-
Springboot RabbitMq源码解析之RabbitListener注解 (四)
1.RabbitListener注解介绍
RabbitListener是Springboot RabbitMq中经常用到的一个注解,将被RabbitListener注解的类和方法封装成MessageListener注入MessageListenerContainer- 当RabbitListener注解在方法上时,对应的方式就是Rabbit消息的监听器
- 当RabbitListener注解在类上时,和RabbitHandle注解配合使用,可以实现不同类型的消息的分发,类中被RabbitHandle注解的方法就是Rabbit消息的监听器
2.EnableRabbit和RabbitBootstrapConfiguration



通过自动配置类RabbitAutoConfiguration将EnableRabbit引入,而EnableRabbit又通过import注解引入了配置类RabbitBootstrapConfiguration
public class RabbitBootstrapConfiguration implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(@Nullable AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition( RabbitListenerConfigUtils.RABBIT_LISTENER_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { registry.registerBeanDefinition(RabbitListenerConfigUtils.RABBIT_LISTENER_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME, new RootBeanDefinition(RabbitListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class)); } if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(RabbitListenerConfigUtils.RABBIT_LISTENER_ENDPOINT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) { registry.registerBeanDefinition(RabbitListenerConfigUtils.RABBIT_LISTENER_ENDPOINT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, new RootBeanDefinition(RabbitListenerEndpointRegistry.class)); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
容器Ioc中注入RabbitListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor和RabbitListenerEndpointRegistry
3.RabbitListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
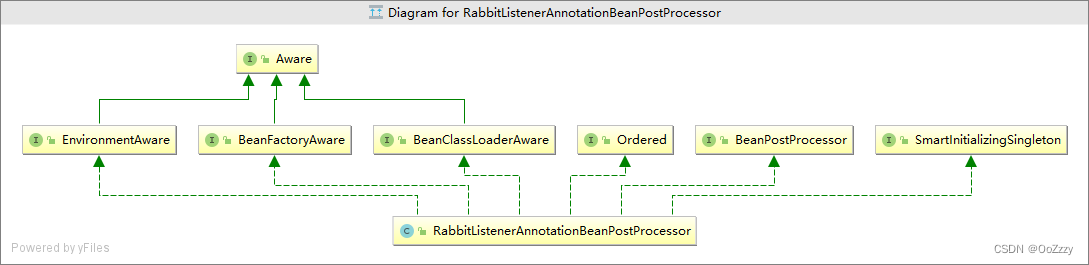
RabbitListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类实现了BeanPostProcessor,Ordered,BeanFactoryAware,BeanClassLoaderAware,EnvironmentAware,SmartInitializingSingleton接口,Ordered表示处理顺序,BeanFactoryAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware主要用于获取对应的BeanFactory,BeanClassLoader, Environment属性,我们主要关注从SmartInitializingSingleton和BeanPostProcessor继承的方法
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() { this.registrar.setBeanFactory(this.beanFactory); if (this.beanFactory instanceof ListableBeanFactory) { Map<String, RabbitListenerConfigurer> instances = ((ListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory).getBeansOfType(RabbitListenerConfigurer.class); for (RabbitListenerConfigurer configurer : instances.values()) { configurer.configureRabbitListeners(this.registrar); } } if (this.registrar.getEndpointRegistry() == null) { if (this.endpointRegistry == null) { Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "BeanFactory must be set to find endpoint registry by bean name"); this.endpointRegistry = this.beanFactory.getBean( RabbitListenerConfigUtils.RABBIT_LISTENER_ENDPOINT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, RabbitListenerEndpointRegistry.class); } this.registrar.setEndpointRegistry(this.endpointRegistry); } if (this.containerFactoryBeanName != null) { this.registrar.setContainerFactoryBeanName(this.containerFactoryBeanName); } // Set the custom handler method factory once resolved by the configurer MessageHandlerMethodFactory handlerMethodFactory = this.registrar.getMessageHandlerMethodFactory(); if (handlerMethodFactory != null) { this.messageHandlerMethodFactory.setMessageHandlerMethodFactory(handlerMethodFactory); } // Actually register all listeners this.registrar.afterPropertiesSet(); // clear the cache - prototype beans will be re-cached. this.typeCache.clear(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
初始化工作,主要是基于自定义配置RabbitListenerConfigurer进行RabbitListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(尤其是registrar元素)的初始化
- postProcessBeforeInitialization
- postProcessAfterInitialization


@Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(final Object bean, final String beanName) throws BeansException { Class<?> targetClass = AopUtils.getTargetClass(bean); final TypeMetadata metadata = this.typeCache.computeIfAbsent(targetClass, this::buildMetadata); for (ListenerMethod lm : metadata.listenerMethods) { for (RabbitListener rabbitListener : lm.annotations) { processAmqpListener(rabbitListener, lm.method, bean, beanName); } } if (metadata.handlerMethods.length > 0) { processMultiMethodListeners(metadata.classAnnotations, metadata.handlerMethods, bean, beanName); } return bean; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
对RabbitListener注解查找和解析
- RabbitListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#buildMetadata
- RabbitListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#processAmqpListener
- RabbitListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#processMultiMethodListeners
4.对RabbitListener注解的解析
RabbitListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#buildMetadata
