个语句的含义如下:btn1是一个按钮对象的引用。setGeometry是一个方法,用于设置按钮的大小和位置。(300,300,300,50)是一个四个数值的元组,分别表示按钮的左边界的x坐标、上边界的y坐标、宽度和高度。
所以,
btn1.setGeometry(300,300,300,50)的意思就是设置btn1这个按钮在界面上的位置为 (300,300),也就是将其左上角移动到屏幕的 (300,300) 位置,并且将其宽度设为300像素,高度设为50像素。1.6 设置单选或多选选中或取消选中
self.male_radio.setChecked(True) # 设置选中 self.female_radio.setChecked(False) # 设置取消选中- 1
- 2
2.文字
2.1 基础文字-QLabel
用于显示文本标签,不支持用户输入。
# 创建一个标题文字 q_label = QLabel("姓名", w)- 1
- 2
2.2 单行文本输入-QLineEdit
用于收集用户输入的单行文本,不支持多行文本。
q_label = QLineEdit("姓名", w)- 1
2.3 多行文本显示-QTextBrowser
用于显示多行文本,支持富文本、HTML等格式,但不支持用户编辑。
q_label = QTextBrowser(w) q_label.append("Hello World")- 1
- 2

2.4 多行文本编辑器-QTextEdit
用于收集用户输入的多行文本,支持富文本、HTML等格式,同时也支持用户编辑。
q_label = QTextEdit(w) q_label.append("Hello World")- 1
- 2

2.5 获取输入框值
(1) 单行文本输入框获取值
name = self.name_input.text()- 1
(2) 多行文本输入框获取值
intro = self.intro_input.toPlainText()- 1
2.6 清空输入框值
(1)单行文本输入框清空值
self.name_input.clear()- 1
(2)多行文本输入框清空值
self.intro_input.clear()- 1
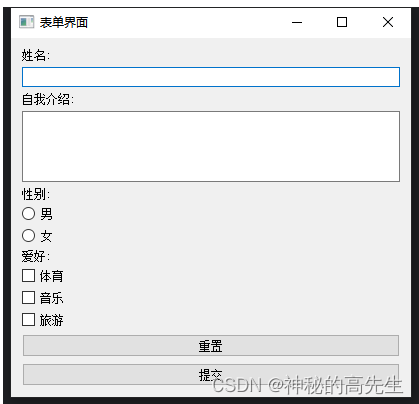
3. 表单综合案例
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QLabel, QLineEdit, QTextEdit, QVBoxLayout, QHBoxLayout, QRadioButton, QCheckBox, QPushButton class FormApp(QWidget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.init_ui() def init_ui(self): self.setWindowTitle('表单界面') self.setGeometry(100, 100, 400, 300) self.name_label = QLabel('姓名:') self.name_input = QLineEdit() self.intro_label = QLabel('自我介绍:') self.intro_input = QTextEdit() self.gender_label = QLabel('性别:') self.male_radio = QRadioButton('男') self.female_radio = QRadioButton('女') self.hobby_label = QLabel('爱好:') self.sports_checkbox = QCheckBox('体育') self.music_checkbox = QCheckBox('音乐') self.travel_checkbox = QCheckBox('旅游') self.reset_button = QPushButton('重置') self.submit_button = QPushButton('提交') self.reset_button.clicked.connect(self.reset_form) self.submit_button.clicked.connect(self.submit_form) layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(self.name_label) layout.addWidget(self.name_input) layout.addWidget(self.intro_label) layout.addWidget(self.intro_input) layout.addWidget(self.gender_label) layout.addWidget(self.male_radio) layout.addWidget(self.female_radio) layout.addWidget(self.hobby_label) layout.addWidget(self.sports_checkbox) layout.addWidget(self.music_checkbox) layout.addWidget(self.travel_checkbox) layout.addWidget(self.reset_button) layout.addWidget(self.submit_button) self.setLayout(layout) def reset_form(self): self.name_input.clear() self.intro_input.clear() self.male_radio.setChecked(True) self.female_radio.setChecked(False) self.sports_checkbox.setChecked(False) self.music_checkbox.setChecked(False) self.travel_checkbox.setChecked(False) def submit_form(self): name = self.name_input.text() intro = self.intro_input.toPlainText() gender = '男' if self.male_radio.isChecked() else '女' hobbies = [] if self.sports_checkbox.isChecked(): hobbies.append('体育') if self.music_checkbox.isChecked(): hobbies.append('音乐') if self.travel_checkbox.isChecked(): hobbies.append('旅游') print('姓名:', name) print('自我介绍:', intro) print('性别:', gender) print('爱好:', ', '.join(hobbies)) if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) form = FormApp() form.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
