-
Java ArrayLIst与顺序表
-
什么是集合类?
Java当中的集合类,其实就是封装号的数据结构
原始的数据结构——>Java当中封装成的集合对应的那个原始的数据结构——>用Java封装的集合对应的。
集合类所在的包:java.util这个包底下 -
顺序表的底层是一个数组,数组作为ArrayList类的成员,在这个类里面提供了对数组的增删改查等操作
ArrayList类中方法的实现:
import java.util.Arrays; public class MyArraylist { public int[] elem; //顺序表的数组 public int usedSize;//当前顺序表数组的大小是几个 //默认容量 private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 10; //常量 public MyArraylist() { this.elem = new int[DEFAULT_SIZE]; //调用构造方法对数组进行初始化 } /** * 打印顺序表: * 根据usedSize判断即可 */ public void display() { for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) { //要学会使用this System.out.print(this.elem[i] + " "); } System.out.println(); } // 新增元素,默认在数组最后新增 public void add(int data) { if(isFull()) { //扩容 this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,this.elem.length*2); } this.elem[usedSize] = data; this.usedSize++; } /** * 判断当前的顺序表是不是满的! * * @return true:满 false代表空 */ public boolean isFull() { if (this.usedSize == this.elem.length) { return true; } return false; //或者直接一条语句 //return this.usedSize == this.elem.length; } private boolean checkPosInAdd(int pos) { if (pos >= 0 && pos <= this.usedSize) { return true;//合法 } return false; } // 在 pos 位置新增元素 public void add(int pos, int data) { if (!checkPosInAdd(pos)) { throw new AddIndexOutExcepetion("新增元素的位置pos不合理"); } if (isFull()) { this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,this.elem.length*2); } //移动数据 for (int i = pos; i < usedSize; i++) { this.elem[i + 1] = this.elem[i]; } this.elem[pos] = data; this.usedSize++; } // 判定是否包含某个元素 public boolean contains(int toFind) { for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) { if (this.elem[i] == toFind) { return true; } } return false; } // 查找某个元素对应的位置 public int indexOf(int toFind) { for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) { if (this.elem[i] == toFind) { return i; } } return -1; } //判断获取元素的位置是否合法 public boolean checkPosInGet(int pos) { if (pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) { return false; } return true; } // 获取 pos 位置的元素 public int get(int pos) { if (!checkPosInGet(pos)) { throw new GetIndexOutExcepetion("查找的位置不在范围内"); } if (isEmpty()) { throw new ArrayEmptyException("数组为空无法获取pos位置元素"); } return this.elem[pos]; } private boolean isEmpty() { if (usedSize == 0) { return true; } return false; } // 给 pos 位置的元素设为【更新为】 value public void set(int pos, int value) { if (!checkPosInGet(pos)) { throw new GetIndexOutExcepetion("更新的位置不合法"); } if (isEmpty()) { throw new ArrayEmptyException("数组为空"); } this.elem[pos] = value; } /** * 删除第一次出现的关键字key * * @param key */ public void remove(int key) { if (isEmpty()) { throw new ArrayEmptyException("顺序表为空,不能删除"); } int index = indexOf(key); //调用方法获得key的下标 if (index == -1) { System.out.println("没有要删除的关键字"); return; } for (int j = index; j < this.usedSize; j++) { this.elem[j] = this.elem[j+1]; } this.usedSize--; // for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) { // if (this.elem[i] == key) { //可通过上述完成的方法来完成 // for (int j = i; j < this.usedSize; j++) { // this.elem[j] = this.elem[j+1]; // } // this.usedSize--; // break; // } // } } // 获取顺序表长度 public int size() { return this.usedSize; } // 清空顺序表 public void clear() { this.usedSize = 0; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
