-
C# 消息 界面卡顿 界面进程 工作进程
一 消息
消息与消息循环,是所有的GUI开发里共同的概念:
消息Message,有的地方也叫事件;
① 鼠标消息;
② 键盘消息;
③ 绘制事件;
④ 窗口最大化、最小化;1 消息循环
消息循环,Message Loop所有的界面消息,都是一个while循环里处理的用伪代码表示:
List<Message>msgList=new List<Message>() while(message=GetMessage()) { 依次处理message.. }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
真实的消息循环
Application.Run(new Form1());- 1
具体的消息处理过程:
protected override void WndProc(ref Message m) { base.WndProc(ref m); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
所有的界面事件回调,本质上都运行在消息循环里,在消息循环里,作进一步的分发处理。
比如,一个Message是鼠标事件,则分发给相应的空间处理。void button1_MouseUp(object sender,MouseEventArgs e) { }- 1
- 2
- 3
运行这个消息循环的线程,就是界面线程,在WinForm里,主线程即界面线程。
static void Main() { Application.Run(new Form1()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
三 界面卡顿
按钮处理程序需要9秒完成;在这个9秒内整个界面是卡主的,不可操作的,为什么?
消息循环:每一个消息处理都要尽快完成while(message=GetMessage()) { switch(消息类型) case 鼠标消息; case 键盘消息; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
所有的消息处理回调,都哟啊尽快返回。当处理时间太长时,界面会有卡顿之感(大于300毫秒左右)
四 工作线程
思考:
如果确实需要处理一件耗时较长的工作…
例如,查询数据库,上传下载,编解码…都可能需要较长时间才能完成。怎么解决?工作线程Work Thread
如果事件处理需要较长时间,应当创建一个线程来处理这个任务。此线程称为“工作线程”。
由于button1_Click()会立即返回,不会引起界面卡顿。界面线程:一直运行,处理界面事件;
工作线程:工作完成后退出;
回顾线程的特点:独立,并行;
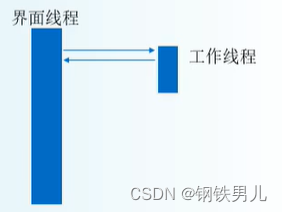
五 界面的更新
错误的实现:
1 创建工作线程;
2 在工作线程中直接更新TextBox的显示;
观察:运行程序,程序会有崩溃提示。
为什么不能在工作线程中直接访问textBox1呢?
在工作线程中访问UI控件时,需使用Invoke方法Control.Invoke(method,args)- 1
当调用Invoke时,实际上推送了一个自定义的消息到消息循环中。当消息被处理时,相应的回调被执行。
正确的实现:
① 定义一个委托类型myCallback;
② 定义一个回调处理ShowProgress;
③ 使用Invoke推送一个自定义事件到消息循环;
注意:Invoke消息的回调也是在界面线程中执行的;第一原则:界面问题的处理不能太久,否则卡顿;
第二原则:当任务时间较长时,则创建工作线程;
第三原则:在工作线程中不可以直接更新UI,需借助Invoke来发送一个自定义的消息;六 Action与Func
委托,实际上是对一类方法的特征描述;
例如:public delegate void selfCallback(string str);- 1
表示的是"参数为striing、返回值为void"的方法;
两个通用的Delegate:
System.Action表示返回值为void的方法;
System.Func 表示返回值不是void的方法;
几乎所有的方法,都可以用这两种委托来表示。
例如:void test1(string a,int b);- 1
由于返回值是void类型,可以用Action表示:
new Action<string,int>(this.test1);- 1
例如:
Student test2(string a,int b)- 1
由于返回值不是void,可以用Func表示
new Func<string,int,Student>(this.test2);- 1
在工作线程里更新UI时,直接使用Action/Func即可,不需要专门定义一个Delegate
this.Invoke(new Action<string>(this.ShowProgress)) public void ShowProgress(string text) { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace Action与Func { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { Thread th = new Thread(new ThreadStart(this.Execute)); th.Start(); } private void Execute() { //此回调处理需要3秒才能完成 this.Invoke(new Action<string>(this.ShowProgress), "3..\r\n"); Thread.Sleep(1000); this.Invoke(new Action<string>(this.ShowProgress), "2..\r\n"); Thread.Sleep(1000); this.Invoke(new Action<string>(this.ShowProgress), "1..\r\n"); Thread.Sleep(1000); this.Invoke(new Action<string>(this.ShowProgress), "OK..\r\n"); } public void ShowProgress(string text) { //这个方法是在消息循环(界面线程)里 textBox1.AppendText(text); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
七 InvokeRequired
Control.InvokeRequired用来判断是不是在工作线程
if(this.InvokeRequired) { //判断当前线程是不是工作线程 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace InvokeRequired { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { Thread th = new Thread(new ThreadStart(this.Execute)); th.Start(); } private void Execute() { ShowProgress("3\r\n"); Thread.Sleep(1000); ShowProgress("2\r\n"); Thread.Sleep(1000); ShowProgress("1\r\n"); Thread.Sleep(1000); ShowProgress("OK\r\n"); } ////// 此方法既可以在工作线程中调用、又可以在界面线程中调用 /// /// public void ShowProgress(string str) { if(this.InvokeRequired) { //从工作线程中调用 Console.Write("Call In Work Thread:" + str); this.Invoke(new Action<string>(this.ShowProgress), str); } else { //从界面线程中调用 Console.WriteLine("Call in Message Loop:" + str); textBox1.AppendText(str); } } } } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
-
相关阅读:
2022CTF培训(三)windows&linux&安卓平台调试机制原理
汽车行驶中是怎么保障轴瓦安全的?
时延抖动和通信的本质
使用canvas给图片添加水印
【无标题】
git使用大全
【GEE笔记10】数值Number(常见指令方法3)
[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计SSM精品旅游项目管理系统(程序+LW)
[Android]Jetpack Compose设置颜色
Git学习(2):Git基础命令
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42291376/article/details/128105784
