-
Spring——AOP原理及流程详解
一、AOP结构介绍
我们先看个简单的AOP例子:
@Aspect @Component public class AopAspect { @Pointcut("execution(* com.example.spkie.AopTest.AopTest.test())") public void aopTest() { } @Before("aopTest()") public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint){ System.out.println("前置通知"); } @Around("aopTest()") public Object aroundExec(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { System.out.println("环绕前置处理"); Object proceed = joinPoint.proceed(); System.out.println("环绕后置处理"); return proceed; } @AfterReturning(value = "aopTest()") public void doAfterReturning(){ System.out.println("doAfterReturning后置通知"); } @After("aopTest()") public void doAfter(){ System.out.println("doAfter最终通知"); } @AfterThrowing(value = "aopTest()",throwing = "e") public void doThrow(Exception e){ System.out.println("异常通知:"+e.getMessage()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
结果:

我们来细数一下有哪些要素?
- @Aspect:切面类,告诉Spring我这个类是个切面,里面有特殊处理方法
- @Pointcut:切点,告诉Spring我要针对什么
- @Before、@Around、@AfterReturning、@After、@AfterThrowing:通知,告诉Spring针对后要做什么处理
要素就这些吧,@Aspect就不说了就是个标识,主要是切点和处理方法吧
@Pointcut
这个注解值的格式是:表达标签 (表达式格式),用白话说就是用了一种表达式来代表我要针对什么来进行特殊处理,表达标签有以下几种,表达式格式各不太一样,这里就不一一介绍了
- execution:用于匹配方法执行的连接点
- within:用于匹配指定类型内的方法执行
- this:用于匹配当前AOP代理对象类型的执行方法;注意是AOP代理对象的类型匹配,这样就可能包括引入接口也类型匹配
- target:用于匹配当前目标对象类型的执行方法;注意是目标对象的类型匹配,这样就不包括引入接口也类型匹配
- args:用于匹配当前执行的方法传入的参数为指定类型的执行方法
- @within:用于匹配所以持有指定注解类型内的方法
- @target:用于匹配当前目标对象类型的执行方法,其中目标对象持有指定的注解
- @args:用于匹配当前执行的方法传入的参数持有指定注解的执行
- @annotation:用于匹配当前执行方法持有指定注解的方法
- bean:Spring AOP扩展的,AspectJ没有对于指示符,用于匹配特定名称的Bean对象的执行方法
通知
我们上述看到了有五种通知注解,分别表示如下,表示有五种特殊处理方式:
- @Before: 前置通知,在目标方法执行前执行
- @Around: 环绕通知,可以在目标方法前、后进行处理,还可以修改目标方法返回值
- @AfterReturning: 后置通知,在目标方法后执行(发生异常便不会执行)
- @After: 最终通知,不管异常还是正常一定都会执行
- @AfterThrowing:异常通知,在目标方法发生异常后执行
原理
一提起AOP可能第一反应就是动态代理,但是真的就只有动态代理这么简单吗?我们看一个动态代理的例子(以JDK动态代理为例):
@Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { Object invoke=null; try{ System.out.println("前置通知:目标方法执行前执行"); invoke = method.invoke(object, args); System.out.println("后置通知:目标方法执行后执行"); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("异常通知:异常才会执行"); }finally { System.out.println("最终通知:一定会执行"); } return invoke; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
这乍一看好像就是这个道理啊,好像全满足了呀,真满足吗?环绕通知要怎么做?通知有多个,有多个处理方法怎么做?总不可能一直往这里面塞吧,还有环绕通知需要在invoke方法外面再套一层吧,有多个的话无限套娃?
那要怎么做?注意看这是不是都是串行执行的,串行执行的拦截处理方法是什么?拦截器链!!
