-
[LeetCode]栈,队列相关题目(C语言实现)
LeetCode20. 有效的括号
题目
给定一个只包括
'(',')','{','}','[',']'的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。要求
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。思路
用栈实现- 如果是左括号, 直接将左括号入栈
- 如果是右括号, 如果此时栈为空, 返回
false; 将栈顶元素弹出栈, 如果栈顶元素不是对应的左括号, 返回false; 如果栈顶元素是对应左括号, 出栈 - 遍历完字符串, 判断此时栈是否为空. 为空返回
true; 不为空返回false
代码实现
#define N 10000 bool isValid(char * s) { char stack[N] = {0,}; //创建栈数组 int top = 0; //top指向栈顶元素的后一个空间 char topVal = 0; //用来存放栈顶元素 while (*s) { //如果是左括号 if (*s == '{' || *s == '(' || *s == '[') { //入栈 stack[top] = *s; top++; } //如果是右括号 else { //如果此时栈为空, 直接返回false if (top == 0) { return false; } topVal = stack[top - 1]; //得到栈顶元素 top--; //栈顶元素出栈 //如果右括号不是其对应的左括号, 直接返回false if ((*s == ']' && topVal != '[') || (*s == ')' && topVal != '(') || (*s == '}' && topVal != '{')) { return false; } } s++; } //如果遍历完字符串, 栈仍为空, 则返回true if (top == 0) return true; else return false; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
LeetCode225. 用队列实现栈
题目
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
要求
实现
MyStack类:void push(int x)将元素 x 压入栈顶。
int pop()移除并返回栈顶元素。
int top()返回栈顶元素。
boolean empty()如果栈是空的,返回true;否则,返回false。思路
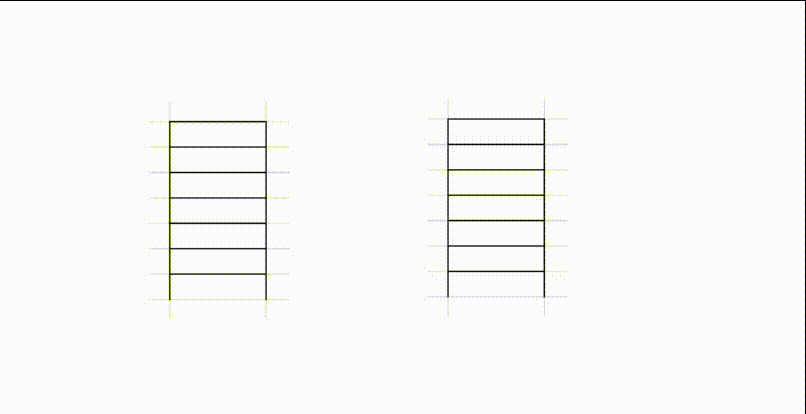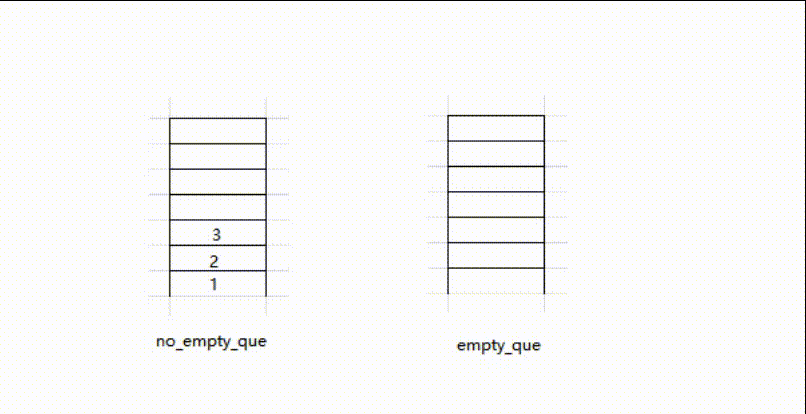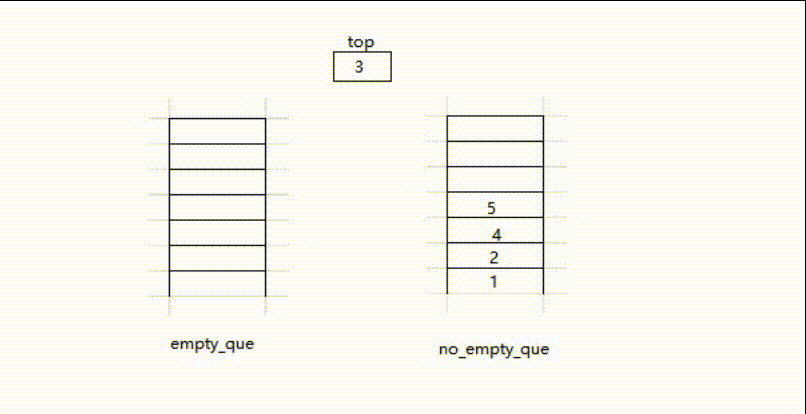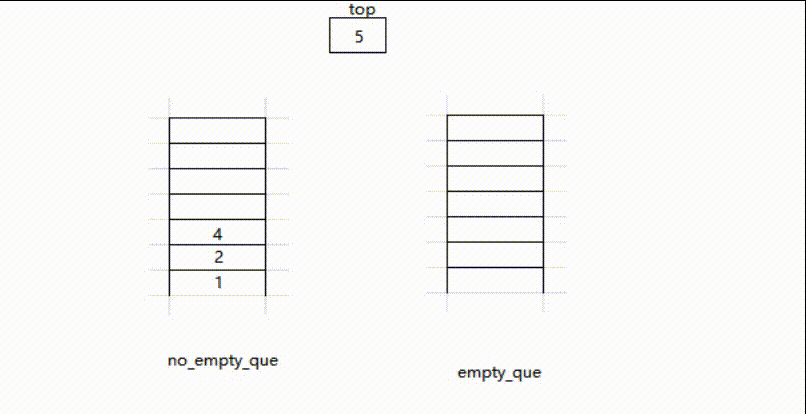
- 使用两个队列,一个队列
no_empty_que存放已经存放的元素,另一个队列empty_que常空 - 当要压栈的时候,将元素压入
no_empty_que - 当要出栈的时候,将
no_empty_que中除队尾元素全部存入empty_que,将队尾元素移出
实例
代码实现
typedef int QDataType; // 链式结构表示队列 typedef struct QListNode { struct QListNode* next; QDataType data; }QNode; // 队列的结构 typedef struct Queue { QNode* front; //指向队列头 QNode* rear; //指向队列尾 int size; //记录队列的元素个数 }Queue; // 初始化队列 void QueueInit(Queue* q) { assert(q); //确保q合法 q->front = q->rear = NULL; //将头和为置为 NULL q->size = 0; } // 判断队列是否为空, 如果为空返回非0, 非空返回0 int QueueEmpty(Queue* q) { assert(q); //确保q合法 if (q->size == 0) { return 1; } else { return 0; } } // 队尾入队列 void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType x) { assert(q); //确保q合法 //创建新结点 QNode* newNode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); newNode->data = x; newNode->next = NULL; //入队列 if (QueueEmpty(q)) { //如果队列为空,直接赋值 q->front = q->rear = newNode; } else { //如果队列不为空,直接尾插 q->rear->next = newNode; q->rear = newNode; } q->size++; } // 队头出队列 void QueuePop(Queue* q) { assert(q); //确保q合法 assert(!QueueEmpty(q)); //确保队列不为空 if (q->size == 1) { //如果只有一个元素,头删的同时还要将尾指针置空 free(q->front); q->front = q->rear = NULL; } else { //如果不止一个元素,则只头删 QNode* nextNode = q->front->next; free(q->front); q->front = nextNode; } q->size--; } // 获取头部元素 QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q) { assert(q); //确保q合法 assert(!QueueEmpty(q)); //确保队列不为空 return q->front->data; } // 获取尾部元素 QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q) { assert(q); //确保q合法 assert(!QueueEmpty(q)); //确保队列不为空 return q->rear->data; } // 获取队列元素个数 int QueueSize(Queue* q) { assert(q); //确保q合法 return q->size; } // 销毁队列 void QueueDestroy(Queue* q) { assert(q); while(!QueueEmpty(q)) { QNode* nextNode = q->front->next; free(q->front); q->front = nextNode; } q->front = q->rear = NULL; q->size = 0; } //用两个队列构成一个栈 typedef struct { Queue queue1; Queue queue2; } MyStack; MyStack* myStackCreate() { MyStack* pst = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack)); QueueInit(&pst->queue1); QueueInit(&pst->queue2); return pst; } void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) { if (!QueueEmpty(&obj->queue1)) { QueuePush(&obj->queue1, x); } else { QueuePush(&obj->queue2, x); } } int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) { Queue* no_empty_que = &obj->queue1; Queue* empty_que = &obj->queue2; if (!QueueEmpty(&obj->queue2)) { no_empty_que = &obj->queue2; empty_que = &obj->queue1; } //弹出有元素的队列直至只剩一个元素 while (QueueSize(no_empty_que) > 1) { QueuePush(empty_que, QueueFront(no_empty_que)); QueuePop(no_empty_que); } int pop = QueueFront(no_empty_que); QueuePop(no_empty_que); return