-
OVIS数据集代码解析
OVIS数据集代码解析
OVIS数据集格式整体和COCO类似,但是是以video的形式存储的,对应的解析代码见:https://github.com/qjy981010/cocoapi/blob/main/PythonAPI/pycocotools/ovis.py。
由于OVIS仅train提供了标注,因此,这里均以train进行说明。
1.init函数
创建一些字典,包括dataset、anns、cats、vids以及vidToAnns、catToVids。
其中dataset是原始标注数据,由json文件读取得到。
这里对其进行详细说明dataset包括5个key:
- info: 主要是存储一些meta信息,如下:
‘description’: ‘OVIS’,
‘url’: ‘http://songbai.site/ovis/’,
‘version’: ‘1.0’,
‘year’: 2021,
‘contributor’: ‘youku’,
‘date_created’: ‘2021-01-01’-
licenses: 存储licenses信息。
-
categories: 类别信息。OVIS一共包括25个类别,每个类别包括三个信息:supercategory表示该类别的超类,OVIS都设置为object,id表示该类别的id,而name则是该类别的字符串名称。
具体类别及对应实例数目如下:
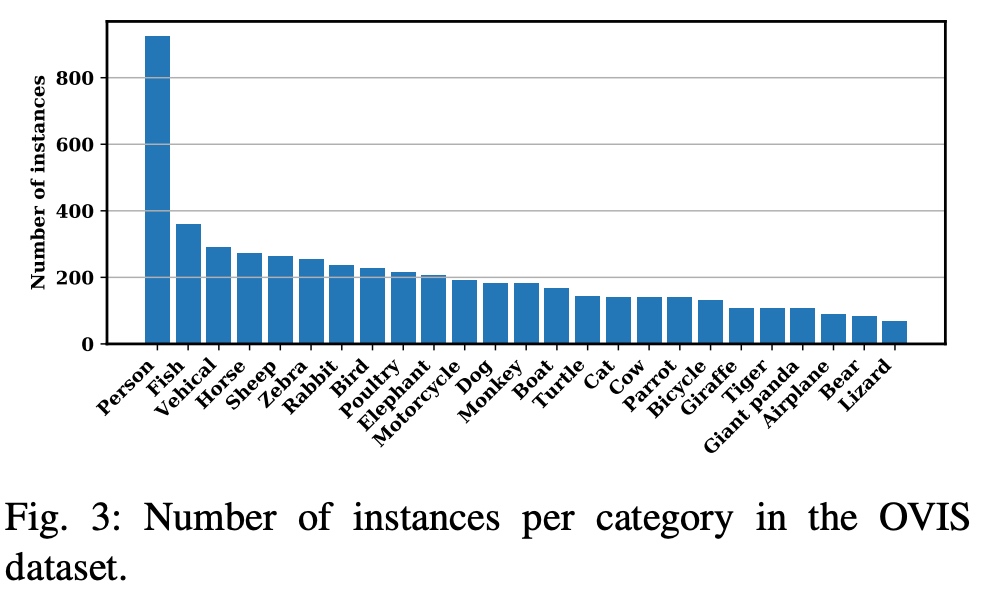
可以看出,person是主要类别。 -
videos: 视频详细信息。训练集一共包含607段视频,每段视频的信息以一个字典构成,因此,videos是一个长为607的列表。
每个视频信息字典包含6个基本属性:
- width: 视频的宽
- height: 视频的长
- license: license id
- file_names: 对应图片的相对路径,例如’85aa3b0e/img_0000001.jpg’,说明该图片位于85aa3b0e视频文件夹下,图片名称为img_0000001.jpg
- id: 视频id
- length: 该视频采样得到的图片数目
-
annotations: 该视频中所有标注实例的信息。这里和coco存在一定差异。由于OVIS是一个视频数据集,这里的实例是针对视频进行描述的。例如一个视频假设有500帧,某一个人物在这个视频中出现了,那么该人物就是一个实例,其在该视频中500帧图片中的实例id都是一致的。这里的标注就是采用以上设置给出的。
每个实例标注由一个字典表示。每个字典有11个基本属性:
- length: 数值全为1,不太清楚具体含义
- category_id: 该实例的类别id
- video_id: 该实例对应所在的视频id
- iscrowd: 这里的iscrowd应该和coco不太一样,不用于区分segmentation的类别。(在coco中,iscrowd=0时意味着segmentation的格式为polygon,iscrowd=1时则意味着segmentation的格式为rle)
- id: 该实例对应的id
- height: 视频帧的长
- width: 视频帧的宽
- segmentations: 该实例的mask标注信息,每一帧都会给出对应的标注,如果当前帧没有该实例,则为None。这里的标注信息以字典形式给出:
- size: 该标注对应的[height, width],用于rle解码
- counts: rle编码
- bboxes: 该实例的bbox标注信息,每一帧都会给出对应的标注。这里的标注以四元组 (x, y, h, w) 形式给出,其中 (x,y) 是左上角坐标。
- areas: 该实例对应的bbox的面积,每一帧都给出。
- occulusion: 该实例的遮挡情况,分为三类no occlusion, slight occlusion 以及 severe occlusion,具体说明可参考原论文。
其余字典(anns、cats、vids以及vidToAnns、catToVids)则是通过createIndex进行填充。
2. createIndex
该函数主要是用于填充在init中创建的一些属性字典。
for ann in self.dataset['annotations']: vidToAnns[ann['video_id']].append(ann) anns[ann['id']] = ann- 1
- 2
- 3
vidToAnns: key为视频的id,而value则为一个列表,里面存储了视频id为key的所有实例信息。
anns: key为实例的id,而value即为该实例。for vid in self.dataset['videos']: vids[vid['id']] = vid- 1
- 2
vids: key为视频id,而value即为该视频信息。
for cat in self.dataset['categories']: cats[cat['id']] = cat- 1
- 2
cats: key为类别id,而value即为该类别信息。
for ann in self.dataset['annotations']: catToVids[ann['category_id']].append(ann['video_id'])- 1
- 2
catToVids: key是类别id,而value则为一个列表,里面存储了类别id为key的所有视频id。
3. 一些常用函数的使用
3.1 getAnnIds
def getAnnIds(self, vidIds=[], catIds=[], areaRng=[], iscrowd=None): """ Get ann ids that satisfy given filter conditions. default skips that filter :param vidIds (int array) : get anns for given vids catIds (int array) : get anns for given cats areaRng (float array) : get anns for given area range (e.g. [0 inf]) iscrowd (boolean) : get anns for given crowd label (False or True) :return: ids (int array) : integer array of ann ids """- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
这个函数的作用在于在给定视频id列表、类别id列表、面积约束范围以及是否包括crowd实例的情况下,输出对应满足条件的ann id。
其大致逻辑是:- 根据给定的视频id,通过vidToAnns来获取所有的实例信息。
- 根据类别id、面积约束范围以及是否包含crowd实例来对得到的实例信息进行筛选。
- 最终返回所有实例对应的id。
3.2 getCatIds
def getCatIds(self, catNms=[], supNms=[], catIds=[]): """ filtering parameters. default skips that filter. :param catNms (str array) : get cats for given cat names :param supNms (str array) : get cats for given supercategory names :param catIds (int array) : get cats for given cat ids :return: ids (int array) : integer array of cat ids """- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
