大家好!我是sum墨,一个一线的底层码农,平时喜欢研究和思考一些技术相关的问题并整理成文,限于本人水平,如果文章和代码有表述不当之处,还请不吝赐教。
以下是正文!
文章背景
我们最近做了很多项目,有些我们是总负责的,有些是合作的。这些项目涉及的系统各种各样,但基本上没有一家公司会主动去做『开放平台』。这是因为投入产出比较低,项目一旦完成就结束了,而且标书里也没有要求做开放平台。虽然这些项目都是业务系统,没有通用能力好开放的,但在同一个项目中,总是有些东西需要打通,还是需要一种轻量、安全的交互方式。

场景分类
(一)单点登录
单点登录是一种方便的登录方式,它可以应用在各种场景中,比如门户网站和小程序跳转。用户只需要在登录门户网站时输入用户名和密码,就可以轻松访问其他相关子系统,无需反复输入登录信息。这不仅方便了用户,还帮助了IT管理人员更好地管理系统。
以百度为例:

这就是一个典型的单点登录案例,那么我们怎么实现单点登录功能呢?
思路分析
从『系统A门户页』点击导航进入『系统B』,用户信息是怎么同步的呢?把信息放在跳转链接上传给系统A肯定不合适,这相当于泄漏了用户信息,方案不可行。我们的做法是:
- 用户输入账号密码进入系统A的门户页;
- 用户点击跳转系统B导航后,系统A会生成一个当前用户唯一标识,一般是一串唯一的字符串,我们将它成为临时授权码,取名为userToken;
- 这个标识会当成一个参数拼接在系统B的跳转链接上,比如:https://systemB.com/index?userToken=xxxx;
- 系统A提供一个根据userToken查询当前用户的接口,比如:https://systemA.com/queryUserByToken?userToken=xxx;
- 进入系统B的首页之后,系统B调用系统A的queryUserByToken接口获取信息。
为了安全起见,这个userToken一般都是有时限性的,过了1个小时就不能用了,而且只能用一次,用完就废弃掉。
我画个时序图解释一下这个逻辑

(二)接口调用
接口调用方式一般有两种:http接口和rpc接口。
1. http接口
我们都知道http接口是什么,也能够轻易地使用Java调用Get、Post请求。然而,我们需要考虑http接口的数据安全问题。当我们在浏览器或者postman工具中调用接口时,数据会以明文形式返回,不需要认证也不需要解密,这显然是不太安全的。我在开发过程中,经常会遇到合作方提供的接口直接以明文返回数据,甚至包括敏感信息如手机号码等。虽然这种方式方便快捷,但总体来说并不太安全和可靠。
想要实现一个相对安全的http接口一般有两种办法:
(1)调用方需要进行认证并获取token,调用接口时需将token放置于请求头或Cookie中。处理方通过过滤器检查token的合法性;

(2)处理方应生成并提供给调用方一个唯一的appId和对应的appSecret。调用方使用这个appId去调用接口,处理方使用appId和appSecret对数据进行加密。调用方获取到数据后,使用同样的appId和appSecret进行解密。
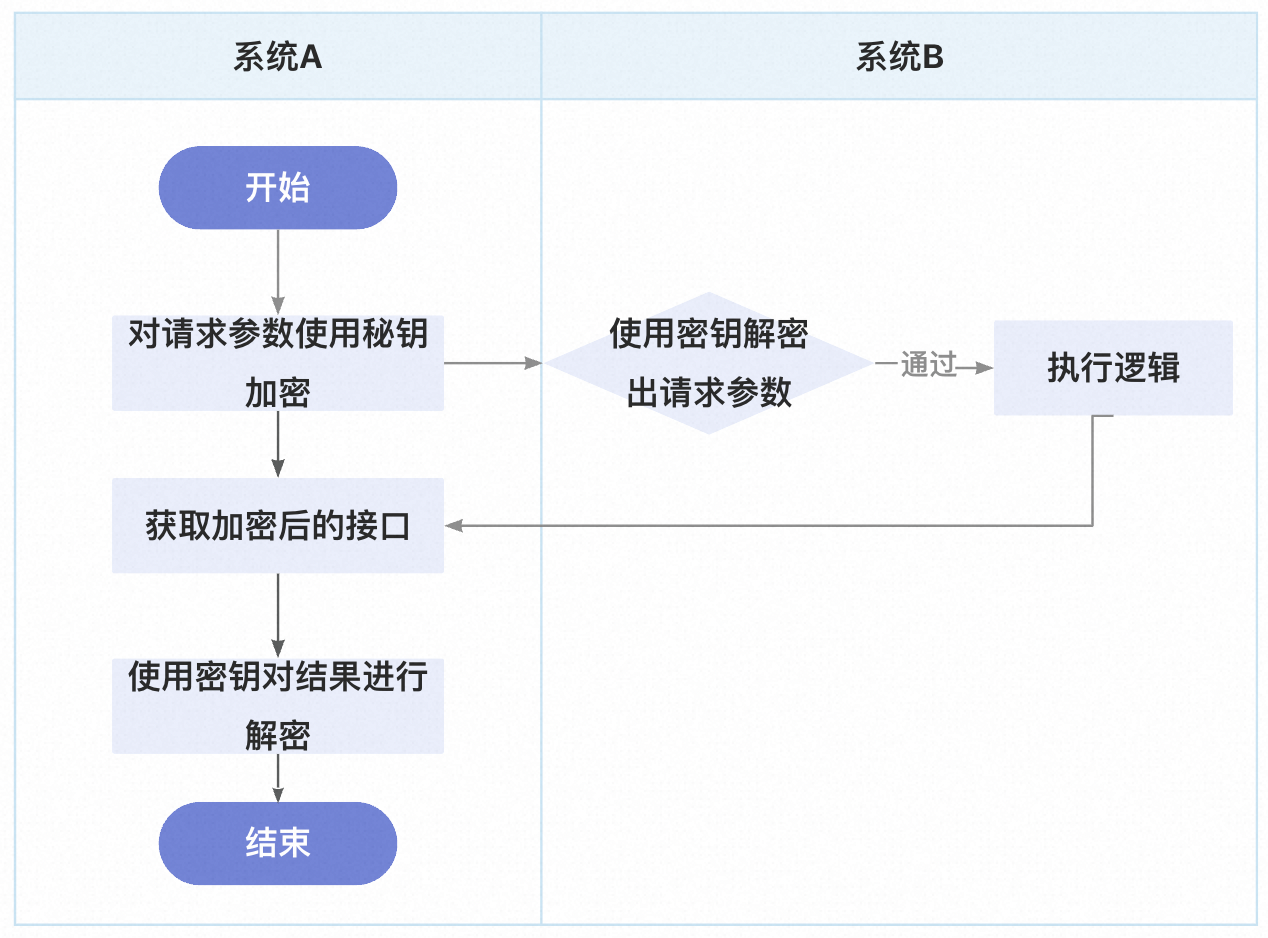
使用请求头或Cookie的方式将token放置于请求中的优点是安全性高,因为token不易被窃取或篡改。而使用appId和appSecret进行加密和解密的方式的优点是方便性高,因为appId和appSecret可以在接口文档或其他途径中公开,调用方只需要使用这些信息即可进行加解密操作,无需每次都进行认证获取token。
因此,两种方式的选择应根据具体情况而定,通常安全性较为重要的场景可以选择使用token方式,而方便性较为重要的场景可以选择使用appId和appSecret方式。
这里我给大家提供一份可用的代码工具类,亲测可用。
EncryptUtil.java
import java.io.IOException;
import java.security.Security;
import java.text.ParseException;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64;
import org.apache.http.HttpEntity;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
import org.apache.http.entity.StringEntity;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients;
import org.apache.http.message.BasicHeader;
import org.apache.http.protocol.HTTP;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import org.bouncycastle.jce.provider.BouncyCastleProvider;
/**
* 需要依赖
*
*
*com.alibaba
*fastjson
*1.2.83
*
*
*
*org.bouncycastle
*bcprov-jdk15on
*1.56
*
*
*
*commons-codec
*commons-codec
*1.14
*
*/
@Slf4j
public class EncryptUtil {
static {
Security.addProvider(new BouncyCastleProvider());
}
private static final String CipherMode = "AES/CBC/PKCS7Padding";
private static final String EncryptAlg = "AES";
private static final String Encode = "UTF-8";
/**
* 加密随机盐
*/
private static final String AESIV = "ff465fdecc764337";
/**
* 加密:有向量16位,结果转base64
*
* @param context
* @return
