源码请到:自然语言处理练习: 学习自然语言处理时候写的一些代码 (gitee.com)
数据来源:
搜狗新闻语料库 由于链接失效,现在使用百度网盘分享
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1RTx2k7V3Ujgg9-Rv8I8IRA?pwd=ujn3
提取码:ujn3
停用词 来源于网络
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ePrf4_gWx8_pTn6PEjTtCw?pwd=5jov
提取码:5jov
字样式文件 来源于网络
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1uVreJY-MKhz1HXzAw5e4VQ?pwd=8ill
提取码:8ill
一、tf-idf简介
TF = 某词在文章中出现的次数/该文章中出现最多词出现的次数
IDF = log(文章总数/包含该词的文章数+1)
TF-IDF = TF * IDF
二、加载数据集
# 载入数据集 df_news = pd.read_table('./data/val.txt', names=['category', 'theme', 'URL', 'content'], encoding='utf-8') df_news = df_news.dropna() print(df_news.head()) print(df_news.shape)
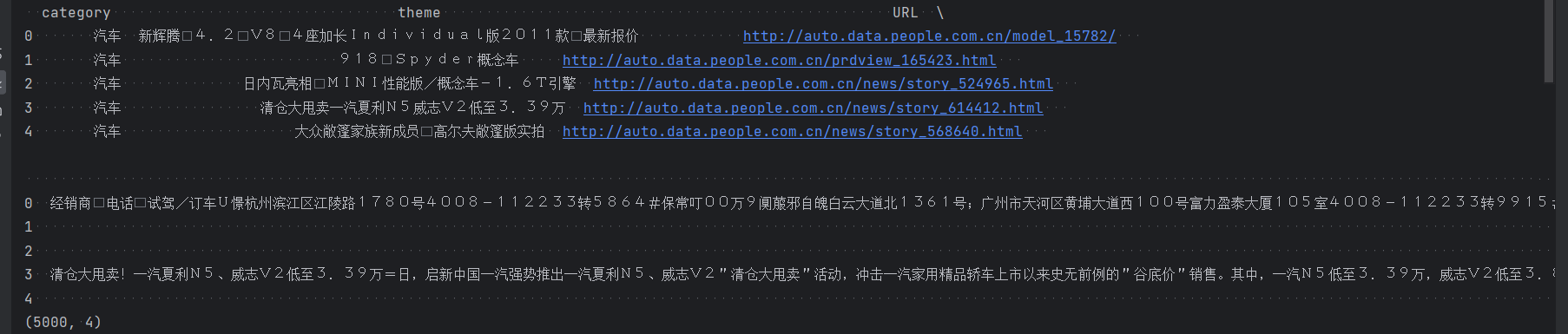
可以看到有5000行4列的数据,其中第一列可以作为新闻分类的标签,最后一列为新闻内容
三、分词
首先将数据转换为list格式
# 转换为list格式 content = df_news.content.values.tolist() print(content[1000])

