-
一文带你了解Spring中的事务管理
前言
本文将涉及以下知识点:
- 事务的基础概念
- spring当中事务的使用
- spring当中事务管理的实现原理
一、事务的基础概念
事务(Transaction)是数据库软件中为了保证数据正确的一种手段。
事务必须满足4个特性:- 原子性:一个事务操作在软件系统中是不可拆分的,要么执行成功,要么执行失败。事务执行过程中有任何步骤失败,都应该回滚事务
- 隔离性:事务与事务之间的执行是隔离开的,互相不影响。
- 持久性:执行成功的事务,数据应该永久保存了,不会丢失。即使服务器系统崩溃或服务器宕机等故障。只要数据库重新启动,那么一定能够将其恢复到事务成功结束后的状态。
- 一致性:事务的一致性是指事务在执行不能破坏数据库数据的完整性和一致性,一个事务在执行之前和执行之后,数据库都必须处以一致性状态。比如:张三给李四转钱,不可能张三被扣了钱,李四没有加钱。
二、spring中事务的使用
首先需要明确一点,spring只是帮助我们管理事务操作,省去我们自己去手动执行相应的事务操作sql。真正的事务实现是由数据库提供的。
spring提供了声明式和编程式两种管理事务的方式。两种方式的使用都非常简单。
声明式事务
spring在使用声明式事务前需要先开启事务管理器,否则事务不会生效。在springboot中开启事务配置是用@EnableTransactionManagement注解表示开启。

