-
pytorch笔记:conv2d
-
feature map 是输入,特征图,输出大小是 ⌊ n h − k h + p h s h ⌋ + 1 × ⌊ n w − k w + p w s w ⌋ + 1 \lfloor \frac{n_h-k_h+p_h}{s_h}\rfloor+1 \times \lfloor \frac{n_w-k_w+p_w}{s_w}\rfloor+1 ⌊shnh−kh+ph⌋+1×⌊swnw−kw+pw⌋+1( p p p不是参数padding,实际上是参数padding的2倍),多通道时卷积核的形状是 c o × c i × k h × k w c_o\times c_i\times k_h\times k_w co×ci×kh×kw,理解是,从输出来讲,对于每一个输出通道,都有输入通道个kernel,所以是 c o × c i c_o\times c_i co×ci,一般随着层数增加,宽高减小,通道数增加

-
nn.Conv2d 中一般 kernel_size 是小奇数(很多是3),padding 设置为 k − 1 2 \frac{k-1}{2} 2k−1(实际上padding的是 k − 1 k-1 k−1,因为参数的意义是左右各padding),padding 可以是 ‘same’
padding controls the amount of padding applied to the input. It can be either a string {‘valid’, ‘same’} or an int / a tuple of ints giving the amount of implicit padding applied on both sides.

-
nn.Conv2d(2,4,3).weight.size() = [4,2,3,3], nn.Conv2d(2,4,3).bias.size() = [4]
-
point-wise convolution 即1x1 卷积仅做了通道的加权融合,没有考虑图片的局部关联性
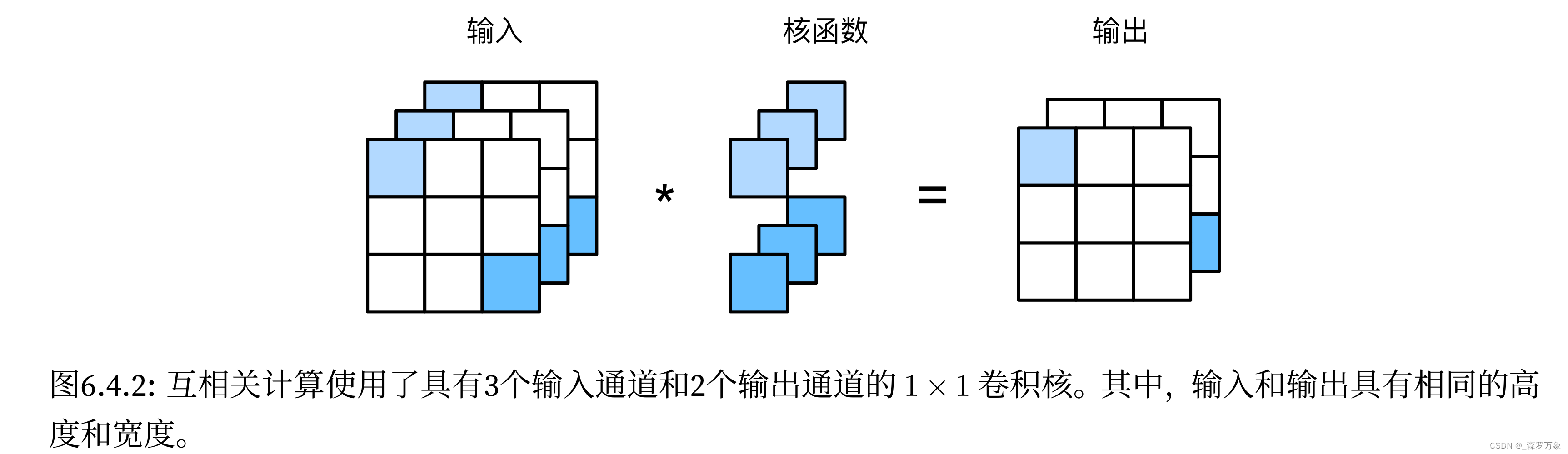
-
depth-wise convolution 是指 Conv2d 中 groups 大于 1 的情况,如果 groups=in_channels 不做通道的融合,分组计算之后合并。分组之后通道融合不充分