*/
public static String encrypt(String context, String sk) {
try {
// 下面这行在进行PKCS7Padding加密时必须加上,否则报错
Security.addProvider(new BouncyCastleProvider());
byte[] content = context.getBytes(Encode);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(CipherMode);
cipher.init(
Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE,
new SecretKeySpec(sk.getBytes(Encode), EncryptAlg),
new IvParameterSpec(AESIV.getBytes(Encode)));
byte[] data = cipher.doFinal(content);
String result = Base64.encodeBase64String(data);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 解密
*
* @param context
* @return
*/
public static String decrypt(String context, String sk) {
try {
byte[] data = Base64.decodeBase64(context);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(CipherMode);
cipher.init(
Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE,
new SecretKeySpec(sk.getBytes(Encode), EncryptAlg),
new IvParameterSpec(AESIV.getBytes(Encode)));
byte[] content = cipher.doFinal(data);
String result = new String(content, Encode);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static String sendPost(String url, JSONObject jsonObject, String encoding)
throws ParseException, IOException {
String body = "";
//创建httpclient对象
CloseableHttpClient client = HttpClients.createDefault();
//创建post方式请求对象
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(url);
//装填参数
StringEntity s = new StringEntity(jsonObject.toString(), "utf-8");
s.setContentEncoding(new BasicHeader(HTTP.CONTENT_TYPE,
"application/json"));
//设置参数到请求对象中
httpPost.setEntity(s);
log.info("请求地址:" + url);
// System.out.println("请求参数:"+nvps.toString());
//设置header信息
//指定报文头【Content-type】、【User-Agent】
// httpPost.setHeader("Content-type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
httpPost.setHeader("Content-type", "application/json");
httpPost.setHeader("User-Agent", "Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 5.0; Windows NT; DigExt)");
//执行请求操作,并拿到结果(同步阻塞)
CloseableHttpResponse response = client.execute(httpPost);
//获取结果实体
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
if (entity != null) {
//按指定编码转换结果实体为String类型
body = EntityUtils.toString(entity, encoding);
}
EntityUtils.consume(entity);
//释放链接
response.close();
return body;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String appId = "appId";
//AES算法支持的密钥长度有128位、192位和256位,其中128位密钥是最常用的。
//因此,如果使用AES算法进行加密和解密,必须确保密钥长度是128位、192位或256位。
//如果使用的是AES-128算法,则密钥长度应该是128位,也就是16个字节;
//如果使用的是AES-192算法,则密钥长度应该是192位,也就是24个字节;
//如果使用的是AES-256算法,则密钥长度应该是256位,也就是32个字节
String appKey = UUIDUtil.generateString(32);
//参数加密
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
jsonObject.put("appId", appId);
jsonObject.put("appKey", appKey);
