-
Redis实战之缓存:查询、添加缓存、更新缓存、缓存预热、缓存穿透、缓存雪崩、缓存击穿 解决方案及实例代码
缓存
什么是缓存?
缓存(Cache), 就是数据交换的缓冲区,俗称的缓存就是缓冲区内的数据,一般从数据库中获取,存储于本地代码。
为什么要使用缓存?
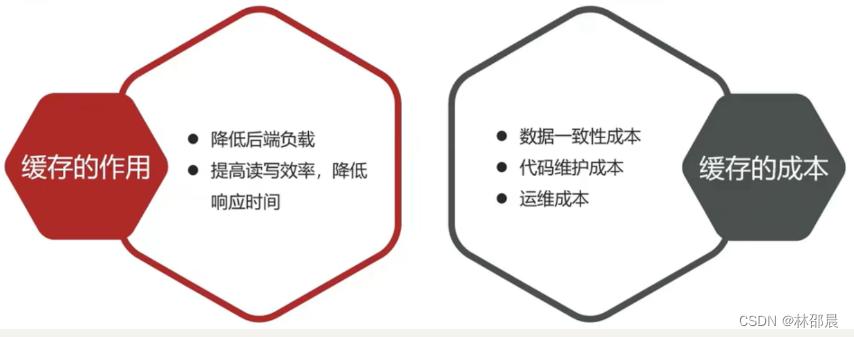
- 缓存数据存储于代码中,而代码运行在内存中,内存的读写性能远高于磁盘,缓存可以大大降低用户访问并发量带来的服务器读写压力;
- 实际开发过程中,企业的数据量,少则几十万,多则几千万,这么大数据量,如果没有缓存来作为"避震器",系统是几乎撑不住的,所以企业会大量运用到缓存技术;
- 但是缓存也会增加代码复杂度和运营的成本
如何使用缓存?
- 浏览器缓存:主要是存在于浏览器端的缓存
- 应用层缓存:可以分为tomcat本地缓存,比如之前提到的map,或者是使用redis作为缓存
- 数据库缓存:在数据库中有一片空间是 buffer pool,增改查数据都会先加载到mysql的缓存中
- CPU缓存:当代计算机最大的问题是 cpu性能提升了,但内存读写速度没有跟上,所以为了适应当下的情况,增加了cpu的L1,L2,L3级的缓存
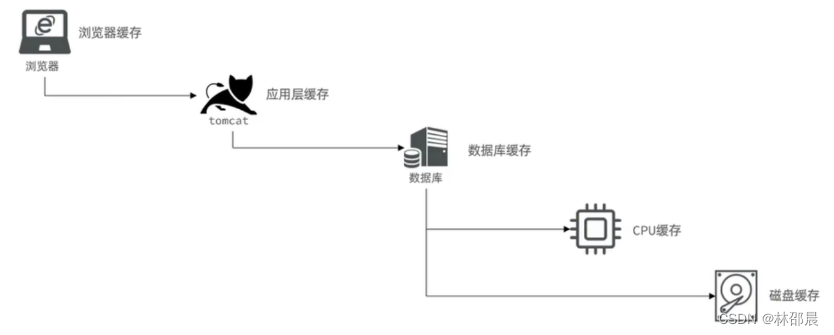
实际开发中,会构筑多级缓存来使系统运行速度进一步提升,本次介绍 redis 中的缓存并发使用。
查询、添加缓存
缓存模型和思路
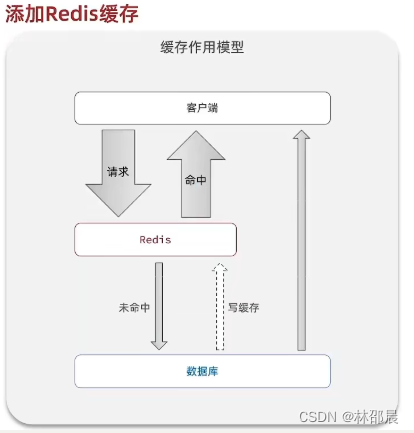
标准的操作方式就是查询数据库之前先查询缓存,如果缓存数据存在,则直接从缓存中返回,如果缓存数据不存在,再查询数据库,然后将数据存入redis。
更新缓存
更新策略
缓存更新是redis为了节约内存而设计出来的一个东西,主要是因为内存数据宝贵,当我们向redis插入太多数据,此时就可能会导致缓存中的数据过多,所以redis会对部分数据进行更新,或者把他叫为淘汰更合适。
- 内存淘汰:redis自动进行,当redis内存达到咱们设定的max-memery的时候,会自动触发淘汰机制,淘汰掉一些不重要的数据(可以自己设置策略方式)
- 超时剔除:当我们给redis设置了过期时间ttl之后,redis会将超时的数据进行删除,方便咱们继续使用缓存
- 主动更新:我们可以手动调用方法把缓存删掉,通常用于解决缓存和数据库不一致问题
数据库缓存不一致解决方案
由于我们的缓存的数据源来自于数据库,而数据库的数据是会发生变化的,因此,如果当数据库中数据发生变化,而缓存却没有同步,此时就会有一致性问题存在。
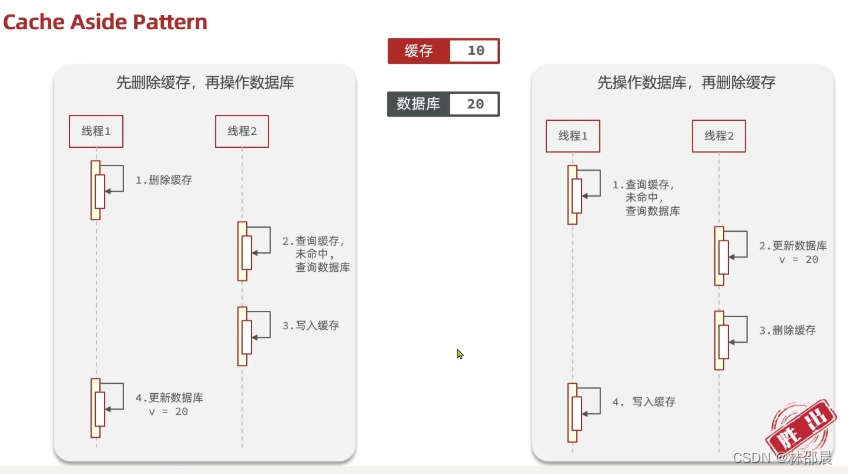
- Cache Aside Pattern: 人工编码方式,缓存调用者在更新完数据库后再去更新缓存,也称之为双写方案
- Read/Write Through Pattern : 由系统本身完成,数据库与缓存的问题交由系统本身去处理
- Write Behind Caching Pattern :调用者只操作缓存,其他线程去异步处理数据库,实现最终一致
综合考虑使用方案一,Cache Aside Pattern。方案一调用者如何处理呢?
删除缓存还是更新缓存?
- 更新缓存:每次更新数据库都更新缓存,无效写操作较多
- 删除缓存:更新数据库时让缓存失效,查询时再更新缓存