将最后一列数据摘出来转换成了一个字符串列表,就可以进行分词操作
# 分词 content_S = [] for line in content: current_segment = jieba.lcut(line) if len(current_segment) > 1 and current_segment != '\r\n': content_S.append(current_segment) print(content_S[1000]) df_content = pd.DataFrame({'content_S': content_S}) print(df_content.head())
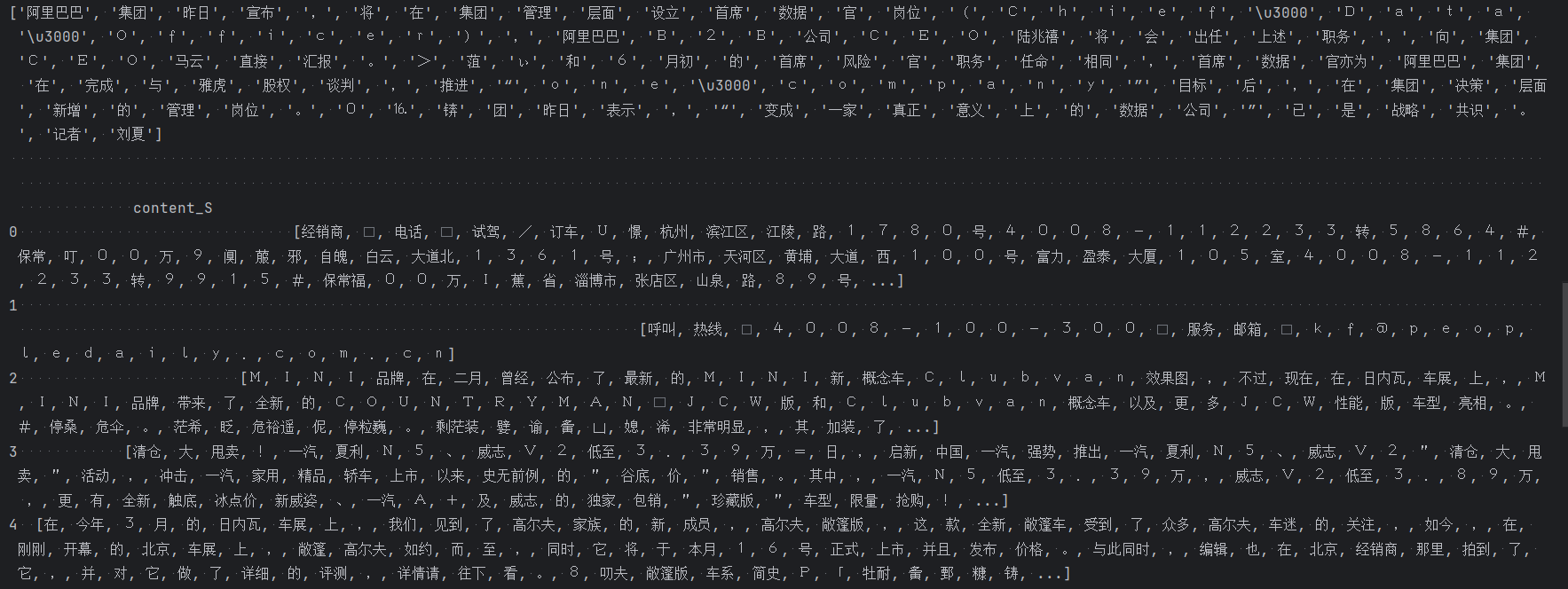
四、去掉停用词
可以看出上面还有许多没有价值的词作干扰,所以我们加载停用词库并且去掉停用词
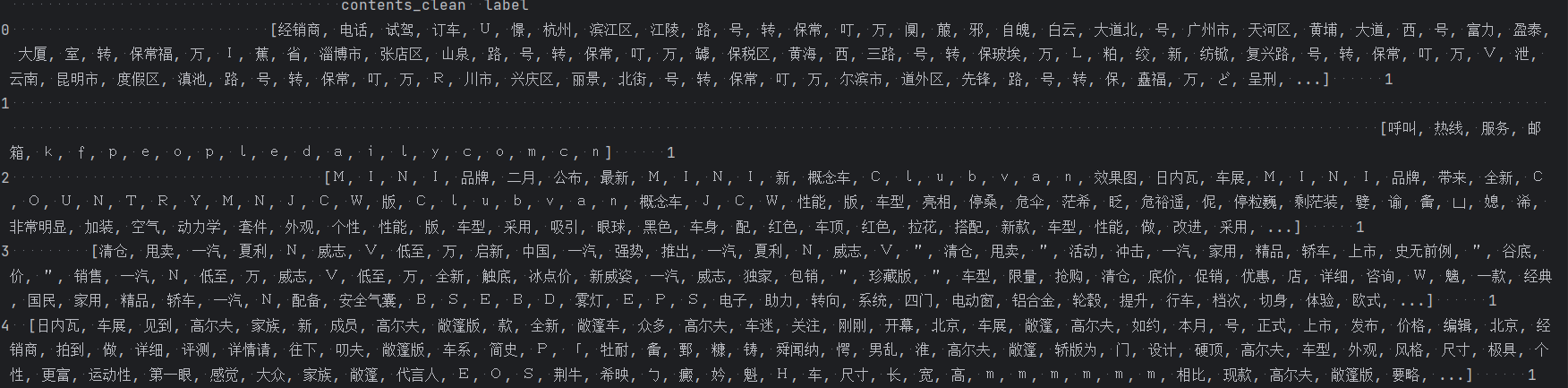
# 加载停用词 stopwords = pd.read_csv('./data/stopwords.txt', index_col=False, sep='\t', quoting=3, names=['stopword'], encoding='utf-8') print(stopwords.head(20)) # 去掉停用词 def drop_stopwords(contents, stopwords): contents_clean = [] all_words = [] for line in contents: line_clean = [] for word in line: if word in stopwords: continue line_clean.append(word) all_words.append(str(word)) contents_clean.append(line_clean) return contents_clean, all_words contents = df_content.content_S.values.tolist() stopwords = stopwords.stopword.values.tolist() contents_clean, all_words = drop_stopwords(contents, stopwords) df_content = pd.DataFrame({'contents_clean': contents_clean}) print(df_content.head()) df_all_words = pd.DataFrame({'all_words': all_words}) print(df_all_words.head())

