-
ES6:ES6 的内置对象扩展
Array 的扩展方法
扩展运算符(展开语法)
扩展运算符可以将数组或者对象转为用逗号分隔的参数序列。
- let ary = [1, 2, 3];
- ...ary // 1, 2, 3
- console.log(...ary); // 1 2 3
- console.log(1, 2, 3)
为什么没有逗号,这个是因为被当做console.log的分割参数
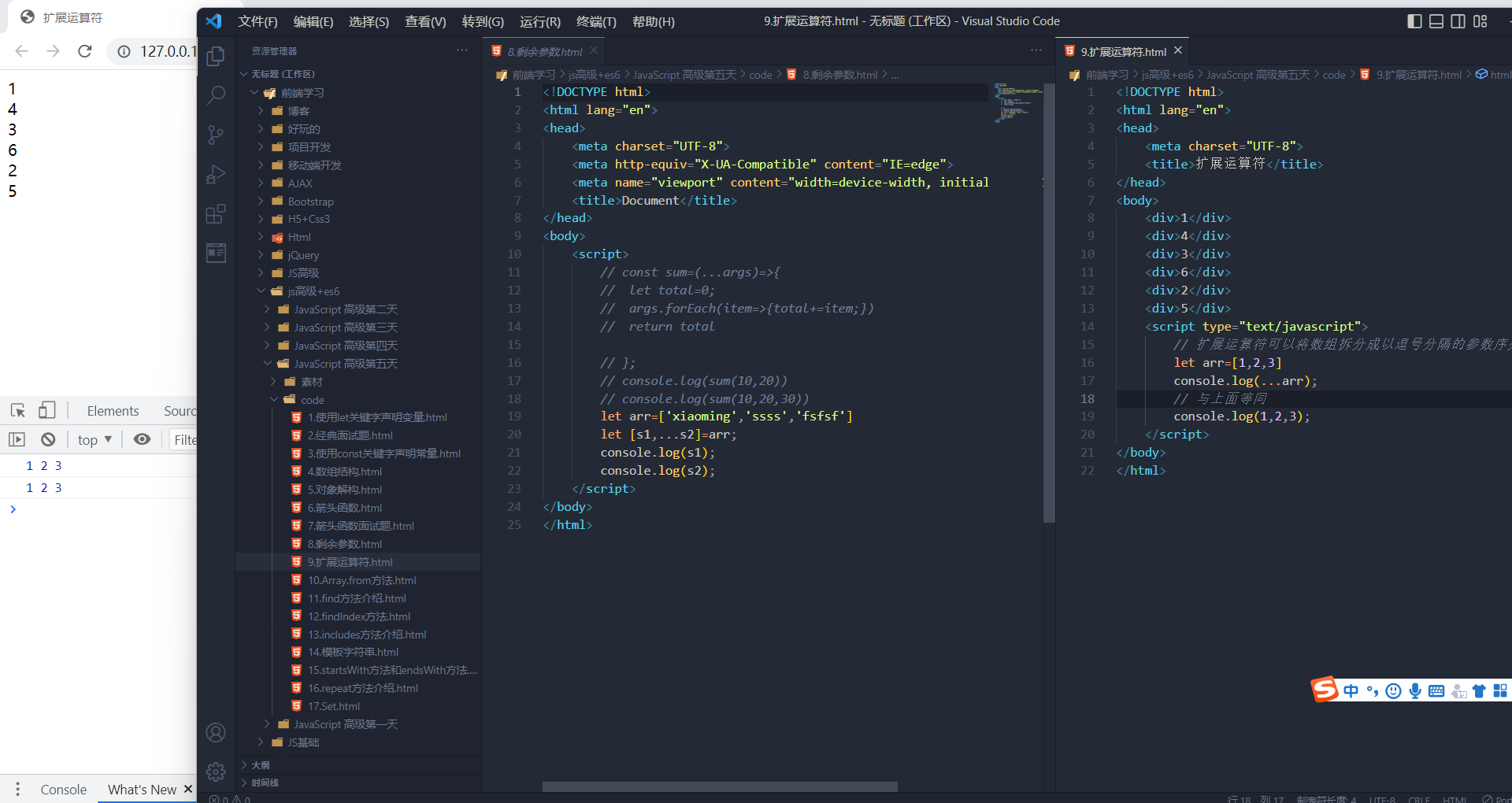
扩展运算符可以应用于合并数组。
- // 方法一
- let ary1 = [1, 2, 3]; let ary2 = [3, 4, 5];
- let ary3 = [...ary1, ...ary2];
- // 方法二
- ary1.push(...ary2);
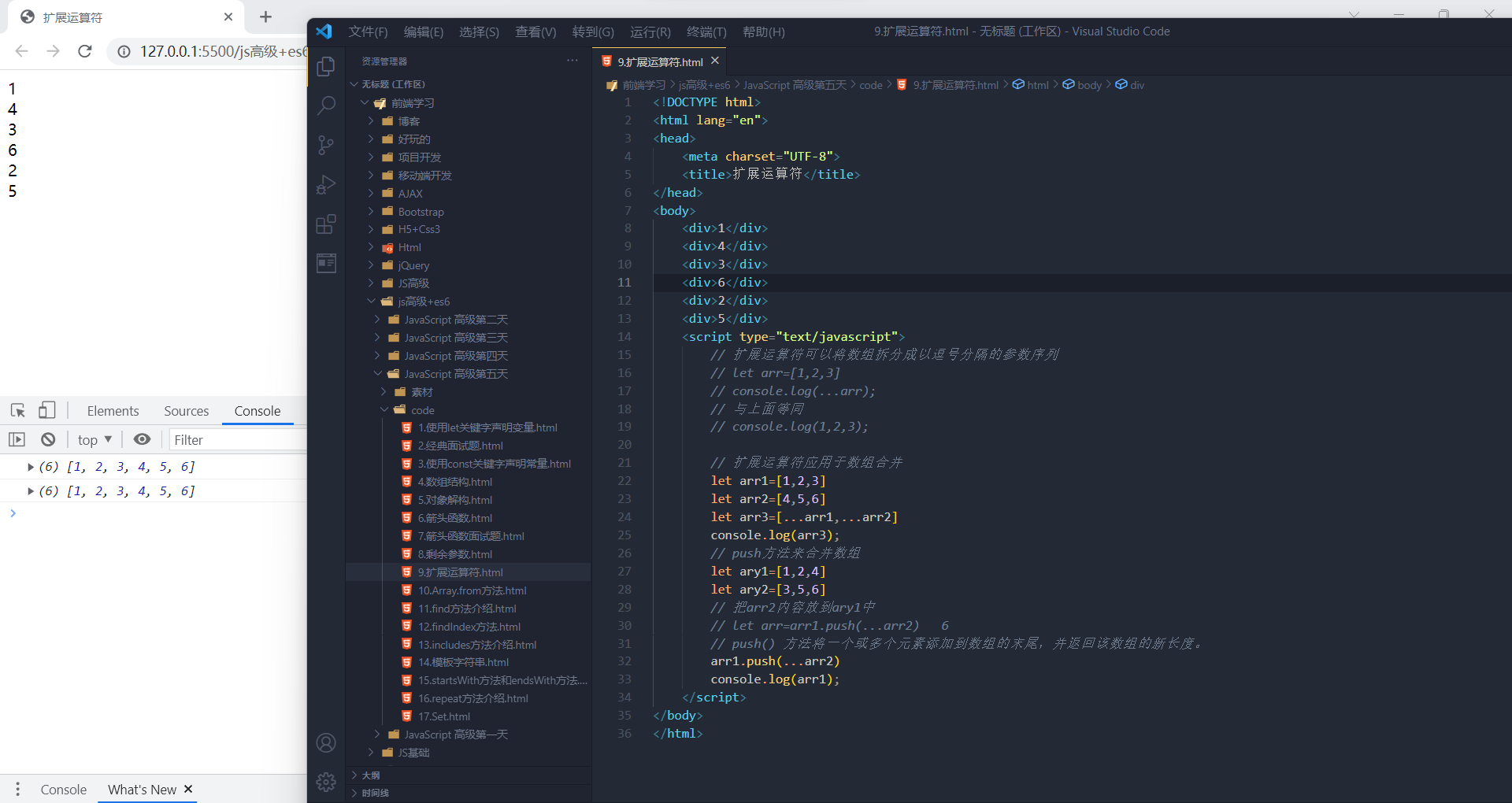
将类数组或可遍历对象转换为真正的数组
- let oDivs = document.getElementsByTagName('div');
