-
【SpringCloud】07 流量管理sentinel
sentinel
Sentinel 是面向分布式服务架构的高可用流量防护组件,主要以流量为切入点,从限流、流量整形、熔断降级、系统负载保护、热点防护等多个维度来帮助开发者保障微服务的稳定性。
1. 微服务中的服务雪崩
服务雪崩效应是一种因“服务提供者的不可用”(原因)导致“服务调用者不可用”(结果),并将不可用逐渐放大的现象。
2. 解决雪崩的方案
造成服务雪崩的原因有很多,包括硬件原因,网络原因,软件原因等等。这里,我们只谈从软件方面,解决服务雪崩的几种解决方案和解决套路,以此来了解微服务架构中相关的技术栈的由来以及使用理由。
-
设置超时:
- 造成线程的挤压都是因为同步远程调用长时间没有得到回复造成的,所以设置超时时间,可以减少线程的长时间占用,避免线程挤压。 流量限制:
- 对服务进行限流,避免服务因并发量过大而造成服务崩掉。 熔断降级:
- 对已经挂掉的服务,直接不再进行调用,而是直接返回结果,这就是熔断。以此避免已经挂掉的服务对调用者造成的影响。 舱壁模式:
-
舱壁模式(Bulkhead)隔离了每个工作负载或服务的关键资源,如连接池、内存和CPU。
使用舱壁 避免了单个工作负载(或服务)消耗掉所有资源,从而导致其他服务出现故障的场景。
这种模式主要是通过防止由一个服务引起的级联故障来增加系统的弹性。
泰坦尼克号沉没的主要原因之一是其舱壁设计失败,水可以通过上面的甲板倒在舱壁的顶部,导致整个船体淹没。
流量管理的主键:hystrix:netflix 和 sentinel:阿里巴巴
3. 使用sentinel
开启sentinel控制台
可以设置接入该控制台的微服务的流量控制 熔断降级。
运行sentinel的jar包
访问控制台界面http://localhost:8080

账户和密码: sentinel/sentinel微服务接入sentinel平台
(1)引入依赖<dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.cloudgroupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinelartifactId> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
(2)配置
spring: cloud: sentinel: transport: dashboard: localhost:8080- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
(3)访问微服务的任意接口
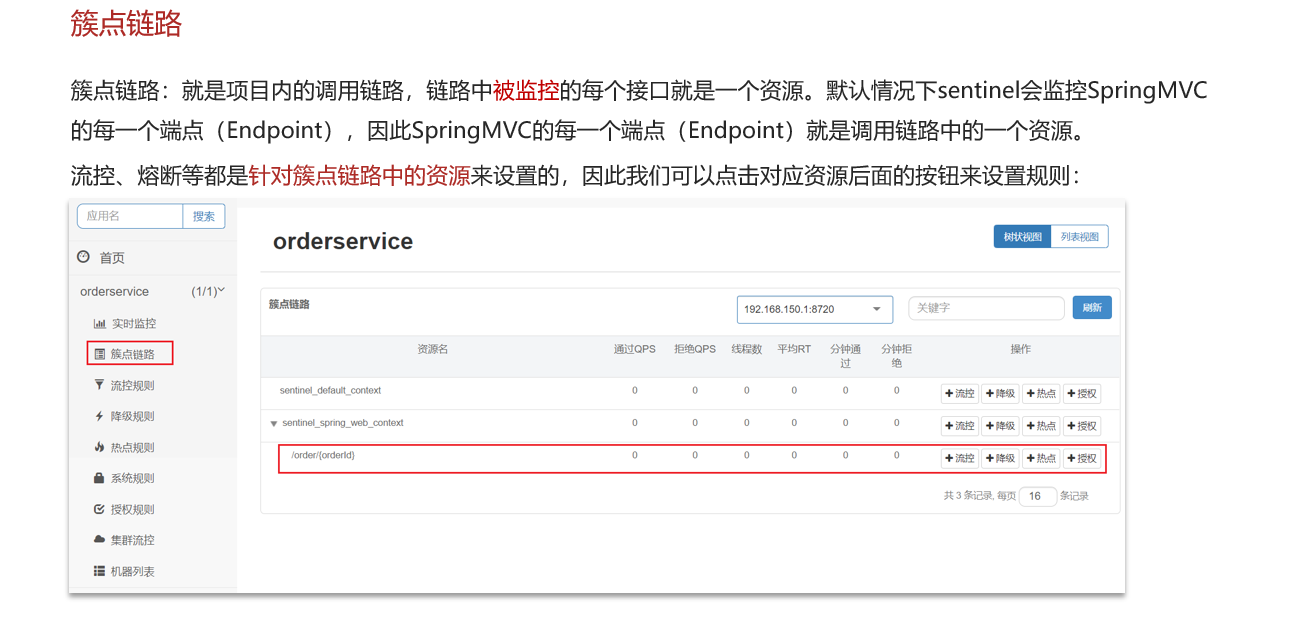
点击资源/order/{orderId}后面的流控按钮,就可以弹出表单。表单中可以添加流控规则,如下图所示:
