-
opencv基础-印度小哥
基础课程
第一章-读取图片、视频和摄像头
Chapter 1 – Read Images Videos and Webcams- 1
图片放在程序所在文件夹下的
Resources/test.png
1.1 opencv读取一张图片并显示:
#include#include #include #include using namespace cv; using namespace std; / Images // void main() { string path = "Resources/test.png"; Mat img = imread(path); imshow("Image", img); waitKey(0); } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
运行后的效果

1.2 opencv读取一段视频并显示:
#include#include #include #include using namespace cv; using namespace std; /// Video // void main() { string path = "Resources/test_video.mp4"; VideoCapture cap(path); Mat img; while (true) { //循环读取视频的帧 cap.read(img); imshow("Image", img); waitKey(2);//每2ms读取一张图 } } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
运行后的效果

1.3 opencv读取摄像头视频并显示:
#include#include #include #include using namespace cv; using namespace std; /// Video // void main() { VideoCapture cap(0); //笔记本自带的摄像头是0,外接的USB摄像头是1、2 Mat img; while (true) { cap.read(img); imshow("image", img); waitKey(1); } } } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
运行后的效果

注意:由于一个程序只能有一个主函数main(),所有这里我们可以先将chapter1.cpp从source files exclude(不是remove删除,而是取消程序对这个程序的读取)

操作过程:

后面如果想把chapter1.cpp程序加载回来的操作:
第二章-基本功能
Chapter 2 – Basic Functions- 1
2.1 将图片转为灰度图
#include#include #include #include using namespace cv; using namespace std; /// Gray // void main() { string path = "Resources/test.png";//读取图片 Mat img = imread(path); Mat imgGray; cvtColor(img,imgGray,COLOR_BGR2GRAY); //将BGR彩色图像转为灰色图像 imshow("Image", img); imshow("Image Gray", imgGray); waitKey(0); } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18

2.2 将图片变得模糊
#include#include #include #include using namespace cv; using namespace std; /// Blur // void main() { string path = "Resources/test.png";//读取图片 Mat img = imread(path); Mat imgGray,imgBlur; cvtColor(img,imgGray,COLOR_BGR2GRAY); //将BGR彩色图像转为灰色图像 GaussianBlur(img, imgBlur,Size(7,7),5,0);//高斯法将图片进行模糊化处理 imshow("Image", img); imshow("Image Gray", imgGray); imshow("Image imgBlur", imgBlur);//别写成 //imshow("Image Gray", imgBlur);否则只显示一张图! waitKey(0); } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19

2.3 将图片进行边缘轮廓检测
#include#include #include #include using namespace cv; using namespace std; /// Canny // void main() { string path = "Resources/test.png";//读取图片 Mat img = imread(path); Mat imgGray,imgBlur, imgCanny; cvtColor(img,imgGray,COLOR_BGR2GRAY); //将BGR彩色图像转为灰色图像 GaussianBlur(img, imgBlur,Size(3,3),3,0);//高斯法将图片进行模糊化处理 Canny(imgBlur,imgCanny,25,75); imshow("Image", img); imshow("Image Gray", imgGray); imshow("Image imgBlur", imgBlur); imshow("Image imgCanny", imgCanny); waitKey(0); } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20

2.4 将已经进行边缘检测的图片进行腐蚀或膨胀
#include#include #include #include using namespace cv; using namespace std; /// Dilation & Erode // void main() { string path = "Resources/test.png";//读取图片 Mat img = imread(path); Mat imgGray,imgBlur, imgCanny,imgDil,imgErode; cvtColor(img,imgGray,COLOR_BGR2GRAY); //将BGR彩色图像转为灰色图像 GaussianBlur(img, imgBlur,Size(3,3),3,0);//高斯法将图片进行模糊化处理 Canny(imgBlur,imgCanny,25,75); Mat kernel = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT,Size(3,3)); //用于将图像中的线条腐蚀(变细)或膨胀(变粗) dilate(imgCanny,imgDil,kernel); erode(imgDil, imgErode, kernel); imshow("Image", img); imshow("Image Gray", imgGray); imshow("Image Blur", imgBlur); imshow("Image Canny", imgCanny); imshow("Image Dilation", imgDil); imshow("Image Erode", imgErode); waitKey(0); } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25

第三章-调整大小和裁剪
Chapter 3 – Resize and Crop- 1
这里再演示一下新建chapter3.cpp程序,将chapter2.cpp程序 exclude。

3.1 将图片调整大小、裁剪
#include#include #include #include using namespace cv; using namespace std; /// Resize and Crop // void main() { string path = "Resources/test.png"; Mat img = imread(path); Mat imgResize, imgCrop; //cout << img.size() << endl; //打印出图片的大小 768X559 resize(img, imgResize, Size(), 0.5, 0.5);//缩放 Rect roi(200, 100, 300, 300); //一个矩形的位置和大小 imgCrop = img(roi);//截取出刚刚矩形内部的部分 imshow("Image", img); imshow("Image Resize", imgResize); imshow("Image Crop", imgCrop); waitKey(0); } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21