4.下拉列表
下拉列表(ComboBox)是一种常见的用户界面元素,它允许用户从预定义的选项列表中选择一个值。下拉列表通常用于提供选择,而不是自由文本输入。
self.label = QLabel('选择您的喜好:') self.combo_box = QComboBox() self.combo_box.addItem('体育') self.combo_box.addItem('音乐') self.combo_box.addItem('旅游')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

4.1 下拉获取值
selected_value = self.comboBox.currentText() # 获取当前选中的文本值 print("Selected Value:", selected_value)- 1
- 2
4.2 下拉清空值
self.comboBox.clear() # 清空下拉框中的所有选项- 1
4.3 下拉框选中值
通过下拉索引值选中(从0开始计数)
default_index = 2 # 设置默认选中的索引(从0开始计数) self.comboBox.setCurrentIndex(default_index)- 1
- 2
通过下拉框值选中
default_text = 'Item 2' # 设置默认选中的文本 self.comboBox.setCurrentText(default_text)- 1
- 2
4.4 下拉框添加元素
items = ['Item 1', 'Item 2', 'Item 3', 'Item 4'] self.comboBox.addItems(items)- 1
- 2
5.滑块
在 PyQt5 中,滑块(QSlider)是用于在一定范围内选择数值的界面元素。它允许用户通过滑动滑块来选择一个值。
self.slider = QSlider() # 默认是水平滑块 self.slider.setMinimum(0) # 设置最小值 self.slider.setMaximum(100) # 设置最大值 self.slider.setValue(50) # 设置默认值 self.slider.setTickPosition(QSlider.TicksBelow) # 设置刻度显示在滑块下方 self.slider.setTickInterval(10) # 设置刻度间隔- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

完整demo
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QSlider, QLabel, QVBoxLayout, QWidget class SliderExample(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.setWindowTitle('Slider Example') self.setGeometry(100, 100, 300, 200) layout = QVBoxLayout() self.slider = QSlider() # 默认是水平滑块 self.slider.setMinimum(0) # 设置最小值 self.slider.setMaximum(100) # 设置最大值 self.slider.setValue(50) # 设置默认值 self.slider.setTickPosition(QSlider.TicksBelow) # 设置刻度显示在滑块下方 self.slider.setTickInterval(10) # 设置刻度间隔 self.valueLabel = QLabel(f"Value: {self.slider.value()}") # 显示当前值的标签 layout.addWidget(self.slider) layout.addWidget(self.valueLabel) self.resetButton = QPushButton('Reset') self.resetButton.clicked.connect(self.resetSlider) layout.addWidget(self.resetButton) self.central_widget = QWidget() self.central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(self.central_widget) self.slider.valueChanged.connect(self.updateValueLabel) # 连接滑块值变化的信号与槽函数 def updateValueLabel(self, value): self.valueLabel.setText(f"Value: {value}") def resetSlider(self): self.slider.setValue(50) # 将滑块值重置为默认值 if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = SliderExample() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
5.1 获取值
self.slider.value()- 1
5.2 重置与设置
self.slider.setValue(50) # 将滑块值重置为默认值- 1
5.3 值变化回调更新
self.slider.valueChanged.connect(self.updateValueLabel) # 连接滑块值变化的信号与槽函数 def updateValueLabel(self, value): self.valueLabel.setText(f"Value: {value}")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
6.进度条
进度条(QProgressBar)是一种用于表示进度或完成度的界面元素。在 PyQt5 中,你可以使用进度条来显示操作的进度,例如文件下载、任务执行等
self.progressBar = QProgressBar() # 创建一个进度条 self.progressBar.setMinimum(0) # 设置最小值:0 self.progressBar.setMaximum(100) # 设置最大值 100 self.progressBar.setValue(0) # 设置初始值 0- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
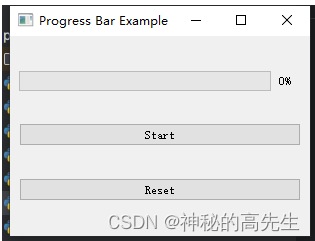
完整demo