- oDivs = [...oDivs];
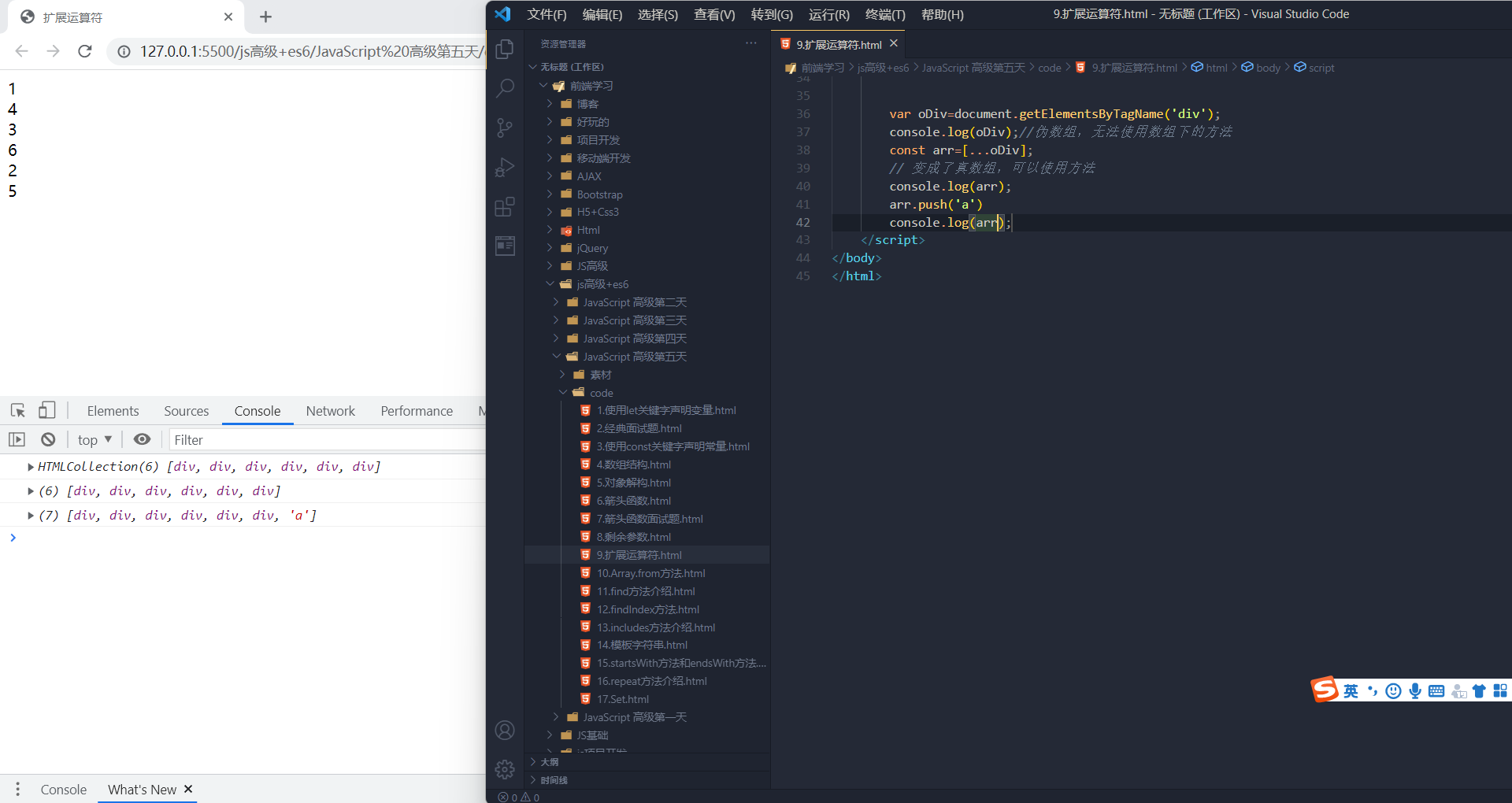 伪数组,无法使用数组下的方法,可以使用扩展运算符变成真正的数组
伪数组,无法使用数组下的方法,可以使用扩展运算符变成真正的数组构造函数方法:Array.from()
将类数组或可遍历对象转换为真正的数组
- let arrayLike = {
- '0': 'a',
- '1': 'b',
- '2': 'c',
- length: 3
- };
- let arr2 = Array.from(arrayLike); // ['a', 'b', 'c']

方法还可以接受第二个参数,作用类似于数组的map方法,用来对每个元素进行处理,将处理后的值放入返回的数组。
- let arrayLike = {
- "0": 1,
- "1": 2,
- "length": 2
- }
- let newAry = Array.from(aryLike, item => item *2)