pop; } int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) { if (!QueueEmpty(&obj->queue1)) { return QueueBack(&obj->queue1); } else { return QueueBack(&obj->queue2); } } bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) { return QueueEmpty(&obj->queue1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->queue2); } void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) { QueueInit(&obj->queue1); QueueInit(&obj->queue2); free(obj); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
LeetCode232. 用栈实现队列
题目
你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):OJ链接
要求
实现
MyQueue类:void push(int x)将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
int pop()从队列的开头移除并返回元素
int peek()返回队列开头的元素
boolean empty()如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false思路
- 使用两个栈,一个专门负责压入数据
push_stack,另一个专门负责弹出数据pop_stack - 当push数据,直接将数据压入
push_stack - 当pop数据,如果
pop_stack为空,先将push_stack中的数据压入,pop_stack,再接将pop_stack的栈顶弹出
实例
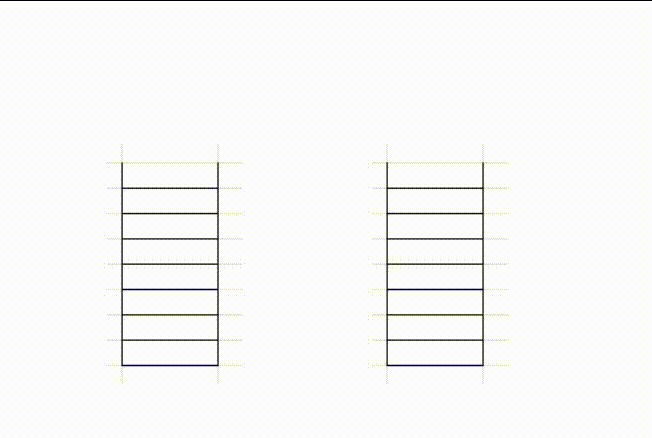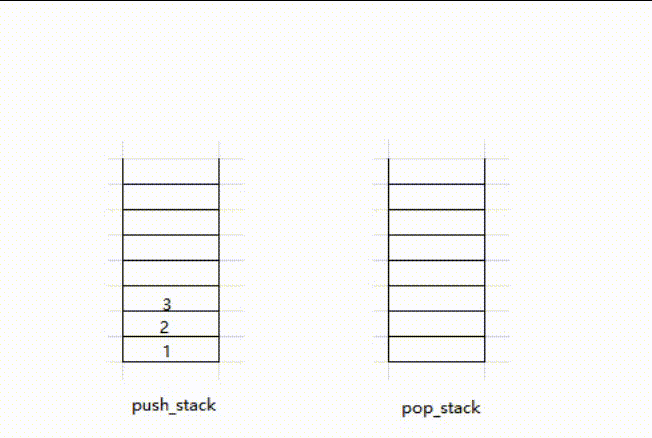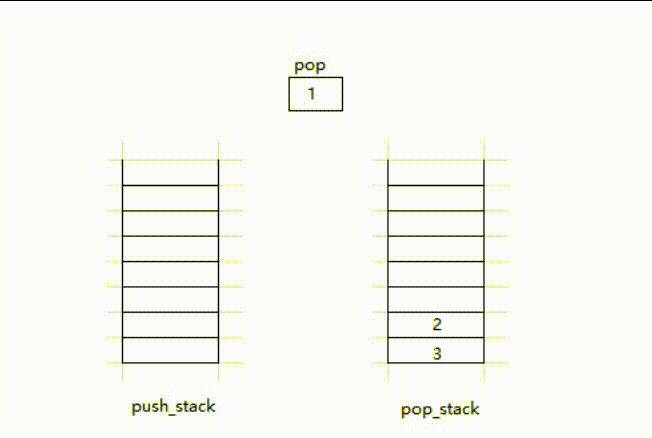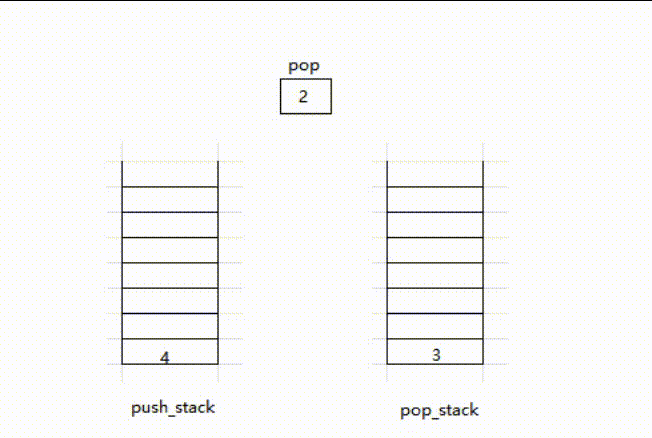
代码实现
typedef int STDataType; typedef struct Stack { STDataType* a; //指向栈空间 int top; //栈顶 int capacity; //容量 }Stack; // 初始化栈 void StackInit(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); ps->a = NULL; ps->top = 0; ps->capacity = 0; } //入栈 void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 //如果容量不够则扩容 if (ps->capacity == ps->top) { int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity; //定义新的容量 STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity); //开辟新的空间 if (tmp == NULL) { perror("malloc error"); exit(-1); } else { ps->a = tmp; ps->capacity = newCapacity; } } //将数据入栈 ps->a[ps->top] = data; ps->top++; } // 出栈 void StackPop(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 assert(!StackEmpty(ps)); //确保栈不为空 ps->top--; } // 检测栈是否为空, 如果为空返回非零结果, 如果不为空返回 0 int StackEmpty(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 if (ps->top > 0) { return 0; } else { return 1; } } // 获取栈顶元素 STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 assert(!StackEmpty(ps)); //确保栈不为空 return ps->a[ps->top - 1]; } // 获取栈中有效元素个数 int StackSize(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 return ps->top; } // 销毁栈 void StackDestroy(Stack* ps) { assert(ps); //确保ps合法 free(ps->a); ps->a = NULL; ps->capacity = 0; ps->top = 0; } typedef struct { Stack push_stack; Stack pop_stack; } MyQueue; MyQueue* myQueueCreate() { MyQueue* que = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue)); StackInit(&que->push_stack); StackInit(&que->pop_stack); return que; } void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) { StackPush(&obj->push_stack, x); } int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) { int pop = myQueuePeek(obj); StackPop(&obj->pop_stack); return pop; } int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) { //如果pop_stack是空的话,将push_stack的所有元素入pop_stack if (StackEmpty(&obj->pop_stack)) { while (!StackEmpty(&obj->push_stack)) { StackPush(&obj->pop_stack, StackTop(&obj->push_stack)); StackPop(&obj->push_stack); } } //如果pop_stack不是空,直接取栈顶元素 int peek = StackTop(&obj->pop_stack); return peek; } bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) { return StackEmpty(&obj->push_stack) && StackEmpty(&obj->pop_stack); } void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) { StackDestroy(&obj->push_stack); StackDestroy(&obj->pop_stack); free(obj); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
LeetCode622. 设计循环队列
题目
设计你的循环队列实现。 循环队列是一种线性数据结构,其操作表现基于 FIFO(先进先出)原则并且队尾被连接在队首之后以形成一个循环。它也被称为“环形缓冲器”。
循环队列的一个好处是我们可以利用这个队列之前用过的空间。在一个普通队列里,一旦一个队列满了,我们就不能插入下一个元素,即使在队列前面仍有空间。但是使用循环队列,我们能使用这些空间去存储新的值。OJ链接
要求
你的实现应该支持如下操作:
MyCircularQueue(k): 构造器,设置队列长度为 k 。
Front: 从队首获取元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
Rear: 获取队尾元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
enQueue(value): 向循环队列插入一个元素。如果成功插入则返回真。
deQueue(): 从循环队列中删除一个元素。如果成功删除则返回真。
isEmpty(): 检查循环队列是否为空。
isFull(): 检查循环队列是否已满。思路