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QProgressBar, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout, QWidget class ProgressBarExample(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.setWindowTitle('Progress Bar Example') self.setGeometry(100, 100, 300, 200) layout = QVBoxLayout() self.progressBar = QProgressBar() # 创建一个进度条 self.progressBar.setMinimum(0) # 设置最小值:0 self.progressBar.setMaximum(100) # 设置最大值 100 self.progressBar.setValue(0) # 设置初始值 0 layout.addWidget(self.progressBar) self.startButton = QPushButton('Start') self.startButton.clicked.connect(self.startProgress) layout.addWidget(self.startButton) self.resetButton = QPushButton('Reset') self.resetButton.clicked.connect(self.resetProgress) layout.addWidget(self.resetButton) self.central_widget = QWidget() self.central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(self.central_widget) def startProgress(self): self.progressBar.setValue(0) # 开始时将进度条值重置为0 for i in range(101): self.progressBar.setValue(i) QApplication.processEvents() # 实时更新界面 if i == 100: self.progressBar.setValue(100) # 完成后将进度条值重置为0 def resetProgress(self): self.progressBar.setValue(0) # 将进度条值重置为0 if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = ProgressBarExample() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
6.1 设置值且更新
self.progressBar.setValue(60) QApplication.processEvents() # 实时更新界面- 1
- 2
6.2 获取值
current_value = self.progressBar.value() print("Current Value:", current_value)- 1
- 2
7. 列表框
在 PyQt5 中,列表框(QListWidget)是用于显示一系列项目(项)的界面元素。每个项目可以包含文本、图像等内容。
self.listWidget = QListWidget() # 创建列表项 items = ['Item 1', 'Item 2', 'Item 3', 'Item 4'] for item_text in items: list_item = QListWidgetItem(item_text) # 创建一个列表项目 self.listWidget.addItem(list_item) # 添加到列表中- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

完整案例:
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QListWidget, QListWidgetItem, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout, QWidget class ListWidgetExample(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.setWindowTitle('List Widget Example') self.setGeometry(100, 100, 300, 200) layout = QVBoxLayout() self.listWidget = QListWidget() # 创建列表项 items = ['Item 1', 'Item 2', 'Item 3', 'Item 4'] for item_text in items: list_item = QListWidgetItem(item_text) # 创建一个列表项目 self.listWidget.addItem(list_item) # 添加到列表中 layout.addWidget(self.listWidget) self.addButton = QPushButton('Add Item') self.addButton.clicked.connect(self.addItem) layout.addWidget(self.addButton) self.removeButton = QPushButton('Remove Item') self.removeButton.clicked.connect(self.removeItem) layout.addWidget(self.removeButton) self.central_widget = QWidget() self.central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(self.central_widget) def addItem(self): new_item_text = 'New Item' new_item = QListWidgetItem(new_item_text) self.listWidget.addItem(new_item) def removeItem(self): selected_items = self.listWidget.selectedItems() for item in selected_items: self.listWidget.takeItem(self.listWidget.row(item)) if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = ListWidgetExample() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
7.1 将列表项目添加到指定列表中
new_item_text = 'New Item' new_item = QListWidgetItem(new_item_text) self.listWidget.addItem(new_item)- 1
- 2
- 3
7.2 移除指定项目
item_to_remove = self.listWidget.item(2) # 获取第3个项目(索引为2) self.listWidget.takeItem(self.listWidget.row(item_to_remove))- 1
- 2
7.3 设置默认选中
default_row = 1 # 设置默认选中第2个项目(索引为1) self.listWidget.setCurrentRow(default_row)- 1