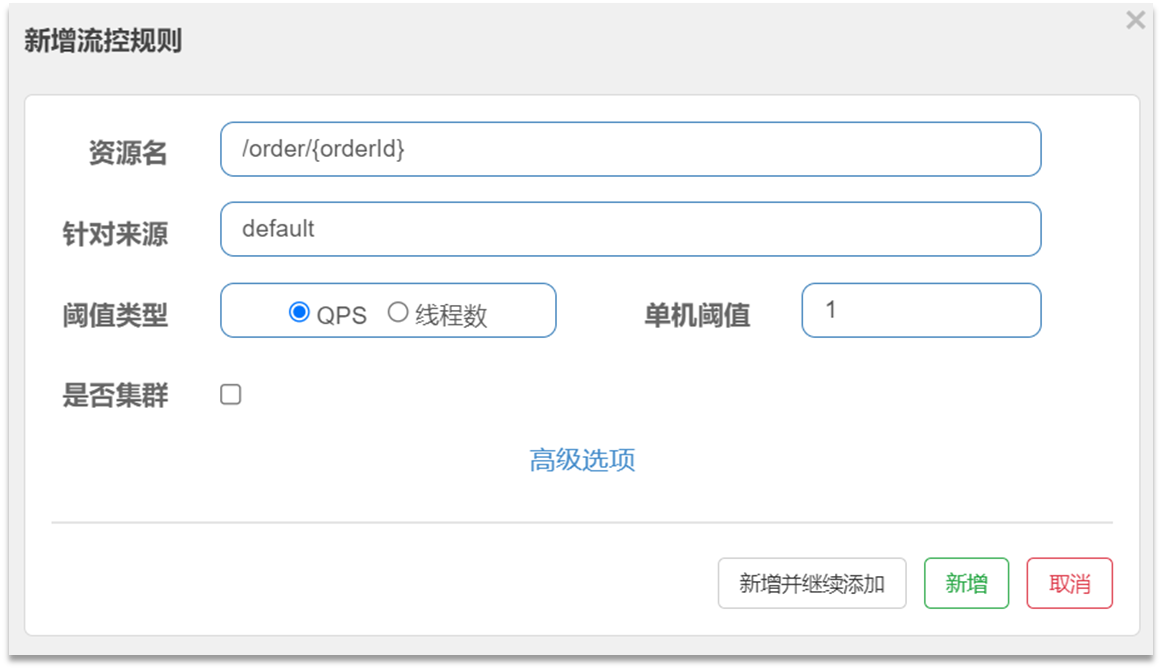
其含义是限制 /order/{orderId}这个资源的单机QPS为1,即每秒只允许1次请求,超出的请求会被拦截并报错。
3.1 三种流控模式
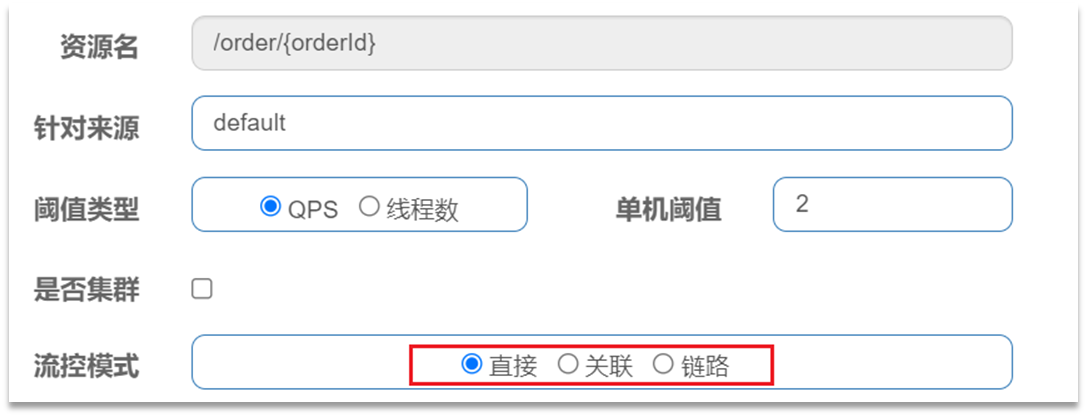
在添加限流规则时,点击高级选项,可以选择三种流控模式:
- 直接:统计当前资源的请求,触发阈值时对当前资源直接限流,也是默认的模式
- 关联:统计与当前资源相关的另一个资源,触发阈值时,对当前资源限流
- 链路:统计从指定链路访问到本资源的请求,触发阈值时,对指定链路限流
3.1.1 关联模式
关联模式:统计与当前资源相关的另一个资源,触发阈值时,对当前资源限流
- 使用场景:比如用户支付时需要修改订单状态,同时用户要查询订单。查询和修改操作会争抢数据库锁,产生竞争。
- 业务需求是有限支付和更新订单的业务,因此当修改订单业务触发阈值时,需要对查询订单业务限流。
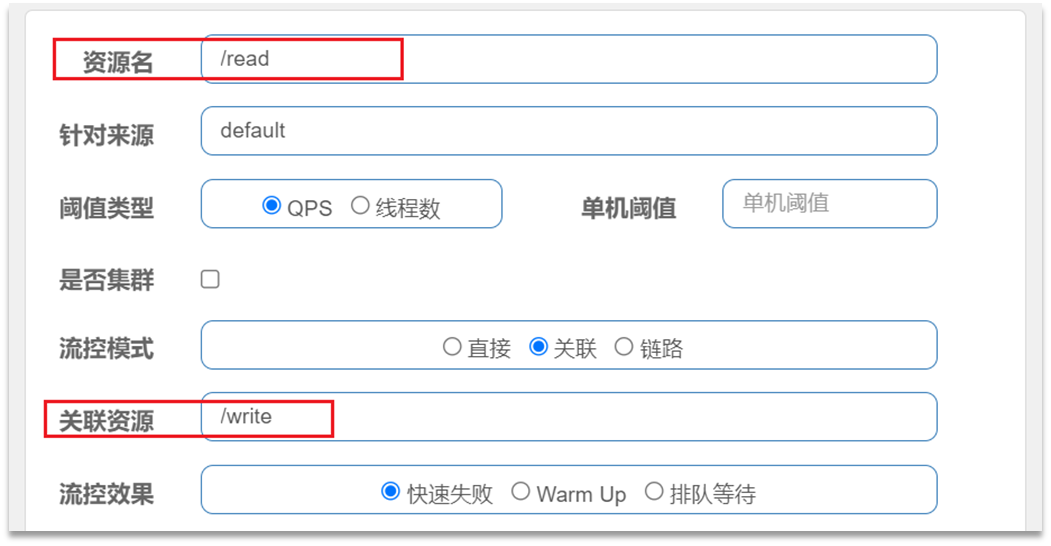
当/write资源访问量触发阈值时,就会对/read资源限流,避免影响/write资源。
满足下面条件可以使用关联模式:
- 两个有竞争关系的资源
- 一个优先级较高,一个优先级较低
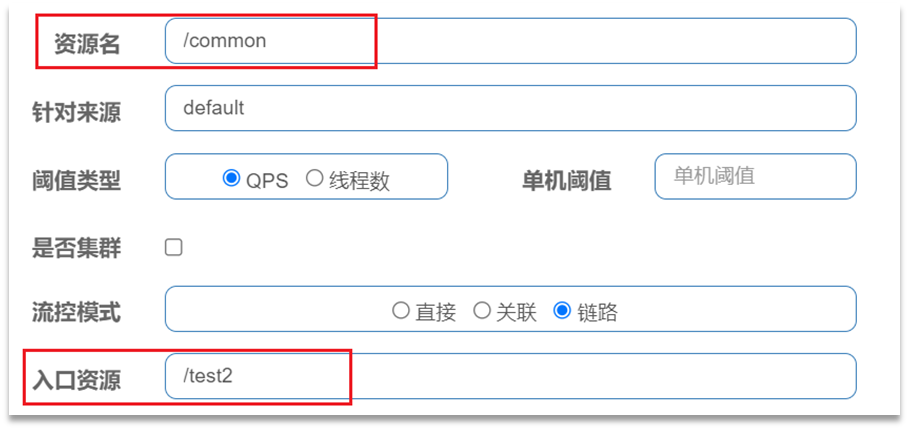
3.1.2 链路模式
链路模式:只针对从指定链路访问到本资源的请求做统计,判断是否超过阈值。
例如有两条请求链路:
-
/test1 -》 /common
-
/test2 -》 /common
如果只希望统计从/test2进入到/common的请求,则可以这样配置:
- Sentinel默认只标记Controller中的方法为资源,如果要标记其它方法,需要利用@SentinelResource注解,示例:

- Sentinel默认会将Controller方法做context整合,导致链路模式的流控失效,需要修改application.yml,添加配置:

4. 流控效果
流控效果是指请求达到流控阈值时应该采取的措施,包括三种:
- 快速失败:达到阈值后,新的请求会被立即拒绝并抛出FlowException异常。是默认的处理方式。
- warm up:预热模式,对超出阈值的请求同样是拒绝并抛出异常。但这种模式阈值会动态变化,从一个较小值逐渐增加到最大阈值。
- 排队等待:让所有的请求按照先后次序排队执行,两个请求的间隔不能小于指定时长
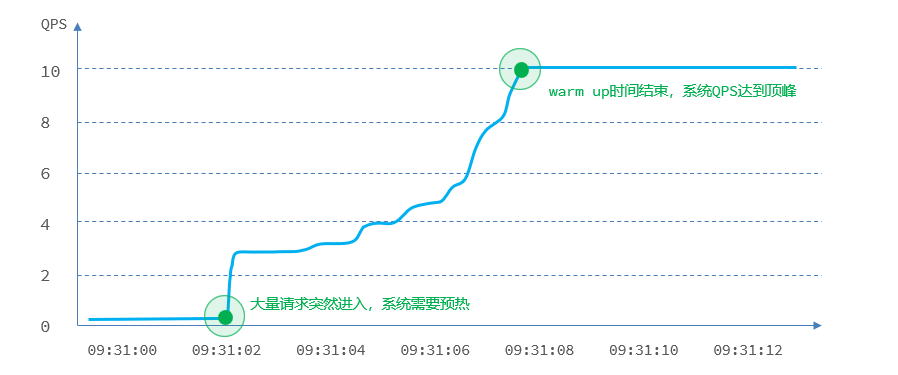
4.1 warm up
warm up也叫预热模式,是应对服务冷启动的一种方案。请求阈值初始值是 threshold / coldFactor,持续指定时长后,逐渐提高到threshold值。而coldFactor的默认值是3.