先操作缓存还是先操作数据库?
- 先删除缓存,再操作数据库
- 先操作数据库,再删除缓存
如何保证缓存与数据库的操作的同时成功或失败?
- 单体系统,将缓存与数据库操作放在一个事务
- 分布式系统,利用TCC等分布式事务方案
案例代码
/** * 查询资源详情 * @param id * @return */ @Override public ResModel<Resource> getResource(Integer id) { String key = CACHE_RESOURCE_KEY + id; //查询缓存 String json = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(json)){//缓存存在 Resource resource = JSONUtil.toBean(json,Resource.class); return ResModel.success(Code.SUCCESS,resource); } //缓存不存在,查询数据库 Resource resource = getById(id); if (resource==null){ return ResModel.error(Code.NON_EXISTENT); } //添加缓存 redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(resource), Duration.ofMinutes(30)); return ResModel.success(Code.SUCCESS,resource); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
/** * 更新资源信息 * @param resource * @return */ public ResModel updateRes(Resource resource) { Integer id = resource.getId(); if (id==null){ return ResModel.error(Code.FAIL); } updateById(resource); redisTemplate.delete(CACHE_RESOURCE_KEY+id); return ResModel.success(Code.UPDATE,resource); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
缓存预热
问题分析
- 请求数量较高
- 主从之间数据吞吐量较大,数据同步操作频度较高
解决方案
前置准备工作:
- 日常例行统计数据访问记录,统计访问频度较高的热点数据
- 利用LRU数据删除策略,构建数据留存队列
- 例如:storm与kafka配合
准备工作:
- 将统计结果中的数据分类,根据级别,redis优先加载级别较高的热点数据
- 利用分布式多服务器同时进行数据读取,提速数据加载过程
- 热点数据主从同时预热
实施:
- 使用脚本程序固定触发数据预热过程
- 如果条件允许,使用了CDN(内容分发网络),效果会更好
总结
缓存预热就是系统启动前,提前将相关的缓存数据直接加载到缓存系统。避免在用户请求的时候,先查询数据库,然后再将数据缓存的问题!用户直接查询事先被预热的缓存数据!