流程如下图所示:
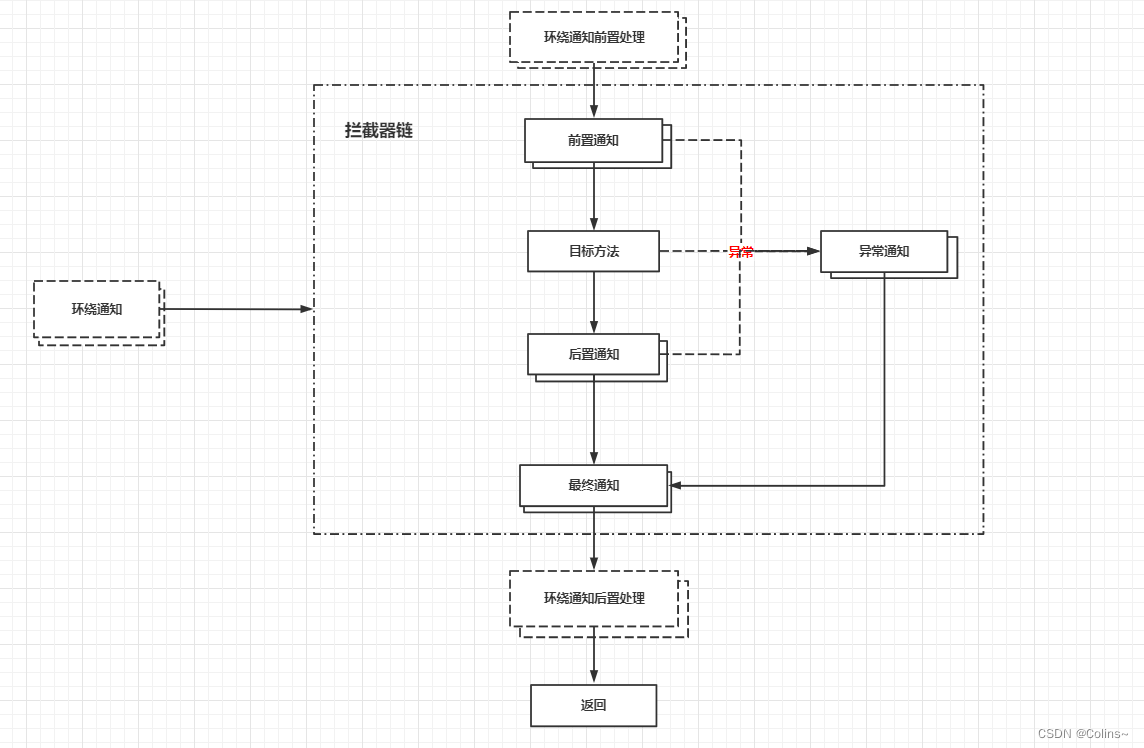
注意看所有通知都是多个:
- 无环绕,无异常的情况下:所有前置通知→目标方法→所有后置通知→所有最终通知→返回
- 无环绕,有异常的情况下:所有前置通知→目标方法→所有异常通知→所有最终通知→返回(这里注意前置、目标、后置任何一个异常都会到异常通知)
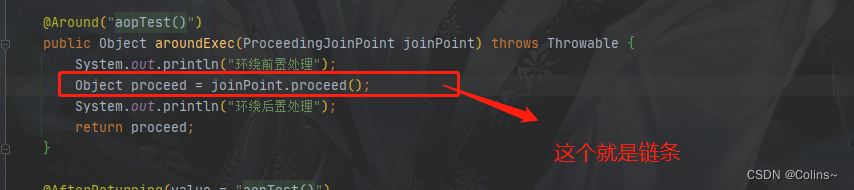
- 有环绕的情况下:先执行环绕前置→再执行链条→然后环绕后置(如下图)
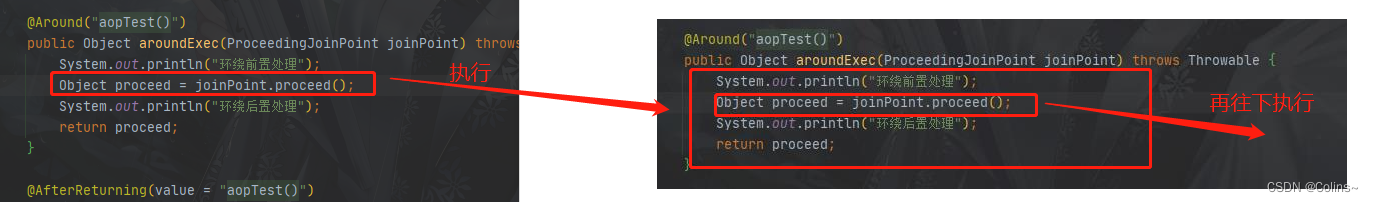
多个环绕会怎样?注意环绕通知本身就是链条的里面的,只不过在最前面执行,多个环绕就会像这样:
好了重点来了,我们知道原理了动态代理+拦截器链,我们需要知道Spring怎么帮我们组装的?