例如,我设置QPS的threshold为10,预热时间为5秒,那么初始阈值就是 10 / 3 ,也就是3,然后在5秒后逐渐增长到10.
4.2 排队等待
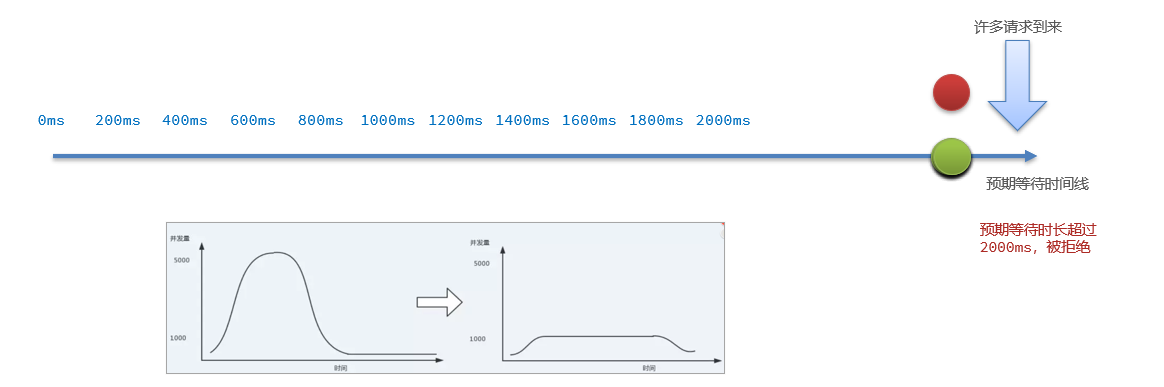
当请求超过QPS阈值时,快速失败和warm up 会拒绝新的请求并抛出异常。而排队等待则是让所有请求进入一个队列中,然后按照阈值允许的时间间隔依次执行。后来的请求必须等待前面执行完成,如果请求预期的等待时间超出最大时长,则会被拒绝。
例如:QPS = 5,意味着每200ms处理一个队列中的请求;timeout = 2000,意味着预期等待超过2000ms的请求会被拒绝并抛出异常
5. 热点参数限流
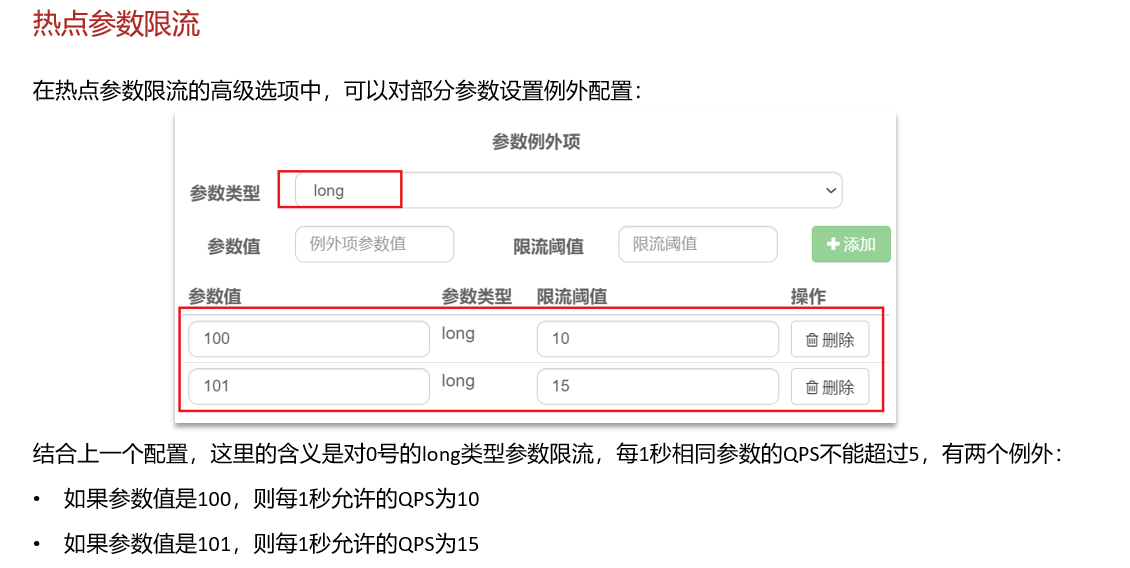
热点参数限流默认对SpringMVC资源无效6. 熔断和降级
6.1 openfeign和sentinel整合
(1)开启feign的sentinel功能
# 开启openfeign的sentinel功能 feign: sentinel: enabled: true- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
(2)创建一个降级类并实现FallbackFactory接口 该接口的泛型就是feign接口类
@Component @Slf4j public class ProductFeignFactory implements FallbackFactory<ProductFeign>{ @Override public ProductFeign create(Throwable throwable) { return new ProductFeign() { @Override public Product getById(Long pid) { log.error("商品微服务故障"+throwable.getMessage()); //默认的一个商品对象 Product product=new Product(); return product; } }; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
(3)在feign调用时使用降级类
//value:调用远程微服务的名称 fallbackFactory:降级类工厂 @FeignClient(value = "shop-product",fallbackFactory = ProductFeignFactory.class) public interface ProductFeign { @GetMapping("/product/getById/{pid}") public Product getById(@PathVariable Long pid); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
6.2 线程隔离(舱壁模式)
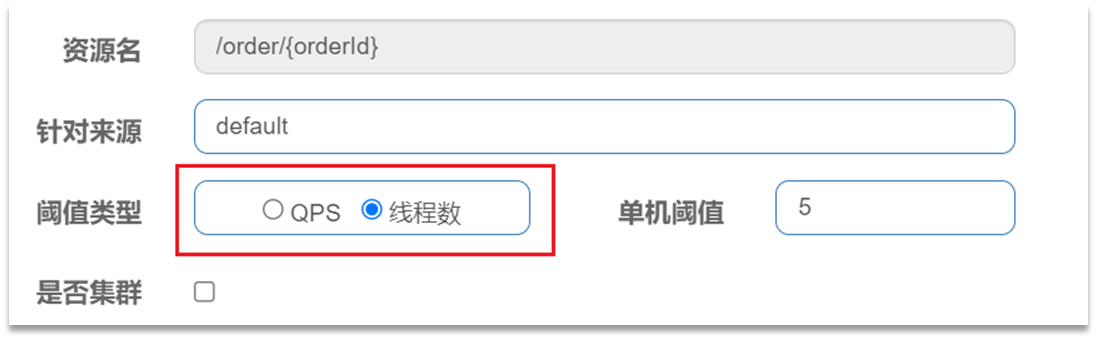
在添加限流规则时,可以选择两种阈值类型:
- QPS:就是每秒的请求数,在快速入门中已经演示过
- 线程数:是该资源能使用用的tomcat线程数的最大值。也就是通过限制线程数量,实现舱壁模式。
线程隔离的两种手段是?