缓存穿透
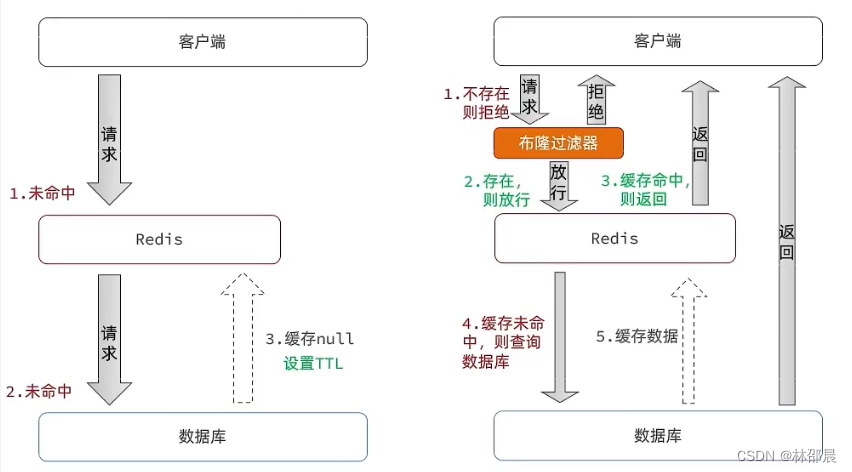
缓存穿透 :缓存穿透是指客户端请求的数据在缓存中和数据库中都不存在,这样缓存永远不会生效,这些请求都会打到数据库。
常见的解决方案有两种:
- 缓存空对象
- 优点:实现简单,维护方便
- 缺点:
- 额外的内存消耗
- 可能造成短期的不一致
- 布隆过滤
- 优点:内存占用较少,没有多余key
- 缺点:
- 实现复杂
- 存在误判可能’
缓存空对象思路分析:当我们客户端访问不存在的数据时,先请求redis,但是此时redis中没有数据,此时会访问到数据库,但是数据库中也没有数据,这个数据穿透了缓存,直击数据库,我们都知道数据库能够承载的并发不如redis这么高,如果大量的请求同时过来访问这种不存在的数据,这些请求就都会访问到数据库,简单的解决方案就是哪怕这个数据在数据库中也不存在,我们也把这个数据存入到redis中去,这样,下次用户过来访问这个不存在的数据,那么在redis中也能找到这个数据就不会进入到缓存了。
布隆过滤:布隆过滤器其实采用的是哈希思想来解决这个问题,通过一个庞大的二进制数组,走哈希思想去判断当前这个要查询的这个数据是否存在,如果布隆过滤器判断存在,则放行,这个请求会去访问redis,哪怕此时redis中的数据过期了,但是数据库中一定存在这个数据,在数据库中查询出来这个数据后,再将其放入到redis中,假设布隆过滤器判断这个数据不存在,则直接返回这种方式优点在于节约内存空间,存在误判,误判原因在于:布隆过滤器走的是哈希思想,只要哈希思想,就可能存在哈希冲突。
总结
缓存穿透产生的原因是什么?
- 用户请求的数据在缓存中和数据库中都不存在,不断发起这样的请求,给数据库带来巨大压力
缓存穿透的解决方案有哪些?