这个函数的作用在于在给定类别名称列表、类超类类别名称列表以及类别id列表的情况下,输出对应满足条件的类别id。
3.3 getVidIds
def getVidIds(self, vidIds=[], catIds=[]): ''' Get vid ids that satisfy given filter conditions. :param vidIds (int array) : get vids for given ids :param catIds (int array) : get vids with all given cats :return: ids (int array) : integer array of vid ids '''- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
这个函数的作用在于在给定视频id列表以及类别id列表的情况下,输出对应满足条件的类别id。
3.4 loadAnns, loadCats and loadVids
这些函数的作用都相近,都是根据提供对应的id列表来获取对应的信息,包括标注、类别以及视频等。
3.5 annToRLE以及annToMask
这两个函数一般使用annToMask,用于将ann转化为对应的binary mask,而annToRLE则是用于对ann进行转化。
def annToRLE(self, ann, frameId): """ Convert annotation which can be polygons, uncompressed RLE to RLE. :return: binary mask (numpy 2D array) """ t = self.vids[ann['video_id']] h, w = t['height'], t['width'] segm = ann['segmentations'][frameId] if type(segm) == list: # polygon -- a single object might consist of multiple parts # we merge all parts into one mask rle code rles = maskUtils.frPyObjects(segm, h, w) rle = maskUtils.merge(rles) elif type(segm['counts']) == list: # uncompressed RLE rle = maskUtils.frPyObjects(segm, h, w) else: # rle rle = segm return rle def annToMask(self, ann, frameId): """ Convert annotation which can be polygons, uncompressed RLE, or RLE to binary mask. :return: binary mask (numpy 2D array) """ rle = self.annToRLE(ann, frameId) m = maskUtils.decode(rle) return m- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
4. 解析代码
这里提供一份用于提取某个特定类别数据的代码,例如以下代码可以提取Person这个类别:
import cv2 import os.path import numpy as np from tqdm import tqdm # https://github.com/qjy981010/cocoapi/blob/main/PythonAPI/pycocotools/ovis.py from ovis import OVIS # a tool function for parallel work from parallel_work import parallel_work PALETTE = [(220, 20, 60), (119, 11, 32), (0, 0, 142), (0, 0, 230), (106, 0, 228), (0, 60, 100), (0, 80, 100), (0, 0, 70), (0, 0, 192), (250, 170, 30), (100, 170, 30), (220, 220, 0), (175, 116, 175), (250, 0, 30), (165, 42, 42), (255, 77, 255), (0, 226, 252), (182, 182, 255), (0, 82, 0), (120, 166, 157), (110, 76, 0), (174, 57, 255), (199, 100, 0), (72, 0, 118), (255, 179, 240), (0, 125, 92), (209, 0, 151), (188, 208, 182), (0, 220, 176), (255, 99, 164), (92, 0, 73), (133, 129, 255), (78, 180, 255), (0, 228, 0), (174, 255, 243), (45, 89, 255), (134, 134, 103), (145, 148, 174), (255, 208, 186), (197, 226, 255), (171, 134, 1), (109, 63, 54), (207, 138, 255), (151, 0, 95), (9, 80, 61), (84, 105, 51), (74, 65, 105), (166, 196, 102), (208, 195, 210), (255, 109, 65), (0, 143, 149), (179, 0, 194), (209, 99, 106), (5, 121, 0), (227, 255, 205), (147, 186, 208), (153, 69, 1), (3, 95, 161), (163, 255, 0), (119, 0, 170), (0, 182, 199), (0, 165, 120), (183, 130, 88), (95, 32, 0), (130, 114, 135), (110, 129, 133), (166, 74, 118), (219, 142, 185), (79, 210, 114), (178, 90, 62), (65, 70, 15), (127, 167, 115), (59, 105, 106), (142, 108, 45), (196, 172, 0), (95, 54, 80), (128, 76, 255), (201, 57, 1), (246, 0, 122), (191, 162, 208)] def load_mask_from_person_video_ids(person_video_ids, ovis, person_cat_id, target_dir): for video_id in person_video_ids: video_info = ovis.vids[video_id] height, width, length = video_info['height'], video_info['width'], video_info['length'] video_anns = ovis.vidToAnns[video_id] person_anns = [anns