-
寻找链表相交结点问题
寻找链表相交结点问题
作者:Grey
原文地址:
题目描述
给定两个可能有环也可能无环的单链表,头节点head1和head2。请实现一个函数,如果两个链表相交,请返回相交的 第一个节点。如果不相交,返回 null。
要求:如果两个链表长度之和为N,时间复杂度请达到
O(N),额外空间复杂度请达到O(1)。类似问题
本题主要的难点是要分析所有可能的情况,因为题目中提到「可能有环也可能无环」。
主要思路
先看大的情况,有如下三种情况
第一种情况:两个链表均无环;
第二种情况:两个链表均有环;
第三种情况:一个有环,一个无环。
首先,第三种情况下,两个链表一定不相交。针对第一种情况,就是寻找链表的入环节点和相交节点问题中提到LeetCode 160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists,现在只分析第二种情况。
由于两个链表都有环,两个链表如果相交,一定只有如下三种情况
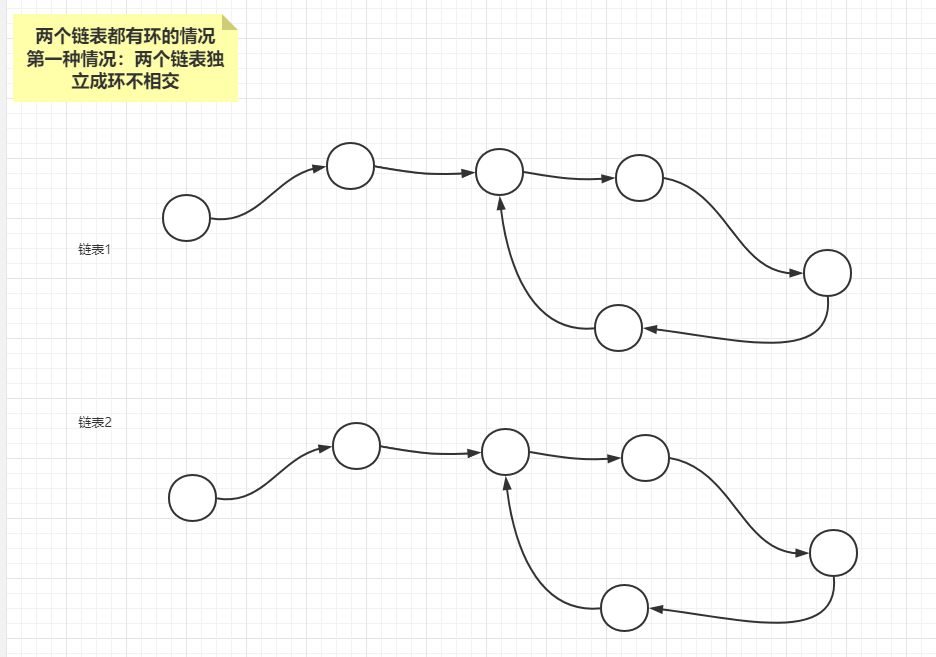
情况1:两个链表独立不相交
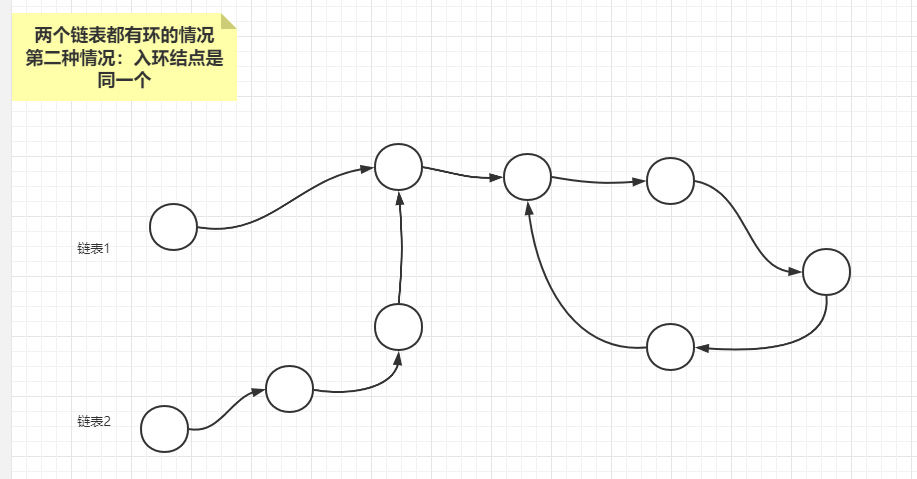
情况2:两个链表的入环结点是同一个
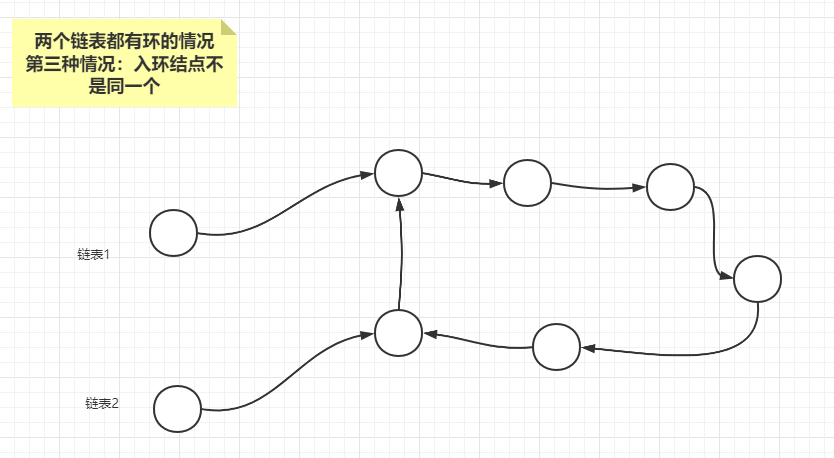
情况3:两个链表的入环结点不是同一个,此时任意一个链表的入环结点都是相交结点。
先从最简单的情况1和情况3进行分析,情况一发生的条件是:两个链表的入环结点(loop1,loop2)不是同一个,判断条件很简单,就是从任意一个链表的入环结点开始遍历一圈,如果都没有遇到另外一个链表的入环结点, 两个链表不相交,属于情况1;
如果从任意一个链表的入环结点开始遍历一圈,遇到了另外一个链表的入环结点,则说明两个链表相交,属于情况3,且任意一个链表的入环结点都是相交结点。
最后分析情况2,两个链表的入环结点如果是同一个,可以记录两个链表的差值,然后让短链表先走差值步以后,长短链表同时开始走,相遇的结点就是第一个相交结点。
完整代码见:
public class Code_FindFirstIntersectNode { public static class List { public int val; public List next; public List(int v) { val = v; } } public static List getIntersectNode(List head1, List head2) { if (head1 == null || head2 == null) { return null; } // 两个均无环 List loop1 = getLoopNode(head1); List loop2 = getLoopNode(head2); if (loop1 == null && loop2 == null) { return noLoop(head1, head2); } // 两个均有环 if (loop1 != null && loop2 != null) { return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2); } // 一个有环一个无环 ,不可能相交 return null; } // 找到链表第一个入环节点,如果无环,返回null public static List getLoopNode(List head) { if (head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null) { return null; } // 慢指针 在第一个节点位置 List slow = head.next; // 快指针,在第二个节点的位置 List fast = head.next.next; while (slow != fast) { if (fast.next == null || fast.next.next == null) { return null; } // 快指针每次走两步 fast = fast.next.next; // 慢指针每次走一步 slow = slow.next; } // 两个指针遇上了,说明有环 // 让快指针回到头部, 慢指针停在原地 fast = head; while (fast != slow) { fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } // 快指针每次走一步,慢指针每次走一步,遇上后,就是入环节点处 return slow; } // 如果两个链表都无环,返回第一个相交节点,如果不想交,返回null public static List noLoop(List head1, List head2) { if (head1 == null || head1 == null) { return null; } // 判断两个链表的长度 int n = 0; List t1 = head1; List t2 = head2; while (t1.next != null) { n++; t1 = t1.next; } while (t2.next != null) { n--; t2 = t2.next; } // 两个链表的末节点不相等 if (t2 != t1) { return null; } // 记录长的链表头节点 List longer = n > 0 ? head1 : head2; // 记录短的链表头节点 List shorter = longer == head1 ? head2 : head1; // 先让长链表走一段距离(这段的长度就是长链表和短链表的长度差) int gap = Math.abs(n); while (gap != 0) { gap--; longer = longer.next; } // 然后长链表和短链表同时开始走,直到相等的节点即为交点 while (longer != shorter) { longer = longer.next; shorter = shorter.next; } return shorter; } // 两个有环链表,返回第一个相交节点,如果不想交返回null public static List bothLoop(List head1, List loop1, List head2, List loop2) { // 只有两种情况 if (loop1 == loop2) { // 1. 未入环就相交 // 这种情况下,两个链表的入环节点是一样 int n = 0; List t1 = head1; List t2 = head2; while (t1 != loop1) { n++; t1 = t1.next; } while (t2 != loop2) { n--; t2 = t2.next; } List longer = n > 0 ? head1 : head2; List shorter = longer == head1 ? head2 : head1; n = Math.abs(n); while (n != 0) { n--; longer = longer.next; } while (longer != shorter) { longer = longer.next; shorter = shorter.next; } return shorter; } else { // 2. 共用环,不在入环处相交,随便一个链表的入环点就是交点 // loop1 != loop2 // 从loop1开始,转一圈回到loop1 // 如果都没有遇到loop2,则不相交 // 如果遇到了loop1,则交点为loop1或者loop2都可以 List t1 = loop1.next; while (t1 != loop1) { if (t1 == loop2) { return loop1; } t1 = t1.next; } return null; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
更多
-
相关阅读:
基于XML管理(bean Spring的入门案例、IOC容器创建对象的方式、获取Bean的三种方式)
Java面试八股文整理
【WebGIS面试经验】(四)第一次社招面试也是第一次线下面试
mysql存储过程和函数
使用 WordPress快速个人建站指南
免费享受企业级安全:雷池社区版WAF,高效专业的Web安全的方案
关于线程池
【SpringCloud】Eureka注册中心 代码详细介绍
httprunner4 – 录制生成测试用例
羡慕 Excel 的高级选择与文本框颜色呈现?Pandas 也可以拥有!! ⛵
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/hotonyhui/article/details/128044178
