-
VTK网格细分-vtkAdaptiveSubdivisionFilter
前言:此博文主要分享VTK中关于细分网格的相关Filter,同时希望能给其他小伙伴一些帮助。
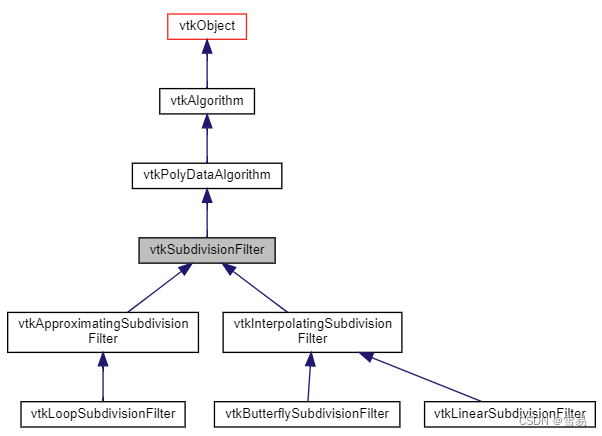
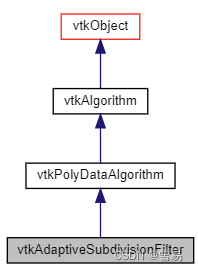
小结:VTK中关于网格细分的Filter包括vtkSubdivisionFilter和vtkAdaptiveSubdivisionFilter。其中vtkSubdivisionFilter又有几个子类,见下图。
现以正方形为例展示各个细分Filter的不同之处(所有的numberOfSubdivision设为2),原始模型为下图:

1. vtkAdaptiveSubdivisionFilter
描述:vtkAdaptiveSubdivisionFilter是基于三角形的最长边或面积进行细分的Filter。新增的点只能插入到边缘上,根据细分的边的数量,插入不同数量的三角形,范围从两个(即两个三角形取代原来的一个)到四个。

参数:
1. MaximumEdgeLength:指定最长边的长度。若长度大于当前设定值,则将其进行剖分。
2. MaximunTriangleArea:指定三角面片的最大面积,若面积大于当前设定值,则进行剖分。若使用这个标准,结果可能会产生non-watertight网格。
算法实现过程:
1. 初始化MaximunEdgeLength = 1.0; MaximunTriangleArea = 1.0;
2. 八种细分方案
- // There are eight possible subdivision cases (each of the three edges may
- // or may not be subdivided). Case 0 just outputs the original triangle;
- // the other cases output between 2 and four triangles. Note that when
- // three triangles are generated, then the diagonal of the quadrilateral
- // produced can go one of two ways. The tetCases is set up so that the two
- // triangles forming the quad are the last two triangles and can be
- // adjusted as necessary.
- int CASE_MASK[3] = { 1, 2, 4 };
- vtkIdType tessCases[16][13] = {
- { 1, 0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, // case 0
- { 2, 0, 3, 2, 3, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, // case 1
- { 2, 0, 1, 4, 4, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, // case 2
- { 3, 3, 1, 4, 3, 4, 2, 2, 0, 3, 0, 0, 0 }, // case 3
- { 2, 0, 1, 5, 5, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, // case 4