- 动态代理很简单就两种方式:JDK和Cglib
- 拦截器链:是不是需要把上述切面里面的方法全提取出来封装好,然后最后组装成链条
- 连接点:拦截器通过什么连接到一起?需要相同的连接点吧
接下来我们就去验证一下
连接点
在Spring里面连接点是Joinpoint这个接口:
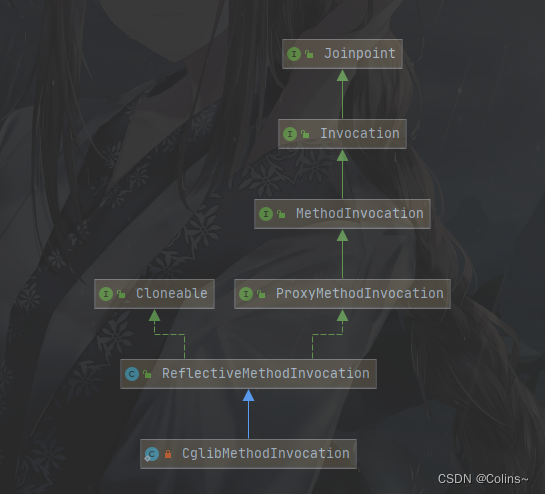
如上图可见就两个实现类:
ReflectiveMethodInvocation:提供给JDK动态代理方式使用
CglibMethodInvocation:提供给Cglib动态代理方式使用
先不管有啥用,,记得先
拦截器
既然知道是拦截器链了,那每个通知方法应该都有对应的拦截器,我们去看看(只看invoke方法哈):
前置通知拦截器MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor:
public class MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, BeforeAdvice, Serializable { private final MethodBeforeAdvice advice; public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) { Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null"); this.advice = advice; } @Nullable public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { //前置处理 这个就是利用反射执行我们定义的前置方法 this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis()); // 调用链条 return mi.proceed(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
后置通知拦截器AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor:
public class AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable { private final AfterReturningAdvice advice; public AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor(AfterReturningAdvice advice) { Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null"); this.advice = advice; } @Nullable public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { //先执行链条 Object retVal = mi.proceed(); // 后利用反射执行我们定义的后置通知方法 this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis()); return retVal; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
异常通知拦截器ThrowsAdviceInterceptor :
public class ThrowsAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice { // 省略............ @Nullable public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { try { // 这个就是链条 return mi.proceed(); } catch (Throwable var4) { // 链条报错了 就异常处理(还需要判断是不是需要处理的异常) // 异常通知可以指定需要处理的异常 Method handlerMethod = this.getExceptionHandler(var4); if (handlerMethod != null) { this.invokeHandlerMethod(mi, var4, handlerMethod); } throw var4; } } // 省略............... }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
最终通知AspectJAfterAdvice :
public class AspectJAfterAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable { public AspectJAfterAdvice(Method aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut, AspectInstanceFactory aif) { super(aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, pointcut, aif); } @Nullable public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { Object var2; try { // 先执行链条 var2 = mi.proceed(); } finally { //最终执行 this.invokeAdviceMethod(this.getJoinPointMatch(), (Object)null, (Throwable)null); } return var2; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
环绕通知AspectJAroundAdvice :
public class AspectJAroundAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable { public AspectJAroundAdvice(Method aspectJAroundAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut, AspectInstanceFactory aif) { super(aspectJAroundAdviceMethod, pointcut, aif); } @Nullable public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { if (!(mi instanceof ProxyMethodInvocation)) { throw new IllegalStateException("MethodInvocation is not a Spring ProxyMethodInvocation: " + mi); } else { ProxyMethodInvocation pmi = (ProxyMethodInvocation)mi; ProceedingJoinPoint pjp = this.lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(pmi); JoinPointMatch jpm = this.getJoinPointMatch(pmi); // 这个就是去执行我们 自己写的环绕通知方法 // 所以环绕通知方法一定会有个参数嘛 joinPoint.proceed()就是执行链条 return this.invokeAdviceMethod(pjp, jpm, (Object)null, (Throwable)null); } } protected ProceedingJoinPoint lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(ProxyMethodInvocation rmi) { return new MethodInvocationProceedingJoinPoint(rmi); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
以上就是关于通知链条里面所有最后会执行的方法,可以看到共同点就是invoke方法的传参MethodInvocation ,这不就是我们之前说的连接点嘛,当然还有很多内置的其他拦截器,但这都跟我们AOP拦截器没关系
以上基础概念相信大家都懂了,接下来我们看看Spring是怎么代理一个Bean的,是怎么为这个Bean组装这些拦截器的
二、Bean介入点
这AOP代理到底是在Bean生成流程中哪个地方介入进来为我们生成代理对象的咧?