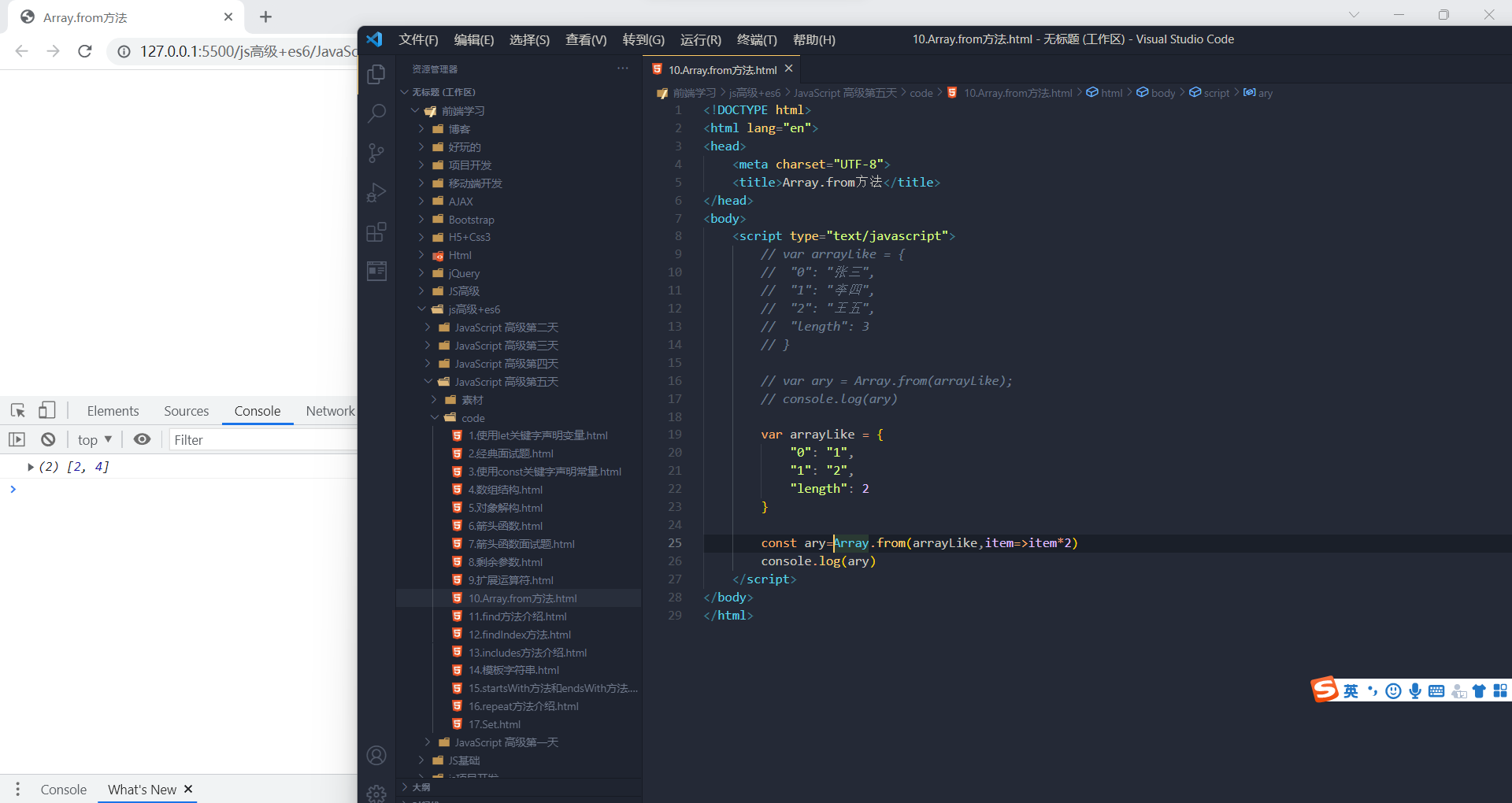
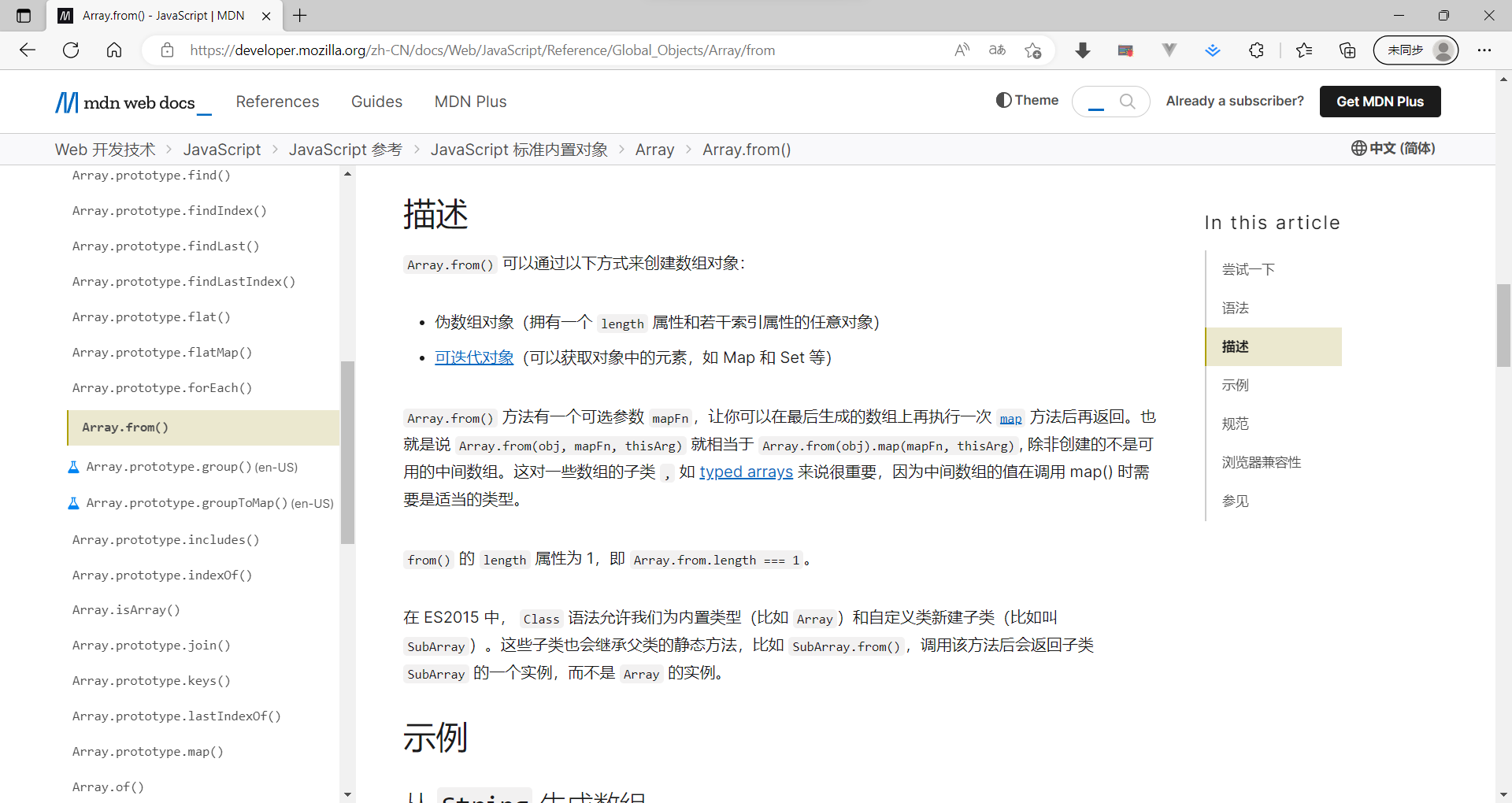 第二个参数,前面有几个数组成员,它就会执行几次
第二个参数,前面有几个数组成员,它就会执行几次 实例方法:find()
用于找出第一个符合条件的数组成员,如果没有找到返回undefined
- let ary = [{
- id: 1,
- name: '张三‘
- }, {
- id: 2,
- name: '李四‘
- }];
- let target = ary
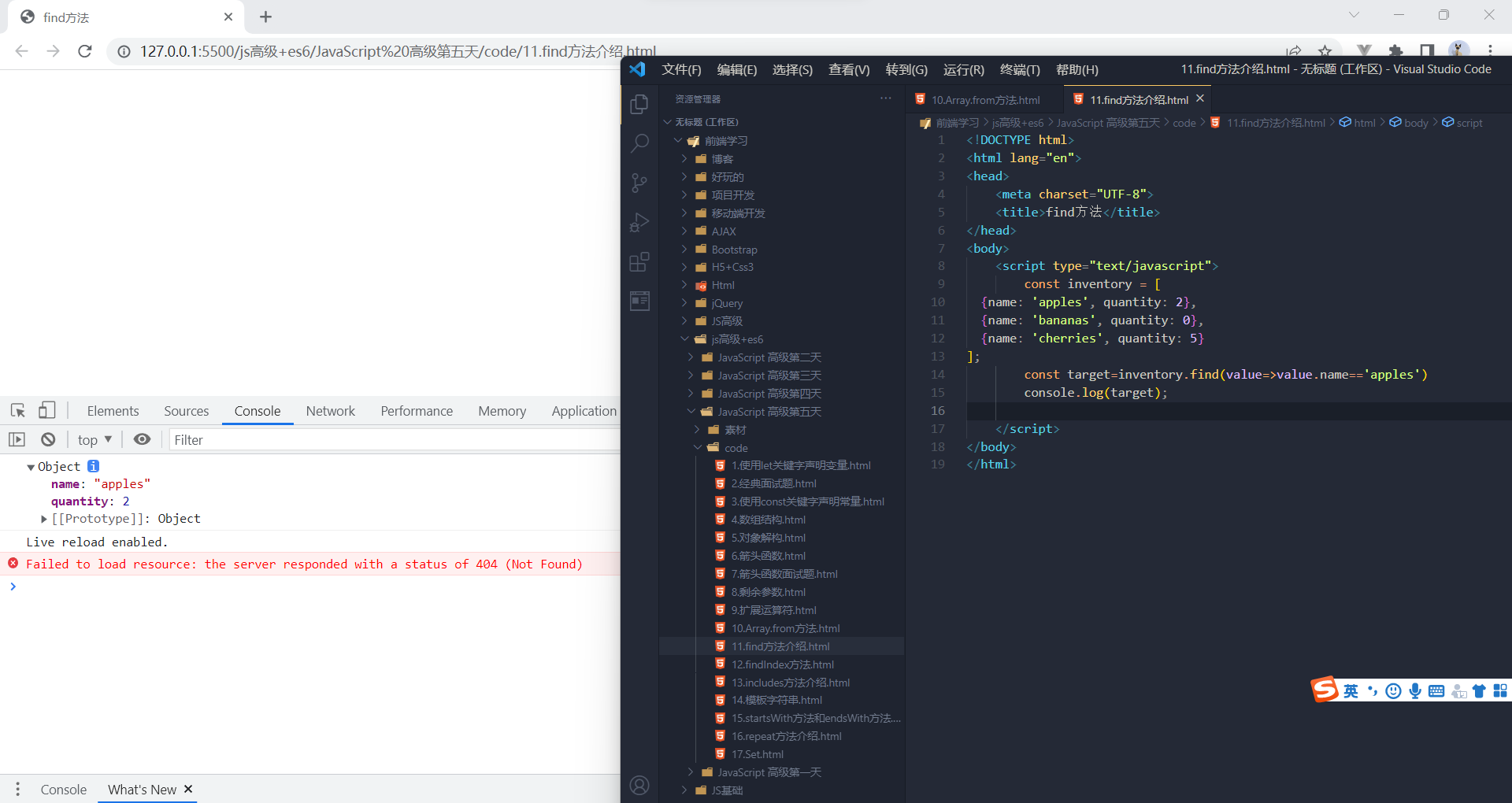
实例方法:findIndex()
用于找出第一个符合条件的数组成员的位置,如果没有找到返回-1
- let ary = [1, 5, 10, 15];
- let index = ary.findIndex((value, index) => value > 9);
- console.log(index); // 2
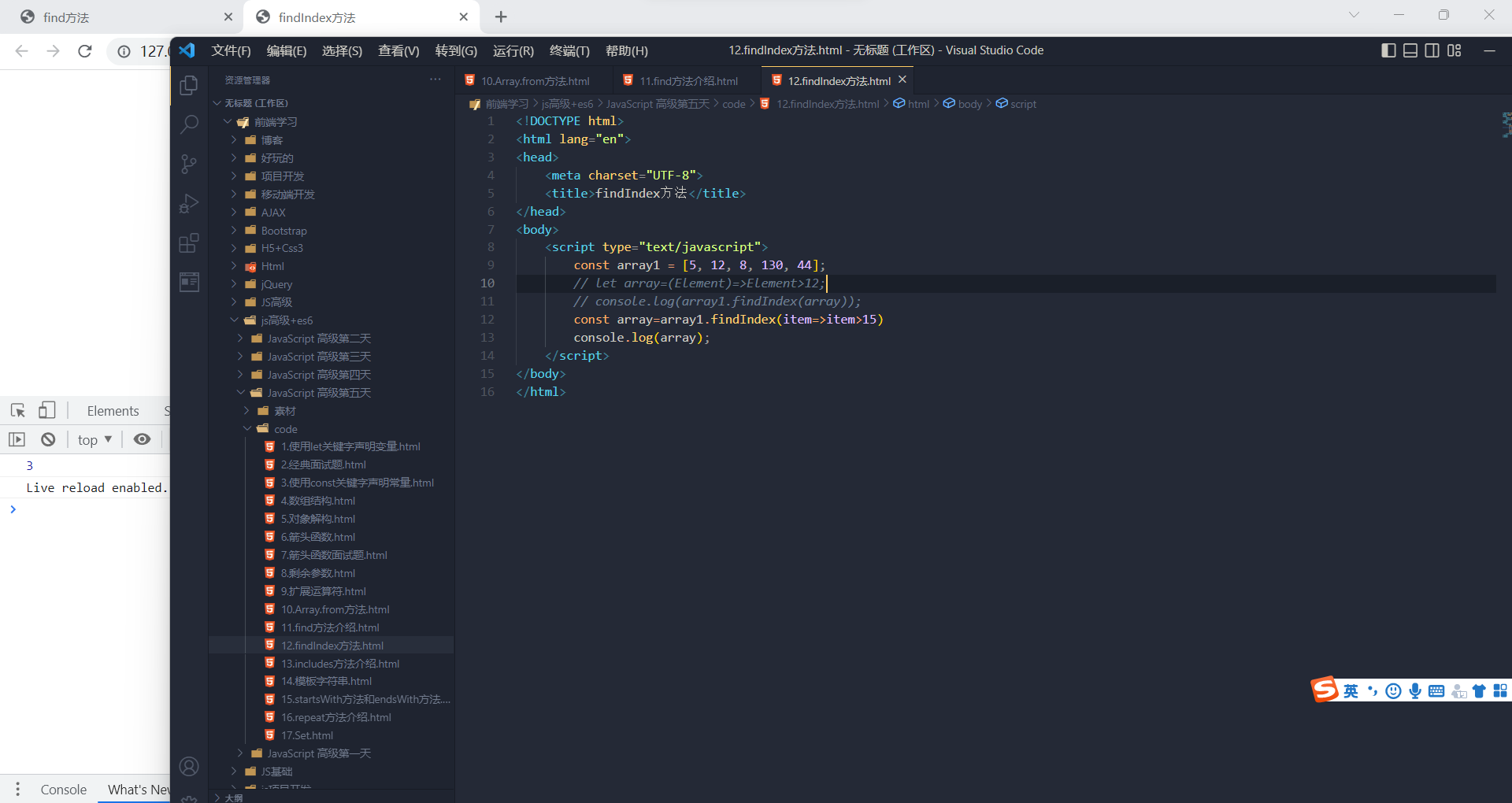