声明式事务是在你的逻辑调用入口添加一个 @Transactional注解,以AOP切面的形式帮助我们开启、提交、回滚事务。
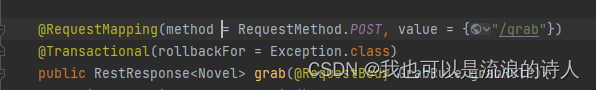
声明式事务最大的优点就是使用简单、基本上对业务逻辑代码无侵入。开发者只需要关注业务逻辑,而不必关心事务的处理。缺点则是在使用@Transactional注解时,有一些会导致事务失效的点,需要特别注意
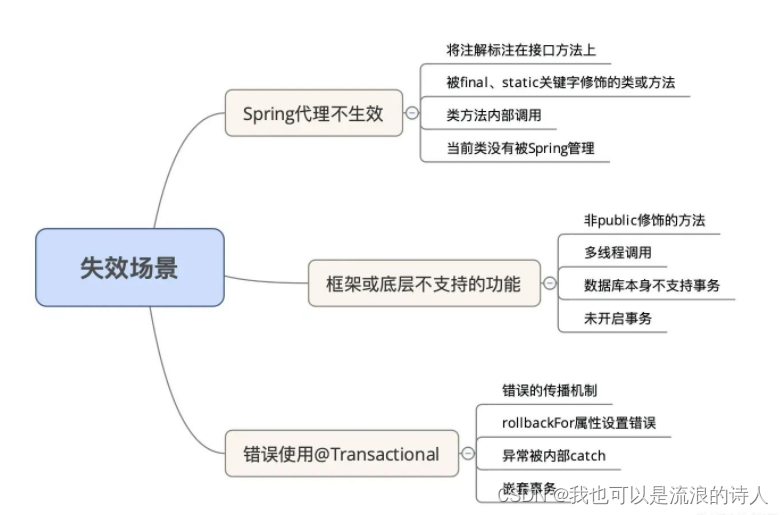
事务失效场景参考
编程式事务
编程式事务通常是由TransactionTemplate类来操作的,这个类是spring官方提供的操作事务的模板类,类路径为:
org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate
TransactionTemplate通过执行execute(params)方法,接收一个TransactionCallback类型的参数。实现的事务管理。使用示例如下:
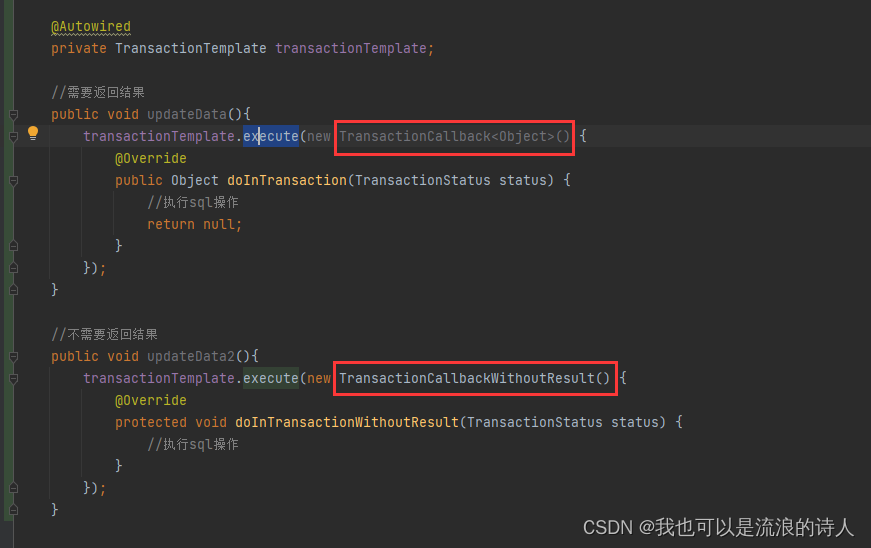
使用编程式事务需要注意,所有的sql操作需要写在doInTransaction()方法体内,否则你的sql执行不会被纳入到事务操作,将不具体事务性。如何选择事务方式
首先,声明式事务、编程式事务二者在底层实现上是一样的。唯一不同的只有使用方面。具体两种方式如何选择的话。
建议业务逻辑复杂情况使用编程式事务,它可以更好的把控业务处理时事务的粗细粒度。如果业务不是很复杂的场景,可以使用声明式事务处理。使用的时候注意一下上面提到的会导致事务失效的点。还有一个点,spring中事务是跟线程绑定的,事务只能控制当前线程的操作。
三、spring中事务管理实现原理
从源码层次带大家看一下spring是怎么帮助我们管理事务的。
从编程式事务的角度出发来看原理的话,非常方便。直接阅读TransactionTemplate模板类的源码即可。
@Nullable public <T> T execute(TransactionCallback<T> action) throws TransactionException { Assert.state(this.transactionManager != null, "No PlatformTransactionManager set"); if (this.transactionManager instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) { return ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)this.transactionManager).execute(this, action); } else { //通过事务管理器开启事务 TransactionStatus status = this.transactionManager.getTransaction(this); Object result; try { //执行业务逻辑,上面说到的sql语句都要放到doInTransaction()方法体内执行,就是在这里调用了 result = action.doInTransaction(status); } catch (Error | RuntimeException var5) { //如果业务逻辑执行有异常,捕获到了直接回滚事务 this.rollbackOnException(status, var5); throw var5; } catch (Throwable var6) { //同上 this.rollbackOnException(status, var6); throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var6, "TransactionCallback threw undeclared checked exception"); } //业务执行完成,commit提交事务 this.transactionManager.commit(status); return result; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
上面TransactionTemplate.execute()方法中完整了罗列了事务管理的整个周期,开启、提交/回滚 。
下面从声明式事务角度来分析一下源码实现,由于声明式事务在使用上只有一个 @Transactional注解,所以需要找到事务aop的切面逻辑才能看到底层实现。由于声明式事务需要开启@EnableTransactionManagement,所以我们从@EnableTransactionManagement注解开始分析。

通过import导入配置类,进来找到这个类:ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration

切入点在AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource类里

添加解析器,用来匹配查询@Transactional注解

AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource.isCandidateClass()方法会匹配查找@Transactional切入点。
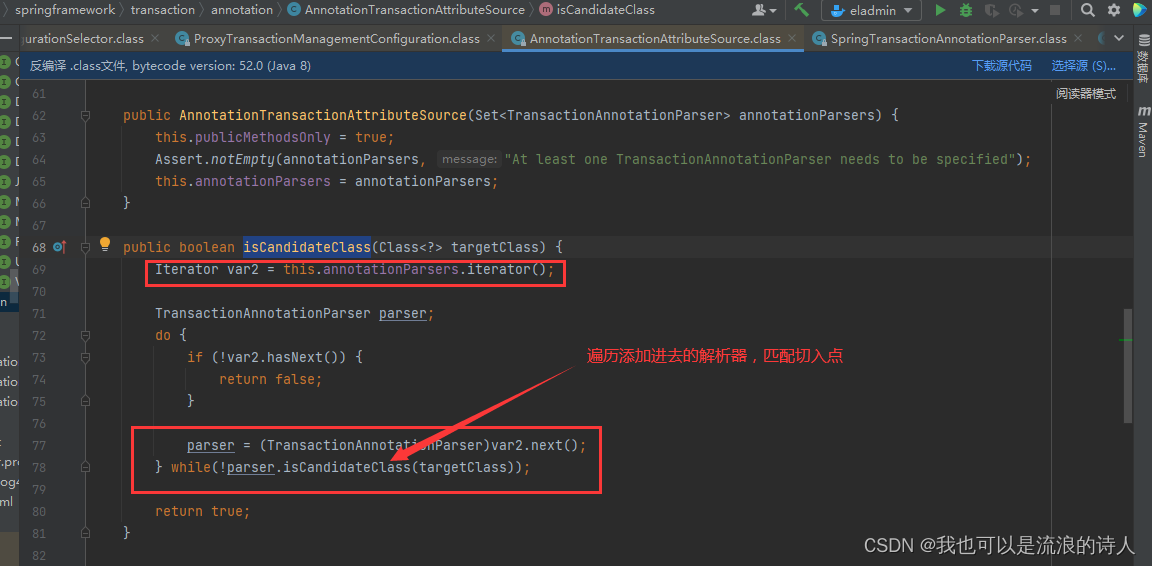
具体的切入匹配是在SpringTransactionAnnotationParser.isCandidateClass()方法下面
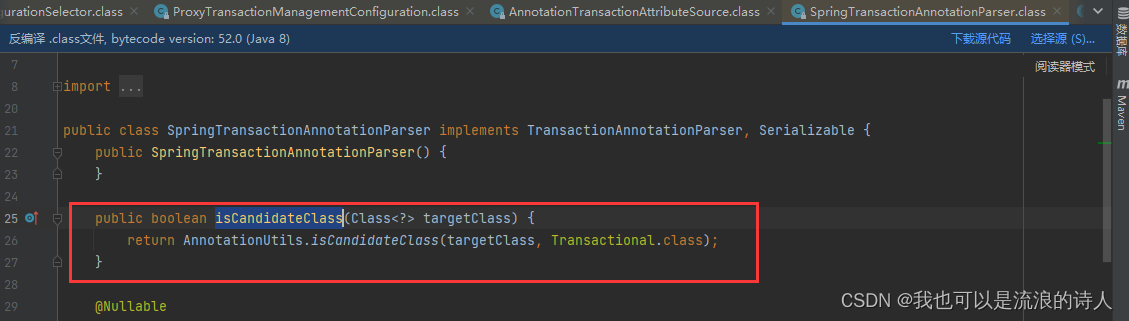
成功匹配到@Transactional注解。接下来就是具体的切面逻辑执行。切面逻辑在TransactionInterceptor类里(为什么切面逻辑在TransactionInterceptor类里,看下spring aop 内部实现)