从AOP配置加载点一看便知,开启AOP的配置注解是 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy(现在已经默认开启了,不需要加注解也行,配置类是AopAutoConfiguration)
EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解内部导入了一个类AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar
AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar
这个类实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口,这个接口之前说过了,可以注册BeanDefination,所以我们要看看注册的这个是什么?干了什么?
沿着那个方法一路往下,发现注册了AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator

AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
这个类可谓是最重要的类了,从下方的类图上看,它实现了很多接口,还有我们非常熟悉的后置处理器,在这里面主要实现了4个方法:
- setBeanFactory:实例化后,初始化前调用
- getEarlyBeanReference:和三级缓存有关,存在循环依赖里面会调用
- postProcessBeforeInstantiation:实例化前执行
- postProcessAfterInitialization:初始化后执行
别看有4个方法,其实下面三个方法内部都会调用一样的方法,只是需要注意在Bean生成流程中的介入点
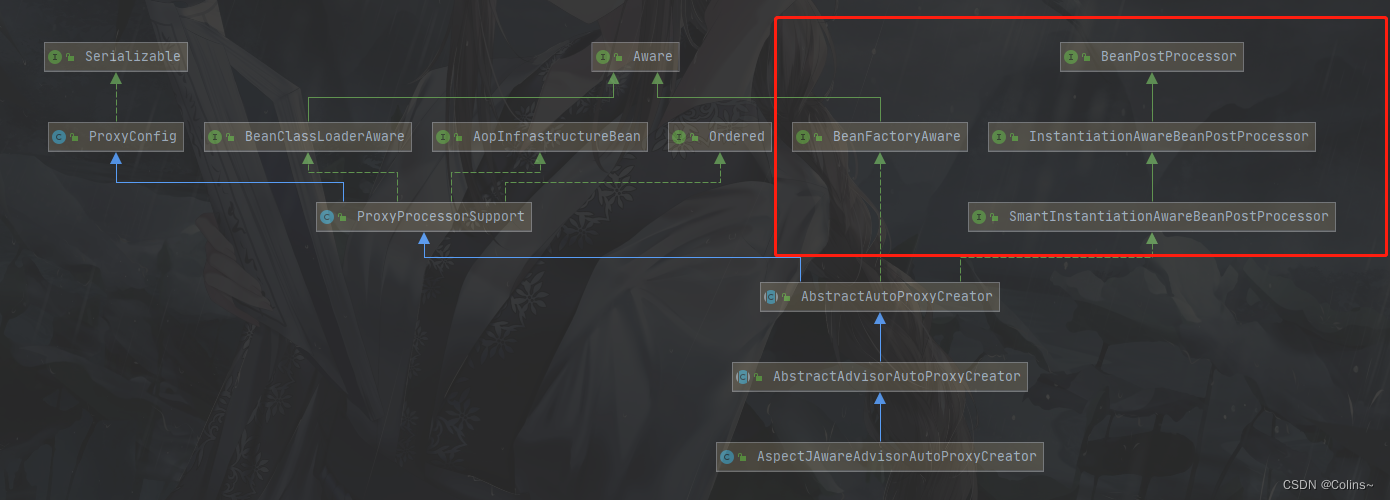
我们先看一下共同方法是哪个,这个类的顶级父类是AbstractAutoProxyCreator,去看看
AbstractAutoProxyCreator
实例前执行
postProcessBeforeInstantiation()
实例前执行,主要是判断代理目标对象是否已经存在了,存在了就走getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法,然后调用createProxy()方法创建代理对象
Object cacheKey = this.getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName); if (!StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) { return null; } if (this.isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || this.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return null; } } // 判断代理目标对象是否已经存在了 存在了就进入代理流程 TargetSource targetSource = this.getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName); if (targetSource != null) { if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName)) { this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName); } Object[] specificInterceptors = this.getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource); // 创建动态代理对象 Object proxy = this.createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource); this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } else { return null; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
初始化后执行
postProcessAfterInitialization
初始化后执行,会调用wrapIfNecessary()方法
//该bean初始化完毕之后,回调该方法判断该bean是否需要被代理 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) { if (bean != null) { Object cacheKey = this.getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName); //如果该bean未执行过AOP,则进行封装;如果执行过,则不再进行封装 if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) { return this.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey); } } return bean; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
wrapIfNecessary()方法也会调用getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法来获取对应的通知处理,如果没获取到通知处理方法说明不需要代理,获取到了就要创建代理对象了createProxy()
注意: 这里的通知处理就是切面里面的通知方法,getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean就是获取所有的切面类里面的切点及通知方法与Bean来匹配,匹配上了说明这个Bean要被代理,同时会封装匹配的切点对应的所有通知方法返回
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) { if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { return bean; } else if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) { return bean; } else if (!this.isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) && !this.shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) { // 获取该bean的所有的通知处理 Object[] specificInterceptors = this.getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, (TargetSource)null); // 获取的通知处理不为空 说明要代理 if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE); // 创建代理 Object proxy = this.createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } else { // 为空就不需要创建代理了 直接返回Bean this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; } } else { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