-
信号量隔离
-
线程池隔离
信号量隔离的特点是?
- 基于计数器模式,简单,开销小
线程池隔离的特点是?
- 基于线程池模式,有额外开销,但隔离控制更强
6.3 熔断降级
熔断降级是解决雪崩问题的重要手段。其思路是由断路器统计服务调用的异常比例、慢请求比例,如果超出阈值则会熔断该服务。即拦截访问该服务的一切请求;而当服务恢复时,断路器会放行访问该服务的请求。
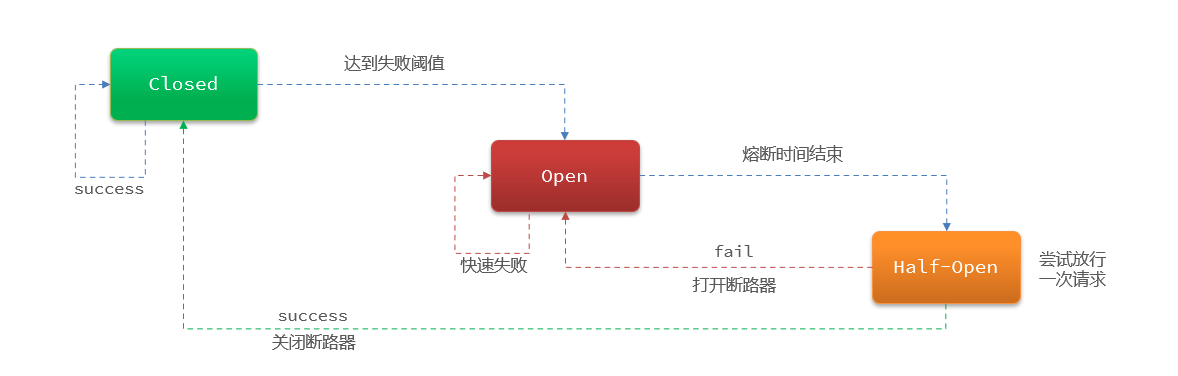
断路器熔断策略有三种:慢调用、异常比例、异常数-
慢调用:业务的响应时长(RT)大于指定时长的请求认定为慢调用请求。在指定时间内,如果请求数量超过设定的最小数量,慢调用比例大于设定的阈值,则触发熔断。例如:
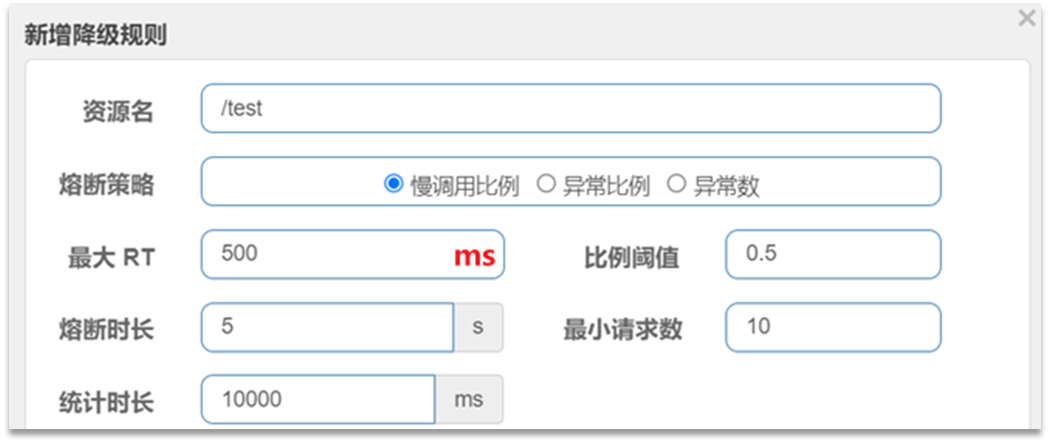
解读:RT超过500ms的调用是慢调用,统计最近10000ms内的请求,如果请求量超过10次,并且慢调用比例不低于0.5,则触发熔断,熔断时长为5秒。然后进入half-open状态,放行一次请求做测试。 -
异常比例或异常数:统计指定时间内的调用,如果调用次数超过指定请求数,并且出现异常的比例达到设定的比例阈值(或超过指定异常数),则触发熔断。例如:
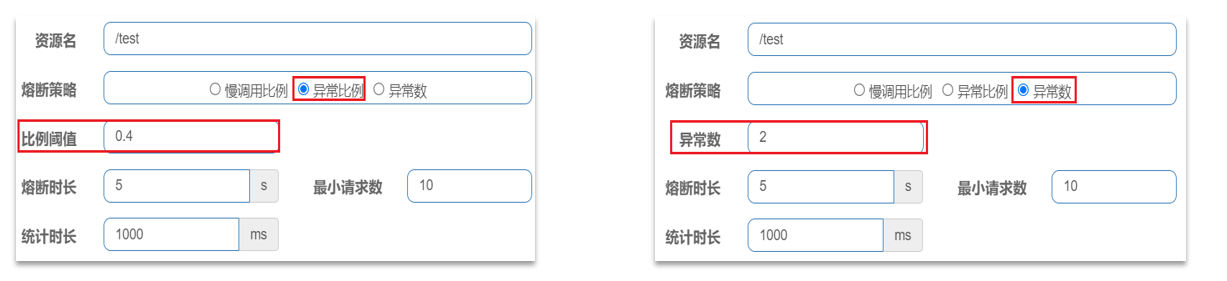
解读:统计最近1000ms内的请求,如果请求量超过10次,并且异常比例不低于0.5,则触发熔断,熔断时长为5秒。然后进入half-open状态,放行一次请求做测试。
Sentinel熔断降级的策略有哪些?