public class AddIndexOutExcepetion extends RuntimeException{ public AddIndexOutExcepetion() { } public AddIndexOutExcepetion(String message) { super(message); } } public class ArrayEmptyException extends RuntimeException{ public ArrayEmptyException() { } public ArrayEmptyException(String message) { super(message); } } public class GetIndexOutExcepetion extends RuntimeException{ public GetIndexOutExcepetion() { } public GetIndexOutExcepetion(String message) { super(message); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- ArrayList是一个泛型类(ArrayList的构造)
实例化ArrayList对象的方法——主要有3种
①调用无参构造方法
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList= new ArrayList<>();- 1
分析源码:
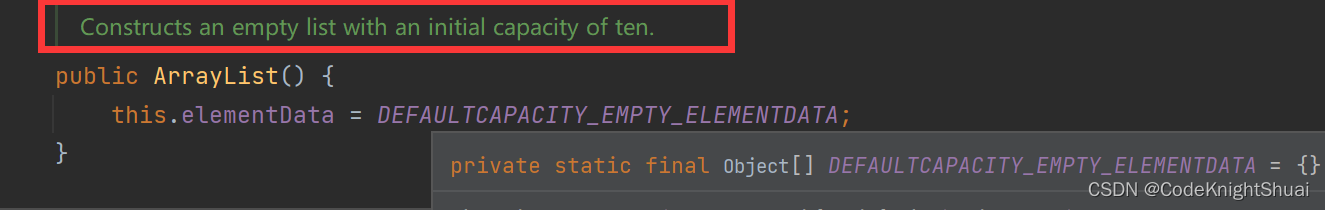
用此方法实例化arraylist的对象的时候,刚开始并没有为arrayList中的元素开辟空间,此时的数组是一个空数组,即相当于elementData = {};,那么如果调用add方法添加元素的时候,就会给数组扩容了,见总结第4点。②传入一个数值(即给定数组容量)
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList= new ArrayList<>(10);- 1
分析源码:

如果传入的数值大于0,则数组的容量就是传入的数值
如果传入的数值等于0,则给一个空数组{}
如果传入的数值小于0,则抛出异常③参数为一个类
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>(); list.add(1); list.add(2); list.add(3); ArrayList<Integer> arrayList= new ArrayList<>(list);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
分析源码:

利用其他Collection构建ArrayList,Collection c,把另一个实现Collection接口的类的集合拿过来作为参数,其中c的类型一定是E或者E的子类。- 当调用无参构造器实例化对象的时候,此时的数组是一个空数组{},若此时调用add方法则会扩容。
public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); arrayList.add(1); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
在上述情况下,第一次调用add方法时,会给arrayList扩容,给其底层的elementData分配内存,大小为10。
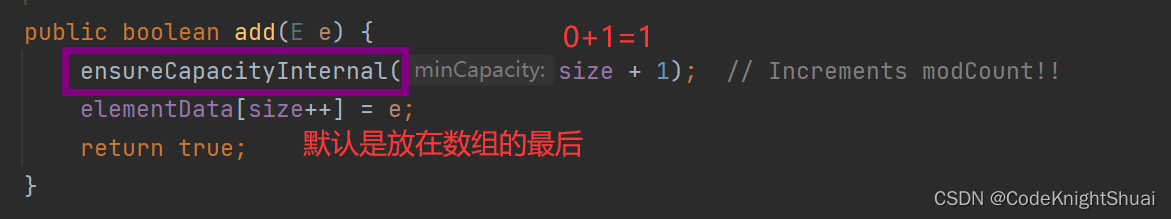
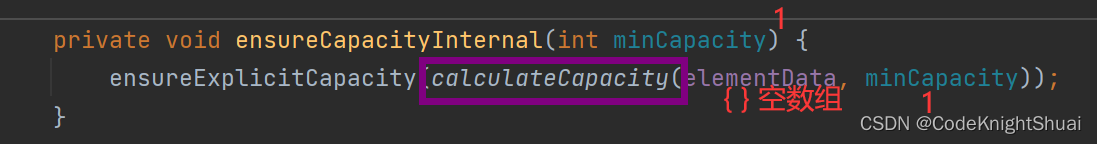