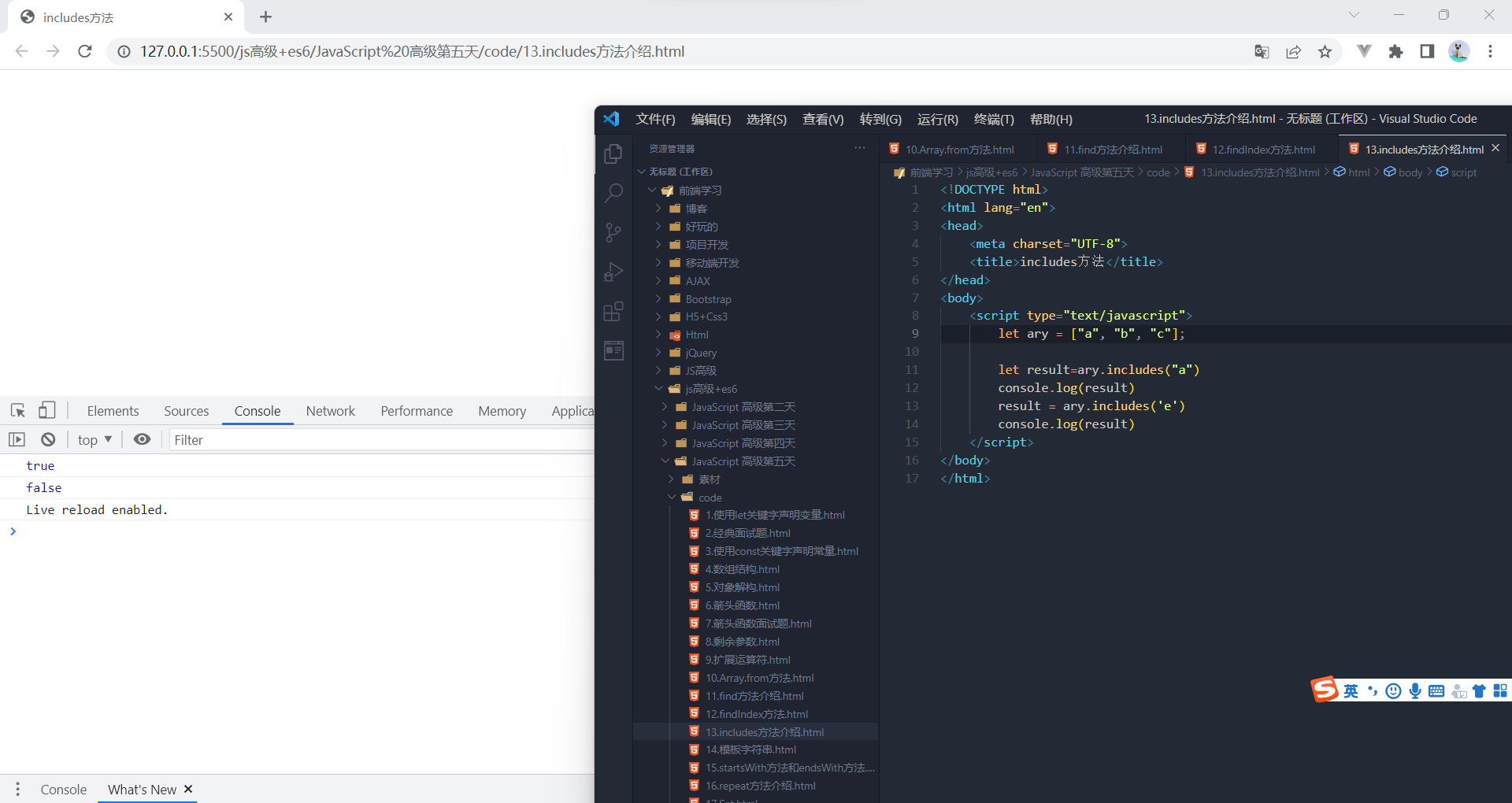
实例方法:includes()
表示某个数组是否包含给定的值,返回布尔值。
- [1, 2, 3].includes(2) // true
- [1, 2, 3].includes(4) // false
 String 的扩展方法
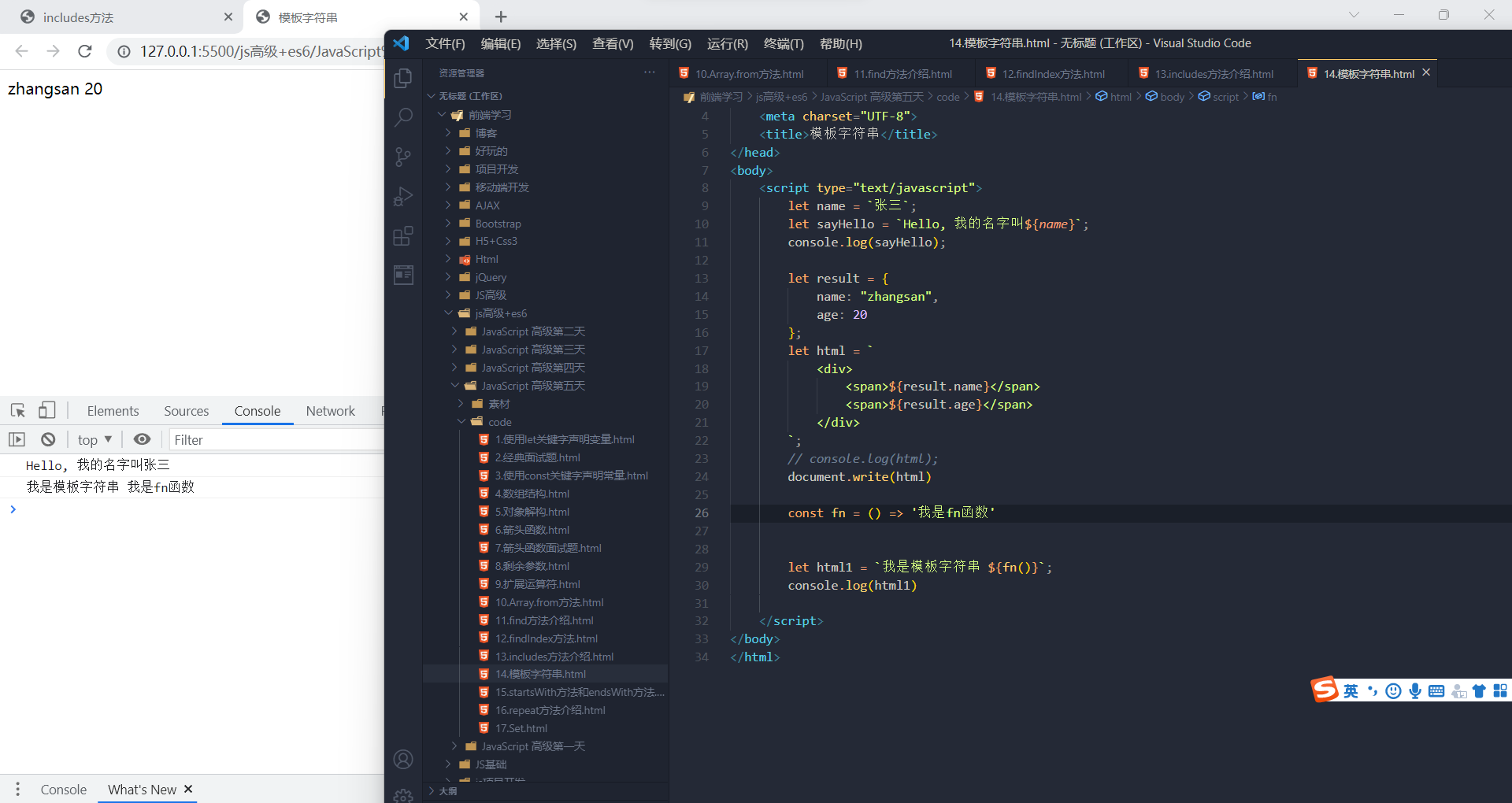
String 的扩展方法模板字符串
ES6新增的创建字符串的方式,使用反引号定义。
let name = `zhangsan`;模板字符串中可以解析变量。
- let name = '张三';
- let sayHello = `hello,my name is ${name}`; // hello, my name is zhangsan
模板字符串中可以换行
- let result = {
- name: 'zhangsan',
- age: 20, sex: '男'
- }
- let html = ` <div>