-
慢调用比例:超过指定时长的调用为慢调用,统计单位时长内慢调用的比例,超过阈值则熔断
-
异常比例:统计单位时长内异常调用的比例,超过阈值则熔断
-
异常数:统计单位时长内异常调用的次数,超过阈值则熔断
7. sentinel定义持久化
上面写的那么多规则,当微服务客户端重启后,规则会丢失。
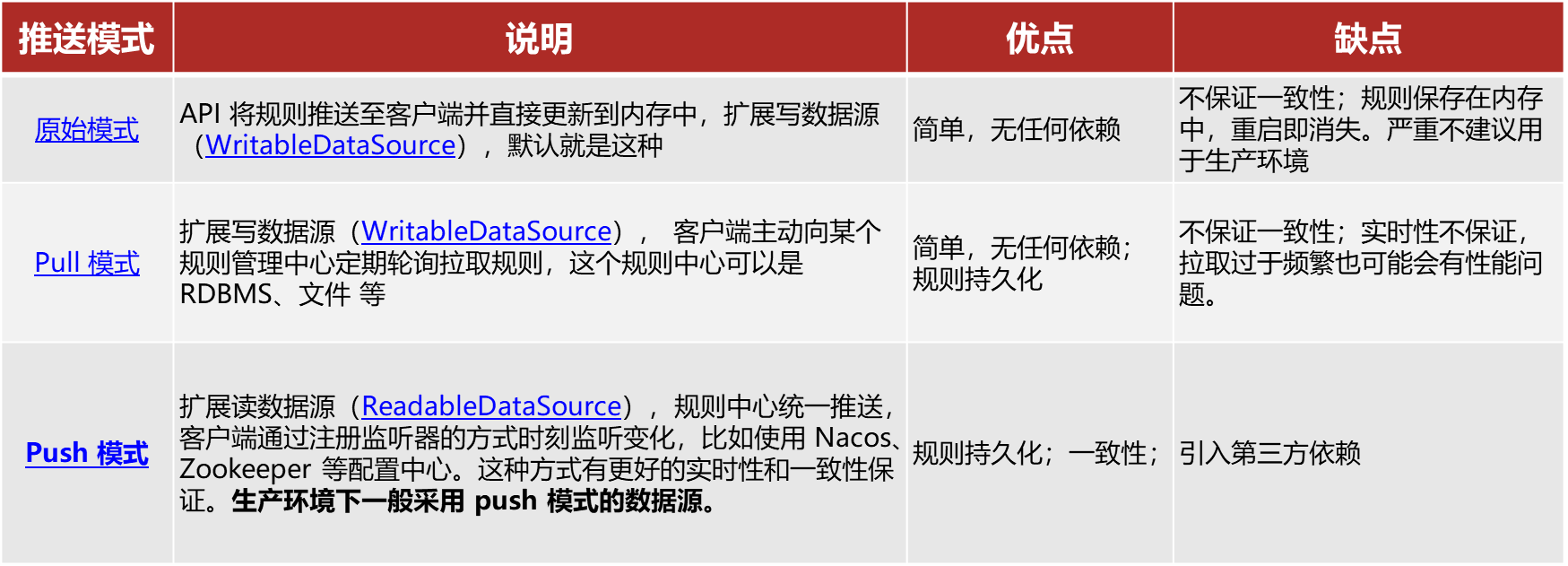
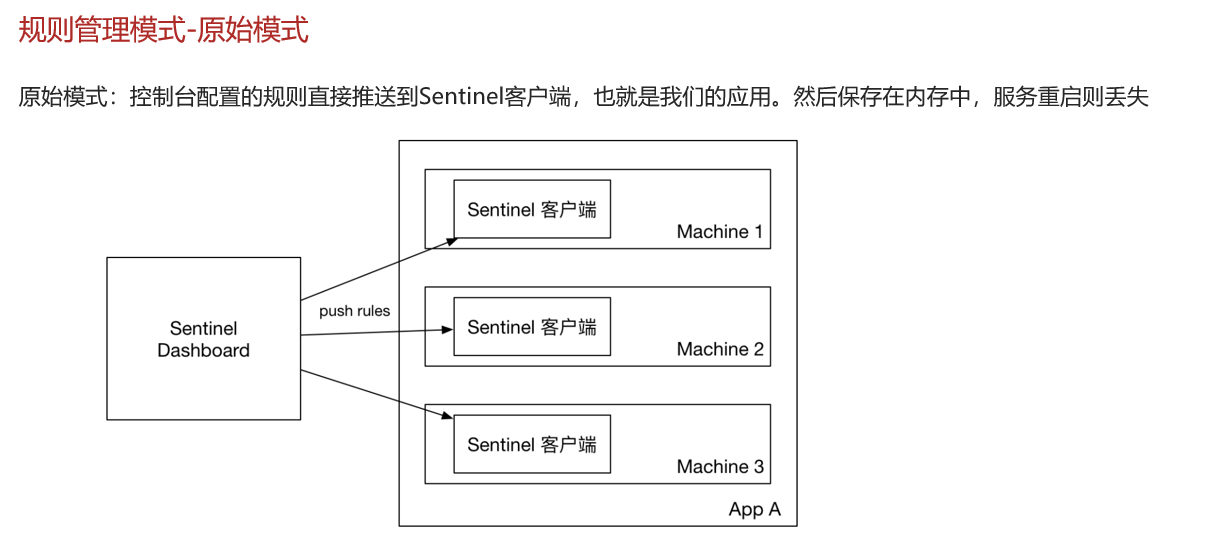
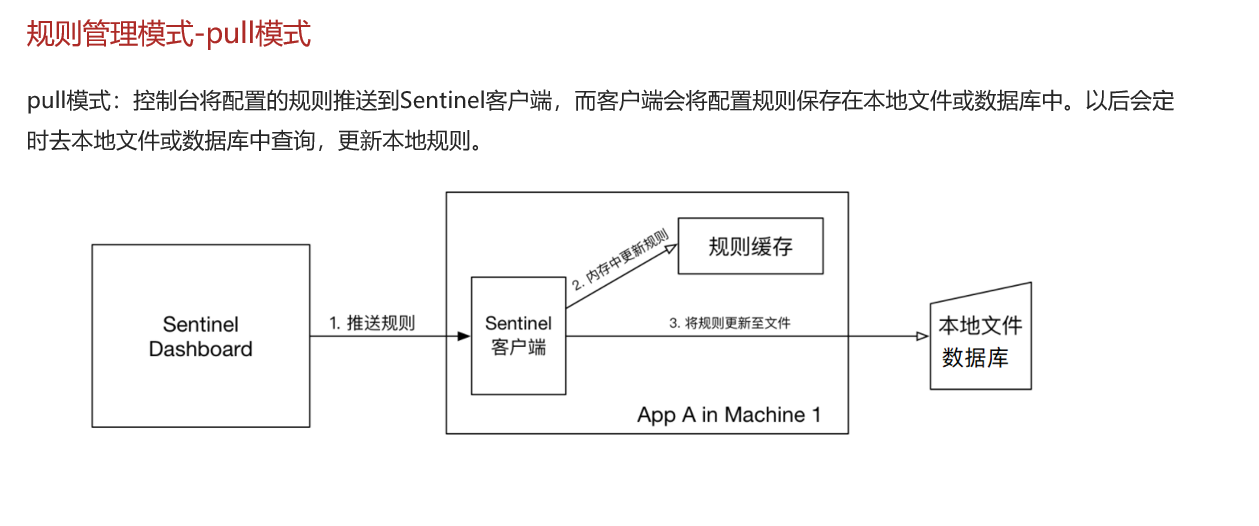
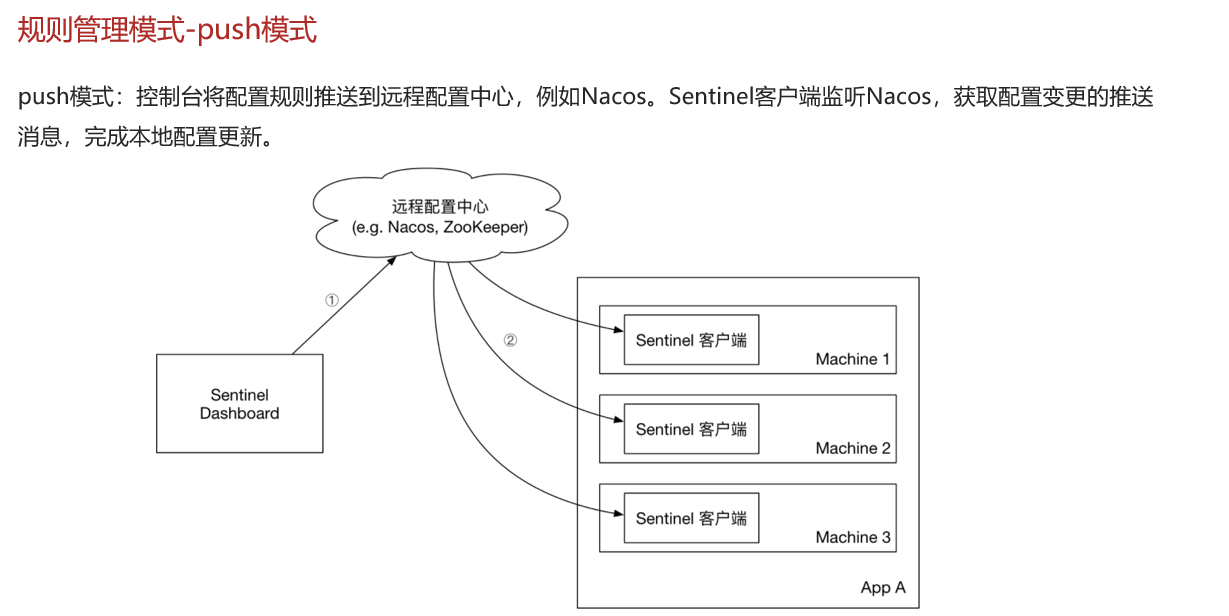
Sentinel的三种配置管理模式是什么?
-
原始模式:保存在内存
-
pull模式:保存在本地文件或数据库,定时去读取,性能会低
-
push模式:保存在nacos,监听变更实时更新,目前企业比较推广的。
sentinle中nacos没有提供 需要你修改sentinel源码,修改后把源码打包为jar,重新启动该jar包。
7.1 pull模式
规则保证到本地文件
(1)定义持久化到文件中的类package com.aaa.order.rule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.command.handler.ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.*; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRuleManager; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRuleManager; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRuleManager; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRuleManager; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.transport.util.WritableDataSourceRegistry; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.List; //用于规则持久化到文件中 public class FilePersistence implements InitFunc { @Value("${spring.application.name}") private String appcationName; @Override public void init() throws Exception { String ruleDir = "D:/sentinel-rules/shop-order" ; String flowRulePath = ruleDir + "/flow-rule.json"; String degradeRulePath = ruleDir + "/degrade-rule.json"; String systemRulePath = ruleDir + "/system-rule.json"; String authorityRulePath = ruleDir + "/authority-rule.json"; String paramFlowRulePath = ruleDir + "/param-flow-rule.json"; this.mkdirIfNotExits(ruleDir); this.createFileIfNotExits(flowRulePath); this.createFileIfNotExits(degradeRulePath); this.createFileIfNotExits(systemRulePath); this.createFileIfNotExits(authorityRulePath); this.createFileIfNotExits(paramFlowRulePath); // 