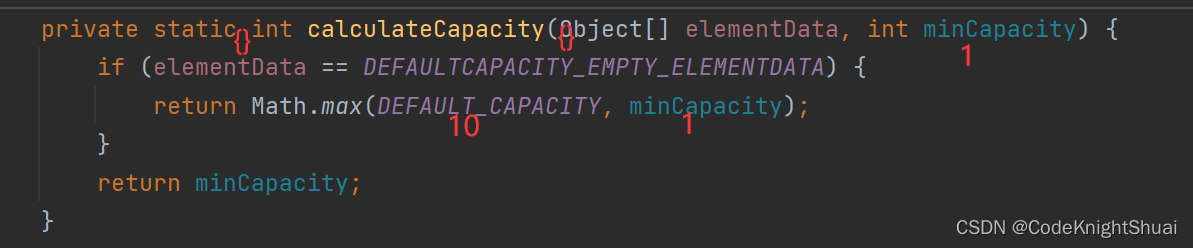
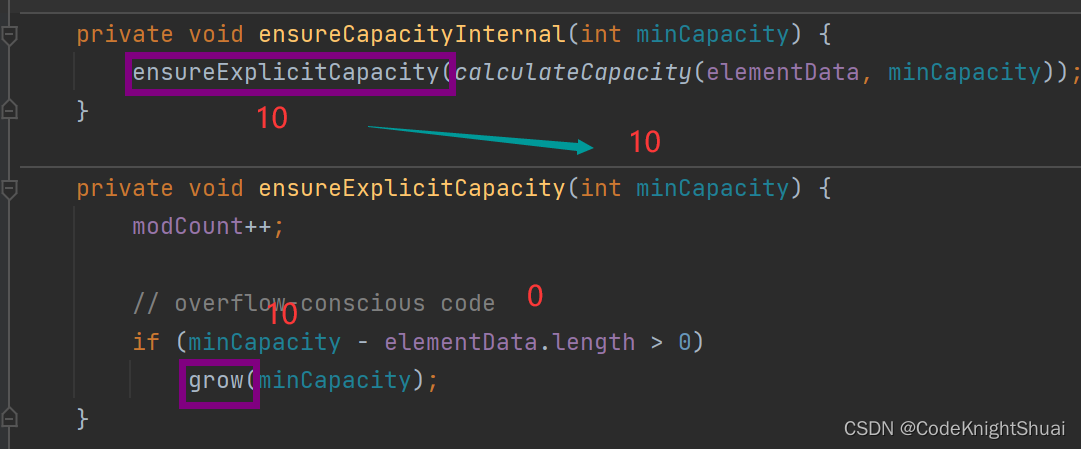
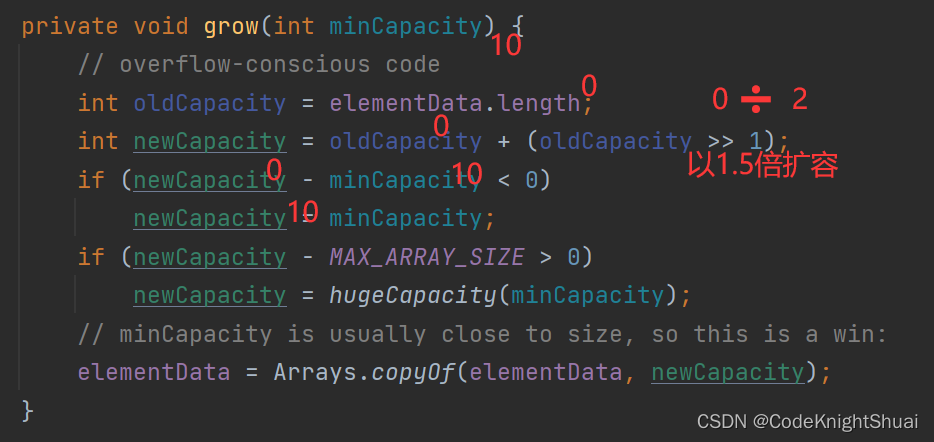
总结:虽然一开始,代码没有分配内存,但是当第一次add的时候,会走到grow方法里分配内存大小,此时elemdata数组最后分配的大小长度是10。- 遍历ArrayList的四种方法
public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); arrayList.add(1); arrayList.add(2); arrayList.add(3); arrayList.add(4); //方法1:toString方法 System.out.println(arrayList); //方法2:for-each方法 for (Integer x: arrayList) { System.out.print(x + " "); } System.out.println(); //方法3:for循环+下标 for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) { System.out.print(arrayList.get(i) + " "); } System.out.println(); //方法4:迭代器 Iterator<Integer> list = arrayList.iterator(); while (list.hasNext()) { System.out.print(list.next() + " "); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
分析:
①toString方法,说明重写了toString方法
但是ArrayList里面并没有重写toString,于是去寻找其父类 AbstractList,也没有重写toString方法,于是去找AbstractList的父类AbstractCollection,终于AbstractCollection中重写了toString方法,就这样被继承到了ArrayList中。
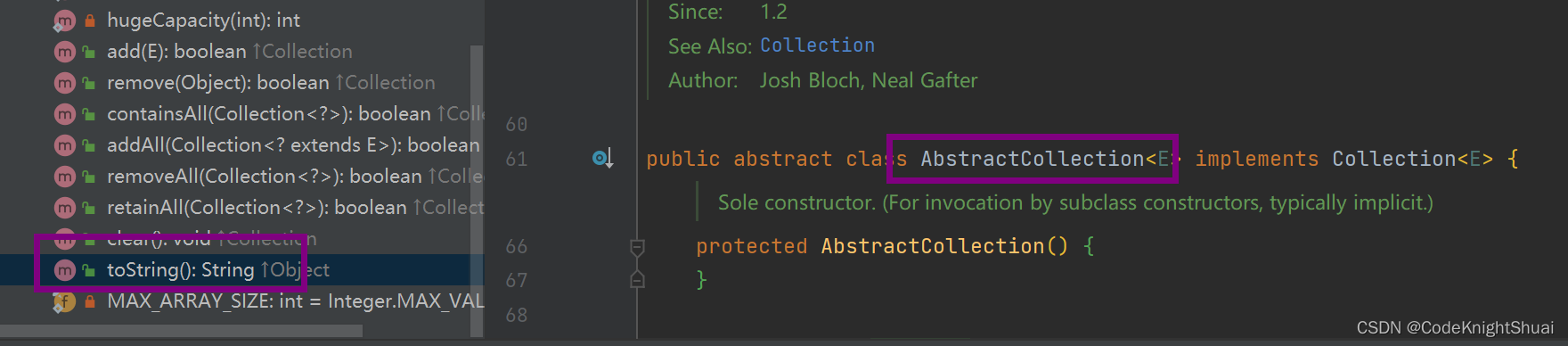
②for-each方法
此时arraylist里面的元素类型是Integer类型。
③for+下标
通过ArrayList中的get(i下标)的方法来遍历数组
④迭代器listIterator
迭代器是设计模式的一种

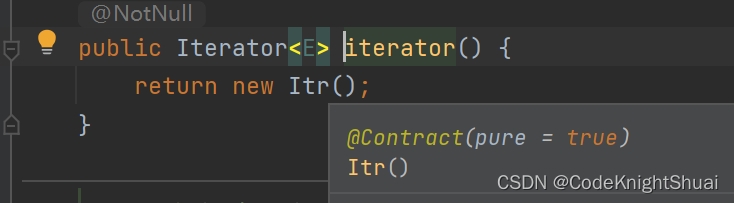
- ArrayList常见操作中的remove和subList方法
①注意E remove(int index) 与 boolean remove(Object o)的区别【方法重载】
删除下标为index位置的元素,并且返回这个元素。
删除元素为o的那个元素,返回值是布尔类型。
那么 remove(1);到底是删除下标为1的那个元素,还是元素值为1的那个元素呢?
public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(1); list.add(2); list.add(3); list.remove(1); System.out.println(list); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
运行结果:
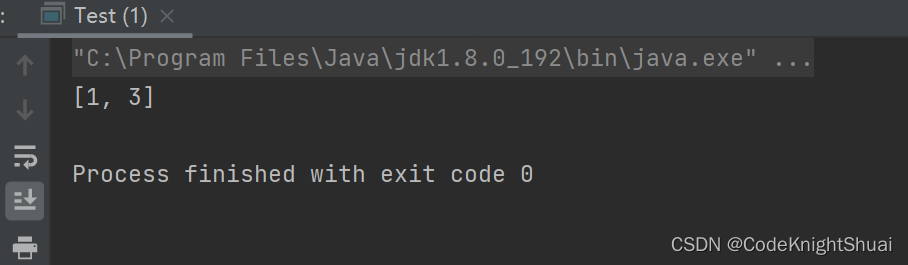