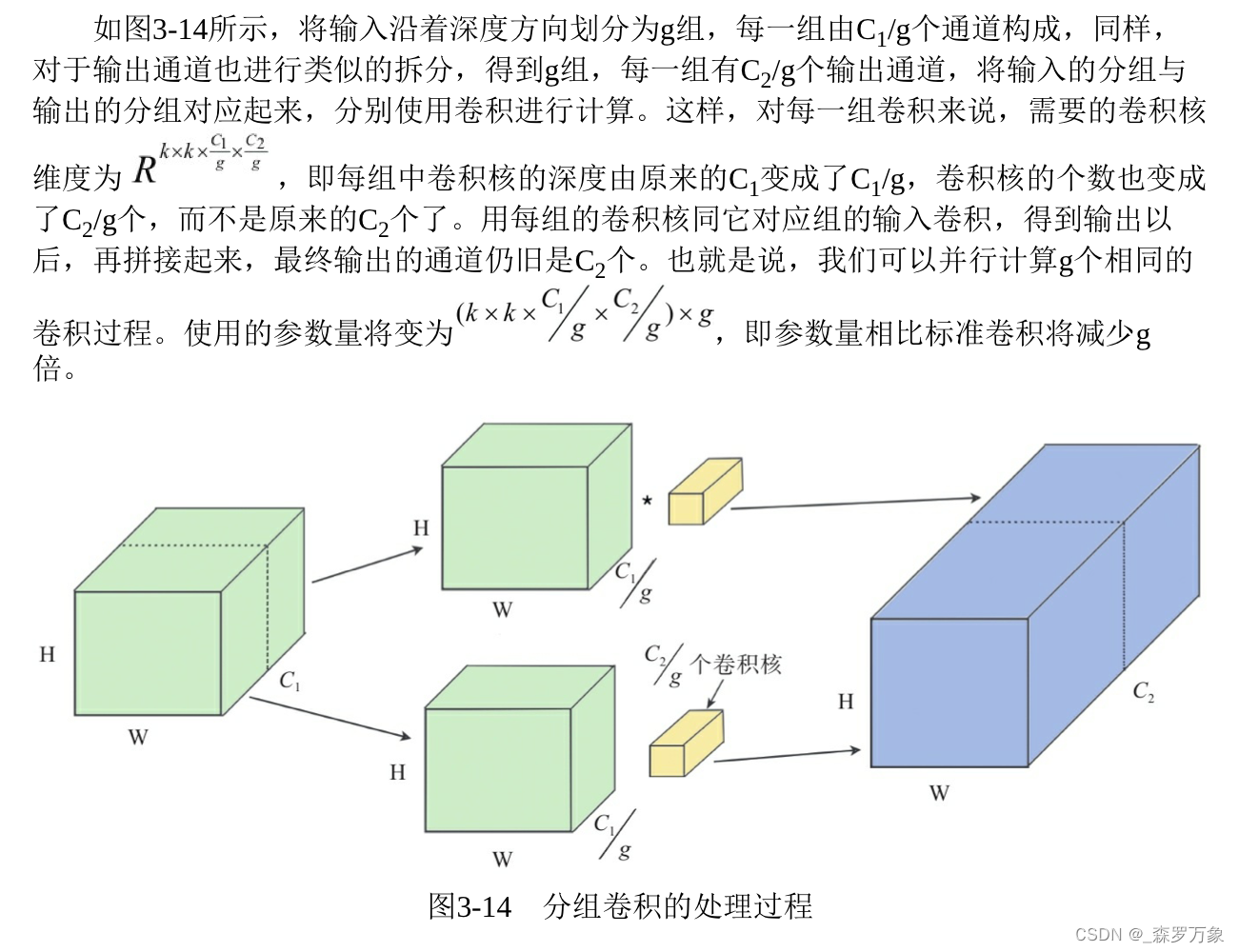
-
dilation 空洞卷积是增加感受野而不增加计算量的方法
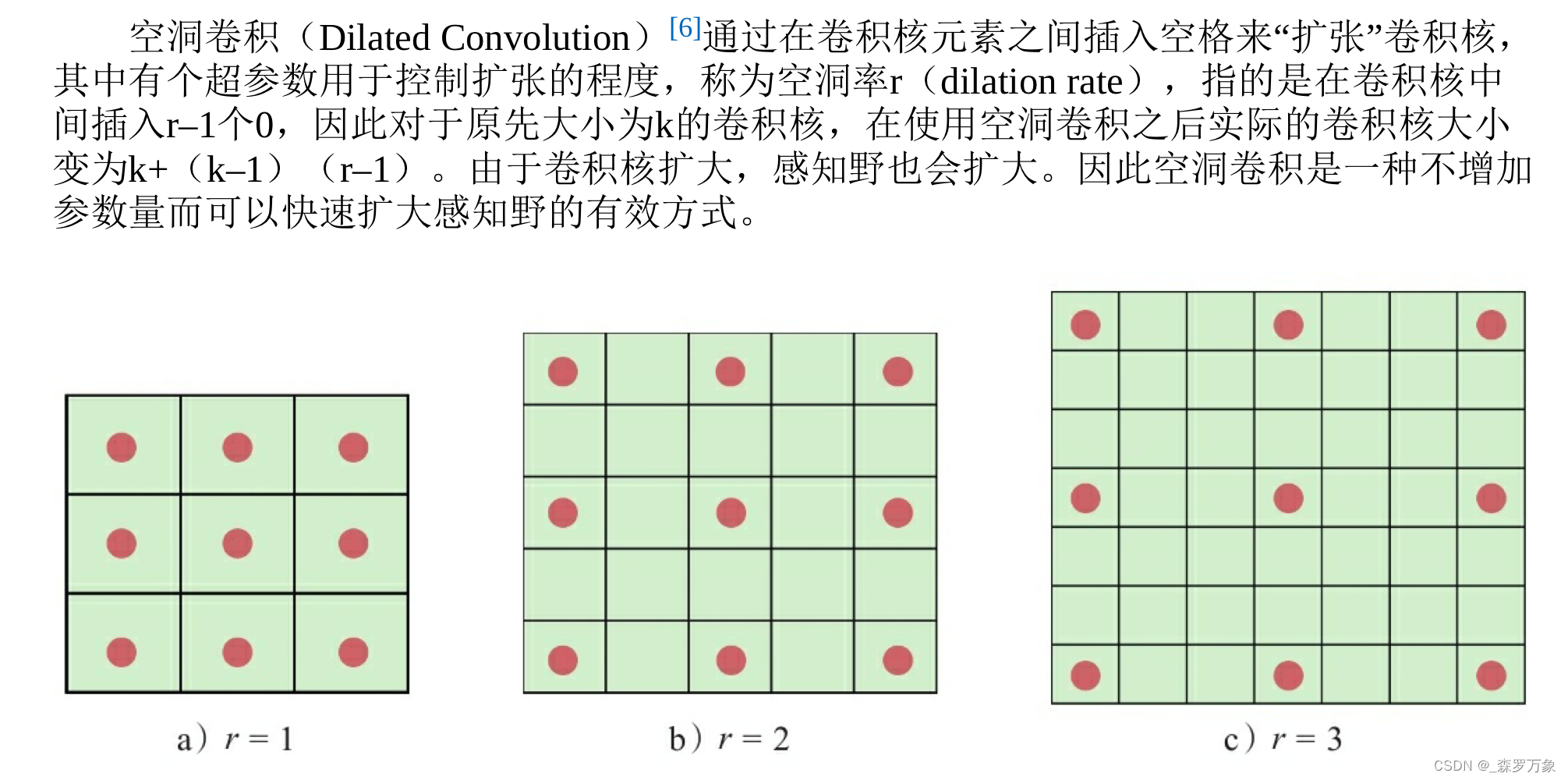
-
ConvMixer : patches are all you need,通过分离通道混合(depth-wise convolution)和空间混合(point-wise convolution)
-
Conv2d运算可以有三种实现:
- 循环对图片截取 kernel 大小的特征图,元素点乘求和
- 把 kernel 拉成列向量,循环对图片截取 kernel 大小的特征图,拉成行向量后堆叠成矩阵,再与 kernel 向量相乘
- 循环把 kernel 填充 0 到图片的大小后再拉直成向量,堆叠成矩阵(kernel_matrix),与图片矩阵相乘
-