- { 3, 0, 3, 5, 5, 3, 1, 1, 2, 5, 0, 0, 0 }, // case 5
- { 3, 5, 4, 2, 0, 1, 4, 4, 5, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, // case 6
- { 4, 0, 3, 5, 3, 1, 4, 5, 3, 4, 5, 4, 2 }, // case 7
- { 1, 0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, // case 0a
- { 2, 0, 3, 2, 3, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, // case 1a
- { 2, 0, 1, 4, 4, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, // case 2a
- { 3, 3, 1, 4, 0, 3, 4, 4, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, // case 3a
- { 2, 0, 1, 5, 5, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, // case 4a
- { 3, 0, 3, 5, 3, 1, 2, 2, 5, 3, 0, 0, 0 }, // case 5a
- { 3, 4, 2, 5, 5, 0, 1, 1, 4, 5, 0, 0, 0 }, // case 6a
- { 4, 0, 3, 5, 3, 1, 4, 5, 3, 4, 5, 4, 2 }, // case 7a
- };
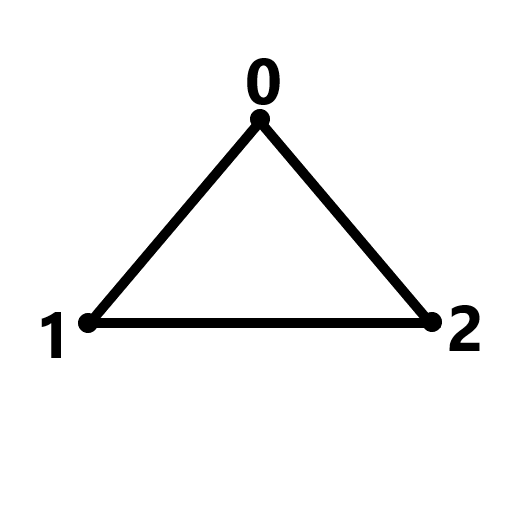
(case0,case0a)
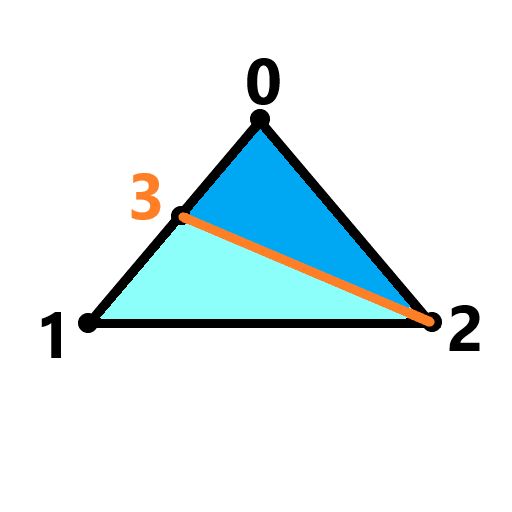
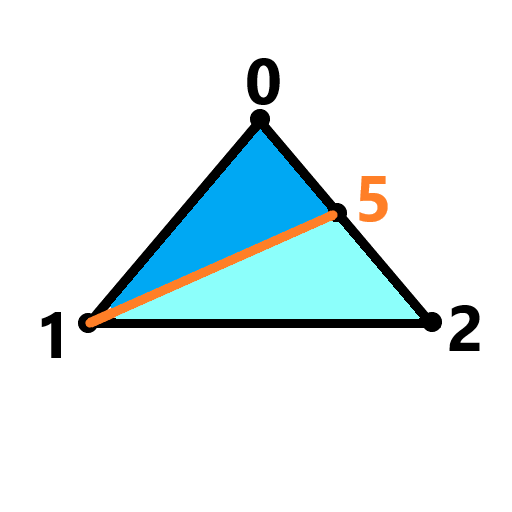
(case1,case1a) (case2,case2a) (case4,case4a)
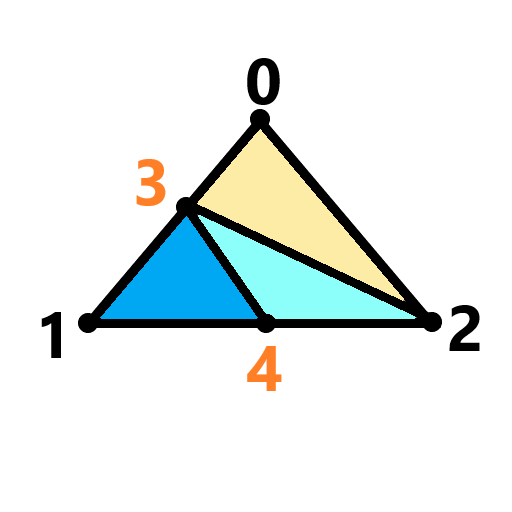
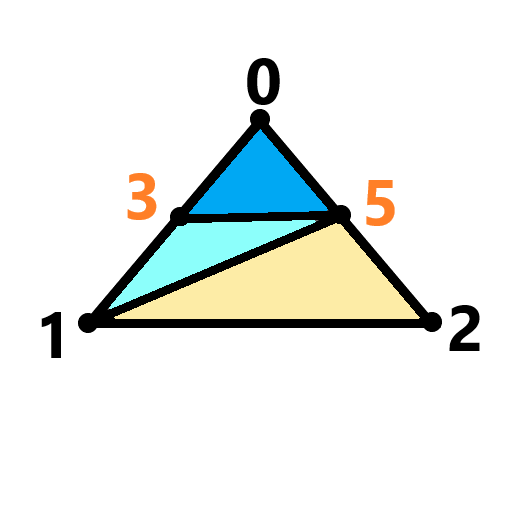

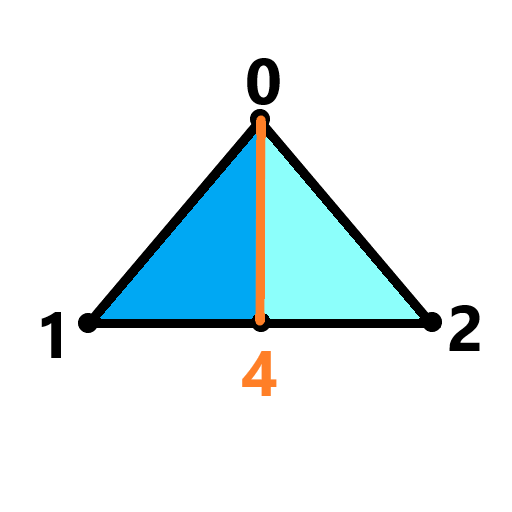
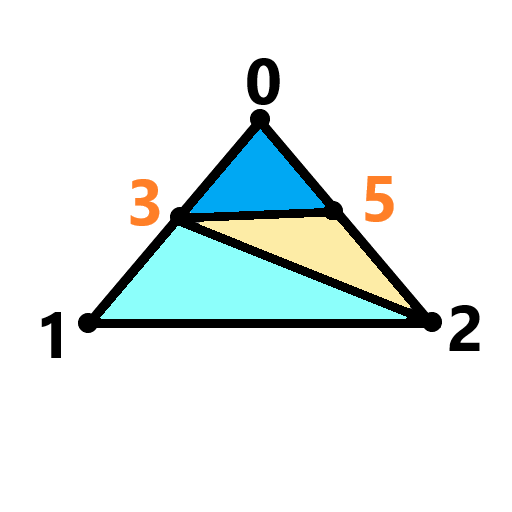
(case3) (case5) (case6)
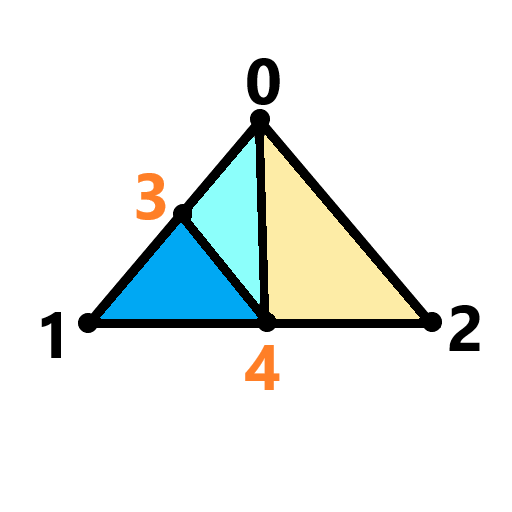

(case3a) (case5a) (case6a)
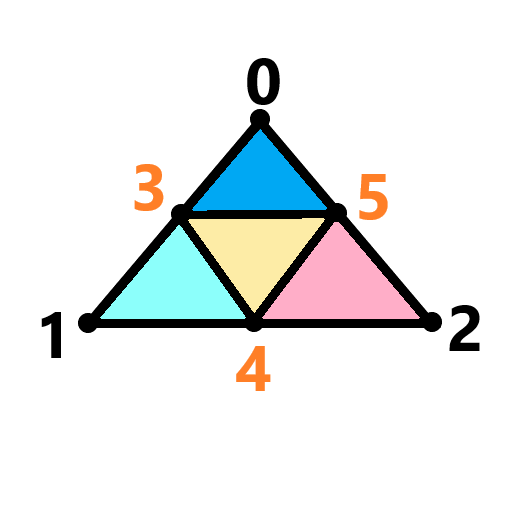
(case7,case7a)
3. 细分逻辑
若三角面片的面积 > 指定最大面积,则采用case7进行分类;
若仅有直线01的长度 > 指定最大长度,则采用case1进行分类;
若仅有直线12的长度 > 指定最大长度,则采用case2进行分类;
若仅有直线20的长度 > 指定最大长度,则采用case4进行分类;
若直线01的长度 > 指定最大长度 && 直线12的长度 > 指定最大长度,则采用case3进行分类;
若直线01的长度 > 指定最大长度 && 直线20的长度 > 指定最大长度,则采用case5进行分类;