第四章-绘制形状和文本
Chapter 4 – Draw Shapes and Text 这里再演示一下新建chapter4.cpp程序,将chapter3.cpp程序 exclude。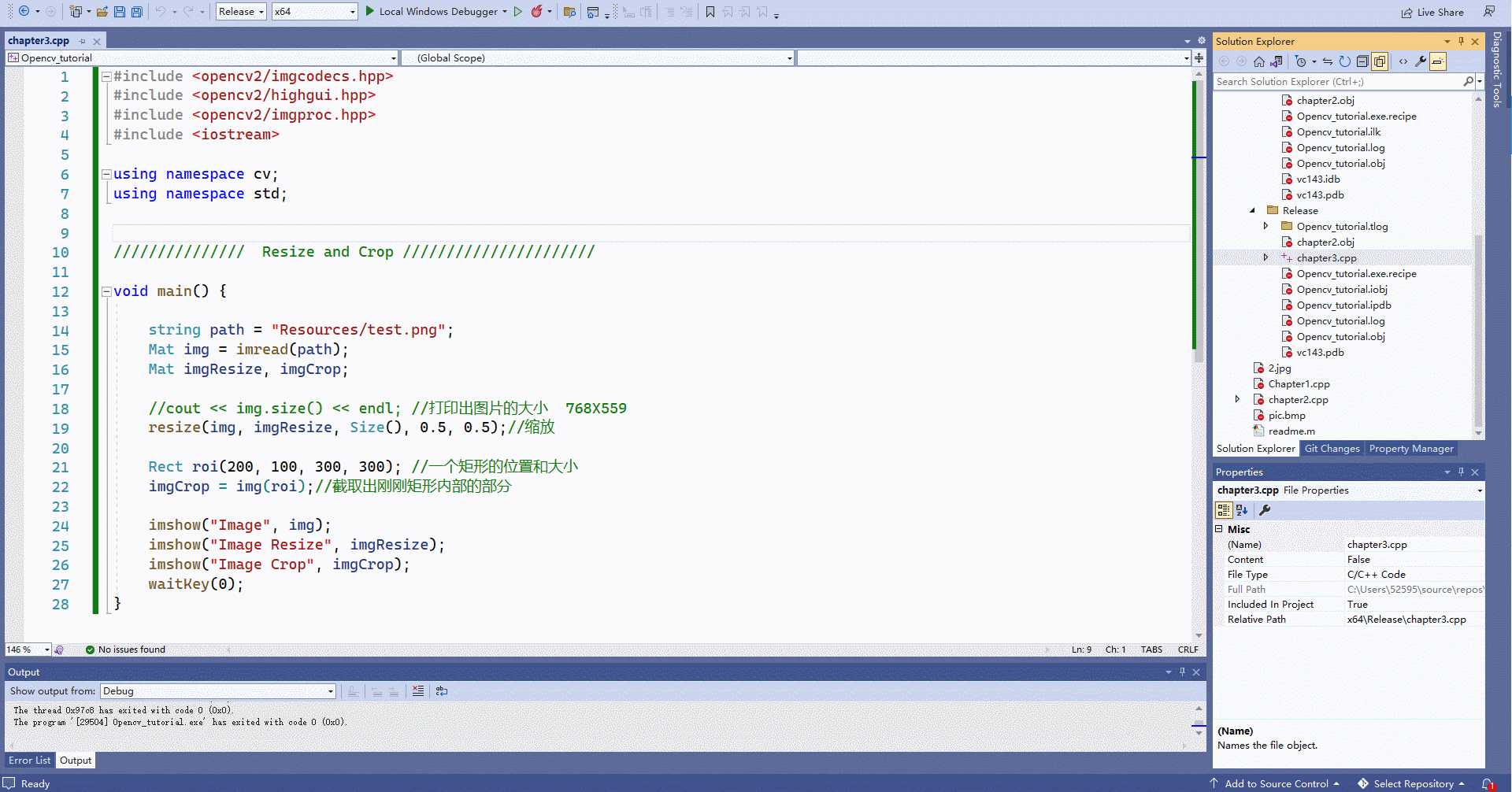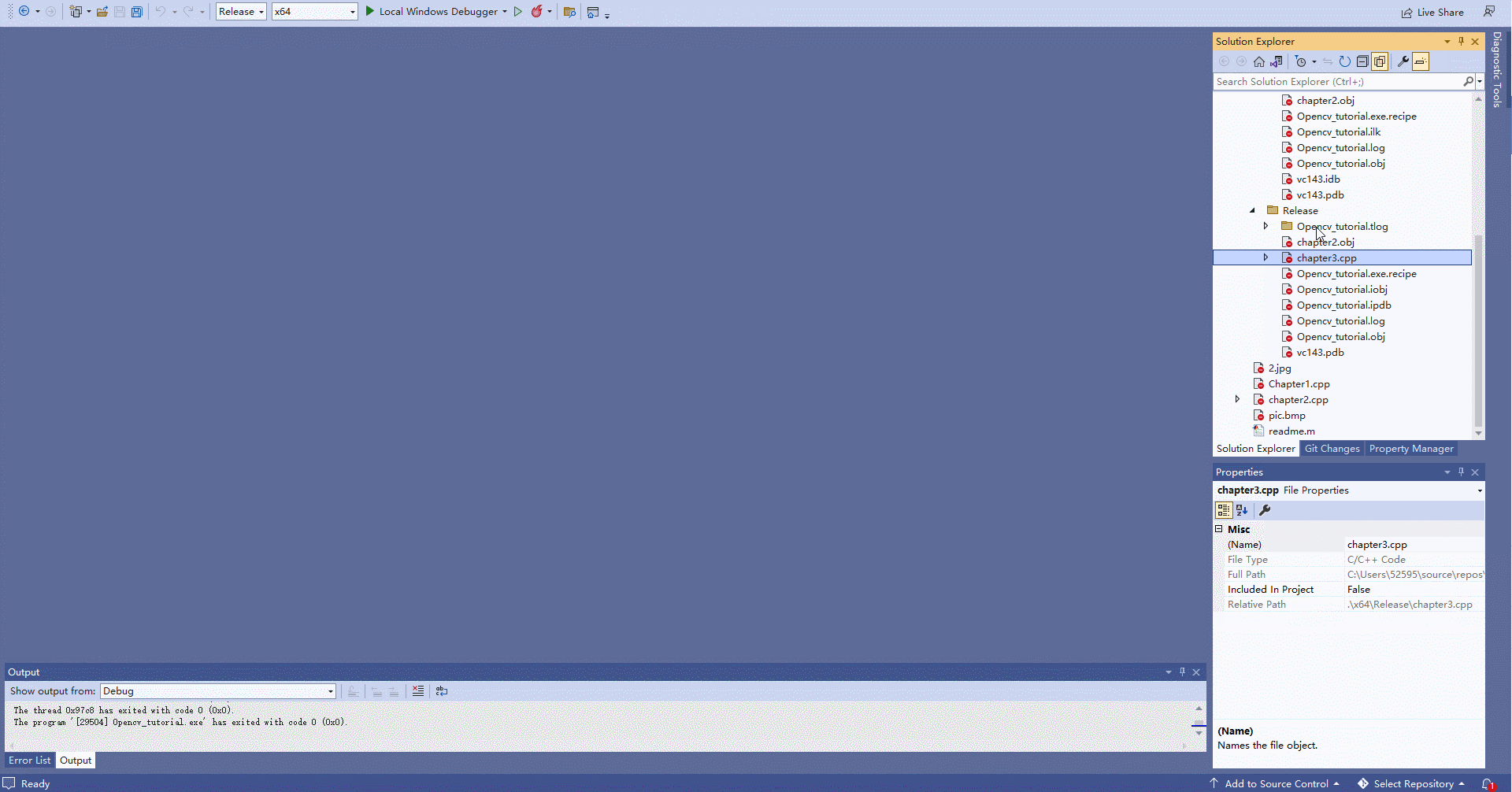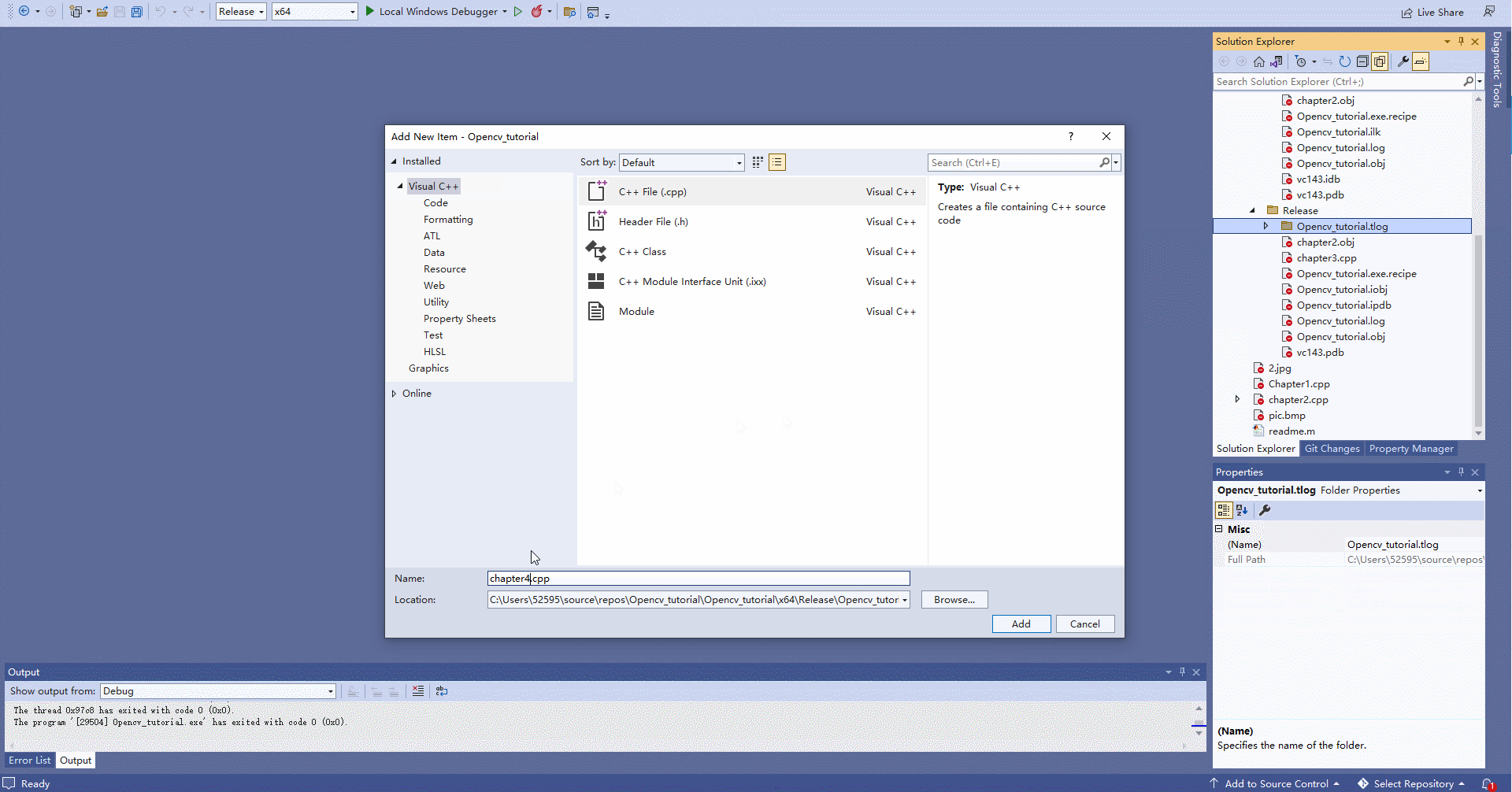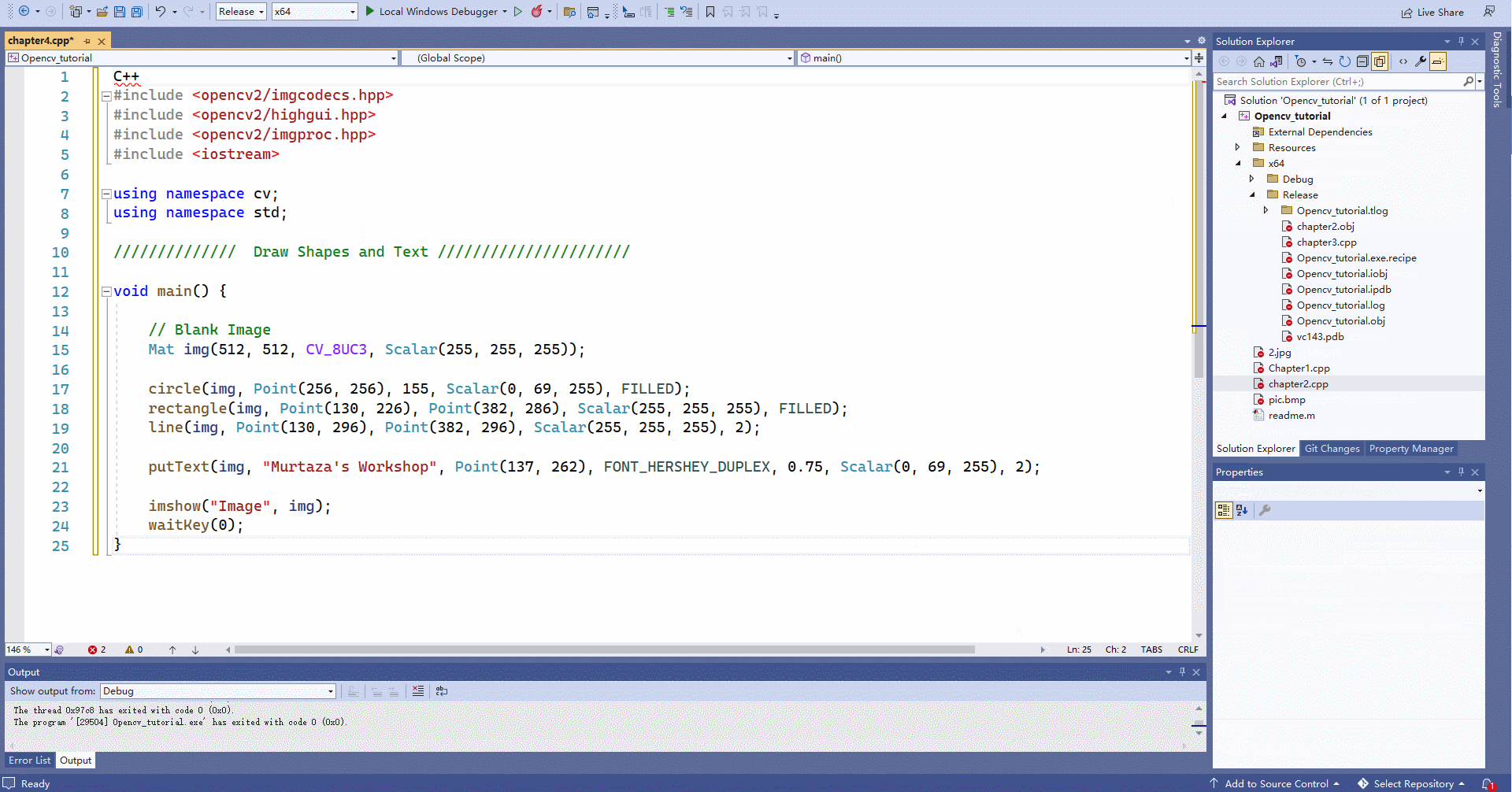- 1
- 2
4.1 在图片中绘制形状和写入文字
#include#include #include #include using namespace cv; using namespace std; // Draw Shapes and Text // void main() { // Blank Image Mat img(512, 512, CV_8UC3, Scalar(255, 255, 255)); //新建一个白色的“画板” circle(img, Point(256, 256), 155, Scalar(0, 69, 255), FILLED);//画圆 rectangle(img, Point(130, 226), Point(382, 286), Scalar(255, 255, 255), FILLED);//画矩形 line(img, Point(130, 296), Point(382, 296), Scalar(255, 255, 255), 2);//画线条 putText(img, "Murtaza's Workshop", Point(137, 262), FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 0.75, Scalar(0, 69, 255), 2);//写文本 imshow("Image", img); waitKey(0); } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18