流控规则 ReadableDataSource<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>( flowRulePath, flowRuleListParser ); FlowRuleManager.register2Property(flowRuleRDS.getProperty()); WritableDataSource<List<FlowRule>> flowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>( flowRulePath, this::encodeJson ); WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerFlowDataSource(flowRuleWDS); // 降级规则 ReadableDataSource<String, List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>( degradeRulePath, degradeRuleListParser ); DegradeRuleManager.register2Property(degradeRuleRDS.getProperty()); WritableDataSource<List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>( degradeRulePath, this::encodeJson ); WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerDegradeDataSource(degradeRuleWDS); // 系统规则 ReadableDataSource<String, List<SystemRule>> systemRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>( systemRulePath, systemRuleListParser ); SystemRuleManager.register2Property(systemRuleRDS.getProperty()); WritableDataSource<List<SystemRule>> systemRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>( systemRulePath, this::encodeJson ); WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerSystemDataSource(systemRuleWDS); // 授权规则 ReadableDataSource<String, List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>( authorityRulePath, authorityRuleListParser ); AuthorityRuleManager.register2Property(authorityRuleRDS.getProperty()); WritableDataSource<List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>( authorityRulePath, this::encodeJson ); WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerAuthorityDataSource(authorityRuleWDS); // 热点参数规则 