若直线12的长度 > 指定最大长度 && 直线20的长度 > 指定最大长度,则采用case6进行分类;
针对case3,case5,case6的分类,再比较case3和case3a,case5和case5a,case6和case6a,选择最优剖分方式。
小结:设定的面积值是由于长度值的。
- int vtkAdaptiveSubdivisionFilter::RequestData(vtkInformation* vtkNotUsed(request),
- vtkInformationVector** inputVector, vtkInformationVector* outputVector)
- {
- // get the info objects
- vtkInformation* inInfo = inputVector[0]->GetInformationObject(0);
- vtkInformation* outInfo = outputVector->GetInformationObject(0);
- // get the input and output and check its validity
- vtkPolyData* input = vtkPolyData::SafeDownCast(inInfo->Get(vtkDataObject::DATA_OBJECT()));
- vtkPolyData* output = vtkPolyData::SafeDownCast(outInfo->Get(vtkDataObject::DATA_OBJECT()));
- vtkIdType numPts = input->GetNumberOfPoints();
- vtkCellArray* inTris = input->GetPolys();
- vtkIdType numTris = inTris->GetNumberOfCells();
- if (numPts < 1 || numTris < 1)
- {
- vtkDebugMacro(<< "No data to subdivide!");
- return 1;
- }
- vtkPointData* inPointData = input->GetPointData();
- vtkCellData* inCellData = input->GetCellData();
- if (inTris->IsHomogeneous() != 3)
- {
- vtkDebugMacro(<< "Filter operates only on triangles!");
- return 1;
- }
- // Need a locator
- if (!this->Locator)
- {
- this->CreateDefaultLocator();
- }
- // The first thing is to take the existing points and push them into the
- // incremental point locator. We know that we are going to use the original
- // points. Note that points are only created and are not swapped as each
- // pass is invoked.
- vtkPoints* inPts = input->GetPoints();
- vtkPoints* newPts = vtkPoints::New();