- 缓存null值
- 布隆过滤
- 增强id的复杂度,避免被猜测id规律
- 做好数据的基础格式校验
- 加强用户权限校验
- 做好热点参数的限流
案例代码
/** * 查询资源详情 * @param id * @return */ @Override public ResModel<Resource> getResource(Integer id) { String key = CACHE_RESOURCE_KEY + id; //查询缓存 String json = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(json)){//缓存存在 Resource resource = JSONUtil.toBean(json,Resource.class); return ResModel.success(Code.SUCCESS,resource); } //命中空值 if (json!=null){ return ResModel.error(Code.NON_EXISTENT); } //缓存不存在,查询数据库 Resource resource = getById(id); if (resource==null){ // 缓存空值解决 缓存穿透,设置较短的过期时间 redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key,"",Duration.ofMinutes(2)); return ResModel.error(Code.NON_EXISTENT); } //添加缓存 redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(resource), Duration.ofMinutes(30)); return ResModel.success(Code.SUCCESS,resource); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
缓存雪崩
缓存雪崩是指在同一时段大量的缓存key同时失效或者Redis服务宕机,导致大量请求到达数据库,带来巨大压力。
解决方案:
- 给不同的Key的TTL添加随机值
- 利用Redis集群提高服务的可用性
- 给缓存业务添加降级限流策略
- 给业务添加多级缓存
缓存击穿
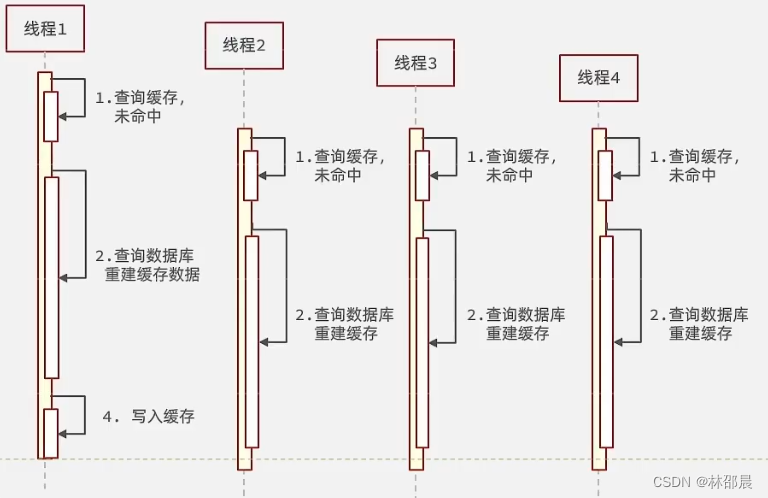
缓存击穿问题也叫热点Key问题,就是一个被高并发访问并且缓存重建业务较复杂的key突然失效了,无数的请求访问会在瞬间给数据库带来巨大的冲击。
解决方案:
- 互斥锁
- 逻辑过期
逻辑分析:假设线程1在查询缓存之后,本来应该去查询数据库,然后把这个数据重新加载到缓存的,此时只要线程1走完这个逻辑,其他线程就都能从缓存中加载这些数据了,但是假设在线程1没有走完的时候,后续的线程2,线程3,线程4同时过来访问当前这个方法, 那么这些线程都不能从缓存中查询到数据,那么他们就会同一时刻来访问查询缓存,都没查到,接着同一时间去访问数据库,同时的去执行数据库代码,对数据库访问压力过大。
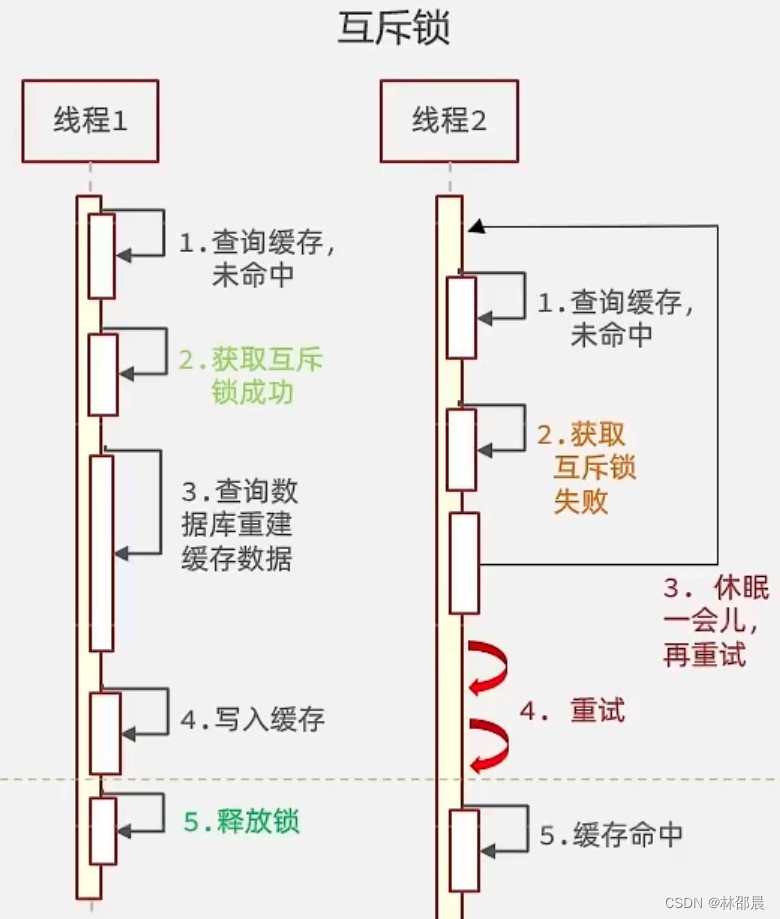
互斥锁
核心思路:利用 redis 的 setnx 方法来表示获取锁,该方法含义是redis中如果没有这个key,则插入成功,返回1,在stringRedisTemplate中返回true, 如果有这个key则插入失败,则返回0,在stringRedisTemplate返回false,我们可以通过true,或者是false,来表示是否有线程成功插入key,成功插入的key的线程我们认为他就是获得到锁的线程。
案例代码
/** * 互斥锁解决 缓存击穿 * @param id * @return */ public ResModel<Resource> queryWithMutex(Integer id){ String key = CACHE_RESOURCE_KEY + id; //查询缓存 String json = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(json)){//缓存存在 Resource resource = JSONUtil.toBean(json,Resource.class); return ResModel.success(Code.SUCCESS,resource); } //命中空值 if (json!=null){ return ResModel.error(Code.NON_EXISTENT); } String lockKey=Mutex_KEY+id; Resource resource = null; try { //尝试获得锁 boolean b = tryLock(lockKey); //没有获得锁,重试 if (!b){ return queryWithMutex(id); } //缓存不存在,查询数据库 resource = getById(id); if (resource==null){ // 缓存空值解决 缓存穿透 redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key,"",Duration.ofMinutes(2)); return ResModel.error(Code.NON_EXISTENT); } //添加缓存 redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(resource), Duration.ofMinutes(30)); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { //释放锁 