分析:此时remove中的参数1识别为下标,而不是对象。那么要删除元素值为1的那个元素如何删除?public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(1); list.add(2); list.add(3); list.remove(new Integer(1)); System.out.println(list); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
运行结果:
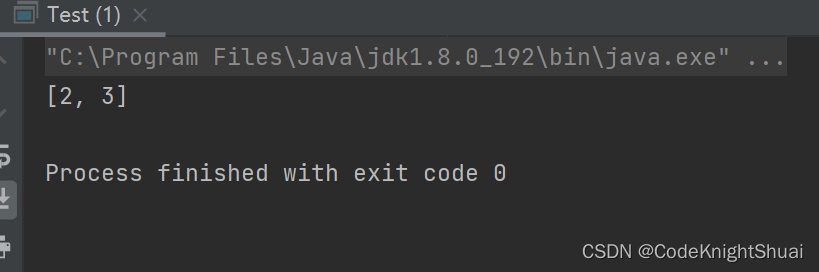
分析:list.remove(new Integer(1));,传入对象,则可以区别开。
②subList方法:返回值是List,截取部分list
LIst< E > subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(1); list.add(2); list.add(3); list.add(4); List<Integer> sub = list.subList(1,3); sub.set(1,999); System.out.println(sub); System.out.println(list); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
运行结果:
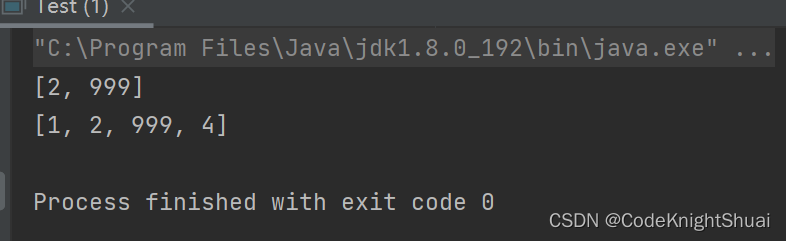
分析:sub.set(1,999);,sub和list的对应位置都变成999,这也说明虽然构成一个新的list返回,但是和ArrayList共用一个elementData数组。- 运用ArrayList知识编程
题目:s1 = “Welcome to world!” ; s2 = “come!”,去除s1中s2包含的字符,则打印输出"Wl t wrld"
代码:
public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "Welcome to world!"; String s2 = "come!"; ArrayList<Character> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) { //看s2中是否包含s1中的字符,所以逐一取出s1中的字符 char ch = s1.charAt(i); if (!s2.contains(ch + "")) { //contains的参数是CharSequence,所以要把字符变成字符串 list.add(ch); } } for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { System.out.print(list.get(i)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
运行结果:
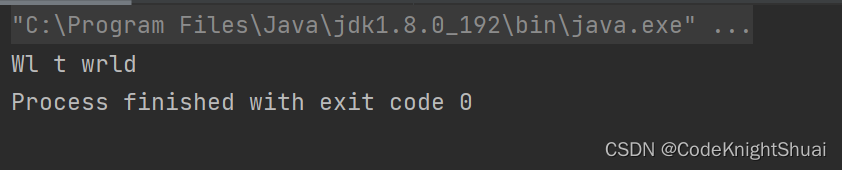
- 杨辉三角(力扣118)
分析:
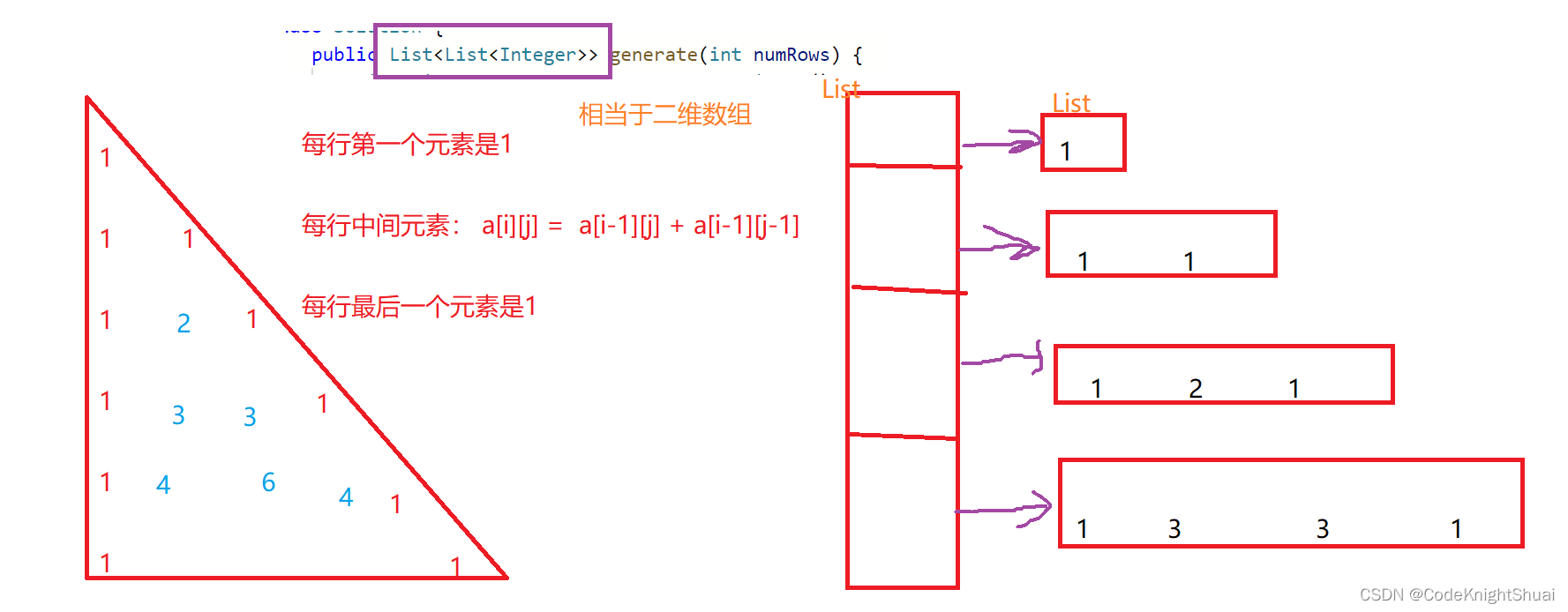
代码:
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) { List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer> row1 = new ArrayList<>(); row1.add(1);//第一行 ret.add(row1); for(int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) { List<Integer> curRow = new ArrayList<>(); //每行第一个元素 curRow.add(1); List<Integer> preRow = ret.get(i - 1); //获取上一行 //每行的中间元素,则要获取上一行 for(int j = 1; j < i; j ++) { int x = preRow.get(j) + preRow.get(j - 1); curRow.add(x); } //每行最后一个元素 curRow.add(1); ret.add(curRow); } return ret; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 删除排序数组中的重复项(力扣26)
分析:

代码:
class Solution { public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) { int count = 1; for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) { if(nums[i] != nums[count - 1]) { nums[count] = nums[i]; count++; } } return count; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 简单的洗牌算法
封装牌类
package demo4; //封装牌 public class Card { private String suit; //花色 private int rank; //牌值 //带参数的构造方法 public Card(String suit, int rank) { this.suit = suit; this.rank = rank; } //get和set方法 public String getSuit() { return suit; } public void setSuit(String suit) { this.suit = suit; } public int getRank() { return rank; } public void setRank(int rank) { this.rank = rank; } //重写toString方法,为了更好打印输出 @Override public String toString() { return "{" +suit + rank + "}"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
游戏类:(实现买牌和洗牌)
package demo4; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Random; public class Game { //牌的四种花色 public static String[] suits = {"♥","♠","♦","♣"}; //买一副牌 public ArrayList<Card> buyCard() { ArrayList<Card> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= 13; j++) { list.add(new Card(suits[i],j)); } } return list; } //洗牌 public void shuffle(ArrayList<Card> list) { Random random = new Random(); for (int i = list.