jsonObject.put("data", "我是内容");
String encrypt = EncryptUtil.encrypt(jsonObject.toJSONString(), appKey);
System.out.println("加密后内容=" + encrypt);
//参数界面
System.out.println("解密后内容=" + EncryptUtil.decrypt(encrypt, appKey));
}
}
UUIDUtil.java
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; import java.util.Random; import java.util.UUID; public class UUIDUtil { public static final String allChar = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"; public static final String letterChar = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"; public static final String numberChar = "0123456789"; public static String[] chars = new String[] { "0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "H", "I", "J", "K", "L", "M", "N", "O", "P", "Q", "R", "S", "T", "U", "V", "W", "X", "Y", "Z" }; /** 用于生成8位唯一标识字符串 */ public static String generateShortUuid() { StringBuffer shortBuffer = new StringBuffer(); String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", ""); for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { String str = uuid.substring(i * 4, i * 4 + 4); int x = Integer.parseInt(str, 16); shortBuffer.append(chars[x % 36]); } return shortBuffer.toString(); } /** * 生成指定长度纯数字唯一标识字符串 * * @param length * @return */ public static String generatePureNumberUuid(int length) { StringBuffer shortBuffer = new StringBuffer(); Random random = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { shortBuffer.append(numberChar.charAt(random.nextInt(10))); } return shortBuffer.toString(); } /** * 由大小写字母、数字组成的随机字符串 * * @param length * @return */ public static String generateString(int length) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); Random random = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { sb.append(allChar.charAt(random.nextInt(allChar.length()))); } return sb.toString(); } /** * 由大小写字母组成的随机字符串 * * @param length * @return */ public static String generateMixString(int length) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); Random random = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { sb.append(letterChar.charAt(random.nextInt(letterChar.length()))); } return sb.toString(); } /** * 由小字字母组成的随机字符串 * * @param length * @return */ public static String generateLowerString(int length) { return generateMixString(length).toLowerCase(); } /** * 由大写字母组成的随机字符串 * * @param length * @return */ public static String generateUpperString(int length) { return generateMixString(length).toUpperCase(); } /** * 产生指字个数的0组成的字符串 * * @param length * @return */ public static String generateZeroString(int length) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { sb.append('0'); } return sb.toString(); } /** * 将数字转化成指字长度的字符串 * * @param num * @param