第五章-将图像进行变形操作
Chapter 5 – Warp Images- 1
5.1 将图片转为灰度图
右键图片,选择其他方式打开-选择画图,然后可以获得图片中不同物体在图片中的坐标(截的动图有点绿…)

左上528,142
左下404,391
右上169,192
右下672.456#include#include #include #include using namespace cv; using namespace std; /// Warp Images // void main() { string path = "Resources/cards.jpg"; Mat img = imread(path); Mat matrix, imgWarp; float w = 250, h = 350; //之后要新创建的图片的大小 Point2f src[4] = { {529,142},{771,190},{405,395},{674,457} }; //找到图片中要提取目标的四个点 Point2f dst[4] = { {0.0f,0.0f},{w,0.0f},{0.0f,h},{w,h} };//将原图片中的目标的四个点映射到新创建的一个图片的四个点上 matrix = getPerspectiveTransform(src, dst);//从四对对应的点计算透视变换.函数计算的是 3*3的满足以下关系的透视转换矩阵: warpPerspective(img, imgWarp, matrix, Point(w, h));//通过透视矩阵把透视变换应用到一个图像上。(就是把原图片中的目标提取出来放到新建的图片中) for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { circle(img, src[i], 10, Scalar(0, 0, 255), FILLED);//将原图片上要提取目标的四个点圈起来 } imshow("Image", img); imshow("Image Warp", imgWarp); waitKey(0); } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
实验效果:

第六章-颜色检测
Chapter 6 – Color Detection- 1
6.1 颜色检测
#include#include #include #include using namespace cv; using namespace std; /// Color Detection // void main() { string path = "Resources/lambo.png";//可以把图片换成shapes.png用于颜色区分检测 Mat img = imread(path); Mat imgHSV, mask; int hmin = 0, smin = 110, vmin = 153; //为了寻找到检测颜色的区间 int hmax = 19, smax = 240, vmax = 255; cvtColor(img, imgHSV, COLOR_BGR2HSV);//将图片转化为HSV格式,便于检测颜色 namedWindow("Trackbars", (640, 200));//创建一个名为"Trackbars"的窗口 createTrackbar("Hue Min", "Trackbars", &hmin, 179);//在"Trackbars"窗口中创建一个名为"Hue Min"的拖条,其值变化区间为(hmin, 179)(hmin最初为0); createTrackbar("Hue Max", "Trackbars", &hmax, 179); createTrackbar("Sat Min", "Trackbars", &smin, 255); createTrackbar("Sat Max", "Trackbars", &smax, 255); createTrackbar("Val Min", "Trackbars", &vmin, 255); createTrackbar("Val Max", "Trackbars", &vmax, 255); while (true) { Scalar lower(hmin, smin, vmin); Scalar upper(hmax, smax, vmax); inRange(imgHSV, lower, upper, mask);//基于imgHSV进行一定范围的颜色检测,最后生成Image Mask imshow("Image", img); imshow("Image HSV", imgHSV); imshow("Image Mask", mask); waitKey(1); } } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31

第七章-形状/轮廓检测
Chapter 7 – Shape/Contour Detection- 1
7.1 形状/轮廓检测
#include#include #include #include using namespace cv; using namespace std; /// Color Detection // void getContours(Mat imgDil, Mat img) { vector<vector<Point>> contours; vector<Vec4i> hierarchy; findContours(imgDil, contours, hierarchy, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE); //drawContours(img, contours, -1, Scalar(255, 0, 255), 2); vector<vector<Point>> conPoly(contours.size()); vector<Rect> boundRect(contours.size()); for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++) //最核心的地方其实是检测出图形的边缘,然后根据边缘角度变化(例如三角形有三条边),矩形有四条边等对检测到的图形进行分类 { int area = contourArea(contours[i]); cout << area << endl; string objectType; if (area > 1000) { float peri = arcLength(contours[i], true); approxPolyDP(contours[i], conPoly[i], 0.02 * peri, true); cout << conPoly[i].size() << endl; boundRect[i] = boundingRect(conPoly[i]); int objCor = (int)conPoly[i].size(); if (objCor == 3) { objectType = "Tri"; } else if (objCor == 4) { float aspRatio = (float)boundRect[i].width / (float)boundRect[i].height; cout << aspRatio << endl; if (aspRatio > 0.95 && aspRatio < 1.05) { objectType = "Square"; } else { objectType = "Rect"; } } else if (objCor > 4) { objectType = "Circle"; } drawContours(img, conPoly, i, Scalar(255, 0, 255), 2); rectangle(img, boundRect[i].tl(), boundRect[i].br(), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 5); putText(img, objectType, { boundRect[i].x,boundRect[i].y - 5 }, FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1, Scalar(0, 69, 255), 2); } } } void main() { string path = "Resources/shapes.png"; Mat img = imread(path); Mat imgGray, imgBlur, imgCanny, imgDil, imgErode; // Preprocessing cvtColor(img, imgGray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY); GaussianBlur(imgGray, imgBlur, Size(3, 3), 3, 0); Canny(imgBlur, imgCanny, 25, 75); Mat kernel = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(3, 3)); dilate(imgCanny, imgDil, kernel); getContours(imgDil, img); imshow("Image", img); //imshow("Image Gray", imgGray); //imshow("Image Blur", imgBlur); //imshow("Image Canny", imgCanny); //imshow("Image Dil", imgDil); waitKey(0); } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
过程演示(不知道为啥拖动窗口就出现绿色了…)