五、计算词频
# 计算词频 words_count = df_all_words.groupby(by=['all_words'])['all_words'].agg(count='count') words_count = words_count.reset_index().sort_values(by=['count'], ascending=False) print(words_count.head())

六、绘制词云
# 绘制词云 wordcloud = WordCloud(font_path='./data/SimHei.ttf', background_color='white', max_font_size=80) word_frequence = {x[0]: x[1] for x in words_count.head(100).values} wordcloud = wordcloud.fit_words(word_frequence) plt.imshow(wordcloud) plt.show()

七、使用tf-idf提取关键词
# tf-idf index = 1000 print(df_news['content'][index]) content_S_str = ''.join(content_S[index]) print(' '.join(jieba.analyse.extract_tags(content_S_str, topK=5, withWeight=False)))

八、使用主题模型提取关键词
# LDA dictionary = corpora.Dictionary(contents_clean) corpus = [dictionary.doc2bow(sentence) for sentence in contents_clean] lda = gensim.models.ldamodel.LdaModel(corpus=corpus, id2word=dictionary, num_topics=20) print(lda.print_topic(1, topn=5)) for topic in lda.print_topics(num_topics=20, num_words=5): print(topic[1])

可以看出第一类词的成分权重

这是所有类型的词成分权重
九、使用贝叶斯算法进行分类
# 贝叶斯算法进行分类 df_train = pd.DataFrame({'contents_clean': contents_clean, 'label': df_news['category']}) print(df_train.tail()) print(df_train.label.unique()) label_mapping = {'汽车': 1, '财经': 2, '科技': 3, '健康': 4, '体育': 5, '教育': 6, '文化': 7, '军事': 8, '娱乐': 9, '时尚': 0} df_train['label'] = df_train['label'].map(label_mapping) print(df_train.head()) x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(df_train['contents_clean'].values, df_train['label'].values) print(x_train[0][1]) words = [] for line_index in range(len(x_train)): words.append(' '.join(x_train[line_index])) print(words[0]) print(len(words)) # 计算词频构造向量 vec = CountVectorizer(analyzer='word', max_features=4000, lowercase=False) vec.fit(words) classifier = MultinomialNB() classifier.fit(vec.transform(words), y_train) test_words = [] for line_index in range(len(x_test)): test_words.append(' '.join(x_test[line_index])) print(test_words[0]) print(len(test_words)) print(classifier.score(vec.transform(test_words), y_test)) # tf-idf构造词向量 vec2 = TfidfVectorizer(analyzer='word', max_features=4000, lowercase=False) vec2.fit(words) classifier = MultinomialNB() classifier.fit(vec2.transform(words), y_train) print(classifier.score(vec2.transform(test_words), y_test)) # 词频构造多维向量形式构造词向量 vec3 = CountVectorizer(analyzer='word', max_features=4000, lowercase=False, ngram_range=(1, 2)) vec3.fit(words) classifier = MultinomialNB() classifier.fit(vec3.transform(words), y_train) print(classifier.score(vec3.transform(test_words), y_test)) # tfidf构造多维向量形式构造词向量 vec4 = TfidfVectorizer(analyzer='word', max_features=4000, lowercase=False, ngram_range=(1, 2)) vec4.fit(words) classifier = MultinomialNB() classifier.fit(vec4.transform(words), y_train) print(classifier.score(vec4.transform(test_words), y_test))




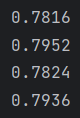
可以看出不同方法构成词向量对结果产生了影响,使用tf-idf方法构建词向量比单纯使用词频构建词向量准确率高一些,将词向量扩充多维比不扩充准确率稍微高一些