- <span>${result.name}</span>
- <span>${result.age}</span>
- <span>${result.sex}</span>
- </div> `;
在模板字符串中可以调用函数。
- const sayHello = function () {
- return '哈哈哈哈 追不到我吧 我就是这么强大';
- };
- let greet = `${sayHello()} 哈哈哈哈`; console.log(greet); // 哈哈哈哈 追不到我吧 我就是这么强大 哈哈哈哈
 实例方法:startsWith() 和 endsWith()
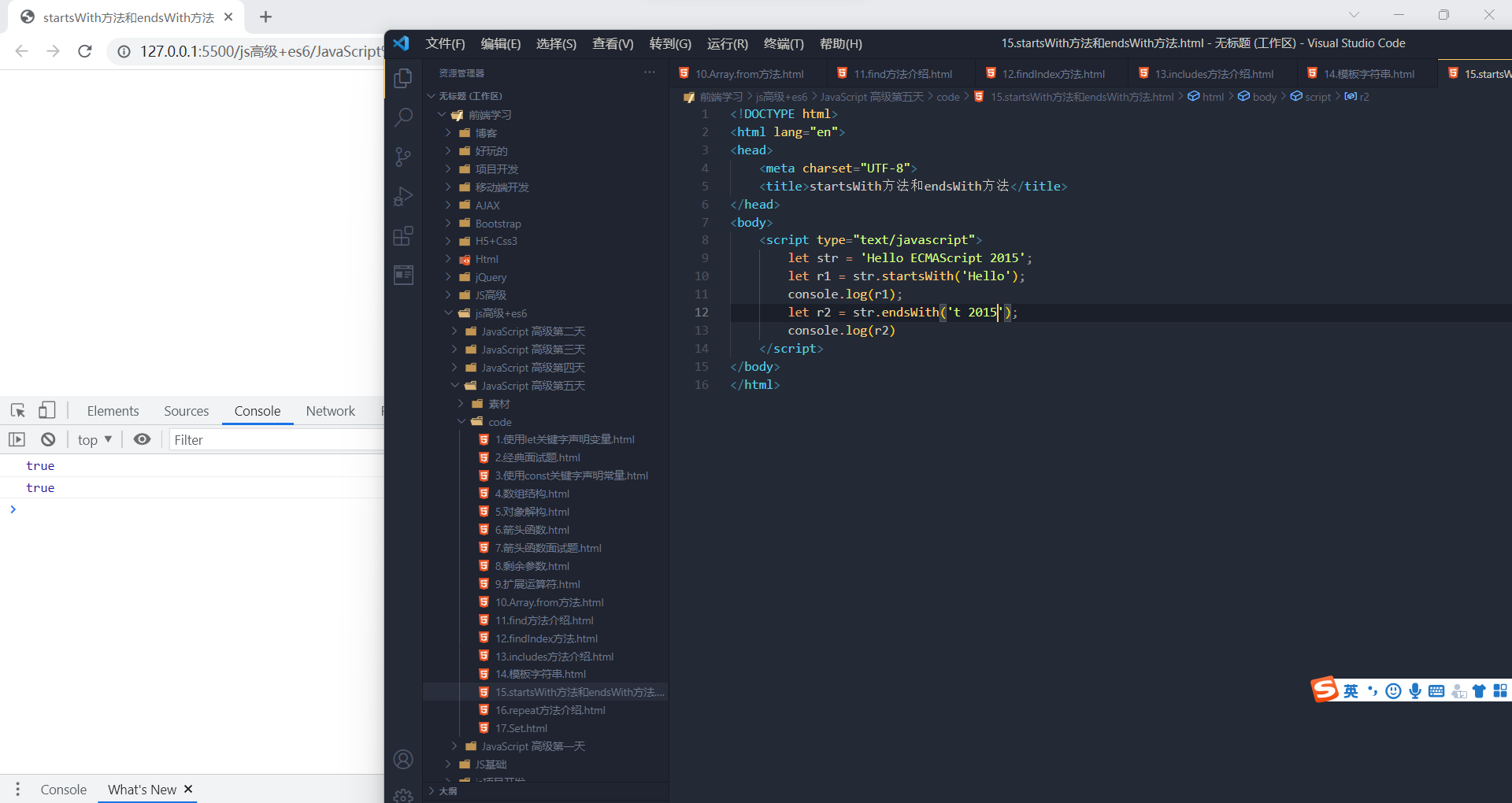
实例方法:startsWith() 和 endsWith()startsWith():表示参数字符串是否在原字符串的头部,返回布尔值
endsWith():表示参数字符串是否在原字符串的尾部,返回布尔值
- let str = 'Hello world!';
- str.startsWith('Hello') // true