卷积是下采样(例如 4 × 4 → 2 × 2 4\times4\rightarrow2\times2 4×4→2×2),转置卷积(也叫反卷积)是上采样(例如 2 × 2 → 4 × 4 2\times2\rightarrow4\times4 2×2→4×4),转置卷积只需将 kernel_matrix 转置之后再与输出相乘即可。上采样可以用于图片生成和分辨率提高
转置卷积只是 shape 转换回原始输入图片的大小,数值并不会返回

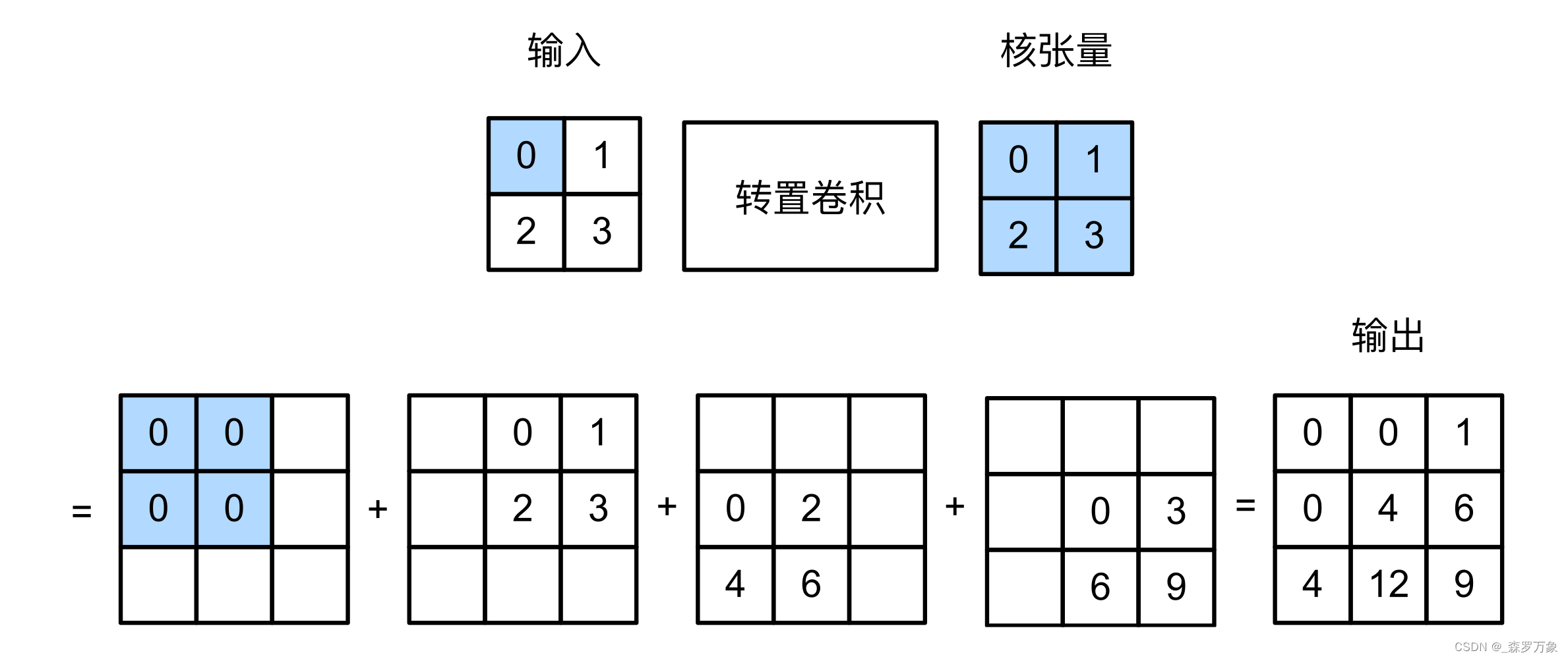
-
-
相关阅读:
元宇宙|高阶音频处理能力,让声音「声临其境」
std::vector 的使用陷阱
Java设计模式之桥接模式
【python基础】——Anaconda下包更新的坑及安装与卸载、及安装后Jupyter Notebook没反应的解决方法
OpenHarmony实战开发-多设备自适应能力
vulnhub靶机ha:wordy
基于UDP协议的接收和发送
2021济南站
广州小程序开发公司怎么找?
shell脚本中语法
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_52812620/article/details/131153153