-
Packet Tracer - 排除单区域 OSPFv2 故障
地址分配表
设备
接口
IP 地址
子网掩码
默认网关
R1
G0/0
172.16.1.1
255.255.255.0
不适用
S0/0/0
172.16.3.1
255.255.255.252
不适用
S0/0/1
192.168.10.5
255.255.255.252
不适用
R2
G0/0
172.16.2.1
255.255.255.0
不适用
S0/0/0
172.16.3.2
255.255.255.252
不适用
S0/0/1
192.168.10.9
255.255.255.252
不适用
S0/1/0
209.165.200.225
255.255.255.224
不适用
R3
G0/0
192.168.1.1
255.255.255.0
不适用
S0/0/0
192.168.10.6
255.255.255.252
不适用
S0/0/1
192.168.10.10
255.255.255.252
不适用
PC1
172.16.1.2
255.255.255.0
172.16.1.1
PC2
NIC
172.16.2.2
255.255.255.0
172.16.2.1
PC3
NIC
192.168.1.2
255.255.255.0
192.168.1.1
拓扑图
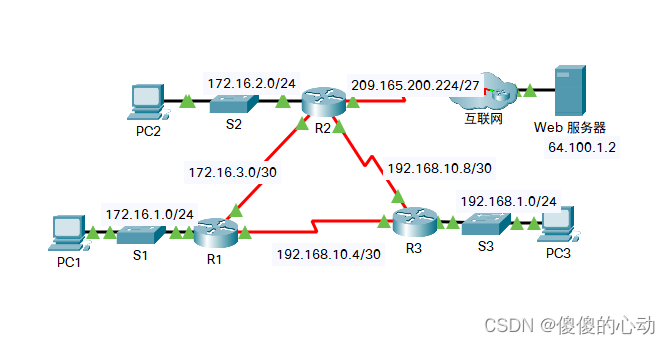
场景
在此练习中,您将使用 ping 和 show 命令来排除 OSPF 路由问题,以识别网络配置中的错误。 然后,您将记录您发现的错误并实施适当的解决方案。 最后,您将验证端到端连接是否已恢复。
故障排除流程
1. 使用测试命令来发现网络中的连接问题,并在记录表中记录问题。
2. 使用验证命令来发现问题的根源,并想出适当的解决方案。 在记录表中记录建议的解决方案。
3. 一次执行一个解决方案,并验证问题是否得到解决。 在记录表中记录解决状态。
4. 如果问题没有得到解决,可能需要首先删除实施的解决方案,然后返回第 2 步。
5. 所有发现的问题都得到解决后,测试端到端连接。
记录表
设备
发现的问题
推荐的解决方案
是否已解决?
R1
未与R3形成邻居关系
删除netowrk 172.16.10.4 0.0.0.3 area 0语句,并改为netowrk 192.168.10.4 0.0.3 area 0
R2
未在R2中更新传播默认静态路由
配置default-information originate
R3
未与R2形成邻居关系
删除R3 S0/0/1界面上的hello-lisse命令。
实验详细步骤:
R1>en
R1#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R1(config)#router ospf 1
R1(config-router)#no network 172.16.10.4 0.0.0.3 area 0
R1(config-router)#network 192.168.10.4 0.0.0.3 area 0
R1(config-router)#end
R1#
R2>en
R2#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R2(config)#router ospf 1
R2(config-router)#default-information originate
R2(config-router)#end
R2#
R3>en
R3#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R3(config)#interface s0/0/1
R3(config-if)#no ip ospf hello-interval
R3(config-if)#end
R3#
实验链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1z2vEfks8x41yDPBogeAbrg?pwd=1022
提取码:1022
--来自百度网盘超级会员V1的分享
-
相关阅读:
【力扣-数据结构和算法-头哨兵】移除链表元素
我去!Python 不愧是脚本之王,这 23 种命令行用法你全部 get 了吗?
【第二章 数据的表示和运算】d1
52. N皇后 II(难度:困难)
数据挖掘实战(1):信用卡违约率分析
[Apache Kafka 3.2源码解析系列]-5- Kafka的发送器对象的初始化
全球约有 150 亿台设备在运行 Java,收费后还能用吗?
百度工程师移动开发避坑指南——Swift语言篇
计算机毕设(附源码)JAVA-SSM基于的图书馆管理系统
【机器学习】为什么会产生过拟合,有哪些方法可以预防或克服过拟合?(面试回答)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_63624418/article/details/127942164