- str.endsWith('!') // true
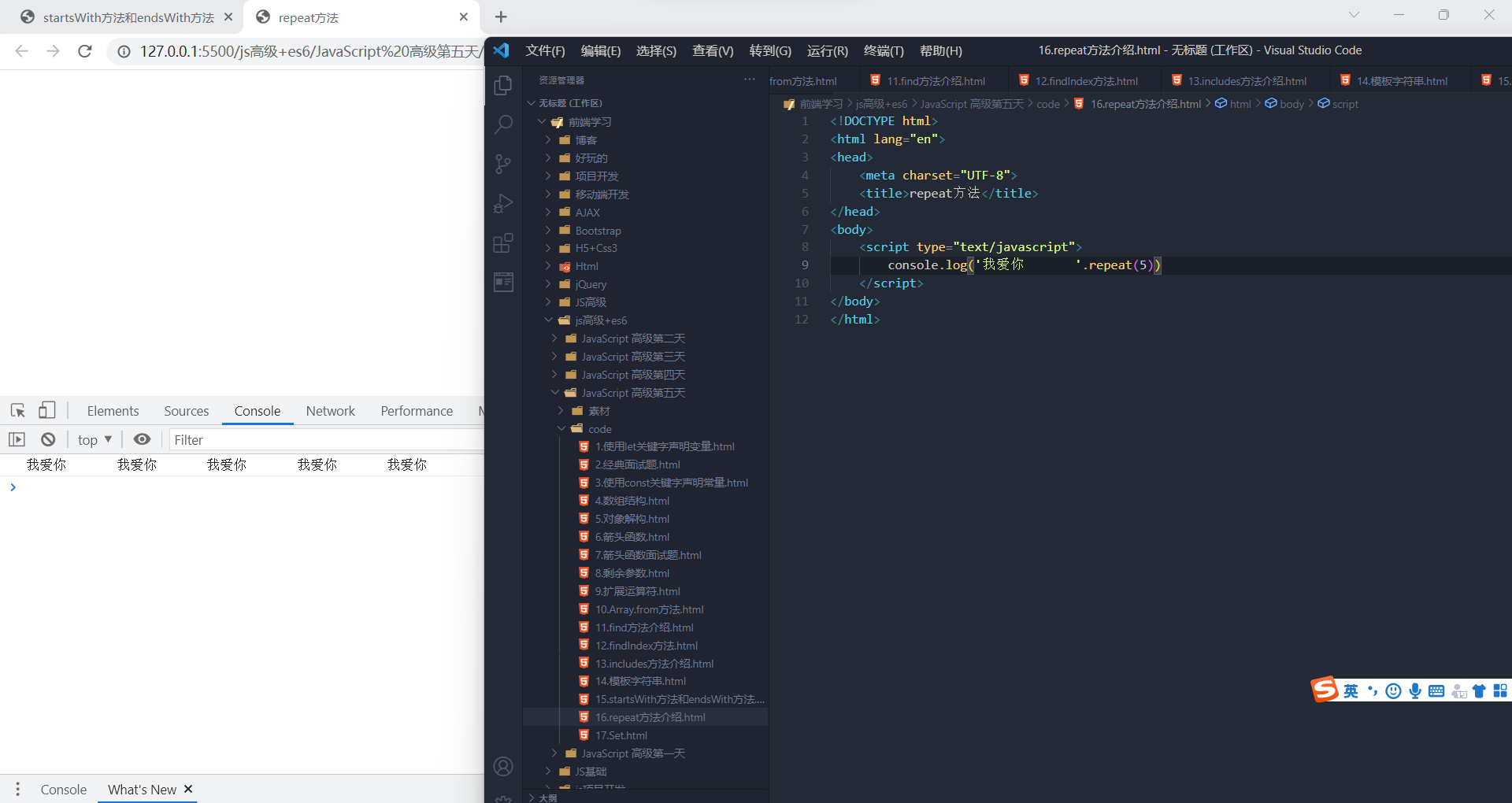
实例方法:repeat()
repeat方法表示将原字符串重复n次,返回一个新字符串。
- 'x'.repeat(3) // "xxx"
- 'hello'.repeat(2) // "hellohello"
Set 数据结构
ES6 提供了新的数据结构 Set。它类似于数组,但是成员的值都是唯一的,没有重复的值。
这个应用场景,像我们电商平台中搜索栏,来记录用户不是重复的搜索历史记录
Set本身是一个构造函数,用来生成 Set 数据结构。
const s = new Set();Set函数可以接受一个数组作为参数,用来初始化。
const set = new Set([1, 2, 3, 4, 4]);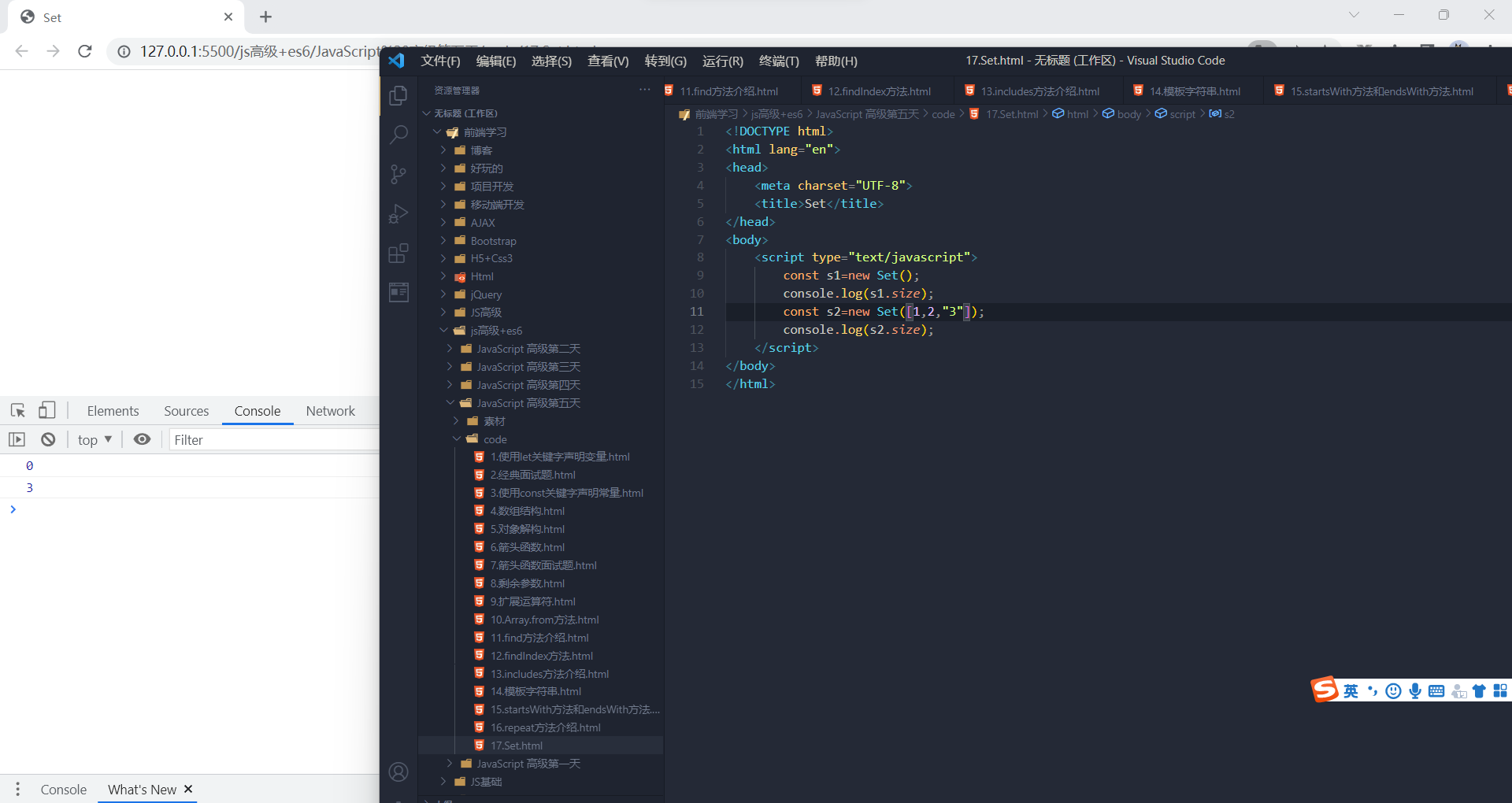
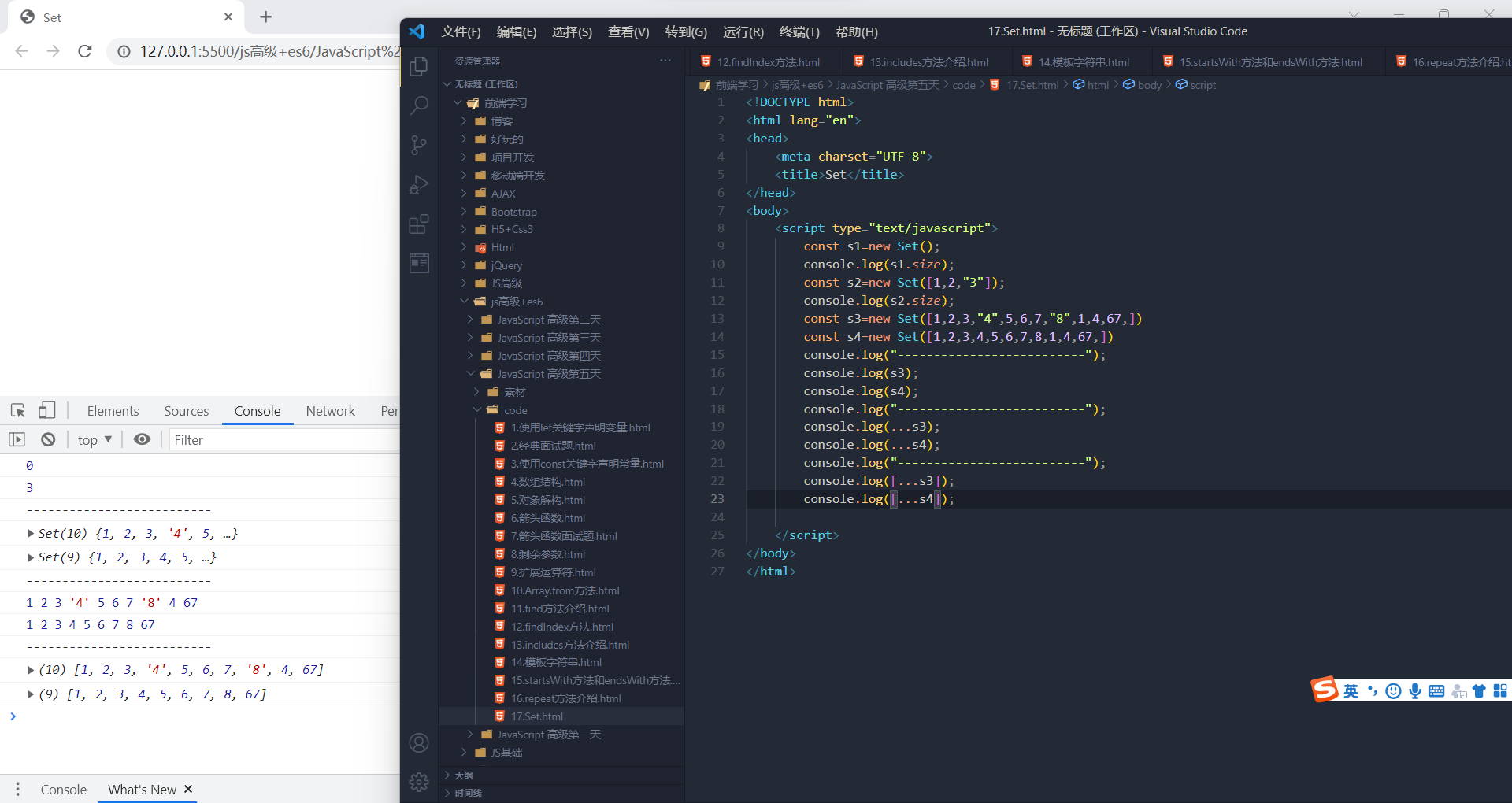 Set()数据结构自身会过滤掉数组中重复的元素