ReadableDataSource<String, List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>( paramFlowRulePath, paramFlowRuleListParser ); ParamFlowRuleManager.register2Property(paramFlowRuleRDS.getProperty()); WritableDataSource<List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>( paramFlowRulePath, this::encodeJson ); ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler.setWritableDataSource(paramFlowRuleWDS); } private Converter<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject( source, new TypeReference<List<FlowRule>>() { } ); private Converter<String, List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject( source, new TypeReference<List<DegradeRule>>() { } ); private Converter<String, List<SystemRule>> systemRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject( source, new TypeReference<List<SystemRule>>() { } ); private Converter<String, List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject( source, new TypeReference<List<AuthorityRule>>() { } ); private Converter<String, List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject( source, new TypeReference<List<ParamFlowRule>>() { } ); private void mkdirIfNotExits(String filePath) throws IOException { File file = new File(filePath); if (!file.exists()) { file.mkdirs(); } } private void createFileIfNotExits(String filePath) throws IOException { File file = new File(filePath); if (!file.exists()) { file.createNewFile(); } } private <T> String encodeJson(T t) { return JSON.toJSONString(t); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
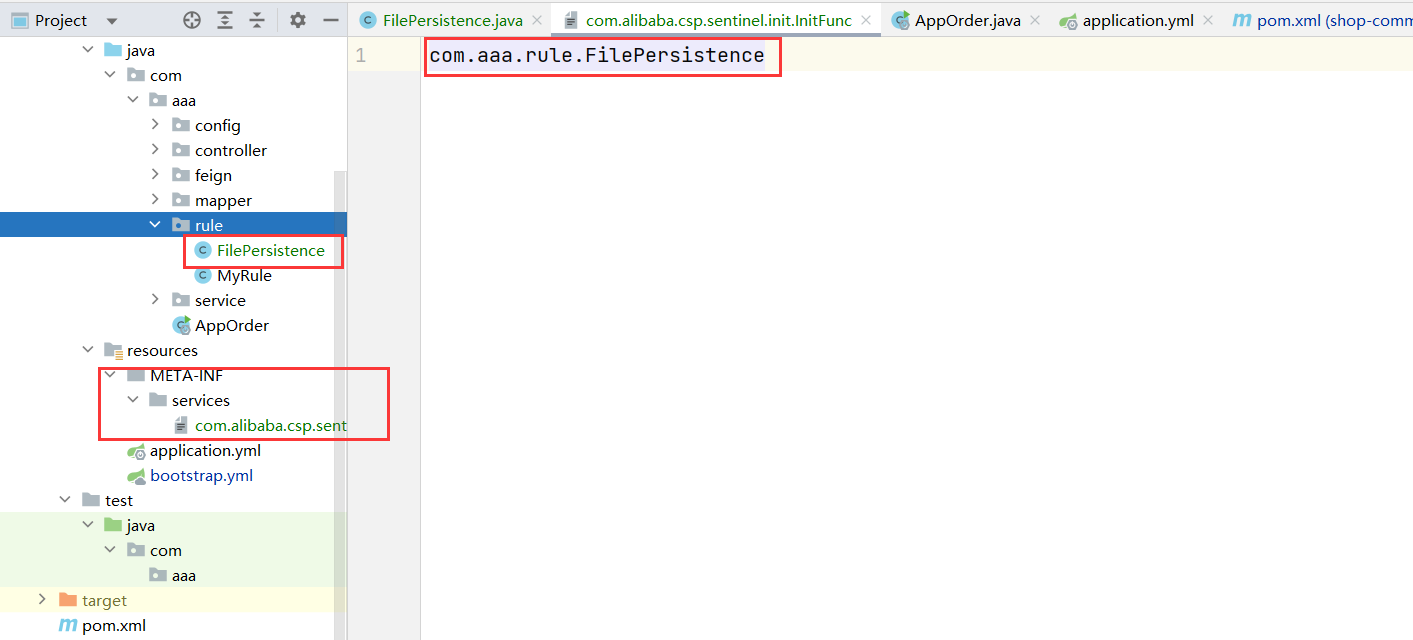
(2)添加配置
在resources下创建配置目录 META-INF/services ,然后添加文件com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc
在文件中添加配置类的全路径
com.aaa.rule.FilePersistence
7.2 push模式
push到配置中心nacos
sentinel 的持久化,我们希望这样:- 可以在 sentinel 控制台中编辑 限流配置,并且同步到 nacos 做持久化