- vtkPointData *swapPointData, *newPointData = vtkPointData::New();
- newPointData->CopyAllocate(inPointData);
- // set precision for the points in the output
- if (this->OutputPointsPrecision == vtkAlgorithm::DEFAULT_PRECISION)
- {
- newPts->SetDataType(inPts->GetDataType());
- }
- else if (this->OutputPointsPrecision == vtkAlgorithm::SINGLE_PRECISION)
- {
- newPts->SetDataType(VTK_FLOAT);
- }
- else if (this->OutputPointsPrecision == vtkAlgorithm::DOUBLE_PRECISION)
- {
- newPts->SetDataType(VTK_DOUBLE);
- }
- this->Locator->InitPointInsertion(newPts, input->GetBounds(), input->GetNumberOfPoints());
- // Load in the already existing points. Also load in the point data
- // associated with the existing points.
- for (vtkIdType ptId = 0; ptId < numPts; ++ptId)
- {
- this->Locator->InsertNextPoint(inPts->GetPoint(ptId));
- newPointData->CopyData(inPointData, ptId, ptId);
- }
- // This is a multipass algorithm. From a list of triangles, check each
- // against the edge length and area criteria. If necessary, break the
- // triangle (using a case table) into smaller triangles by inserting one or
- // more points on edges (the edge is broken at its midpoint). The new
- // triangles are placed into a new list which serves as the starting point
- // for the next pass. An important note: triangles are split independently
- // without neighbor "links" (i.e.,cell links) and new points are merged
- // into the locator. Since the algorithm treats edges on triangles in an
- // identical way, the end result is that triangle neighbors remain
- // compatible (due to conincident point merging).