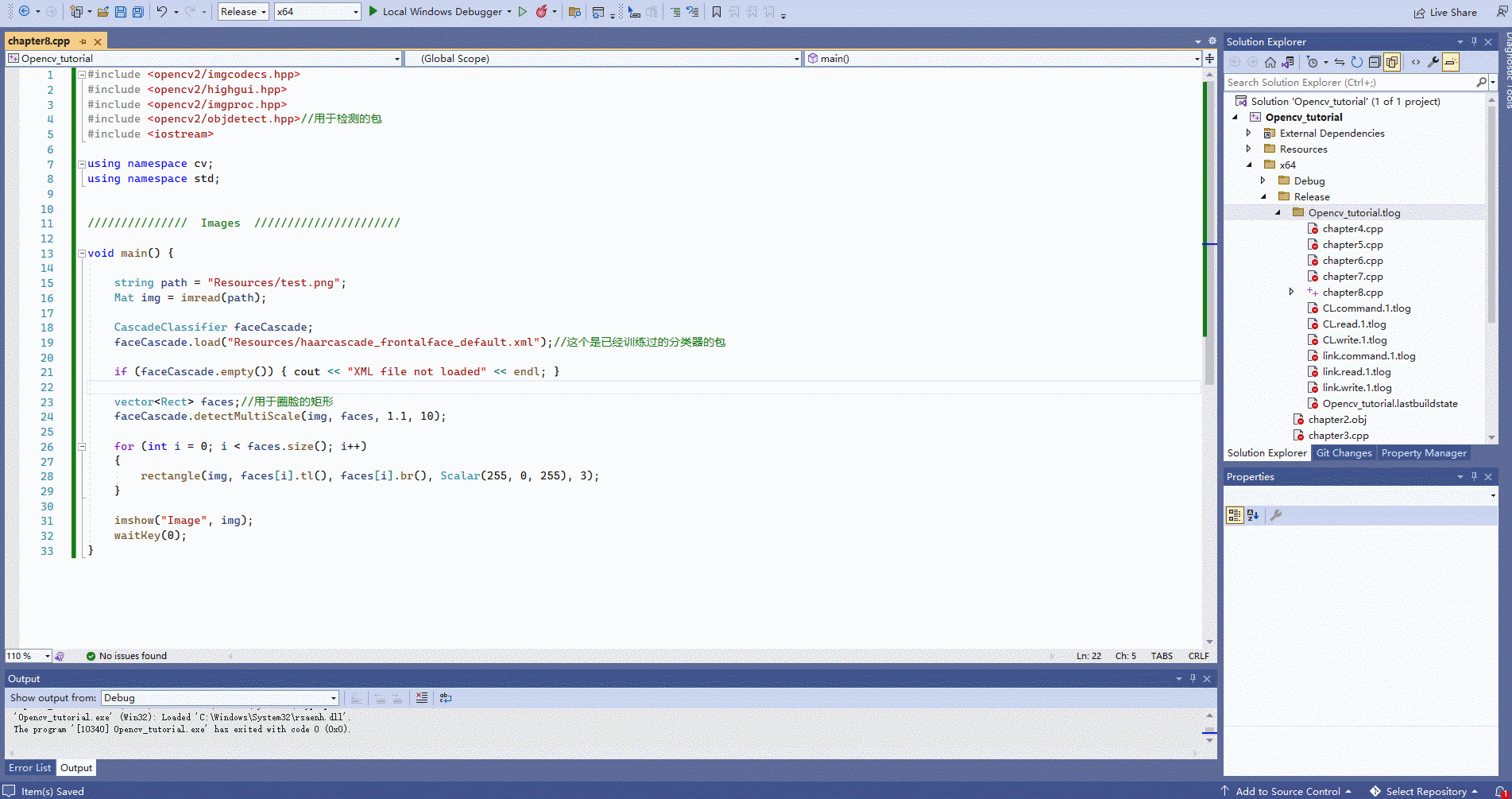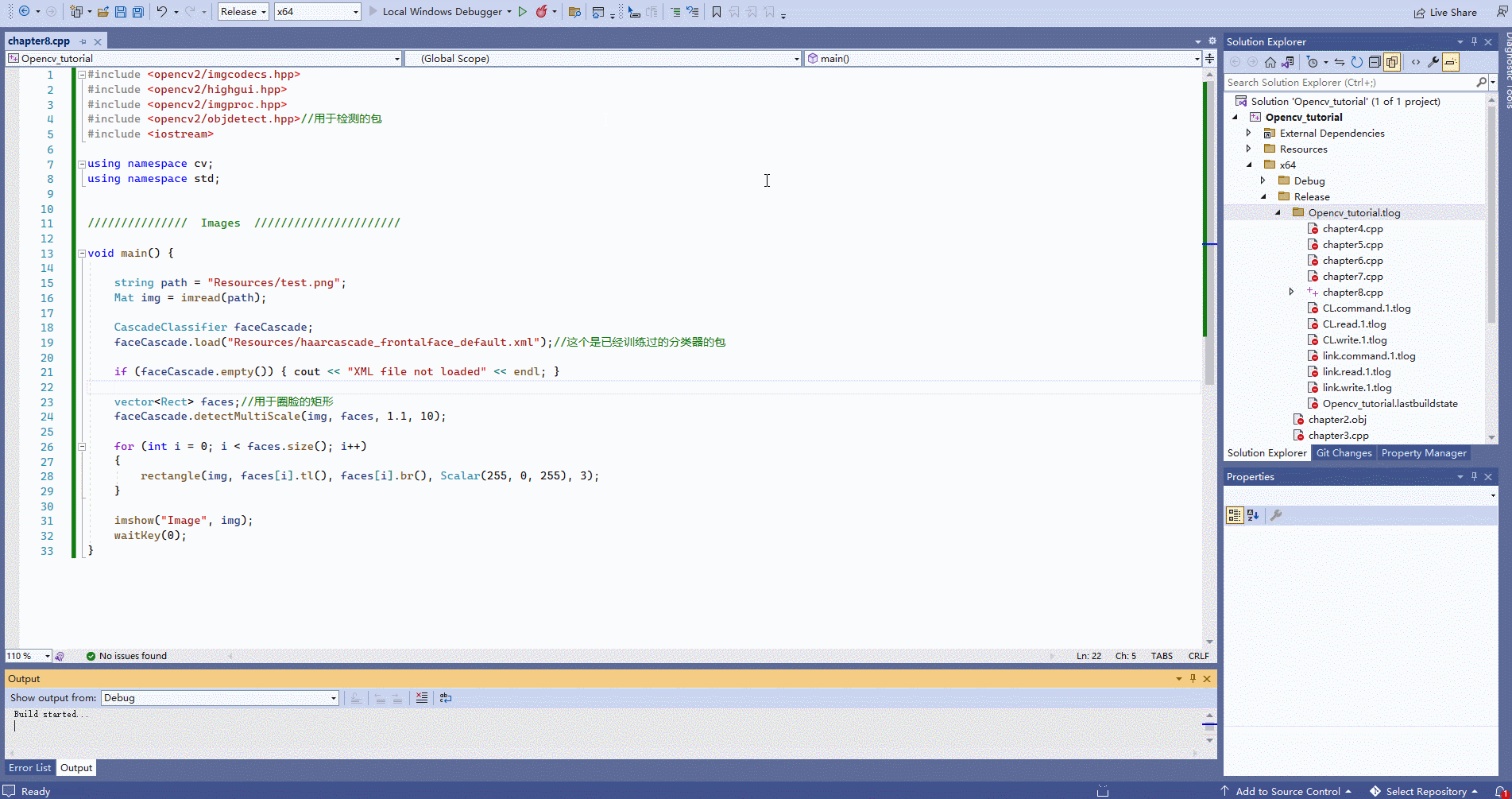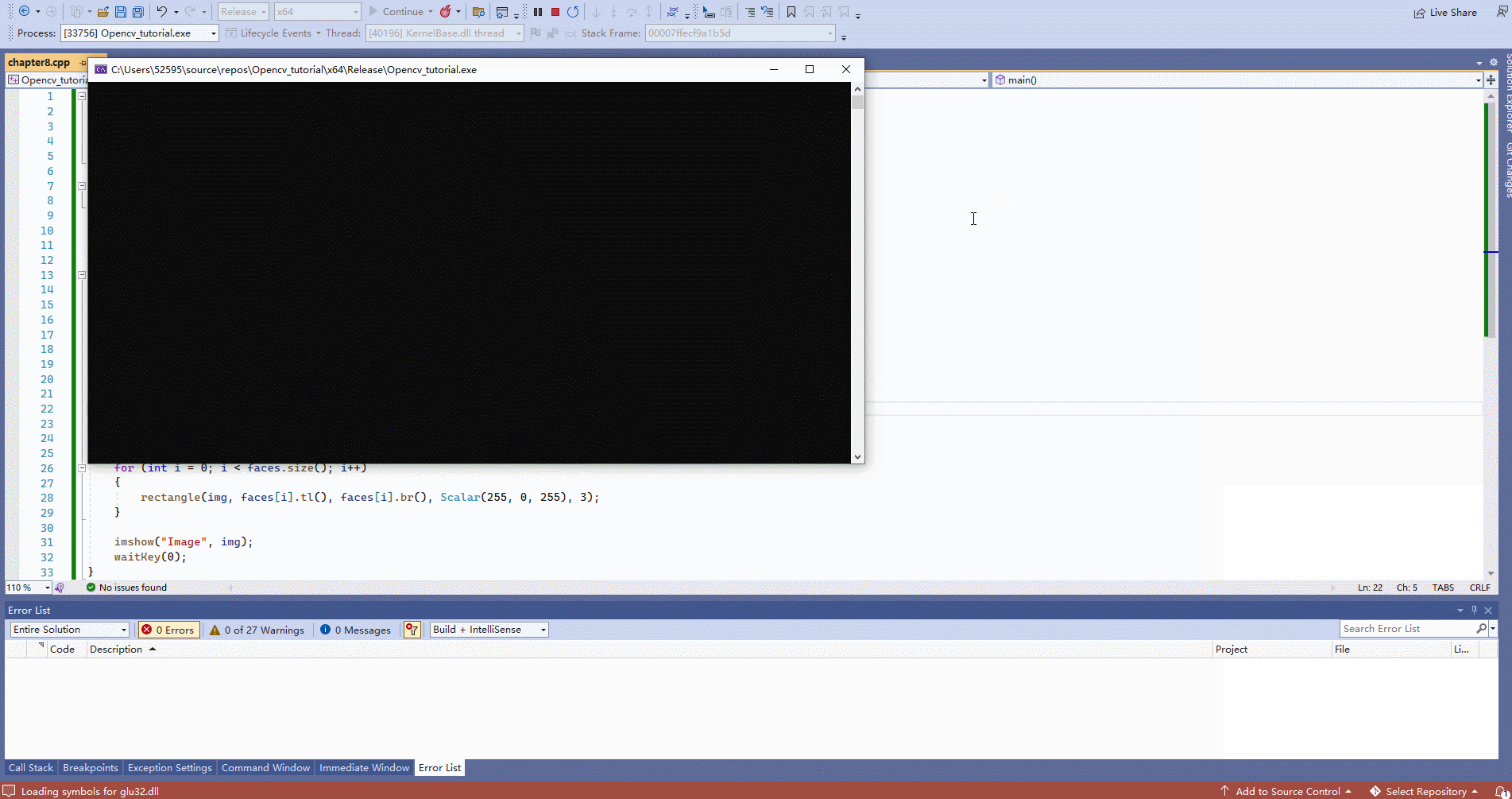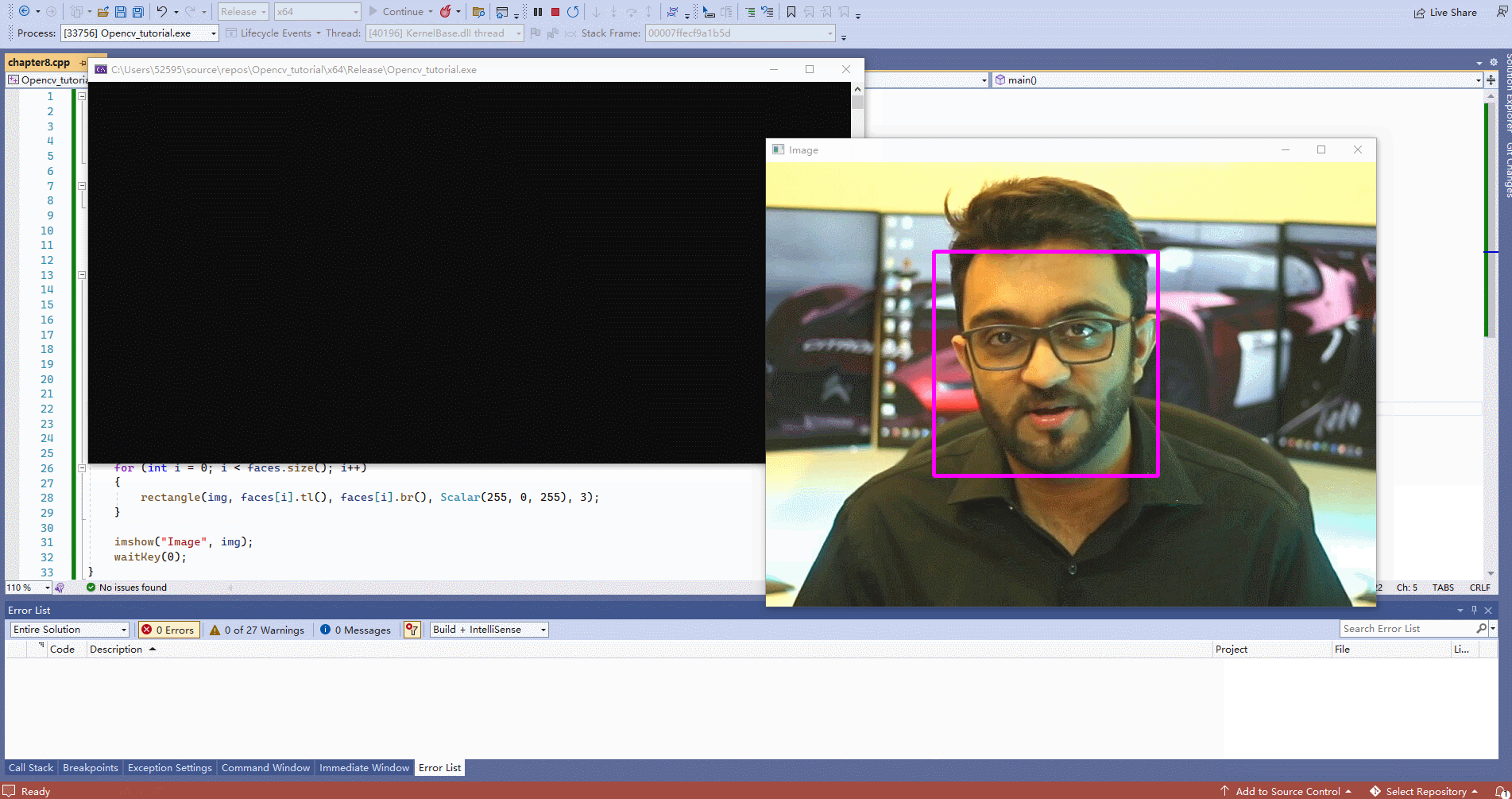
第八章-人脸识别
Chapter 8 – Face Detection- 1
#include#include #include #include //用于检测的包 #include using namespace cv; using namespace std; /// Images // void main() { string path = "Resources/test.png"; Mat img = imread(path); CascadeClassifier faceCascade; faceCascade.load("Resources/haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml");//这个是已经训练过的分类器的包 if (faceCascade.empty()) { cout << "XML file not loaded" << endl; } vector<Rect> faces;//用于圈脸的矩形 faceCascade.detectMultiScale(img, faces, 1.1, 10); for (int i = 0; i < faces.size(); i++) { rectangle(img, faces[i].tl(), faces[i].br(), Scalar(255, 0, 255), 3); } imshow("Image", img); waitKey(0); } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
小项目
1. 虚拟画家
Project 1 – Virtual Paint
#include#include #include #include using namespace cv; using namespace std; / Project 1 - Virtual Painter // Mat img; VideoCapture cap(0); vector<vector<int>> newPoints; // to store all points / COLOR VALUES // hmin, smin, vmin hmax, smax, vmax vector<vector<int>> myColors{ {124,48,117,143,170,255}, // Purple {68,72,156,102,126,255} };// Green vector<Scalar> myColorValues{ {255,0,255}, // Purple {0,255,0} };// Green Point getContours(Mat image) { vector<vector<Point>> contours; vector<Vec4i> hierarchy; findContours(image, contours, hierarchy, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE); //drawContours(img, contours, -1, Scalar(255, 0, 255), 2); vector<vector<Point>> conPoly(contours.size()); vector<Rect> boundRect(contours.size()); Point myPoint(0, 0); for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++) { int area = contourArea(contours[i]); cout << area << endl; string objectType; if (area > 1000) { float peri = arcLength(contours[i], true); approxPolyDP(contours[i], conPoly[i], 0.02 * peri, true); cout << conPoly[i].size() << endl; boundRect[i] = boundingRect(conPoly[i]); myPoint.x = boundRect[i].x + boundRect[i].width / 2; myPoint.y = boundRect[i].y; //drawContours(img, conPoly, i, Scalar(255, 0, 255), 2); //rectangle(img, boundRect[i].tl(), boundRect[i].br(), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 5); } } return myPoint; } vector<vector<int>> findColor(Mat img) { Mat imgHSV; cvtColor(img, imgHSV, COLOR_BGR2HSV); for (int i = 0; i < myColors.size(); i++) { Scalar