-
九、【React基础】组件的生命周期
访问官网 ReactDOM 了解更多DOM 的特定方法
1、旧生命周期
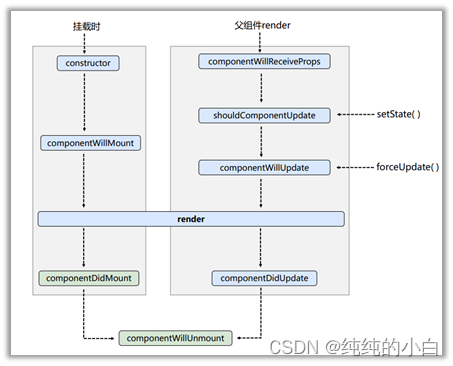
当前版本虽然依然全部可用,但是自16.x版本就开始说要删除其中的
componentWillMount、componentWillReceiveProps、componentWillUpdate;而且这三个钩子也基本万年不用一次,建议不要使用1.1、单组件生命周期
1.1.1、生命周期
1.1.1.1、初始化阶段:由 ReactDOM.render() 触发—初次渲染
-
constructor()
-
componentWillMount():组件挂载前置;组件将被挂载
-
render() 必用
-
componentDidMount():组件挂载完毕 常用
- 可以接收2个参数
(prevProps, prevState),既挂载前收到的props和初始化时创建的state - 一般在这个钩子中做一些初始化的事,例如:开启定时器、发送网络请求、订阅消息
- 可以接收2个参数
1.1.1.2、更新阶段:由组件内部 this.setSate() 或父组件重新render触发
-
shouldComponentUpdate():组件更新阀门,判断是否进行更新
- 可以接收2个参数
(nextProps, nextState) - 可直接调
forceUpdate()绕过阀门进行强制更新
- 可以接收2个参数
-
componentWillUpdate():组件更新前置;组件将要更新
- 可以接收3个参数
(prevProps, prevState, snapshot)
- 可以接收3个参数
-
render() 必用
-
componentDidUpdate():组件更新完毕
1.1.1.3、卸载组件:由 ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode() 触发
- componentWillUnmount():组件卸载前置;组件将要被卸载,这里可以交代后事 常用
- 一般在这个钩子中做一些收尾的事,例如:关闭定时器、取消订阅消息
1.1.2、CODE
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>2_react生命周期(旧)title> head> <body> <div id="test">div> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react.development.js">script> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react-dom.development.js">script> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/babel.min.js">script> <script type="text/babel"> //创建组件 class Count extends React.Component { //构造器 constructor(props) { console.log('Count---constructor'); super(props) //初始化状态 this.state = { count: 0 } } //组件将要挂载的钩子 componentWillMount() { console.log('Count--组件挂载前置--componentWillMount'); } //组件挂载完毕的钩子 componentDidMount() { console.log('Count--组件挂载完毕--componentDidMount'); } //控制组件更新的“阀门” shouldComponentUpdate() { console.log('Count--组件更新阀门--shouldComponentUpdate'); return true // 必须返回boolean且只有返回true才会继续执行更新流程 } //组件将要更新的钩子 componentWillUpdate() { console.log('Count--组件更新前置--componentWillUpdate'); } //组件更新完毕的钩子 componentDidUpdate() { console.log('Count--组件更新完毕--componentDidUpdate'); } //组件将要卸载的钩子 componentWillUnmount() { console.log('Count--组件卸载前置--componentWillUnmount'); } //加1按钮的回调 add = () => { //获取原状态 const { count } = this.state //更新状态 this.setState({ count: count + 1 }) } //卸载组件按钮的回调 death = () => { ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById('test')) } //强制更新按钮的回调 force = () => { this.forceUpdate() // 绕过更新阀门直接强制更新 } render() { console.log('Count--组件渲染钩子--render'); const { count } = this.state return ( <div> <h2>当前求和为:{count}</h2> <button onClick={this.add}>点我+1</button> <button onClick={this.death}>卸载组件</button> <button onClick={this.force}>不更改任何状态中的数据,强制更新一下</button> </div> ) } } //渲染组件 ReactDOM.render(<Count />, document.getElementById('test')) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
1.1.3、Result

1.2、嵌套组件生命周期
1.2.1、组件将要接收 props
- componentWillReceiveProps(props):组件接收 props 前置
- 注意点:第一次传的不算(首次渲染不会调此钩子),如果更名为 componentWillReceiveNewProps 更好理解
1.2.2、CODE
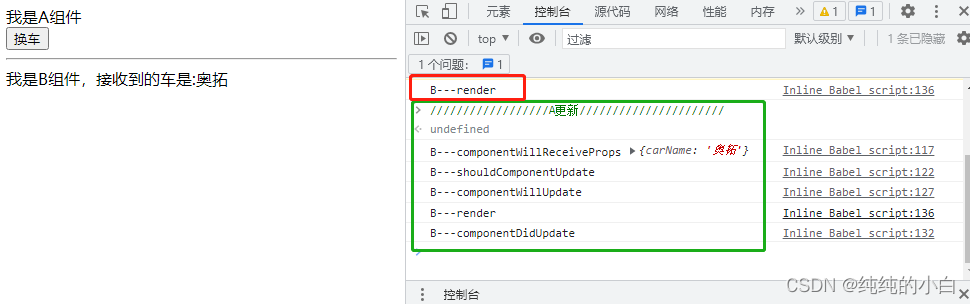
