-
链表经典算法题目
1.回文链表
编写一个函数,检查输入的链表是否是回文的。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2 输出: false- 1
- 2
示例 2:
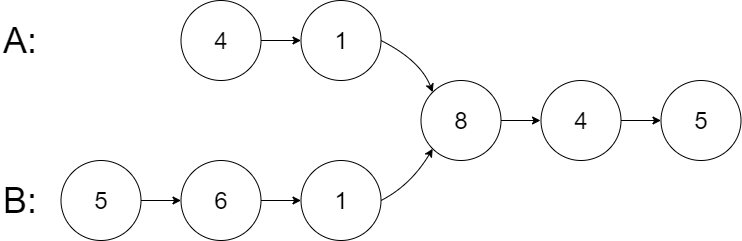
输入: 1->2->2->1 输出: true- 1
- 2
笔试的写法
重点是快速code,不考虑空间复杂度,怎么简单怎么来
思路:把链表的数据依次压入栈中,然后弹出比较
class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) { if(head == null || head.next == null) { return true; } Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack(); ListNode cur = head; while(cur != null) { stack.push(cur); cur = cur.next; } cur = head; while(cur != null) { if(cur.val != stack.pop().val){ return false; } cur = cur.next; } return true; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
面试的写法
对于这种比较简单的题目,想要出彩,就要考虑优化的点,考虑空间复杂度,压缩空间。
思路:使用快慢指针,找到中间的节点,然后从中间节点反转链表,头尾同时遍历比较,最后再把反转的链表恢复过来。
class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) { if(head == null || head.next == null) { return true; } ListNode slow = head; ListNode fast = head; // 进行一轮快慢指针 // fast!=null && fast.next!=null while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } // 从慢指针处反转链表 ListNode cur = slow; ListNode next = slow.next; slow.next = null; while(next != null) { ListNode nextnext = next.next; next.next = cur; cur = next; next = nextnext; } //判断回文 ListNode l = head; ListNode r = cur; while(r != null) { if(l.val!=r.val) { next = cur.next; while(next != null) { ListNode nextnext = next.next; next.next = cur; cur = next; next = nextnext; } return false; } l = l.next; r = r.next; } //把反转链表恢复 next = cur.next; while(next != null) { ListNode nextnext = next.next; next.next = cur; cur = next; next = nextnext; } return true; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
2. 复杂链表的复制
请实现
copyRandomList函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个next指针指向下一个节点,还有一个random指针指向链表中的任意节点或者null。示例 1:
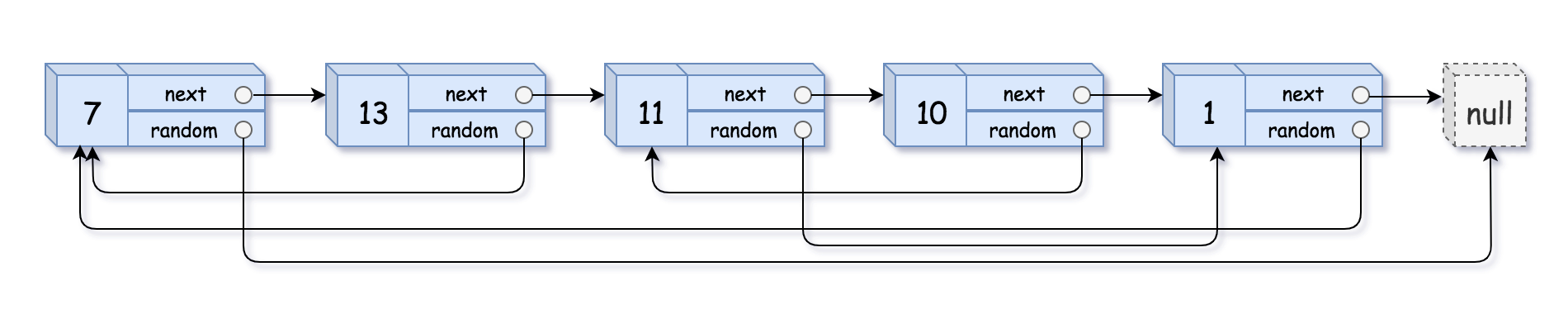
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] 输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]- 1
- 2
示例 2:

输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]] 输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]- 1
- 2
示例 3:

输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]] 输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]- 1
- 2
示例 4:
输入:head = [] 输出:[] 解释:给定的链表为空(空指针),因此返回 null。- 1
- 2
- 3
笔试的写法
重点是快速code,不考虑空间复杂度,怎么简单怎么来
思路:利用一个map,把原链表的Node当作key,新复制的Node当作value,然后利用Map的映射关系把原链表的Node的next和random复制到新复制的Node中
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { int val; Node next; Node random; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } */ class Solution { public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { // 不考率空间复杂度的写法 HashMap<Node,Node> mapNode = new HashMap(); Node cur = head; while(cur != null) { mapNode.put(cur,new Node(cur.val)); cur = cur.next; } cur = head; while(cur != null) { mapNode.get(cur).next = mapNode.get(cur.next); mapNode.get(cur).random = mapNode.get(cur.random); cur = cur.next; } return mapNode.get(head); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
面试的写法
对于这种比较简单的题目,想要出彩,就要考虑优化的点,考虑空间复杂度,压缩空间。
思路: 在Node后面串一个复制的Node,然后给复制的Node的random赋值,把复制的Node从老链表里拆出来
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { int val; Node next; Node random; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } */ class Solution { public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { if(head == null) { return null; } // 考率空间复杂度的写法 O(1) Node cur = head; // 在Node后面串一个复制的Node while(cur != null) { Node cp = new Node(cur.val); Node next = cur.next; cur.next = cp; cp.next = next; cur = next; } cur = head; // 给复制的Node的random赋值 while(cur != null) { if(cur.random != null) { cur.next.random = cur.random.next; }else{ cur.next.random = null; } cur = cur.next.next; } // 把复制的Node从老链表里拆出来 cur = head; Node newHead = cur.next; while(cur != null) { Node next = cur.next.next; Node cp = cur.next; cur.next = next; cp.next = next != null?next.next:null; cur = next; } return newHead; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
3.环形链表
给定一个链表的头节点
head,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回null。如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪
next指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数pos来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果pos是-1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。不允许修改 链表。
示例 1:

输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。- 1
- 2
- 3
示例 2:

输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0 输出:返回索引为 0 的链表节点 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。- 1
- 2
- 3
示例 3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1 输出:返回 null 解释:链表中没有环。- 1
- 2
- 3
面试的写法
思路: 使用快慢指针,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,第一次相遇后快指针回到头节点,快指针和慢指针一次走一步,再次相遇的节点就是入环节点。
public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { if(head==null||head.next==null){ return null; } ListNode slow = head; ListNode fast = head; int cnt = 0; boolean flag = false; while(fast != null&&fast.next != null) { if(fast == slow&&cnt>0) { fast = head; if(!flag){ flag = true; if(slow==head) { return head; } }else{ return slow; } } if(!flag) { fast = fast.next.next; }else { fast = fast.next; } slow = slow.next; cnt++; } return null; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
4.相交链表
给你两个单链表的头节点
headA和headB,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回null。图示两个链表在节点
c1开始相交**:**题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
自定义评测:
评测系统 的输入如下(你设计的程序 不适用 此输入):
intersectVal- 相交的起始节点的值。如果不存在相交节点,这一值为0listA- 第一个链表listB- 第二个链表skipA- 在listA中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数skipB- 在listB中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数
评测系统将根据这些输入创建链式数据结构,并将两个头节点
headA和headB传递给你的程序。如果程序能够正确返回相交节点,那么你的解决方案将被 视作正确答案 。示例 1:
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 输出:Intersected at '8' 解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。 从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,6,1,8,4,5]。 在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。 — 请注意相交节点的值不为 1,因为在链表 A 和链表 B 之中值为 1 的节点 (A 中第二个节点和 B 中第三个节点) 是不同的节点。换句话说,它们在内存中指向两个不同的位置,而链表 A 和链表 B 中值为 8 的节点 (A 中第三个节点,B 中第四个节点) 在内存中指向相同的位置。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
示例 2:
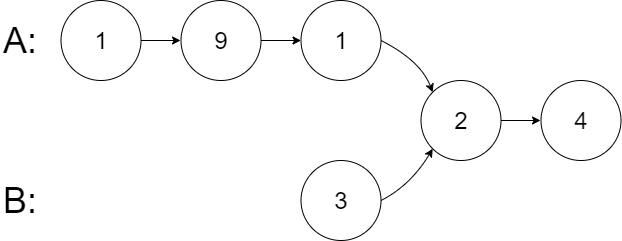
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 输出:Intersected at '2' 解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。 从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [1,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。 在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
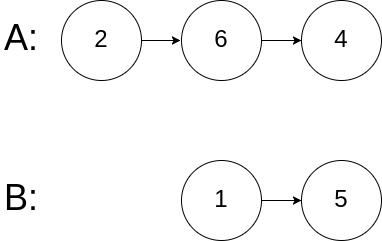
示例 3:
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 输出:null 解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。 由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。 这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
面试的写法
思路:如果两个单链表相交,两个链表尾节点一定是同一个节点。遍历两个链表,如果链表相交,算出两个链表的差值,把长的链表的差值先走完,然后同时遍历两个链表,找到相交节点。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { if(headA==null||headB==null) { return null; } ListNode curA = headA; ListNode curB = headB; int lenA = 0; int lenB = 0; while(curA.next!=null){ lenA++; curA = curA.next; } while(curB.next!=null){ lenB++; curB = curB.next; } int cha = 0; if(curA==curB){ cha = lenB - lenA >= 0?lenB - lenA:lenA - lenB; }else{ return null; } curA = headA; curB = headB; if(lenB - lenA >= 0){ for(int i=0;i<cha;i++){ curB = curB.next; } } else { for(int i=0;i<cha;i++){ curA = curA.next; } } while(curA != null && curB != null){ if(curA==curB){ return curA; } curA = curA.next; curB = curB.next; } return null; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
-
相关阅读:
卷积神经网络CNN手写数字识别案例
关于Java开发Idea中编码,解码以及解决中文乱码的实践经验
在非IOS系统打开HEIC格式图片
《计算机视觉中的多视图几何》笔记(6)
Python超入门(3)__迅速上手操作掌握Python
【C++11保姆级教程】空指针(nullptr),long long类型,char16_t和char32_t类型
Spring Cloud Alibaba+saas企业架构技术选型+架构全景业务图 + 架构典型部署方案
SNMP 网络协议介绍
算法设计作业
Linux硬链接、软链接
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42575907/article/details/128059997