private TypeMetadata buildMetadata(Class<?> targetClass) { Collection<RabbitListener> classLevelListeners = findListenerAnnotations(targetClass); final boolean hasClassLevelListeners = classLevelListeners.size() > 0; final List<ListenerMethod> methods = new ArrayList<>(); final List<Method> multiMethods = new ArrayList<>(); ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(targetClass, method -> { Collection<RabbitListener> listenerAnnotations = findListenerAnnotations(method); if (listenerAnnotations.size() > 0) { methods.add(new ListenerMethod(method, listenerAnnotations.toArray(new RabbitListener[listenerAnnotations.size()]))); } if (hasClassLevelListeners) { RabbitHandler rabbitHandler = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, RabbitHandler.class); if (rabbitHandler != null) { multiMethods.add(method); } } }, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS); if (methods.isEmpty() && multiMethods.isEmpty()) { return TypeMetadata.EMPTY; } return new TypeMetadata( methods.toArray(new ListenerMethod[methods.size()]), multiMethods.toArray(new Method[multiMethods.size()]), classLevelListeners.toArray(new RabbitListener[classLevelListeners.size()])); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
RabbitListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor就是针对每一个bean类进行解析,针对类上的
RabbitListener注解、方法上的RabbitHandle注解和方法上的RabbitListener注解解析后封装到TypeMetadata类中通过RabbitListenerAnotationBeanPostProcessor#buildMetadata查找并封装成TypeMetadata分别交给
processAmqpListener和processMultiMethodListeners进行解析protected void processAmqpListener(RabbitListener rabbitListener, Method method, Object bean, String beanName) { Method methodToUse = checkProxy(method, bean); MethodRabbitListenerEndpoint endpoint = new MethodRabbitListenerEndpoint(); endpoint.setMethod(methodToUse); endpoint.setBeanFactory(this.beanFactory); endpoint.setReturnExceptions(resolveExpressionAsBoolean(rabbitListener.returnExceptions())); String errorHandlerBeanName = resolveExpressionAsString(rabbitListener.errorHandler(), "errorHandler"); if (StringUtils.hasText(errorHandlerBeanName)) { endpoint.setErrorHandler(this.beanFactory.getBean(errorHandlerBeanName, RabbitListenerErrorHandler.class)); } processListener(endpoint, rabbitListener, bean, methodToUse, beanName); } private void processMultiMethodListeners(RabbitListener[] classLevelListeners, Method[] multiMethods, Object bean, String beanName) { List<Method> checkedMethods = new ArrayList<Method>(); for (Method method : multiMethods) { checkedMethods.add(checkProxy(method, bean)); } for (RabbitListener classLevelListener : classLevelListeners) { MultiMethodRabbitListenerEndpoint endpoint = new MultiMethodRabbitListenerEndpoint(checkedMethods, bean); endpoint.setBeanFactory(this.beanFactory); processListener(endpoint, classLevelListener, bean, bean.getClass(), beanName); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
RabbitListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#processAmqpListener针对被RabbitListener注解的方法进行解析,
RabbitListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessot#processMultiMethodListeners针对RabbitListener注解的类中被RabbitHandle注解的方法进行解析新建
MultiMethodRabbitListenerEndpoint对象,针对两种方式的差异进行部分属性的初始化后交给RabbitListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor进行后续处理processListenerprotected void processListener(MethodRabbitListenerEndpoint endpoint, RabbitListener rabbitListener, Object bean, Object adminTarget, String beanName) { endpoint.setBean(bean); endpoint.setMessageHandlerMethodFactory(this.messageHandlerMethodFactory); endpoint.setId(getEndpointId(rabbitListener)); endpoint.setQueueNames(resolveQueues(rabbitListener)); endpoint.setConcurrency(resolveExpressionAsStringOrInteger(rabbitListener.concurrency(), "concurrency")); String group = rabbitListener.group(); if (StringUtils.hasText(group)) { Object resolvedGroup = resolveExpression(group); if (resolvedGroup instanceof String) { endpoint.setGroup((String) resolvedGroup); } } String autoStartup = rabbitListener.autoStartup(); if (StringUtils.hasText(autoStartup)) { endpoint.setAutoStartup(resolveExpressionAsBoolean(autoStartup)); } endpoint.setExclusive(rabbitListener.exclusive()); String priority = resolve(rabbitListener.priority()); if (StringUtils.hasText(priority)) { try { endpoint.setPriority(Integer.valueOf(priority)); } catch (NumberFormatException ex) { throw new BeanInitializationException("Invalid priority value for " + rabbitListener + " (must be an integer)", ex); } } String rabbitAdmin = resolve(rabbitListener.admin()); if (StringUtils.hasText(rabbitAdmin)) { Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "BeanFactory must be set to resolve RabbitAdmin by bean name"); try { endpoint.setAdmin(this.beanFactory.getBean(rabbitAdmin, RabbitAdmin.class)); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not register rabbit listener endpoint on [" + adminTarget + "], no " + RabbitAdmin.class.getSimpleName() + " with id '" + rabbitAdmin + "' was found in the application context", ex); } } RabbitListenerContainerFactory<?