Set()数据结构自身会过滤掉数组中重复的元素 实例方法
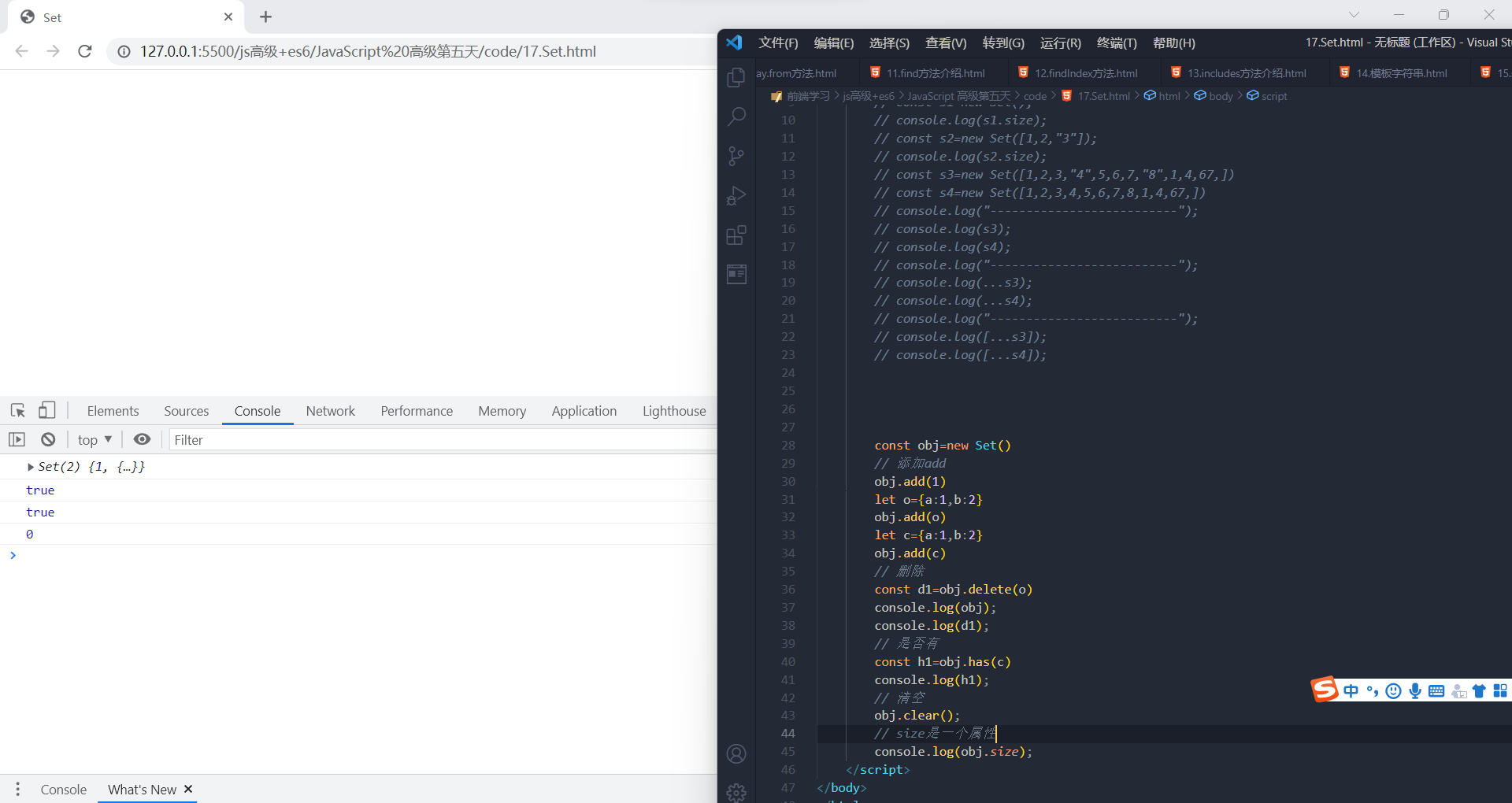
add(value):添加某个值,返回 Set 结构本身
delete(value):删除某个值,返回一个布尔值,表示删除是否成功
has(value):返回一个布尔值,表示该值是否为 Set 的成员
clear():清除所有成员,没有返回值
- const s = new Set();
- s.add(1).add(2).add(3); // 向 set 结构中添加值
- s.delete(2) // 删除 set 结构中的2值
- s.has(1) // 表示 set 结构中是否有1这个值 返回布尔值
- s.clear() // 清除 set 结构中的所有值
 遍历
遍历Set 结构的实例与数组一样,也拥有forEach方法,用于对每个成员执行某种操作,没有返回值。
s.forEach(value => console.log(value))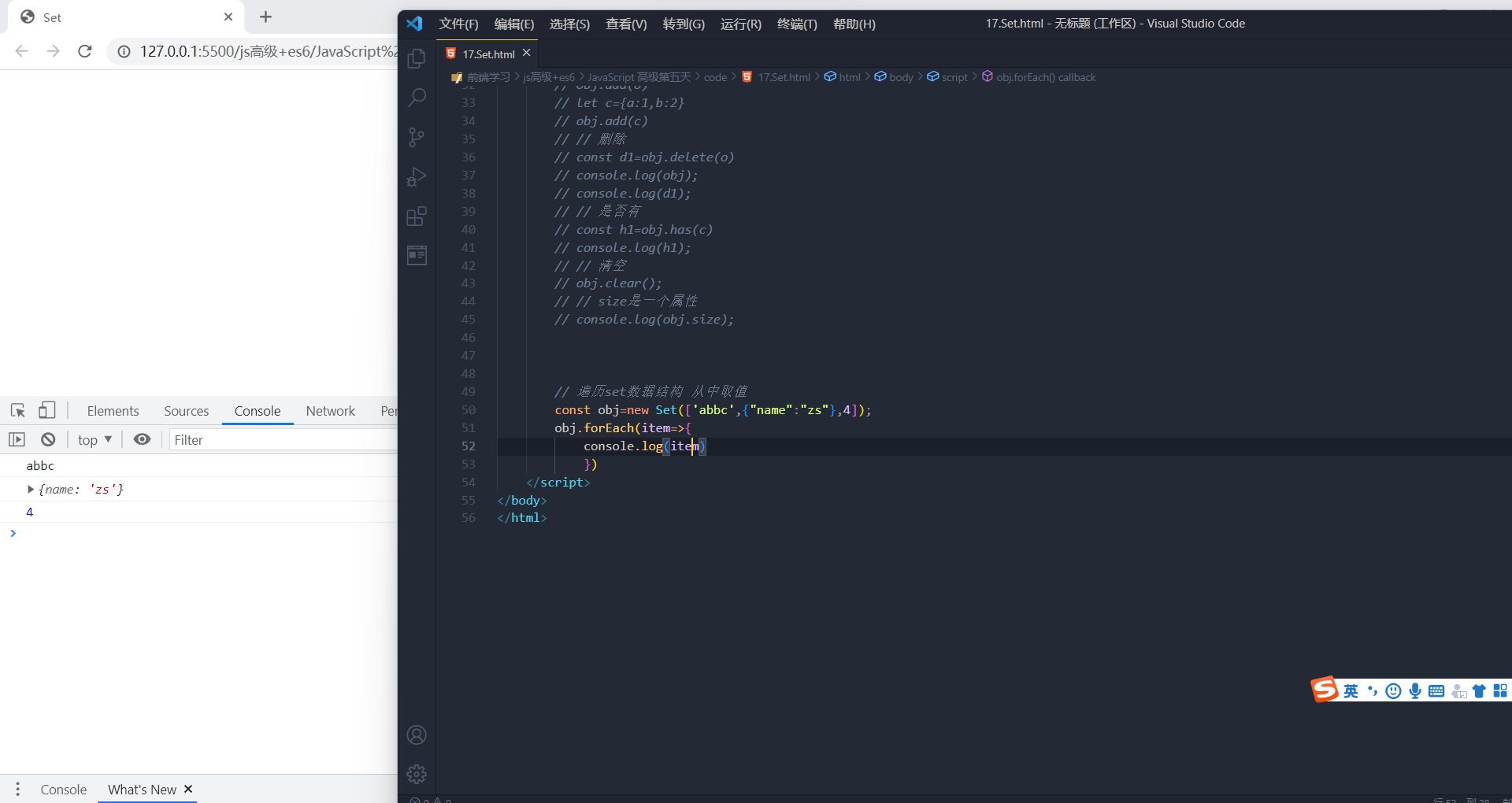
-
相关阅读:
【Vue篇】Vue 项目下载、介绍(详细版)
软件工程毕业设计课题(20)基于JAVA毕业设计在线选座购票电影院网站系统毕设作品项目
pytorch -- torch.nn.Module
C++ 基础入门 之 注释 ( // 和 /**/ )/变量 /常量 ( #define 和 const )/关键字/标识符(变量名)命名规则
Java电子招投标采购系统源码-适合于招标代理、政府采购、企业采购、等业务的企业
Kotlin学习之2
【论文笔记】policy-space response oracles (PSRO)
面试官:你对Redis缓存了解吗?面对这11道面试题你是否有很多问号?
python 性能优化实例练习二 —— 细节优化(ctypes等,未完)
使用U3D、pico开发VR(一)——将unity的场景在设备中呈现
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_64612659/article/details/128170925