lower(myColors[i][0], myColors[i][1], myColors[i][2]); Scalar upper(myColors[i][3], myColors[i][4], myColors[i][5]); Mat mask; inRange(imgHSV, lower, upper, mask); //imshow(to_string(i), mask); Point myPoint = getContours(mask); if (myPoint.x != 0 ) { newPoints.push_back({ myPoint.x,myPoint.y,i }); } } return newPoints; } void drawOnCanvas(vector<vector<int>> newPoints, vector<Scalar> myColorValues) { for (int i = 0; i < newPoints.size(); i++) { circle(img, Point(newPoints[i][0],newPoints[i][1]), 10, myColorValues[newPoints[i][2]], FILLED); } } void main() { while (true) { cap.read(img); newPoints = findColor(img); drawOnCanvas(newPoints, myColorValues); imshow("Image", img); waitKey(1); } } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
2. 文档扫描仪
Project 2 – Document Scanner
3. 虚拟画家
Project 1 – Virtual Paint
-
相关阅读:
【Leetcode每日一题:1662.检查俩个字符串数组是否相等~~~遍历+模拟+StringBuilder】
Unity优化技巧,此时无光胜有光
知识图谱从入门到应用——知识图谱的发展
基于STM32倒车雷达系统(OLED显示)(Proteus仿真+程序+设计报告)
直播切片想要快速批量制作应该怎么做?
【软件教程】如何用C++交叉编译出能在Android运行的ELF程序或so动态库
【Gazebo入门教程】第一讲 Gazebo的安装、UI界面、SDF文件介绍
Django入门1
(带教程)商业版SEO关键词按天计费系统:关键词排名优化、代理服务、手机自适应及搭建教程
八股整理(计网,os)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44649945/article/details/126379540