> factory = null; String containerFactoryBeanName = resolve(rabbitListener.containerFactory()); if (StringUtils.hasText(containerFactoryBeanName)) { Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "BeanFactory must be set to obtain container factory by bean name"); try { factory = this.beanFactory.getBean(containerFactoryBeanName, RabbitListenerContainerFactory.class); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not register rabbit listener endpoint on [" + adminTarget + "] for bean " + beanName + ", no " + RabbitListenerContainerFactory.class.getSimpleName() + " with id '" + containerFactoryBeanName + "' was found in the application context", ex); } } this.registrar.registerEndpoint(endpoint, factory); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
根据RabbitListener注解的属性进行
MethodRabbitListenerEndpoint的属性设置和校验,最后通过RabbitListenerEndpointRegistrar#registerEndpoint方法将MethodRabbitListenerEndpoint注入容器RabbitListenerContainerFactory5.RabbitListenerEndpointRegistrar
@Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { registerAllEndpoints(); } protected void registerAllEndpoints() { synchronized (this.endpointDescriptors) { for (AmqpListenerEndpointDescriptor descriptor : this.endpointDescriptors) { this.endpointRegistry.registerListenerContainer( descriptor.endpoint, resolveContainerFactory(descriptor)); } this.startImmediately = true; // trigger immediate startup } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
RabbitListenerEndpointRegistrar#registerEndpoint
public void registerEndpoint(RabbitListenerEndpoint endpoint, RabbitListenerContainerFactory<?> factory) { Assert.notNull(endpoint, "Endpoint must be set"); Assert.hasText(endpoint.getId(), "Endpoint id must be set"); // Factory may be null, we defer the resolution right before actually creating the container AmqpListenerEndpointDescriptor descriptor = new AmqpListenerEndpointDescriptor(endpoint, factory); synchronized (this.endpointDescriptors) { if (this.startImmediately) { // Register and start immediately this.endpointRegistry.registerListenerContainer(descriptor.endpoint, resolveContainerFactory(descriptor), true); } else { this.endpointDescriptors.add(descriptor); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
RabbitListenerEndpointRegistry#registerListenerContainer进行注册监听器的容器
RabbitListenerEndpointRegistry#registerListenerContainer
public void registerListenerContainer(RabbitListenerEndpoint endpoint, RabbitListenerContainerFactory<?> factory, boolean startImmediately) { Assert.notNull(endpoint, "Endpoint must not be null"); Assert.notNull(factory, "Factory must not be null"); String id = endpoint.getId(); Assert.hasText(id, "Endpoint id must not be empty"); synchronized (this.listenerContainers) { Assert.state(!this.listenerContainers.containsKey(id), "Another endpoint is already registered with id '" + id + "'"); MessageListenerContainer container = createListenerContainer(endpoint, factory); this.listenerContainers.put(id, container); if (StringUtils.hasText(endpoint.getGroup()) && this.applicationContext != null) { List<MessageListenerContainer> containerGroup; if (this.applicationContext.containsBean(endpoint.getGroup())) { containerGroup = this.applicationContext.getBean(endpoint.getGroup(), List.class); } else { containerGroup = new ArrayList<MessageListenerContainer>(); this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton(endpoint.getGroup(), containerGroup); } containerGroup.add(container); } if (startImmediately) { startIfNecessary(container); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
基于RabbitListenerEndpoint根据监听器的容器工厂类生成一个
监听器的容器,并且整个注册过程是同步的,同时最多只能有一个endpoint在注册RabbitListenerEndpointRegistry#start
@Override public void start() { for (MessageListenerContainer listenerContainer : getListenerContainers()) { startIfNecessary(listenerContainer); } } private void startIfNecessary(MessageListenerContainer listenerContainer) { if (this.contextRefreshed || listenerContainer.isAutoStartup()) { listenerContainer.start(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
调用MessageListenerContainer#start方法, 监听器的启动。
-
相关阅读:
【详解配置文件系列】es7配置文件详解
(十六)网络编程
栈和队列--数据结构
Day9力扣打卡
MySQL之索引
记一次 .NET 某RFID标签管理系统 CPU 暴涨分析
股票价格排行榜查询易语言代码
窗口函数大揭秘!轻松计算数据累计占比,玩转数据分析的绝佳利器
golang template 使用
人工智能生成内容AIGC:AIGC for Various Data Modalities: A Survey
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43141726/article/details/128165679