- //这是一个多通道算法。从三角形列表中,根据边长和面积标准检查每个三角形。如果有必要,通过在边缘
- //上插入一个或多个点(边缘在中点被打破),将三角形(使用案例表)分割成更小的三角形。
- //新的三角形被放置到一个新的列表中,作为下一遍的起点。
- //一个重要的注意事项:三角形是独立分割的,没有相邻的“链接”(即单元格链接),新的点被合并到定位器
- //中。由于该算法以相同的方式处理三角形上的边,最终结果是三角形邻居保持兼容(由于重合点合并)。
- auto cellIter = vtk::TakeSmartPointer(inTris->NewIterator());
- vtkCellArray *swapTris, *newTris = vtkCellArray::New();
- newTris->AllocateEstimate(2 * numTris, 3);
- vtkCellData *swapCellData, *newCellData = vtkCellData::New();
- newCellData->CopyAllocate(inCellData);
- int i;
- double area, eLengths[3];
- double maxLen2 = this->MaximumEdgeLength * this->MaximumEdgeLength;
- double maxArea = this->MaximumTriangleArea;
- double x[6][3]; // three vertices plus potential mid-edge points
- const vtkIdType* tri;
- vtkIdType triId;
- vtkIdType newId;
- vtkIdType passNum;
- vtkIdType totalTriangles = 0;
- bool changesMade;
- for (passNum = 0, changesMade = true; passNum < this->MaximumNumberOfPasses &&
- totalTriangles < this->MaximumNumberOfTriangles && changesMade;
- ++passNum)
- {
- changesMade = false;
- for (cellIter->GoToFirstCell(); !cellIter->IsDoneWithTraversal(); cellIter->GoToNextCell())
- {
- triId = cellIter->GetCurrentCellId();
- {
- vtkIdType unused;
- cellIter->GetCurrentCell(unused, tri);
- }
- newPts->GetPoint(tri[0], x[0]);
- newPts->GetPoint(tri[1], x[1]);
- newPts->GetPoint(tri[2], x[2]);
- eLengths[0] = vtkMath::Distance2BetweenPoints(x[0], x[1]);
- eLengths[1] = vtkMath::Distance2BetweenPoints(x[1], x[2]);
- eLengths[2] = vtkMath::Distance2BetweenPoints(x[2], x[0]);
- area = vtkTriangle::TriangleArea(x[0], x[1], x[2]);
- // Various subdivision cases are possible
- unsigned char subCase = 0;
- if (area > maxArea)
- {
- subCase = 7;
- }
- else
- {
- for (i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
- {
- if (eLengths[i] > maxLen2)
- {
- subCase |= CASE_MASK[i];
- }
- }
- } // determine edges to divide
- // If not just outputting original triangle then changes are made
- if (subCase > 0)
- {
- changesMade = true;
- }
- // Now create new points and triangles dividing edges as appropriate.
- double xNew[3];
- vtkIdType ptIds[6];
- ptIds[0] = tri[0];
- ptIds[1] = tri[1];
- ptIds[2] = tri[2];
- for (i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
- {
- if (subCase & CASE_MASK[i]) // ith edge needs subdivision
- {
- xNew[0] = 0.5 * (x[i][0] + x[(i + 1) % 3][0]);
- xNew[1] = 0.5 * (x[i][1] + x[(i + 1) % 3][1]);
- xNew[2] = 0.5 * (x[i][2] + x[(i + 1) % 3][2]);
- if ((ptIds[3 + i] = this->Locator->IsInsertedPoint(xNew)) < 0)
- {
- ptIds[3 + i] = this->Locator->InsertNextPoint(xNew);
- newPointData->InterpolateEdge(inPointData, ptIds[3 + i], tri[i], tri[(i + 1) % 3], 0.5);
- }
- }
- }
- // The tessellation may vary based on geometric concerns (selecting best
- // diagonal during triangulation of quadrilateral)
- vtkIdType newTIds[3], *subTess;
- subTess = SelectTessellation(subCase, ptIds, newPts);
- vtkIdType numTessTris = *subTess++;
- for (i = 0; i < numTessTris; ++i, subTess += 3)
- {
- newTIds[0] = ptIds[subTess[0]];
- newTIds[1] = ptIds[subTess[1]];
- newTIds[2] = ptIds[subTess[2]];
- newId = newTris->InsertNextCell(3, newTIds);
- newCellData->CopyData(inCellData, triId, newId);
- if (++totalTriangles >= this->MaximumNumberOfTriangles)
- {
- break;
- }
- }
- } // for all triangles in this pass
- // Prepare for the next pass, which means swapping input and output.
- // Remember that the initial pass uses the filter input; subsequent passes
- // cannot modify the input to a new cell array must be created to support
- // the swapping.
