-
【数据结构】如何应用堆解决海量数据的问题

堆(Heap数据结构堆在计算机科学中有着广泛的应用,今天来介绍两种堆的应用:堆排序、Top-k问题🍉
堆排序
堆排序是一种基于堆数据结构的排序算法。它的基本思想是,将待排序的序列构建成一个大根堆(或小根堆),然后依次取出堆顶元素(即最大值或最小值),将其放入已排序序列的末尾,再将剩余的元素重新调整为一个新的堆。重复这个过程,直到所有元素都被取出并放入已排序序列中。
具体来说,堆排序的过程如下:
- 将待排序的长度为n序列构建成一个大根堆(或小根堆)。这个过程可以从最后一个非叶子节点开始,依次向前进行,保证每个子树都是一个大根堆(或小根堆)。
- 取出堆顶元素(即最大值或最小值),将其放入已排序序列的末尾。
- 将剩余(n-1)的元素重新调整为一个新的堆。
- 重复步骤 2 和步骤 3,直到所有元素都被取出并放入已排序序列中。最终得到的序列就是排好序的。
最终得到的序列就是排好序的。
堆排序的时间复杂度为 O(nlogn),空间复杂度为 O(1)。
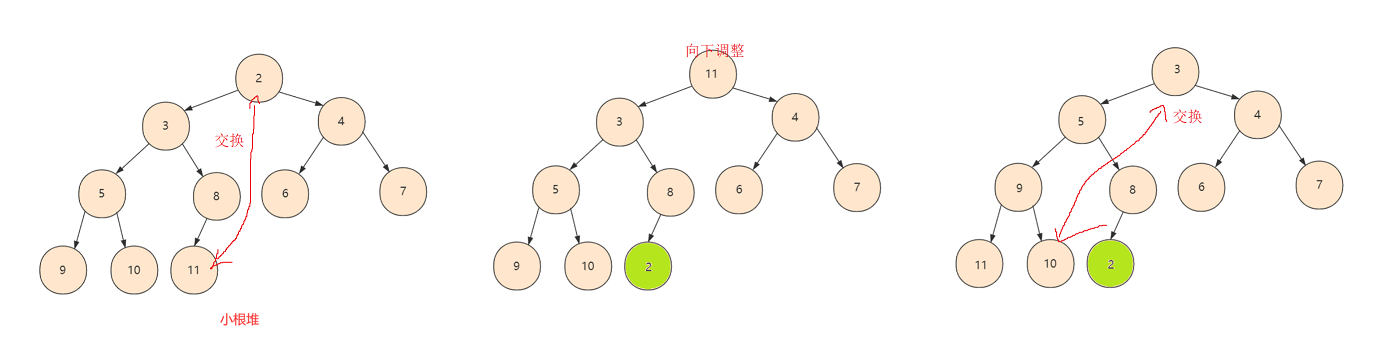
向下调整法
从非叶节点的最后一个数据的下标开始,每次取出孩子中较大或较小的数(看是大堆还是小堆)向下进行调整,由于每多一层,下层是上层的二倍,这种办法直接可以省略掉最后一层,也可以达到建堆的目的,所以这种办法为更优的办法。
由于需要向下调整,所以这种办法需要找到子节点,我们已经知道父结点的运算了,子结点就是父节点的逆运算。
结合上面所说,实现代码如下:void AdjustDown(HeapDataType* arr, int n, int parent)//向下调整 { assert(arr); int child = parent * 2 + 1; while (child < n) { if (child<n - 1 && arr[child] > arr[child + 1]) { child = child + 1; } if (arr[child] < arr[parent]) { swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]); } parent = child; child = child * 2 + 1; } } void HeapSort(int* a,int n)//堆排序 { for (int i = (n - 2) / 2; i >= 0; i--) { AdjustDown(a, n,i); } for (int i = n-1; i > 0; i--) { swap(&a[0], &a[i]); AdjustDown(a, i, 0); } for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { printf("%d ", a[i]); } } int main() { int arr[] = { 1,4,6,2,4,8,5,8,3,111,4,5,32,44 }; HeapSort(arr, sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int)); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
Top-k问题
Top-k 问题是指在一个数据集中找到前 k 个最大(或最小)的元素。一般情况下数据量都比较大。 比如:专业前10名、世界500强、富豪榜、游戏中前100的活跃玩家等。
下面是使用堆排序实现 Top-k 问题的具体步骤:
- 创建一个大小为 k 的小根堆,用于存储当前的前 k 个最大元素。
- 将前 k 个元素插入小根堆中。
- 遍历剩余的元素,对于每个元素执行以下操作:
- 如果当前元素比堆顶元素大,则将堆顶元素弹出,再将当前元素插入堆中。
- 遍历完所有元素后,小根堆中剩余的 k 个元素就是前 k 个最大元素。
使用堆排序实现 Top-k 问题的时间复杂度为 O(nlogk),空间复杂度为 O(k),其中 n 是数据集的大小。这种方法适用于数据集较大的情况,但需要额外的空间来存储堆。
代码实现- 生成一个有10000随机数的文件
void CreateNDate() //生成一个有10000个随机数的文件 { int n = 10000; srand(time(0)); const char* file = "data.txt"; FILE* fin = fopen(file, "w"); if (fin == NULL) { perror("fopen error"); return; } for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { int x = rand() % 10000; fprintf(fin, "%d\n", x); } fclose(fin); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
按上述步骤进行排序
void AdjustDown(HeapDataType* arr, int n, int parent)//向下调整 { assert(arr); int child = parent * 2 + 1; while (child < n) { if (child<n - 1 && arr[child] > arr[child + 1]) { child = child + 1; } if (arr[child] < arr[parent]) { swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]); } parent = child; child = child * 2 + 1; } } void PrintTopK(int k) { const char* file = "data.txt"; FILE* fin = fopen(file, "r"); if (fin == NULL) { perror("fopen error"); return; } int* heap = (int*)malloc(k * sizeof(int)); int x; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { fscanf(fin,"%d",&heap[i] );//将前k个元素放到数组里 } for (int i = (k - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--) //将k个元素建立一个小堆 { AdjustDown(heap, k, i); } while (!feof(fin)) { fscanf(fin, "%d", &x); if (heap[0] < x) { heap[0] = x; //将剩余n-k个元素依次与堆顶元素交换,不满则则替换 AdjustDown(heap,k,0); } } fclose(fin); for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { printf("%d ", heap[i]); } } int main() { CreateNDate(); PrintTopK(10); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
✨本文收录于数据结构理解与实现
当你喜欢一篇文章时,点赞、收藏和关注是最好的支持方式。如果你喜欢我的文章,请不要吝啬你的支持,点赞👍、收藏⭐和关注都是对我最好的鼓励。感谢你们的支持!
-
相关阅读:
法国博士后招聘|国家科学研究中心 (CNRS) 计算生物学
LeetCode 面试题 04.09. 二叉搜索树序列
Java_抽象类
卷积神经网络(包含代码与相应图解)
2023年考PMP证书有什么意义?一定要清楚!
es6模块化
C++求最大公因数(gcd)的六重境界
263 丑数
【JS】牛客专项练习02
代码随想录 | 二叉树的遍历
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_65596720/article/details/130904289