- 在 nacos 中修改了限流配置,也可以同步到 sentinel 控制台
要实现上述第一个功能需要对 sentinel 控制台的源码有所了解,并加依改造。
但 GitHub 上已经有人改造好了,做了个加强版控制台。
https://github.com/CHENZHENNAME/sentinel-dashboard-nacos
7.2.1 修改sentinel
- 打开上述网址 下载到本地
- 解压上面的文件:
- 打开根目录下的 pom.xml ,修改 sentinel 的版本

- 进入项目根目录,cmd,执行命令
mvn clean package
- 打包后生产在target目录下
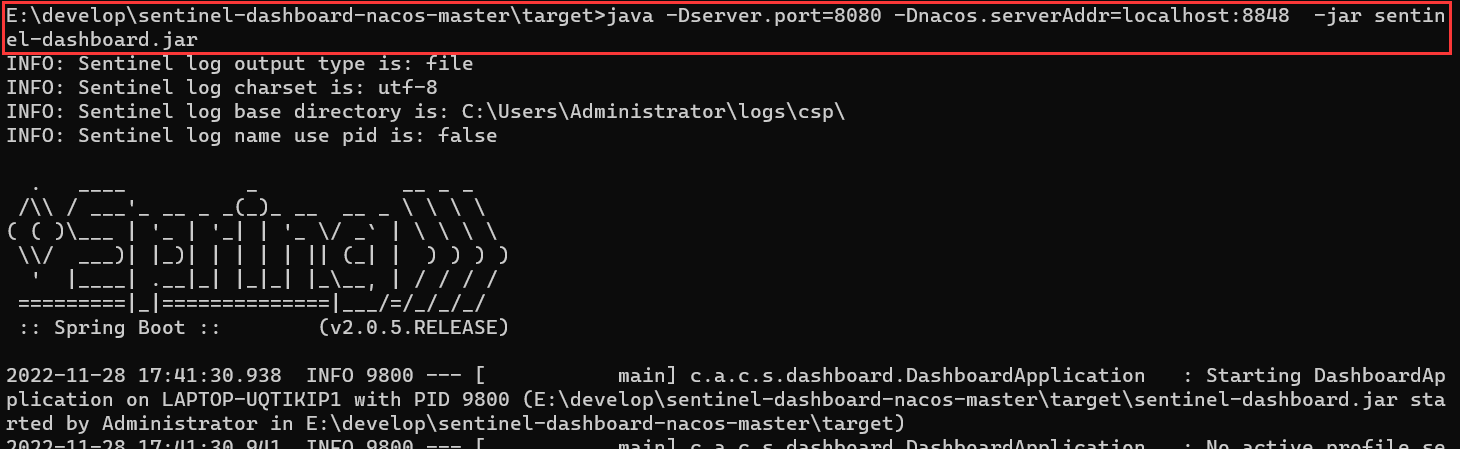
- 执行命令,启动控制台:
java -Dserver.port=8080 -Dnacos.serverAddr=localhost:8848 -jar sentinel-dashboard.jar
-Dserver.port 控制台端口号
-Dnacos.serverAddr: nacos 地址
-Dnacos.namespace: 你项目所在的 nacos 命名空间 如果命名空间就是public可以省略该参数
7.2.2 微服务客户端接入sentinel控制面板
- 引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.cspgroupId> <artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacosartifactId> <version>1.8.1version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 修改配置文件
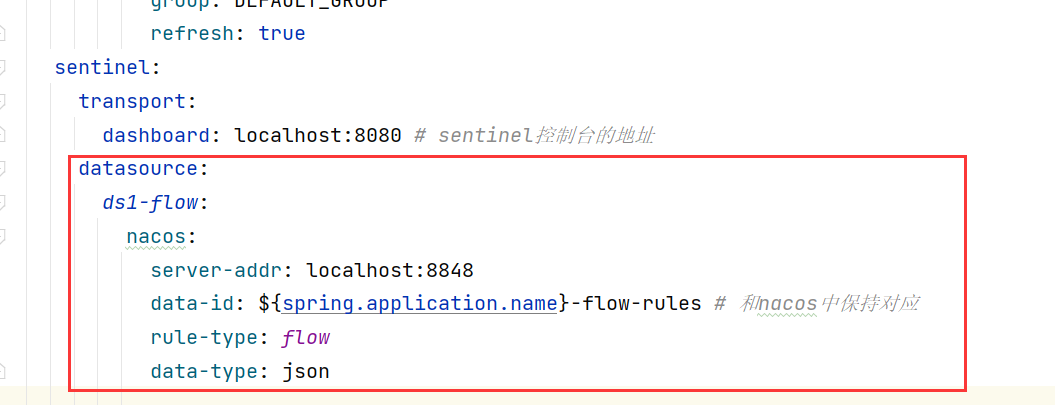
启动微服务
然后浏览器访问:http://localhost:8080 , 最开始什么都没有,然后访问你自己的项目的任意一个要限流的接口,则 左侧会出现对于的 服务名称
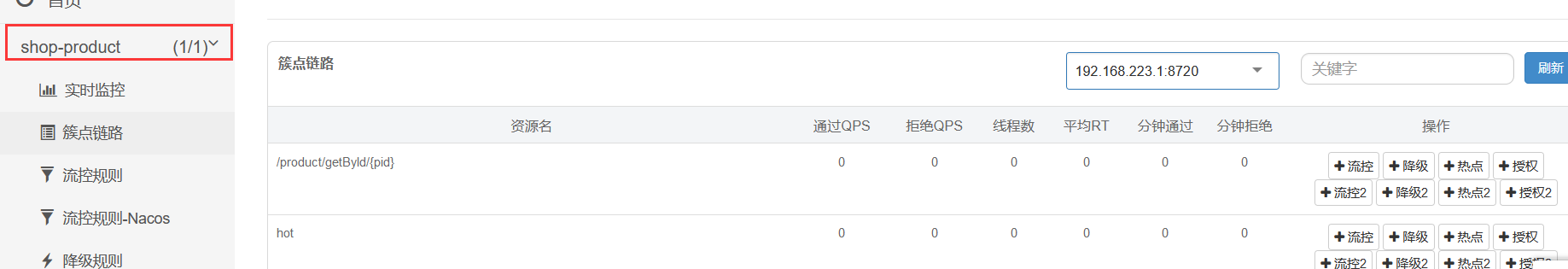
点击 簇点链路,新增 一个流控规则:
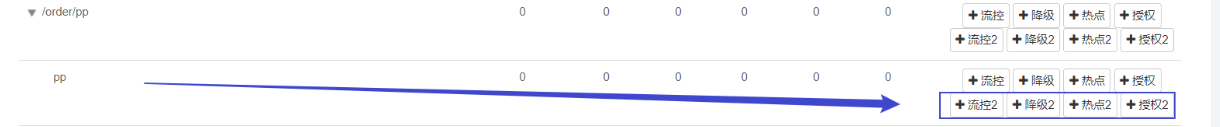
注意,一定要点 带 2 的,只有带 2 的才能推送到 nacos,在 流控规则 选项中添加也不行,只能点击 蓝色方框 才能推送到 nacos
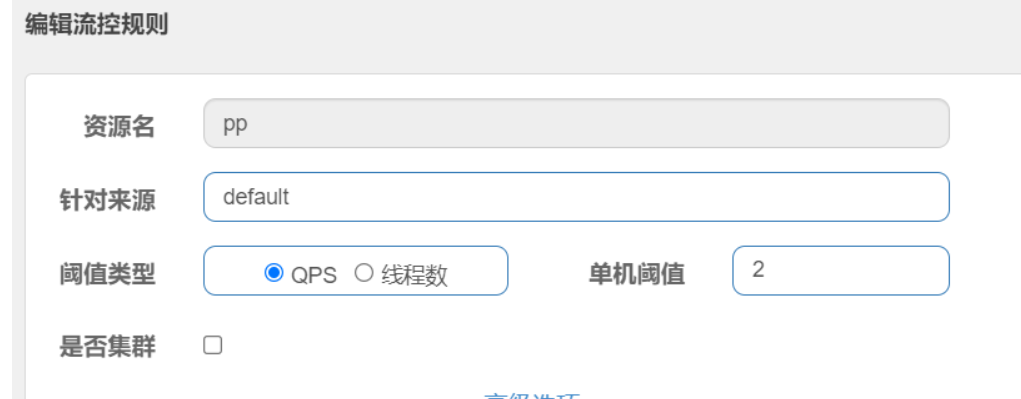
添加成功后,nacos 中,你指定的命名空间下会自动生成
${application-name}-flow-rules格式的配置文件
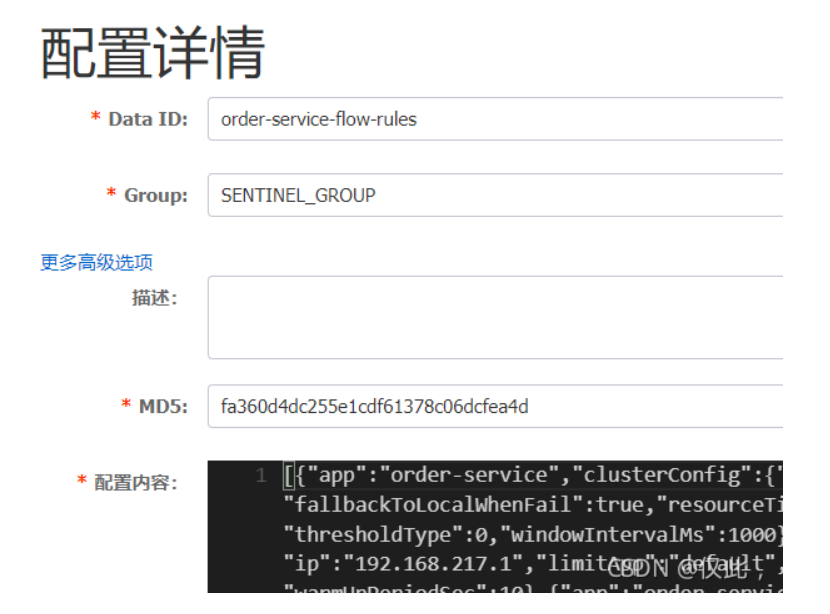
当你在 sentinel 控制台中,无论增加规则,还是修改规则,都会同步到 nacos;相反,修改 nacos 中 配置文件的限流规则,也会同步到 sentinel 。 -
相关阅读:
04、添加 com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat -- jackson-dataformat-xml 依赖报错
第16章总结
Spring的AOP开发-基于xml配置的AOP
Arduino框架下通过TFT_eSPI库驱动ESP32+合宙1.54“ 电子墨水屏(e-paper)显示
低代码平台要怎么选?便宜其实也有好货!
java计算机毕业设计微服务毕业论文管理系统源码+系统+数据库+lw文档
Windows系统电脑本地部署AI音乐创作工具并实现无公网IP远程使用
cmake入门
DHorse系列文章之日志收集
WEBSCRAPER关于Element的问题
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_60969145/article/details/128076739