- if (passNum == 0)
- {
- inTris = vtkCellArray::New();
- inCellData = vtkCellData::New();
- inCellData->CopyAllocate(newCellData);
- inPointData = vtkPointData::New();
- inPointData->CopyAllocate(newPointData);
- }
- // Prepare for new triangles
- swapTris = newTris;
- newTris = inTris;
- inTris = swapTris;
- cellIter = vtk::TakeSmartPointer(inTris->NewIterator());
- numTris = inTris->GetNumberOfCells();
- newTris->Reset();
- newTris->AllocateEstimate(2 * numTris, 3);
- // Prepare for new cell data
- swapCellData = newCellData;
- newCellData = inCellData;
- inCellData = swapCellData;
- // Prepare for new point data
- numPts = newPts->GetNumberOfPoints();
- swapPointData = newPointData;
- newPointData = inPointData;
- inPointData = swapPointData;
- for (vtkIdType ptId = 0; ptId < numPts; ++ptId)
- {
- newPointData->CopyData(inPointData, ptId, ptId);
- }
- } // for another pass
- // Configure output and clean up
- output->SetPoints(newPts);
- newPts->Delete();
- output->GetPointData()->ShallowCopy(inPointData);
- newPointData->Delete();
- output->SetPolys(inTris);
- inTris->Delete();
- newTris->Delete();
- output->GetCellData()->ShallowCopy(inCellData);
- inCellData->Delete();
- inPointData->Delete();
- newCellData->Delete();
- return 1;
- }
2. vtkLoopSubdivisionFilter
描述:vtkLoopSubdivisionFilter是一个近似细分的子类,它为网格中的每个三角形创建四个新的三角形。


算法实现原理:
1) GenerateSubdivisionPoints:生成细分的点
for (针对输入PolyData的所有Point)
{
a. 获取当前点关联的其它点,并确认关联点的比重;
b. 根据关联点的坐标和各自的比重计算当前点的新的坐标;
c. 将新的点集更新至输出PolyData。
}
2)将细分出的新增点连接生成Cell
3. vtkButterflySubdivisionFilter
描述:vtkButterflySubdivisionFilter是一个插值细分的子类,它采用蝴蝶细分的方法为网格中的每个三角形创建四个新的三角形。
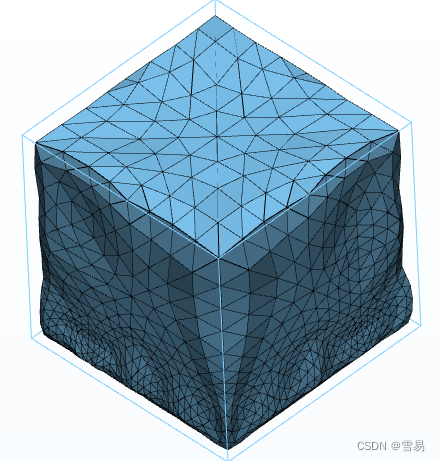
4. vtkLinearSubdivisionFilter
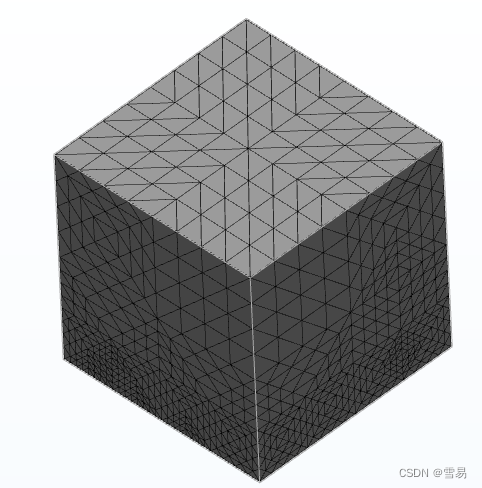
描述:vtkLinearSubdivisionFilter是一个插值细分的子类,同样为网格中的每个三角形创建四个新的三角形。
-
相关阅读:
使用流处理 List集合中根据对象某一参数处理集合
实战:springboot整合rabbitMQ
vector--erase()安全删除指定元素
ArrayList 和 LinkedList 的区别
基于opencv实现简单人脸检测
MHA高可用配置及故障切换
http1和http2的主要区别
JVM篇---第十篇
k8s根ca证书最多10年调整为100年或任意时间
《大数据之路:阿里巴巴大数据实践》-第1篇 数据技术篇 -第4章 离线数据开发
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40041064/article/details/128118621