unlock(lockKey); } return ResModel.success(Code.SUCCESS,resource); } /** * 获得锁 * @param key * @return */ private boolean tryLock(String key) { Boolean flag = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "1", Duration.ofSeconds(10)); return BooleanUtil.isTrue(flag); } /** * 释放锁 * @param key */ private void unlock(String key) { redisTemplate.delete(key); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
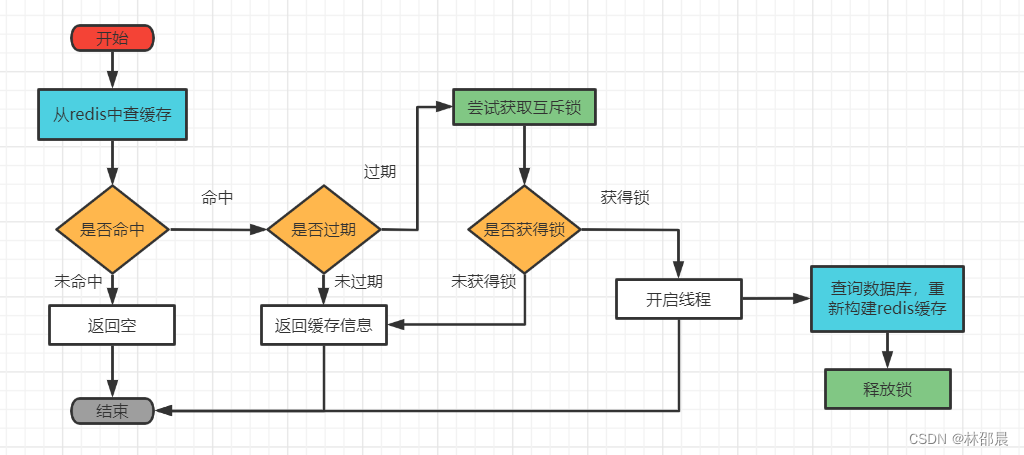
逻辑过期
思路分析:当用户开始查询redis时,判断是否命中,如果没有命中则直接返回空数据,不查询数据库,而一旦命中后,将value取出,判断value中的过期时间是否满足,如果没有过期,则直接返回redis中的数据,如果过期,则在开启独立线程后直接返回之前的数据,独立线程去重构数据,重构完成后释放互斥锁。
案例代码
//创建线程池 private static final ExecutorService THREAD_POOL= Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); /** * 逻辑过期时间解决 缓存击穿 * @param id * @return */ public ResModel<Resource> queryWithLogicalExpire(Integer id) { String key = CACHE_RESOURCE_KEY + id; //查询缓存 String json = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); if (StrUtil.isBlank(json)){//缓存不存在 return ResModel.error(Code.NON_EXISTENT); } //缓存存在 RedisData redisData = JSONUtil.toBean(json, RedisData.class); Resource resource = JSONUtil.toBean((JSONObject) redisData.getData(), Resource.class); LocalDateTime expireTime = redisData.getExpireTime(); if (expireTime.isAfter(LocalDateTime.now())){ //未过期 return ResModel.success(Code.SUCCESS,resource); } //过期 String lockKey=Mutex_KEY+id; boolean b = tryLock(lockKey); if (b){ THREAD_POOL.submit(()->{ try { Resource res = getById(id); RedisData rd = new RedisData(); rd.setData(res); //更新逻辑过期时间 rd.setExpireTime(LocalDateTime.now().plusMinutes(30)); //添加缓存 redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(rd)); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { //释放锁 unlock(key); } }); } return ResModel.success(Code.SUCCESS,resource); } /** * 获得锁 * @param key * @return */ private boolean tryLock(String key) { Boolean flag = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "1", Duration.ofSeconds(10)); return BooleanUtil.isTrue(flag); } /** * 释放锁 * @param key */ private void unlock(String key) { redisTemplate.delete(key); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
封装Redis工具类
基于StringRedisTemplate封装一个缓存工具类,满足下列需求:
- 方法1:将任意Java对象序列化为json并存储在string类型的key中,并且可以设置TTL过期时间
- 方法2:将任意Java对象序列化为json并存储在string类型的key中,并且可以设置逻辑过期时间,用于处理缓存击穿问题
- 方法3:根据指定的key查询缓存,并反序列化为指定类型,利用缓存空值的方式解决缓存穿透问题
- 方法4:根据指定的key查询缓存,并反序列化为指定类型,需要利用逻辑过期解决缓存击穿问题
- 方法5:根据指定的key查询缓存,并反序列化为指定类型,需要互斥锁解决缓存击穿问题