进入TransactionInterceptor.invoke()方法。
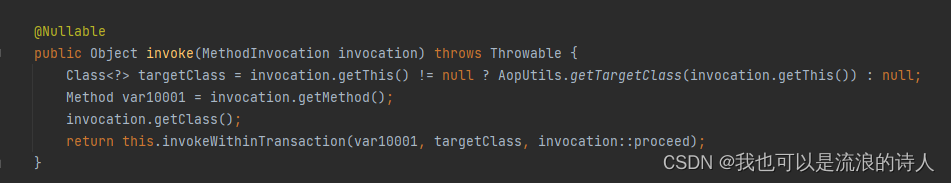
为什么看invoke方法?实现了MethodInterceptor接口、看下TransactionInterceptor类的继承关系。
继续跟invoke方法,来到TransactionAspectSupport类下的invokeWithinTransaction方法@Nullable protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass, TransactionAspectSupport.InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable { TransactionAttributeSource tas = this.getTransactionAttributeSource(); TransactionAttribute txAttr = tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null; TransactionManager tm = this.determineTransactionManager(txAttr); if (this.reactiveAdapterRegistry != null && tm instanceof ReactiveTransactionManager) { TransactionAspectSupport.ReactiveTransactionSupport txSupport = (TransactionAspectSupport.ReactiveTransactionSupport)this.transactionSupportCache.computeIfAbsent(method, (key) -> { if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(method.getDeclaringClass()) && TransactionAspectSupport.KotlinDelegate.isSuspend(method)) { throw new TransactionUsageException("Unsupported annotated transaction on suspending function detected: " + method + ". Use TransactionalOperator.transactional extensions instead."); } else { ReactiveAdapter adapter = this.reactiveAdapterRegistry.getAdapter(method.getReturnType()); if (adapter == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot apply reactive transaction to non-reactive return type: " + method.getReturnType()); } else { return new TransactionAspectSupport.ReactiveTransactionSupport(adapter); } } }); return txSupport.invokeWithinTransaction(method, targetClass, invocation, txAttr, (ReactiveTransactionManager)tm); } else { PlatformTransactionManager ptm = this.asPlatformTransactionManager(tm); String joinpointIdentification = this.methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr); if (txAttr != null && ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) { TransactionAspectSupport.ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new TransactionAspectSupport.ThrowableHolder(); Object result; try { result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)ptm).execute(txAttr, (statusx) -> { TransactionAspectSupport.TransactionInfo txInfo = this.prepareTransactionInfo(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, statusx); Object var9; try { Object retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation(); if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && TransactionAspectSupport.VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) { retVal = TransactionAspectSupport.VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, statusx); } var9 = retVal; return var9; } catch (Throwable var13) { if (txAttr.rollbackOn(var13)) { if (var13 instanceof RuntimeException) { throw (RuntimeException)var13; } throw new TransactionAspectSupport.ThrowableHolderException(var13); } throwableHolder.throwable = var13; var9 = null; } finally { this.cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo); } return var9; }); } catch (TransactionAspectSupport.ThrowableHolderException var20) { throw var20.getCause(); } catch (TransactionSystemException var21) { if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) { this.logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable); var21.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable); } throw var21; } catch (Throwable var22) { if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) { this.logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable); } throw var22; } if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) { throw throwableHolder.throwable; } else { return result; } } else { //主要逻辑在这,默认走的是这段代码块,开启事务 TransactionAspectSupport.TransactionInfo txInfo = this.createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification); Object retVal; try { //执行业务逻辑 retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation(); } catch (Throwable var18) { //异常回滚事务 this.completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, var18); throw var18; } finally { this.cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo); } if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && TransactionAspectSupport.VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) { TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus(); if (status != null && txAttr != null) { retVal = TransactionAspectSupport.VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status); } } //业务执行完成,commit提交事务 this.commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo); return retVal; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
到大致讲一下:spring在帮我们开启事务的时候是通过设置 自动提交autocommit=0 开启一条事务,提交/回滚的时候都是通过JDBC DataSource获取数据库连接,执行commit/rollback 命令完成的。大家可以按照上面代码标注的注释点一层一层点进去查看。
底层跟踪下去,声明式以及编程式事务都是由AbstractPlatformTransactionManager默认的事务管理器处理。
开启事务处理链路:AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.getTransaction() => AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.startTransaction() => AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.doBegin() => DataSourceTransactionManager.doBegin()

提交事务处理链路:AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.doCommit() => DataSourceTransactionManager.doCommit()
protected void doCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) { DataSourceTransactionManager.DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionManager.DataSourceTransactionObject)status.getTransaction(); //获取数据库连接 Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection(); if (status.isDebug()) { this.logger.debug("Committing JDBC transaction on Connection [" + con + "]"); } try { //根据具体数据库驱动实现,执行不同提交事务语法 con.commit(); } catch (SQLException var5) { throw new TransactionSystemException("Could not commit JDBC transaction", var5); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
以mysql举例,底层会执行commit命令:con.commit() => com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl.commit()