循环依赖会调用
getEarlyBeanReference
三级缓存,存在循环依赖则会调用,这里put进去代表已经生成代理了,所以后续初始化后调用的时候会get判断一次,这个也会调用wrapIfNecessary() 方法
public Object getEarlyBeanReference(Object bean, String beanName) { Object cacheKey = this.getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName); this.earlyProxyReferences.put(cacheKey, bean); return this.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
总结
所以会在Bean实例化前、循环依赖、初始化后介入处理,当然只会处理一次,最终都会调用getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法来对Bean进行切点匹配,匹配上了就调用createProxy方法生成代理对象然后返回
三、处理切面
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean()
会先获取所有的切面其下的通知方法,然后根据切点表达式去和这个Bean对象匹配,将匹配成功的通知方法返回,这就说明该Bean需要被代理,匹配成功的通知方法排序后就是需要执行的方法调用链
@Nullable protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) { // 获取所有切面其下的切面通知方法 Listadvisors = this.findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName); // 为空返回空数组 不为空转成数组返回 return advisors.isEmpty() ? DO_NOT_PROXY : advisors.toArray(); } // 获取所有切面及其下的切面通知方法 protected List findEligibleAdvisors(Class beanClass, String beanName) { // 获取所有切面及其下的切面通知方法 List candidateAdvisors = this.findCandidateAdvisors(); // 从中根据切点筛选出符合Bean的通知方法 List eligibleAdvisors = this.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName); this.extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) { eligibleAdvisors = this.sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); } return eligibleAdvisors; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
获取所有切面其下通知方法
获取切面
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.findCandidateAdvisors
有个父类的方法是获取一些实现了Advisor接口的Bean,我们重点关注被@Aspect注解标识的Bean的处理
protected ListfindCandidateAdvisors() { // 获取所有实现了Advisor接口的Bean 有些内置的比如事务 List advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors(); if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) { // 获取被注解@Aspect标识的Bean 以及其下的切点和通知方法 advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors()); } return advisors; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors
会遍历所有的Bean找到其中被注解 @Aspect 标识的,然后去处理其下的切点和通知方法
public ListbuildAspectJAdvisors() { List aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames; if (aspectNames == null) { synchronized(this) { aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames; if (aspectNames == null) { List advisors = new ArrayList(); List aspectNames = new ArrayList(); String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false); String[] var18 = beanNames; int var19 = beanNames.length; // 遍历所有的Bean for(int var7 = 0; var7 < var19; ++var7) { String beanName = var18[var7]; if (this.isEligibleBean(beanName)) { Class beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName, false); // 判断是否被@Aspect注解标识 标示的就需要去处理其下的切点和通知方法 if (beanType != null && this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) { aspectNames.add(beanName); AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName); if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) { MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName); // 去获取其下的切点和通知方法 List classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory); if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) { this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors); } else { this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory); } advisors.addAll(classAdvisors); } // 省略.............. } } } this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames; return advisors; } } } // 省略.............. } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