- 为了确保方便判断空和满情况,将循环队列的空间比设定长度加1
- 入队列和出队列相关
front和rear不是简单的加一或减一 rear指向队尾下一个空间,front指向队头元素
代码实现
typedef struct { int* a; //存放队列元素 int front; //指向队头元素 int rear; //指向队尾下一个元素 int k; //循环队列的大小 } MyCircularQueue; MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) { MyCircularQueue* cq = (MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue)); cq->a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (k + 1)); cq->front = cq->rear = 0; cq->k = k; return cq; } bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) { return obj->front == obj->rear; } bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) { return (obj->rear + 1) % (obj->k + 1) == obj->front; } bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) { //如果满了,插入失败 if (myCircularQueueIsFull(obj)) { return false; } //如果不满,进行插入,注意rear的大小 obj->a[obj->rear] = value; obj->rear = (obj->rear + 1) % (obj->k + 1); return true; } bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) { //如果没有元素,删除失败 if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)) { return false; } //直接修改front的值即可 obj->front = (obj->front + 1) % (obj->k + 1); return true; } int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) { if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)) { return -1; } return obj->a[obj->front]; } int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) { if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)) { return -1; } return obj->a[(obj->rear + obj->k) % (obj->k + 1)]; } void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) { free(obj->a); free(obj); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
-
相关阅读:
volatile关键字在并发中有哪些作用?
李炎恢ECMAScript6 / ES6+(二)
大二Web课程设计期末考试——基于HTML+CSS+JavaScript+jQuery电商类化妆品购物商城
plink描述性统计--等位基因频率、缺失值
Linux 常用命令
【一包通刷】晶晨S905L3A/B_完美AI语音线刷包_打开ADB_ROOT权限
图像处理:模糊图像判断
大学生影视主题网页制作 腾龙电影网页设计模板 学生静态网页作业成品 dreamweaver电影HTML网站制作
sip广播10W网络有源吸顶喇叭
Linux 安装配置Nginx
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Kuzuba/article/details/132747314