- 2
7.4 清空选中
self.listWidget.clearSelection()- 1
8. 表格
在 PyQt5 中,表格(QTableWidget)是一个用于显示二维表格数据的界面元素。它类似于电子表格,可以在单元格中显示文本、图像等内容。
self.tableWidget = QTableWidget(4, 3) # 创建一个4行3列的表格 # 设置3个表头 self.tableWidget.setHorizontalHeaderLabels(['Column 1', 'Column 2', 'Column 3'])- 1
- 2
- 3
for row in range(4): for col in range(3): item = QTableWidgetItem(data[row][col]) # 创建一个表格元素 data[行][列] self.tableWidget.setItem(row, col, item) # 添加元素- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

完整案例:
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QTableWidget, QTableWidgetItem, QVBoxLayout, QWidget class TableWidgetExample(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.setWindowTitle('Table Widget Example') self.setGeometry(100, 100, 400, 300) layout = QVBoxLayout() self.tableWidget = QTableWidget(4, 3) # 创建一个4行3列的表格 # 设置3个表头 self.tableWidget.setHorizontalHeaderLabels(['Column 1', 'Column 2', 'Column 3']) self.populateTable() layout.addWidget(self.tableWidget) self.central_widget = QWidget() self.central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(self.central_widget) def populateTable(self): data = [ ['Row 1, Col 1', 'Row 1, Col 2', 'Row 1, Col 3'], ['Row 2, Col 1', 'Row 2, Col 2', 'Row 2, Col 3'], ['Row 3, Col 1', 'Row 3, Col 2', 'Row 3, Col 3'], ['Row 4, Col 1', 'Row 4, Col 2', 'Row 4, Col 3'] ] for row in range(4): for col in range(3): item = QTableWidgetItem(data[row][col]) # 创建一个表格元素 data[行][列] self.tableWidget.setItem(row, col, item) # 添加元素 if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = TableWidgetExample() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
8.1添加行
使用
insertRow(row)方法可以在指定位置插入一行。pythonCopy code tableWidget.insertRow(row_index)- 1
- 2
8.2添加列
使用
insertColumn(column)方法可以在指定位置插入一列。pythonCopy code tableWidget.insertColumn(column_index)- 1
- 2
8.3 设置单元格内容
使用
setItem(row, column, item)方法可以将一个 QTableWidgetItem 对象放置到指定行和列的单元格中。pythonCopy codeitem = QTableWidgetItem("Cell Value") tableWidget.setItem(row_index, column_index, item)- 1
- 2
8.4 获取单元格内容
使用
item(row, column)方法可以获取指定行和列的单元格中的 QTableWidgetItem 对象。pythonCopy codeitem = tableWidget.item(row_index, column_index) cell_value = item.text() if item is not None else ""- 1
- 2
8.6 合并单元格
使用
setSpan(row, column, row_span, column_span)方法可以合并指定范围内的单元格。pythonCopy code tableWidget.setSpan(row_index, column_index, row_span, column_span)- 1
- 2
8.7 清除内容
使用
clear()方法可以清除表格中的所有内容。pythonCopy code tableWidget.clear()- 1
- 2
8.8 移除行和列
使用
removeRow(row)和removeColumn(column)方法可以移除指定行和列。pythonCopy codetableWidget.removeRow(row_index) tableWidget.removeColumn(column_index)- 1
- 2
8.9 设置单元格对齐
使用
item(row, column).setTextAlignment(alignment)方法可以设置指定单元格的文本对齐方式。pythonCopy codeitem = QTableWidgetItem("Aligned Text") item.setTextAlignment(Qt.AlignCenter) # 或者 Qt.AlignLeft, Qt.AlignRight, Qt.AlignTop, Qt.AlignBottom 等 tableWidget.setItem(row_index, column_index, item)- 1
- 2
- 3
8.10 综合案例-带操作列的表格