@Component public class CacheClient { private final StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate; //创建线程池 private static final ExecutorService CACHE_REBUILD_EXECUTOR = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); public CacheClient(StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate) { this.stringRedisTemplate = stringRedisTemplate; } /** * 将任意Java对象序列化为json并存储在string类型的key中,并且可以设置TTL过期时间 * @param key * @param value * @param time * @param unit */ public void set(String key, Object value, Long time, TimeUnit unit) { stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(value), time, unit); } /** * 将任意Java对象序列化为json并存储在string类型的key中,并且可以设置逻辑过期时间,用于处理缓 存击穿问题 * @param key * @param value * @param time * @param unit */ public void setWithLogicalExpire(String key, Object value, Long time, TimeUnit unit) { // 设置逻辑过期 RedisData redisData = new RedisData(); redisData.setData(value); redisData.setExpireTime(LocalDateTime.now().plusSeconds(unit.toSeconds(time))); // 写入Redis stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(redisData)); } /** * 根据指定的key查询缓存,并反序列化为指定类型,利用缓存空值的方式解决 缓存穿透问题 * @param keyPrefix key的前缀 * @param id id * @param type 返回值类型 * @param dbFallback 数据库回调函数 * @param time 时间 * @param unit 单位 * @param返回值类型 * @param public <R,ID> R queryWithPassThrough( String keyPrefix, ID id, Class<R> type, Function<ID, R> dbFallback, Long time, TimeUnit unit){ String key = keyPrefix + id; // 1.从redis查询缓存 String json = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); // 2.判断是否存在 if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(json)) { // 3.存在,直接返回 return JSONUtil.toBean(json, type); } // 判断命中的是否是空值 if (json != null) { // 返回空 return null; } // 4.不存在,根据id查询数据库 R r = dbFallback.apply(id); // 5.不存在,添加空值缓存 if (r == null) { // 将空值写入redis stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, "", 2, TimeUnit.MINUTES); // 返回空 return null; } // 6.存在,写入redis this.set(key, r, time, unit); return r; } /** * 逻辑过期时间解决 缓存击穿 * @param keyPrefix key的前缀 * @param id id * @param type 返回值类型 * @param dbFallback 数据库回调函数 * @param time 时间 * @param unit 单位 * @paramid类型 * @return */ 返回值类型 * @param public <R, ID> R queryWithLogicalExpire( String keyPrefix, ID id, Class<R> type, Function<ID, R> dbFallback, Long time, TimeUnit unit) { String key = keyPrefix + id; // 1.从redis查询缓存 String json = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); // 2.判断是否存在 if (StrUtil.isBlank(json)) { // 3.不存在,直接返回 return null; } // 4.命中,需要先把json反序列化为对象 RedisData redisData = JSONUtil.toBean(json, RedisData.class); R r = JSONUtil.toBean((JSONObject) redisData.getData(), type); LocalDateTime expireTime = redisData.getExpireTime(); // 5.