回滚事务同理:AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.doCommit() => DataSourceTransactionManager.rollback()
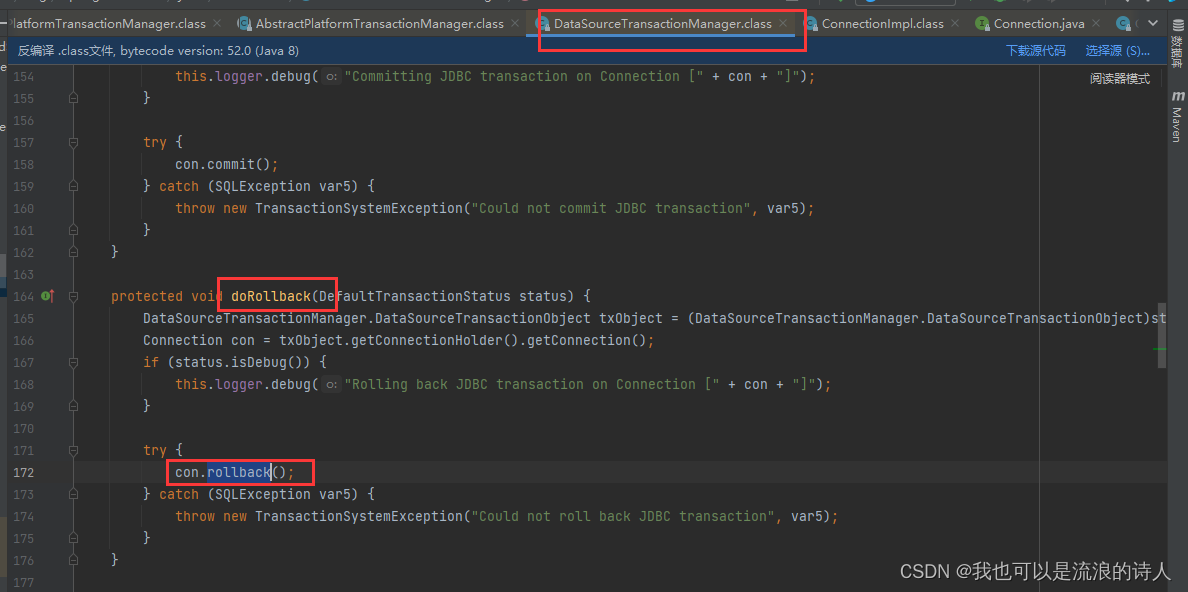
在mysql驱动下的实现:
con.rollback() => com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl.rollback()
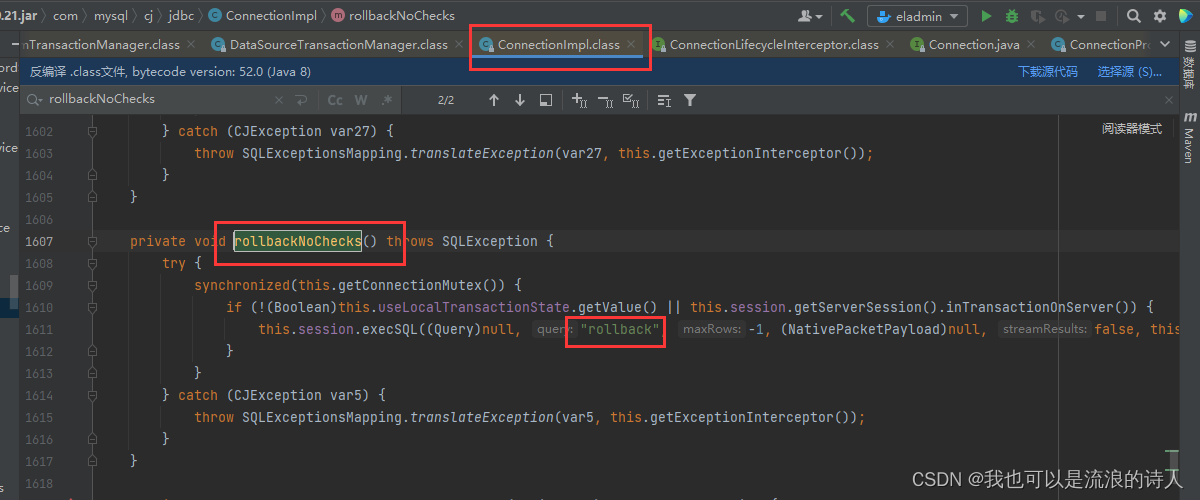
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl.rollback() => com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl.rollbackNoChecks()

-
相关阅读:
ATFX汇市:瑞士央行连续第二次降息,USDCHF猛涨
自动化安装系统问题记录
Es的核心概念
“蔚来杯“2022牛客暑期多校训练营4,签到题NDKHL
redis可视化管理软件Redis Desktop Manager2022
pytorch升级打怪(三)
Flutter 遇到的问题整理
NumPy中einsum使用笔记
【小程序】微信小程序云开发笔记详细教程(建议收藏)
【企业数字化】企业数字化技术应用5大技术趋势
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42394044/article/details/128066323