for anns in video_anns if anns['category_id'] == person_cat_id] for frame_id in tqdm(range(length)): frame_mask = np.zeros((height, width), dtype=np.uint8) for ann in person_anns: if ann['segmentations'][frame_id] is None: continue mask = ovis.annToMask(ann, frame_id) mask_id = max(np.unique(frame_mask)) + 1 frame_mask = np.where(mask > 0, mask_id, frame_mask) if len(np.unique(frame_mask)) > 0: file_path = video_info['file_names'][frame_id] video_name, frame_name = file_path.split('/') os.makedirs(os.path.join(target_dir, video_name), exist_ok=True) cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(target_dir, video_name, frame_name.replace('jpg', 'png')), frame_mask) def load_mask_from_ovis(ovis_root): subsets = ['train'] for subset in subsets: target_dir = os.path.join(ovis_root, 'labels', subset) os.makedirs(target_dir, exist_ok=True) json_file = os.path.join(ovis_root, f'annotations_{subset}.json') ovis = OVIS(json_file) # get person cat id person_cat_id = ovis.getCatIds(catNms=['Person'])[0] print(person_cat_id) # get person video ids person_video_ids = ovis.getVidIds(catIds=person_cat_id) print(person_video_ids) parallel_work(person_video_ids, load_mask_from_person_video_ids, ovis, person_cat_id, target_dir) def visualization_label_files(label_files, target_dir): for root, file in label_files: video_name = root.split('/')[-1] os.makedirs(os.path.join(target_dir, video_name), exist_ok=True) raw_mask = cv2.imread(os.path.join(root, file), 0) h, w = raw_mask.shape[:2] color_mask = np.zeros((h, w, 3)) instance_ids = np.unique(raw_mask)[1:] for instance_id in instance_ids: ci = int(instance_id) % len(PALETTE) color_mask[:, :, 0][raw_mask == instance_id] = PALETTE[ci][0] color_mask[:, :, 1][raw_mask == instance_id] = PALETTE[ci][1] color_mask[:, :, 2][raw_mask == instance_id] = PALETTE[ci][2] cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(target_dir, video_name, file), color_mask) def visualization(ovis_root): subsets = ['train'] for subset in subsets: label_dir = os.path.join(ovis_root, 'labels', subset) target_dir = os.path.join(ovis_root, 'visualizations', subset) label_files = [] for root, dirs, files in os.walk(label_dir): for file in tqdm(files, total=len(files)): if file.endswith('png'): label_files.append((root, file)) parallel_work(label_files, visualization_label_files, target_dir) if __name__ == '__main__': ovis_root = '/data/data/segmenation/instance_segmentation/OVIS' load_mask_from_ovis(ovis_root) visualization(ovis_root)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
parallel_work是一个工具函数:
import numpy as np import multiprocessing def parallel_work(datas, worker, *args): n_cpu = multiprocessing.cpu_count() print('n_cpu', n_cpu) num_data = len(datas) stride = int(np.ceil(num_data / n_cpu)) processes = [] for i in range(n_cpu): end = min((i + 1) * stride, num_data) worker_data = datas[i * stride:end] process = multiprocessing.Process( target=worker, args=(worker_data, *args), ) processes.append(process) process.start() for process in processes: process.join()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
-
相关阅读:
Java异常编程题(巩固语法)
Redis 学习笔记
406. 根据身高重建队列
ElasticSearch全文检索技术
教你实现物联网HMI/网关的趋势功能
Scala函数式编程
【小白专用23.10.22 已验证】windows 11 安装PHP8.2 +Apache2.4
Linux ————VI编辑器
webpack工作原理
ElasticSearch基本用法
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39778049/article/details/128008291