fixdlenth * @return */ public static String toFixdLengthString(long num, int fixdlenth) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); String strNum = String.valueOf(num); if (fixdlenth - strNum.length() >= 0) { sb.append(generateZeroString(fixdlenth - strNum.length())); } else { throw new RuntimeException("将数字" + num + "转化为长度为" + fixdlenth + "的字符串发生异常!"); } sb.append(strNum); return sb.toString(); } /** * 将数字转化成指字长度的字符串 * * @param num * @param fixdlenth * @return */ public static String toFixdLengthString(int num, int fixdlenth) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); String strNum = String.valueOf(num); if (fixdlenth - strNum.length() >= 0) { sb.append(generateZeroString(fixdlenth - strNum.length())); } else { throw new RuntimeException("将数字" + num + "转化为长度为" + fixdlenth + "的字符串发生异常!"); } sb.append(strNum); return sb.toString(); } // 生成订单编号,时间戳+后8位随机字符串 public static String getOrderNo() { String orderNo = ""; String sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS").format(new Date()); orderNo = sdf + generateShortUuid(); return orderNo; } /** * 这个方法只支持最大长度为32的随机字符串,如要支持更大长度的,可以适当修改此方法,如前面补、后面补,或者多个uuid相连接 * * @param length * @return */ private static String toFixedLengthStringByUUID(int length) { // 也可以通过UUID来随机生成 UUID uuid = UUID.randomUUID(); return uuid.toString().replace("-", "").substring(0, length); } // 生成订单编号,时间戳+后8位随机字符串 public static String getBarCode() { String barCode = ""; String sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd").format(new Date()); barCode = sdf + generatePureNumberUuid(4); return barCode; } }
2. RPC接口
RPC(Remote Procedure Call)远程过程调用是一种进程间通信的方式,可以让不同的系统之间通过网络进行通信和交互。然而,由于RPC接口需要事先定义好接口的参数、返回值、异常等,并且多方合作的开发框架要大致一样,因此其应用场景比较受限制。此外,不同系统之间的RPC接口需要保持兼容性,否则可能会出现接口不匹配、数据传输错误等问题。因此,在使用RPC接口时,需要进行充分考虑和设计,以确保接口的正确性和可靠性。虽然RPC接口的应用场景有限,但在特定的场景下,RPC接口可以提供高效、可靠的通信方式,如分布式架构中系统间的服务调用。
我在工作中只遇到过一次RPC调用的情况。当时,我与公司的不同部门合作,我们使用了同一套框架,他们提供的是RPC接口,我只需引入他们的jar包就能轻松调用他们的服务。不过,除了公司内部,我很少遇到其他机构或公司使用RPC调用的方式。通常,大多数外部接口服务都是通过HTTP接口实现的。
(三)中间件交互
这里我引用一下ChatGPT的回答:

我遇到的情况:有一次,A方需要主动将数据推送给B方,于是提出了用消息队列的方案,一听两方都觉得既解耦又方便,于是开始行动。A方在自己的服务器上部署了消息队列,但没想到,各方的服务器环境是隔离的,网络不通,B方根本无法连接到A方的消息队列。他们于是找到了私有云的运维人员,问他们能不能做开放端口、IP加白等一大堆操作,但不知道啥原因就是不行。最后他们只好改为B方提供一个Http接口,A方主动调用接口把数据送过去才得以解决。。。
总结一下
在多系统合作的场景中,系统间的交互是非常关键的。交互协议的一致性、数据格式的一致性、安全性保障、错误处理机制、交互频率、监控和日志记录等方面,都需要特别注意,以确保系统间的交互稳定和可靠。
-
交互协议的一致性是系统间进行数据传输的基础,需要明确定义请求和响应报文格式、数据类型、处理规则等。数据格式的一致性也非常重要,需要确定数据交换的格式和编码方式,避免由于格式不一致而导致的数据解析异常。
-
安全性保障是防止系统中出现非法访问和数据泄漏的重要手段,需要采用各种安全措施来保障系统的安全性。
-
错误处理机制需要考虑系统中可能出现的各种异常情况,并对不同的异常情况进行分类处理,确保信息及时反馈给用户。
-
交互频率需要根据实际情况来制定,避免频繁的调用造成系统压力过大。
-
监控和日志记录需要对系统进行实时监控,及时发现和处理问题,并记录日志以便进行排查和分析。
作者:不若为止
欢迎任何形式的转载,但请务必注明出处。
限于本人水平,如果文章和代码有表述不当之处,还请不吝赐教。