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QTableWidget, QTableWidgetItem, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout, QWidget class TableWithButtonsExample(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.setWindowTitle('Table with Buttons Example') self.setGeometry(100, 100, 600, 400) layout = QVBoxLayout() self.tableWidget = QTableWidget(4, 4) # 创建一个4行4列的表格 self.tableWidget.setHorizontalHeaderLabels(['Select', 'Name', 'Age', 'Actions']) self.populateTable() layout.addWidget(self.tableWidget) self.central_widget = QWidget() self.central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(self.central_widget) def populateTable(self): data = [ {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 25}, {'name': 'Bob', 'age': 30}, {'name': 'Carol', 'age': 28}, {'name': 'David', 'age': 22} ] for row, item_data in enumerate(data): select_item = QTableWidgetItem() select_item.setFlags(select_item.flags() | Qt.ItemIsUserCheckable) select_item.setCheckState(Qt.Unchecked) self.tableWidget.setItem(row, 0, select_item) name_item = QTableWidgetItem(item_data['name']) self.tableWidget.setItem(row, 1, name_item) age_item = QTableWidgetItem(str(item_data['age'])) self.tableWidget.setItem(row, 2, age_item) view_button = QPushButton('View') edit_button = QPushButton('Edit') delete_button = QPushButton('Delete') button_container = QWidget() button_layout = QHBoxLayout() button_layout.addWidget(view_button) button_layout.addWidget(edit_button) button_layout.addWidget(delete_button) button_container.setLayout(button_layout) self.tableWidget.setCellWidget(row, 3, button_container) if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = TableWithButtonsExample() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65

9. 时间选择器
在 PyQt5 中,可以使用 QDateTimeEdit 组件来实现日期时间选择器。
self.dateTimeEdit = QDateTimeEdit() # 创建一个时间选择器 self.dateTimeEdit.setDateTime(QDateTime.currentDateTime()) # 设置默认值为当前日期时间- 1
- 2
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QDateTimeEdit, QVBoxLayout, QPushButton, QLabel, QWidget from PyQt5.QtCore import QDateTime class DateTimePickerExample(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.setWindowTitle('Date Time Picker Example') self.setGeometry(100, 100, 300, 200) layout = QVBoxLayout() self.dateTimeEdit = QDateTimeEdit() # 创建一个时间选择器 self.dateTimeEdit.setDateTime(QDateTime.currentDateTime()) # 设置默认值为当前日期时间 layout.addWidget(self.dateTimeEdit) self.getValueButton = QPushButton('Get Value') self.getValueButton.clicked.connect(self.getValue) layout.addWidget(self.getValueButton) self.clearValueButton = QPushButton('Clear Value') self.clearValueButton.clicked.connect(self.clearValue) layout.addWidget(self.clearValueButton) self.valueLabel = QLabel() layout.addWidget(self.valueLabel) self.central_widget = QWidget() self.central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(self.central_widget) def getValue(self): selected_datetime = self.dateTimeEdit.dateTime() formatted_datetime = selected_datetime.toString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") self.valueLabel.setText(f"Selected Value: {formatted_datetime}") def clearValue(self): self.dateTimeEdit.clear() # 清空日期时间选择器的值 self.valueLabel.setText("Selected Value: Cleared") if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = DateTimePickerExample() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
9.1 设置时间
self.dateTimeEdit.setDateTime(QDateTime.currentDateTime()) # 设置默认值为当前日期时间- 1
使用字符串日期设置:
time_str = "2023-08-21 15:30:00" datetime_value = QDateTime.fromString(time_str, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") self.dateTimeEdit.setDateTime(datetime_value)- 1
- 2
- 3
9.2 获取时间
selected_datetime = self.dateTimeEdit.dateTime() formatted_datetime = selected_datetime.toString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")- 1
- 2
10. 文件选择器
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QPushButton, QFileDialog class FileDialogExample(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.setGeometry(100, 100, 300, 200) self.setWindowTitle('File Dialog Example') self.button = QPushButton('Open File Dialog', self) self.button.setGeometry(100, 100, 150, 30) self.button.clicked.connect(self.showFileDialog) def showFileDialog(self): options = QFileDialog.Options() options |= QFileDialog.ReadOnly # 可选:设置文件选择框为只读模式 file_path, _ = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, "Open File", "", "All Files (*);;Text Files (*.txt)", options=options) if file_path: print("Selected file:", file_path) if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) ex = FileDialogExample() ex.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
点击按钮会弹出一个文件选择框,允许你选择文件。你可以根据自己的需求进行修改和扩展。在
getOpenFileName方法中,你可以通过调整第四个参数的字符串来指定不同的文件过滤器。这个参数使用了一种类似于 “文件类型描述 (*扩展名);;文件类型描述 (*扩展名)” 的格式。11. 显示图片
在 PyQt5 中,你可以使用
QLabel来显示图片。要显示图片,你需要使用QPixmap创建一个图像对象,然后将它设置给QLabel的setPixmap方法。import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QLabel, QVBoxLayout, QWidget from PyQt5.QtGui import QPixmap class ImageDisplayExample(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.setGeometry(100, 100, 400, 300) self.setWindowTitle('Image Display Example') central_widget = QWidget(self) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) layout = QVBoxLayout() central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.image_label = QLabel(self) layout.addWidget(self.image_label) self.loadImage() def loadImage(self): pixmap = QPixmap('path_to_your_image.jpg') # 替换为你的图片路径 self.image_label.setPixmap(pixmap) self.image_label.setAlignment(Qt.AlignCenter) if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) ex = ImageDisplayExample() ex.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
在这个案例中,你需要将
'path_to_your_image.jpg'替换为你自己的图片文件的路径。QPixmap类用于加载图片,而QLabel则用于显示图像。通过调用setPixmap方法,你可以将加载的图像设置给QLabel,然后使用setAlignment方法来设置图像在QLabel中的对齐方式。
12. 工具栏
使用
QMenu和QToolBar来创建菜单和工具栏。菜单用于创建应用程序的导航菜单,而工具栏则提供了快速访问常用功能的方式import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QAction, QMenu, QToolBar class MenuAndToolbarExample(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600) self.setWindowTitle('Menu and Toolbar Example') self.createMenu() self.createToolbar() def createMenu(self): menubar = self.menuBar() file_menu = menubar.addMenu('File') edit_menu = menubar.addMenu('Edit') new_action = QAction('New', self) new_action.triggered.connect(self.newFile) file_menu.addAction(new_action) open_action = QAction('Open', self) open_action.triggered.connect(self.openFile) file_menu.addAction(open_action) exit_action = QAction('Exit', self) exit_action.triggered.connect(self.close) file_menu.addAction(exit_action) undo_action = QAction('Undo', self) edit_menu.addAction(undo_action) redo_action = QAction('Redo', self) edit_menu.addAction(redo_action) def