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) { int j = random.nextInt(i); //在当前牌之前随机取一张牌交换 swap(list,i,j); } } //交换牌 private void swap(ArrayList<Card> list, int i, int j) { Card tmp = list.get(i); list.set(i,list.get(j)); list.set(j,tmp); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
测试类:调用游戏类方法,并发牌
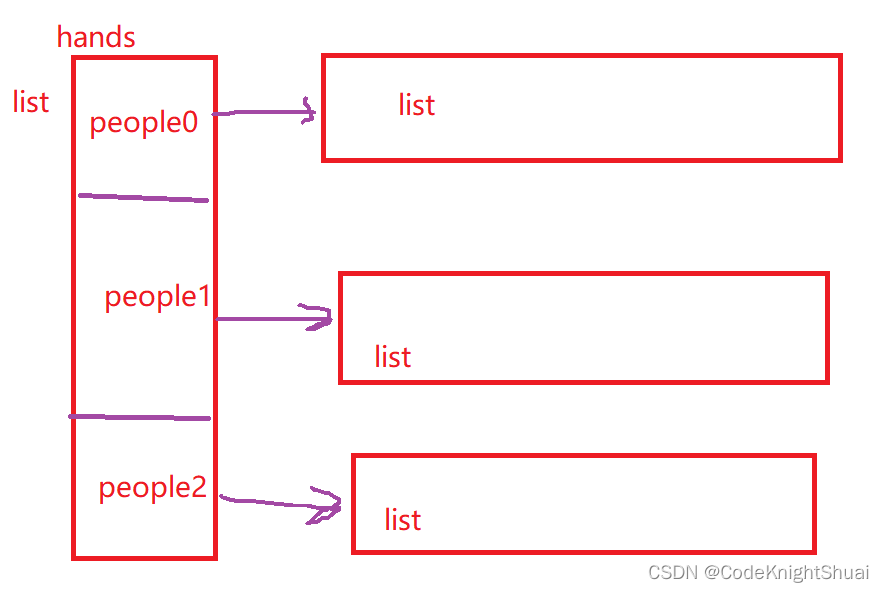
package demo4; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Game game = new Game(); //买牌 ArrayList<Card> list = game.buyCard(); System.out.println(list); //洗牌 game.shuffle(list); System.out.println(list); //发牌 (三个人,每个人轮流抓5张牌) //3个人,每个人手里的牌 List<Card> people0 = new ArrayList<>(); List<Card> people1 = new ArrayList<>(); List<Card> people2 = new ArrayList<>(); //具备关联关系,利用二维数组 List<List<Card>> hands = new ArrayList<>(); hands.add(people0); hands.add(people1); hands.add(people2); //外层:每次发5张牌 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { //内层,一共3个人 for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { hands.get(j).add(list.remove(0)); //每次都是揭0下标的牌,删除0下标的值,会返回0下标值对应的那张牌 } } System.out.println("发牌了!"); for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { System.out.println(hands.get(i)); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
运行结果:
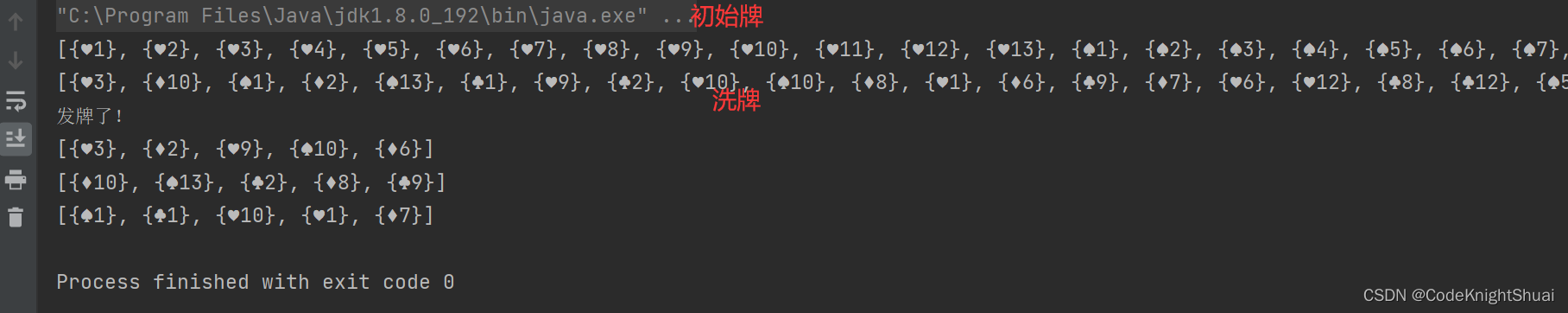
对于发牌的分析:
-
-
相关阅读:
创意指南丨VR游览沉浸式空间体验
MySQL的数据类型
什么是数据同步利器DataX,如何使用?
User 10 must be unlocked for widgets to be available
java使用poi生成excel
ObjectARX简单自定义实体的实现
shell实现部署ftp提供共享yum仓库
linux centos系统命令安装
数据可视化软件使用
【面试经典150 | 数组】合并两个有序数组
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44070116/article/details/128118044