判断是否过期 if(expireTime.isAfter(LocalDateTime.now())) { // 5.1.未过期,直接返回缓存信息 return r; } // 6.已过期,缓存重建 // 6.1.获取互斥锁 String lockKey = "lock:" + id; boolean isLock = tryLock(lockKey); // 6.2.判断是否获取锁成功 if (isLock){ // 6.3.成功,开启独立线程,实现缓存重建 CACHE_REBUILD_EXECUTOR.submit(() -> { try { // 查询数据库 R newR = dbFallback.apply(id); // 重建缓存 this.setWithLogicalExpire(key, newR, time, unit); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); }finally { // 释放锁 unlock(lockKey); } }); } // 6.4.返回过期的缓存信息 return r; } /** * 互斥锁解决 缓存击穿 * @param keyPrefix key的前缀 * @param id id * @param type 返回值类型 * @param dbFallback 数据库回调函数 * @param time 时间 * @param unit 单位 * @paramid类型 * @return */ 返回值类型 * @param public <R, ID> R queryWithMutex( String keyPrefix, ID id, Class<R> type, Function<ID, R> dbFallback, Long time, TimeUnit unit) { String key = keyPrefix + id; // 1.从redis查询缓存 String shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); // 2.判断是否存在 if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(shopJson)) { // 3.存在,直接返回 return JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, type); } // 判断命中的是否是空值 if (shopJson != null) { // 返回空值 return null; } // 4.实现缓存重建 // 4.1.获取互斥锁 String lockKey = "lock:" + id; R r = null; try { boolean isLock = tryLock(lockKey); // 4.2.判断是否获取成功 if (!isLock) { // 4.3.获取锁失败,休眠并重试 Thread.sleep(50); return queryWithMutex(keyPrefix, id, type, dbFallback, time, unit); } // 4.4.获取锁成功,根据id查询数据库 r = dbFallback.apply(id); // 5.不存在,缓存空值 if (r == null) { // 将空值写入redis stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, "", 2, TimeUnit.MINUTES); // 返回空值 return null; } // 6.存在,写入redis this.set(key, r, time, unit); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); }finally { // 7.释放锁 unlock(lockKey); } // 8.返回 return r; } /** * 尝试获取锁 * @param key * @return */ private boolean tryLock(String key) { Boolean flag = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "1", 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS); return BooleanUtil.isTrue(flag); } /** * 释放锁 * @param key */ private void unlock(String key) { stringRedisTemplate.delete(key); } }id类型 * @return */ - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
-
相关阅读:
Linux NTP时间同步服务、NFS网络文件共享存储服务
【深度学习】GPU使用教程
新版HI3559AV100开发注意事项
苹果电脑壁纸软件Irvue for mac激活
5G专网在工业场景中的应用及仿真
MC Instruction Decoder
凹凸贴图如何提高物体的真实感
从手动操作到自动化管理,如何实现企业身份业务全面自动化?
Spring源码深度解析(四):Spring框架后置处理器PostProcessor详解
Google拟放弃博通自行研发AI芯片 | 百能云芯
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_54429571/article/details/128080195