createToolbar(self): toolbar = QToolBar(self) self.addToolBar(toolbar) new_action = QAction('New', self) new_action.triggered.connect(self.newFile) toolbar.addAction(new_action) open_action = QAction('Open', self) open_action.triggered.connect(self.openFile) toolbar.addAction(open_action) save_action = QAction('Save', self) toolbar.addAction(save_action) def newFile(self): print("New File") def openFile(self): print("Open File") if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) ex = MenuAndToolbarExample() ex.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67

我们创建了一个具有简单菜单和工具栏的窗口。
QMenu用于创建菜单,QToolBar用于创建工具栏。我们创建了一个 “File” 菜单和一个 “Edit” 菜单,每个菜单都有相应的操作。在工具栏中,我们放置了 “New” 和 “Open” 功能的按钮。当点击菜单项或工具栏按钮时,与之相关联的槽函数将被触发。在这个案例中,点击 “New” 或 “Open” 菜单项或工具栏按钮会分别调用
newFile和openFile方法,这里我们只是打印了一些文本,但你可以在这些方法中执行自己的操作。13. 隐藏窗口栏和设置窗口图标
13.1 隐藏窗口栏
self.setWindowFlags(Qt.FramelessWindowHint) # 设置窗口标志位为无边框- 1

13.2 设置窗口图标
要在 PyQt5 中设置窗口的小图标(窗口图标),你可以使用
QIcon类来加载图标文件,并将其设置给窗口对象的setWindowIcon方法from PyQt5.QtGui import QIcon icon = QIcon('path_to_your_icon.png') # 替换为你的图标文件路径 self.setWindowIcon(icon)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

14. 网页视图
首先第一步需要安装PyQtWebEngine模块
pip install PyQtWebEngine- 1
编写代码
import sys from PyQt5.QtCore import QUrl from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QVBoxLayout, QWidget from PyQt5.QtWebEngineWidgets import QWebEngineView class WebViewExample(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.init_ui() def init_ui(self): self.setWindowTitle('网页视图示例') self.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600) self.webview = QWebEngineView() self.webview.setUrl(QUrl('https://www.baidu.com')) # Load the OpenAI website layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(self.webview) central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) example = WebViewExample() example.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
15.音频和视频播放器
QMediaPlayer来实现音频和视频播放功能。QMediaPlayer是一个多媒体播放器,它可以用来播放音频和视频文件。15.1 音乐播放器
import sys from PyQt5.QtCore import QUrl from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout, QWidget from PyQt5.QtMultimedia import QMediaPlayer, QMediaContent class AudioPlayerExample(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.init_ui() def init_ui(self): self.setWindowTitle('音频播放器示例') self.setGeometry(100, 100, 300, 100) self.media_player = QMediaPlayer() self.media_player.setMedia(QMediaContent(QUrl.fromLocalFile('static/msc.mp3'))) # Replace with your audio file path self.play_button = QPushButton('播放') self.play_button.clicked.connect(self.play_audio) self.stop_button = QPushButton('暂停') self.stop_button.clicked.connect(self.stop_audio) layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(self.play_button) layout.addWidget(self.stop_button) central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) def play_audio(self): self.media_player.play() def stop_audio(self): self.media_player.pause() if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) example = AudioPlayerExample() example.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
16. 弹窗
16.1 消息框