获取切面下的通知方法
ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvisors
遍历切面下的所有方法,去找方法上是否有相应的注解,如果有则需要封装处理
public ListgetAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) { Class aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass(); String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName(); this.validate(aspectClass); MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory = new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory); List advisors = new ArrayList(); // 获取切面下的所有方法 Iterator var6 = this.getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass).iterator(); // 遍历所有方法 while(var6.hasNext()) { Method method = (Method)var6.next(); // 判断该方法是否被相关注解标识 标识的方法处理后封装返回 Advisor advisor = this.getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, 0, aspectName); if (advisor != null) { advisors.add(advisor); } } // 省略...... return advisors; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvisor
遍历我需要的注解,在方法上找注解是否存在,存在的就需要封装处理
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) { this.validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass()); // 获取方法上的注解 实际就是遍历需要的注解 一个个找 AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = this.getPointcut(candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass()); // 没有对应的注解就返回null 有对应的注解就需要处理封装后返回 return expressionPointcut == null ? null : new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod, this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName); } private AspectJExpressionPointcut getPointcut(Method candidateAdviceMethod, Class candidateAspectClass) { // 看下面方法 AspectJAnnotation aspectJAnnotation = AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod); if (aspectJAnnotation == null) { return null; } else { // 找到了就设置一下切点上的表达式 AspectJExpressionPointcut ajexp = new AspectJExpressionPointcut(candidateAspectClass, new String[0], new Class[0]); ajexp.setExpression(aspectJAnnotation.getPointcutExpression()); if (this.beanFactory != null) { ajexp.setBeanFactory(this.beanFactory); } return ajexp; } } // ASPECTJ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES = new Class[]{Pointcut.class, Around.class, Before.class, After.class, AfterReturning.class, AfterThrowing.class}; protected static AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.AspectJAnnotation findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(Method method) { // 遍历需要的注解,一个一个找 Class[] var1 = ASPECTJ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES; int var2 = var1.length; for(int var3 = 0; var3 < var2; ++var3) { Class clazz = var1[var3]; AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.AspectJAnnotation foundAnnotation = findAnnotation(method, clazz); if (foundAnnotation != null) { return foundAnnotation; } } return null; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
通知方法的封装
InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
这个在构造里面就会对通知方法进行处理封装
public InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut, Method aspectJAdviceMethod, AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) { this.declaredPointcut = declaredPointcut; this.declaringClass = aspectJAdviceMethod.getDeclaringClass(); this.methodName = aspectJAdviceMethod.getName(); this.parameterTypes = aspectJAdviceMethod.getParameterTypes(); this.aspectJAdviceMethod = aspectJAdviceMethod; this.aspectJAdvisorFactory = aspectJAdvisorFactory; this.aspectInstanceFactory = aspectInstanceFactory; this.declarationOrder = declarationOrder; this.aspectName = aspectName; if (aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) { Pointcut preInstantiationPointcut = Pointcuts.union(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getPerClausePointcut(), this.declaredPointcut); this.pointcut = new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl.PerTargetInstantiationModelPointcut(this.declaredPointcut, preInstantiationPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); this.lazy = true; } else { this.pointcut = this.declaredPointcut; this.lazy = false; // 封装通知方法 this.instantiatedAdvice = this.instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvice
所有的通知方法都会被封装成对应处理类
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) { Class candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass(); this.validate(candidateAspectClass); AspectJAnnotation aspectJAnnotation = AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod); if (aspectJAnnotation == null) { return null; } else if (!this.isAspect(candidateAspectClass)) { throw new AopConfigException("Advice must be declared inside an aspect type: Offending method '" + candidateAdviceMethod + "' in class [" + candidateAspectClass.getName() + "]"); } else { if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Found AspectJ method: " + candidateAdviceMethod); } Object springAdvice; // 根据方法上的注解类型 封装对应的通知方法处理类 switch(aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) { case AtPointcut: if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'"); } return null; case AtAround: springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); break; case AtBefore: springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); break; case AtAfter: springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); break; case AtAfterReturning: springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning)aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation(); if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) { ((AbstractAspectJAdvice)springAdvice).setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning()); } break; case AtAfterThrowing: springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory); AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing)aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation(); if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) { ((AbstractAspectJAdvice)springAdvice).setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing()); } break; default: throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod); } ((AbstractAspectJAdvice)springAdvice).setAspectName(aspectName); ((AbstractAspectJAdvice)springAdvice).setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder); String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod); if (argNames != null) { ((AbstractAspectJAdvice)springAdvice).setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames); } ((AbstractAspectJAdvice)springAdvice).calculateArgumentBindings(); return (Advice)springAdvice; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
通知方法与Bean匹配
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.findAdvisorsThatCanApply