//父组件A class A extends React.Component { //初始化状态 state = { carName: '奔驰' } changeCar = () => { this.setState({ carName: '奥拓' }) } render() { return ( <div> <div>我是A组件</div> <button onClick={this.changeCar}>换车</button> <hr /> <B carName={this.state.carName} /> </div> ) } } //子组件B class B extends React.Component { //组件将要接收新的props的钩子 componentWillReceiveProps(props) { console.log('B---componentWillReceiveProps', props); } //控制组件更新的“阀门” shouldComponentUpdate() { console.log('B---shouldComponentUpdate'); return true } //组件将要更新的钩子 componentWillUpdate() { console.log('B---componentWillUpdate'); } //组件更新完毕的钩子 componentDidUpdate() { console.log('B---componentDidUpdate'); } render() { console.log('B---render'); return ( <div>我是B组件,接收到的车是:{this.props.carName}</div> ) } } //渲染组件 ReactDOM.render(<A/>, document.getElementById('test'))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
1.2.3、Result
2、新生命周期
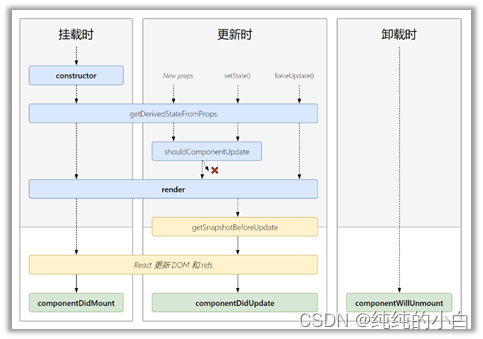
2.1、变化
2.1.1、即将废弃的 3 个老钩子
componentWillMountcomponentWillReceivePropscomponentWillUpdate
如果在新版本想继续使用这三个废弃的钩子,则必须在前面加上 “UNSAFE_” 前缀,这里的 “unsafe” 不是指安全性,而是表示使用这些生命周期的代码在 React 的未来版本中更有可能出现 bug,尤其是在启用异步渲染之后。具体可参考官博 异步渲染之更新(为未来规划计)。
2.1.2、新增 2 个钩子(万年不用)
- getDerivedStateFromProps:从Props获取派生状态。此方法适用于==罕见==的用例,即 state 的值在任何时候都取决于 props。派生状态会导致代码冗余,并使组件难以维护
- 可以接收2个参数,没错就是
(props, state) - 必须声明为
static静态方法 - 必须返回一个
state对象或者null
- 可以接收2个参数,没错就是
- getSnapshotBeforeUpdate:在最近一次渲染输出(提交到 DOM 节点)之前调用。它使得组件能在发生更改之前从 DOM 中捕获一些信息(例如,滚动位置)。此生命周期方法的任何返回值将作为参数传递给
componentDidUpdate()。此用法并不常见,但它可能出现在 UI 处理中,如需要以特殊方式处理滚动位置的聊天线程等。- 可以接收2个参数
(prevProps, prevState) - 必须返回 snapshot 的值或
null
- 可以接收2个参数
2.2、新生命周期
新钩子已经红色标出,由于根本不用,所以未加粗突出,甚至完全可以忽略这俩小透明
2.2.1、初始化阶段:由 ReactDOM.render() 触发—初次渲染
-
constructor()
-
static getDerivedStateFromProps() -
render() 必用
-
componentDidMount() 常用
2.2.2、更新阶段:由组件内部 this.setSate() 或父组件重新render触发
-
static getDerivedStateFromProps() -
shouldComponentUpdate()
-
render() 必用
-
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate -
componentDidUpdate()
2.2.3、卸载组件:由 ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode() 触发
- componentWillUnmount() 常用
2.3、CODE for getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>4_getSnapShotBeforeUpdate的使用场景title> <style> .list{ width: 200px; height: 150px; background-color: skyblue; overflow: auto; } .news{ height: 30px; } style> head> <body> <div id="test">div> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/17.0.1/react.development.js">script> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/17.0.1/react-dom.development.js">script> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/17.0.1/babel.min.js">script> <script type="text/babel"> class NewsList extends React.Component{ state = {newsArr:[]} componentDidMount(){ setInterval(() => { //获取原状态 const {newsArr} = this.state //模拟一条新闻 const news = '新闻'+ (newsArr.length+1) //更新状态 this.setState({newsArr:[news,...newsArr]}) }, 1000); } getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(){ return this.refs.list.scrollHeight } componentDidUpdate(preProps,preState,height){ this.refs.list.scrollTop += this.refs.list.scrollHeight - height } render(){ return( <div className="list" ref="list"> { this.state.newsArr.map((n,index)=>{ return <div key={index} className="news">{n}</div> }) } </div> ) } } ReactDOM.render(<NewsList/>,document.getElementById('test')) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
2.4、Result
滑动到哪就可以让内容停在哪,不会随着数据增加而被压到底下

小白学习参考视频:尚硅谷React教程
中文官网:State & 生命周期
-
-
相关阅读:
11月30日(第二天)
【EI会议征稿通知】第四届电网系统与绿色能源国际学术会议(PGSGE 2024)
Java 多线程
再见 Xshell ,这款开源的终端工具逼格更高
探索ABP的EventHub解决方案
更多模型,更强功能,快来开箱新一代图像分类开源框架
Linux命令行教程:使用head和tail命令快速查看文件的开头和结尾
新人福利——Cheat Engine功能之基础篇
淘宝api接口大全(参数返回值说明)
C++入门(上)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_30769437/article/details/128039775