QMessageBox:用于显示各种类型的消息框,如信息、警告、错误等。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QPushButton, QMessageBox class MyWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() button = QPushButton("Show Message Box", self) button.clicked.connect(self.show_message_box) def show_message_box(self): QMessageBox.information(self, "Information", "This is an information message.") app = QApplication([]) window = MyWindow() window.show() app.exec_()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
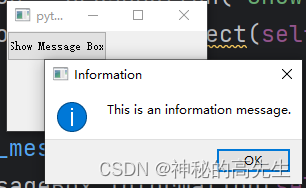
16.2 操作对话框
QInputDialog:用于获取用户输入的对话框。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QPushButton, QInputDialog class MyWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() button = QPushButton("Get Input", self) button.clicked.connect(self.get_input) def get_input(self): text, ok = QInputDialog.getText(self, "Input Dialog", "Enter your name:") if ok: print(f"Entered name: {text}") app = QApplication([]) window = MyWindow() window.show() app.exec_()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
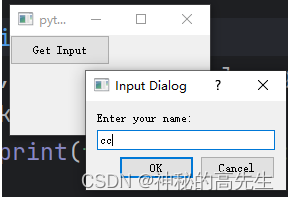
16.3 文件对话框
QFileDialog:用于打开文件对话框或保存文件对话框。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QPushButton, QFileDialog class MyWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() button = QPushButton("Open File", self) button.clicked.connect(self.open_file) def open_file(self): options = QFileDialog.Options() options |= QFileDialog.ReadOnly file_name, _ = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, "Open File", "", "All Files (*)", options=options) if file_name: print(f"Selected file: {file_name}") app = QApplication([]) window = MyWindow() window.show() app.exec_()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
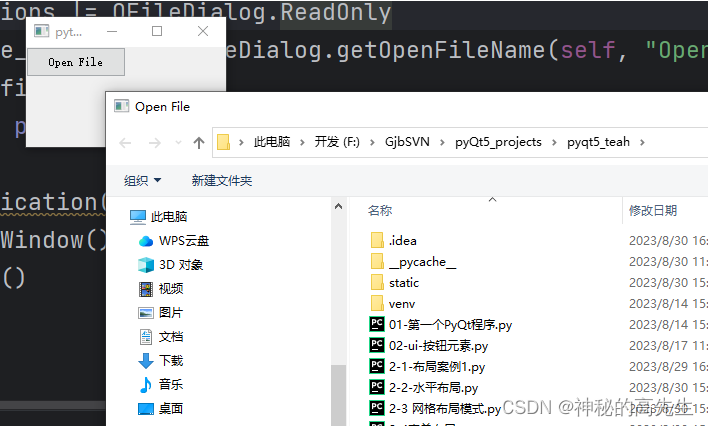
代码解释:
options |= QFileDialog.ReadOnly- 1
这个代码的意思是将
options变量与QFileDialog.ReadOnly进行按位或操作,并将结果赋值给options变量。QFileDialog.ReadOnly是一个常量,它表示一个标志,用于在QFileDialog中设置只读选项。当你按位或操作符|将这个标志与其他选项组合时,你可以在QFileDialog中设置多个选项。例如,假设你有以下代码:
options = QFileDialog.Options() options |= QFileDialog.ReadOnly options |= QFileDialog.DontUseNativeDialog- 1
- 2
- 3
这里,我们首先创建了一个空的
QFileDialog.Options对象。然后,通过options |= QFileDialog.ReadOnly,我们将只读选项添加到了options中。接着,通过options |= QFileDialog.DontUseNativeDialog,我们又将不使用原生对话框的选项添加到了options中。最终,
options变量会包含这两个选项的组合,你可以将其传递给QFileDialog的相关方法,以便按照所选的选项来打开文件对话框。17. 打包方法
17.1 环境准备
首先安装pyinstaller,使用安装命令:pip install pyinstaller;使用清华大学镜像源加快速度
pip install pyinstaller -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple- 1
17.2 进行打包
我们写的python脚本是不能脱离python解释器单独运行的,所以在打包的时候,至少会将python解释器和脚本一起打包,同样,为了打包的exe能正常运行,会把我们所有安装的第三方包一并打包到exe。
即使我们的项目只使用的一个requests包,但是可能我们还安装了其他n个包,但是他不管,因为包和包只有依赖关系的。比如我们只装了一个requests包,但是requests包会顺带装了一些其他依赖的小包,所以为了安全,只能将所有第三方包+python解释器一起打包。
1. 单文件打包
去除控制台打包
pyinstaller -F -w 文件地址- 1
带控制台打包
pyinstaller -F 文件地址- 1
打包指定exe 图标打包
pyinstaller -F -i 图标 主文件- 1
2. 多文件打包
pyinstaller [主文件] -p [其他文件1] -p [其他文件2] --hidden-import [自建模块1] --hidden-import [自建模块2]- 1
-
相关阅读:
Android样式和主题背景
个人博客系统
行情黯淡的新财季,中概股的确定性在哪里?
不可不知的USB2.0/USB3.0/HDMI静电防护方案
STL常用容器——String容器的使用
中集集团全球港航人工智能高科技独角兽中集飞瞳贯彻国家智慧港口战略,全球最先进港航AI核心技术和工业级产品超一流智慧港口解决方案
SpringBoot 03 Yaml语法、松散绑定和JSR303数据校验
基于springboot的健身管理系统
初识微服务技术栈
汇编语言(6)使用JCC指令构造分支与循环
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/gjb760662328/article/details/132765000