protected ListfindAdvisorsThatCanApply(List candidateAdvisors, Class beanClass, String beanName) { ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(beanName); List var4; try { // 通知方法集合与Bean匹配 var4 = AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass); } finally { ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName((String)null); } return var4; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
总结
所以这一步会找到所有的切面,遍历其下的所有切点和通知方法,然后根据切点中的表达式去与Bean对象匹配,获取所有匹配成功的通知方法,将这些通知方法排序后就是最后的方法执行链,同时也说明该Bean需要被代理,所以需要创建代理对象
四、创建代理对象
AbstractAutoProxyCreator.createProxy
这里实际就是在创建代理对象前填充一下必要信息,然后创建代理对象,默认是采用JDK动态代理,如果被代理的目标对象不是接口,则会采用Cglib动态代理
- CglibAopProxy:Cglib动态代理逻辑类
- JdkDynamicAopProxy:Jdk动态代理逻辑类(我们以这个为例)
protected Object createProxy(Class beanClass, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) { if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) { AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory)this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass); } ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(); proxyFactory.copyFrom(this); // 省略一大段........... // 匹配成功的某些通知方法会被包装成拦截器 上面说过了 Advisor[] advisors = this.buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors); proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors); proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource); this.customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory); proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy); if (this.advisorsPreFiltered()) { proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true); } ClassLoader classLoader = this.getProxyClassLoader(); if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader && classLoader != beanClass.getClassLoader()) { classLoader = ((SmartClassLoader)classLoader).getOriginalClassLoader(); } // 上面设置搞定后 就要获取代理对象 JDK还是Cglib return proxyFactory.getProxy(classLoader); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
JdkDynamicAopProxy.getProxy
这一步很简单就是直接创建代理对象,处理类是this,说明该类本身就是处理类
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource()); } return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, this.proxiedInterfaces, this); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
五、代理执行方法
我们以JDK动态代理为例,最终代理对象在执行方法的时候就会调用该方法:
JdkDynamicAopProxy.invoke
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { Object oldProxy = null; boolean setProxyContext = false; TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource; Object target = null; Class var8; try { // 省略........... if (method.getDeclaringClass() != DecoratingProxy.class) { Object retVal; // 省略........... target = targetSource.getTarget(); Class targetClass = target != null ? target.getClass() : null; // 根据具体要执行的方法 再去之前匹配成功的通知方法集合中找对应的增强方法 // 前面匹配的通知方法集合并不一定是针对类下的所有方法 所以还需要匹配一次 List- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
六、总结
- AOP代理对象的生成是在Bean实例化前、循环依赖、初始化后这三个位置判断生成的(以初始化后为主,其他两个阶段属于特殊阶段)
- 通过获取所有的切面下的通知方法以切点表达式来与Bean匹配,来判断该Bean是否需要被代理,同时准备好了与该Bean相关的所有增强方法
- AOP默认采用JDK动态代理的方式,如果被代理目标对象不是接口,则会采用Cglib的代理方法
- AOP的底层原理虽然是动态代理,但是我觉得最重要的还是执行的方法调用链非常巧妙
- 在逻辑实现上:每种通知在调用链上执行的方式及其执行顺序决定了其扮演的角色
- 每个通知最后执行类在前面已经给出,可直接查看学习
最后附上个执行结构图
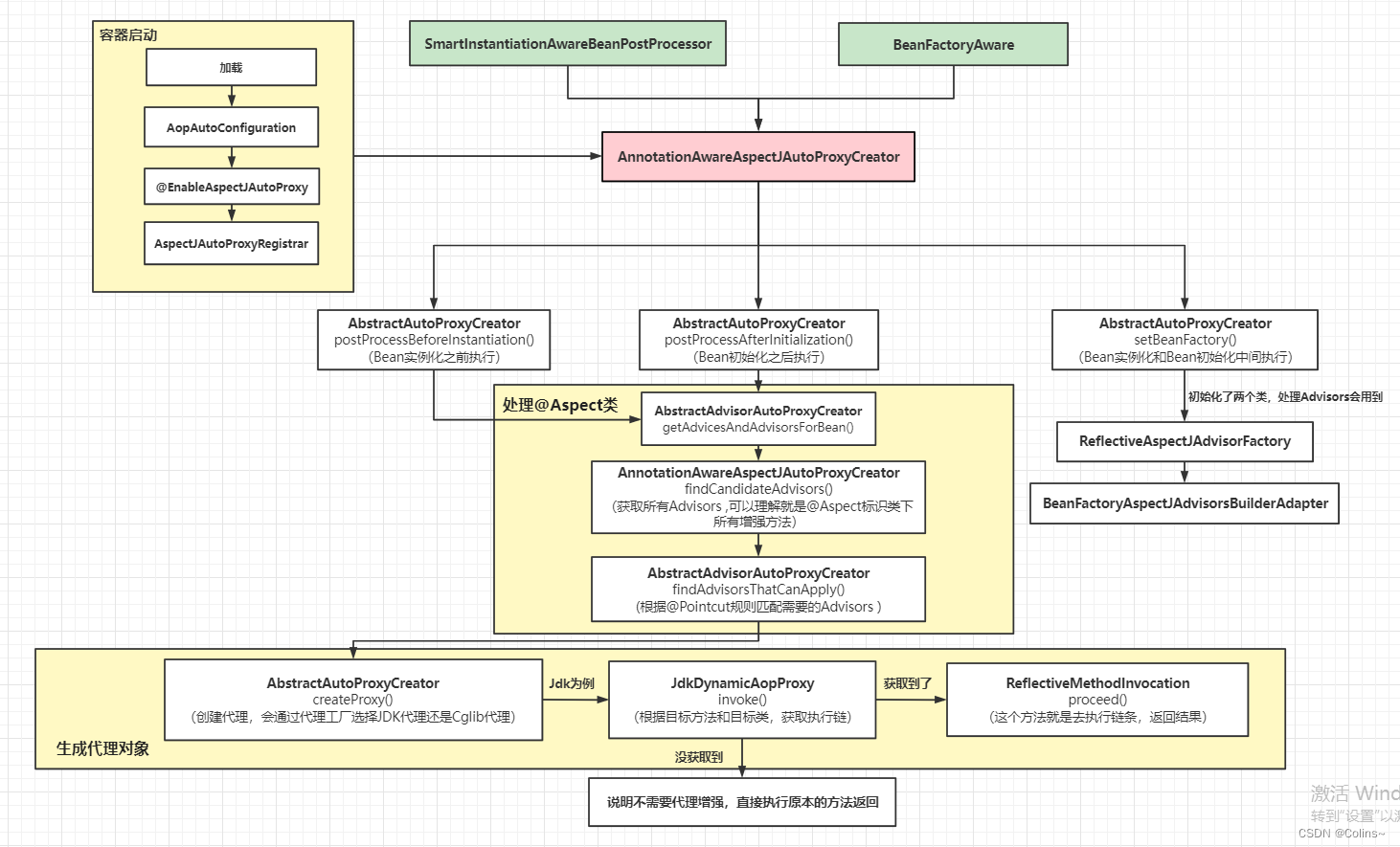
个人博客: 全是干货,相信不会让你失望
-
相关阅读:
3D编程模式:依赖隔离模式
使用Vercel托管python后端API——引包引环境,手把手详细教程
sklearn快速入门教程:(三)机器学习的通用模式及实现方法 学习笔记
IDEA常用快捷键以及调试
vue中使用高德地图的热力图方法1
小程序 canvas 2d 绘制海报
C# 后台处理 webp图片
我用Redis分布式锁,抢了瓶茅台,然后GG了~~
AAC 音频数据结构实例分析:
简单易用,效果卓越的电子期刊制作网站
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44102992/article/details/128087883
