-
数据结构 | 带头双向循环链表【无懈可击的链式结构】
🌳前言
- 在上一文中,我们讲到了【单链表】,这种单链表的结构呢是所有链表之中最简单的,因为它不带头、是单向的,而且不循环,所以看起来非常得简洁,看过我这篇文章的小伙伴应该可以知晓。其各种算法结构实现起来确实非常麻烦,各种二级指针的传参以及各种边界条件的判断,都需要很熟练的指针把控技巧
- 但我们还是需要这种简单的结构,因为简洁的单链表一般可以作为其他复杂数据结构的子结构,比如说哈希桶、图的邻接表等等,这个我后续都会讲解到
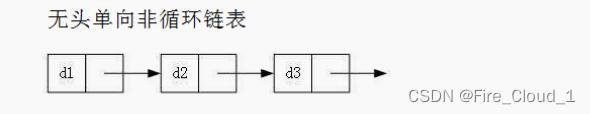
- 那我们只学习这一种链表结构就可以了吗,答案是:不可以。因为单链表的结构虽然简单,但是缺陷太多,实现起来非常的繁琐,不利于企业中的开发,于是我们就需要学习另一种链表的数据结构叫做【双链表】,也就是本节所要介绍的内容,对于双链表,我要介绍的这种是最复杂的,也就是【带头双向循环链表】,可以看到,与单链表相比,它不带头但是我带头,它是单向我是双向,它不循环但是我循环
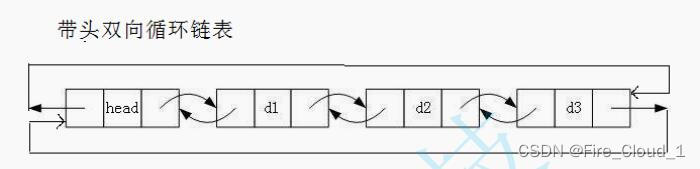
- 那有同学说,这完全就是一个极端呀,这么复杂的数据结构我能学的会吗😢,单链表已经复杂成这个样子,那它不是更加复杂了?
- 那我告诉你,其实这个结构并不复杂,只是它看起来比较复杂,但是实现起来却非常方便,先给你吃一个定心丸,接下去我们就好好来研究一下这个复杂的结构
🌳结构声明
- 首先来看一下它的结构声明是怎样的。可以看到,其具有一个data域和两个指针域,连个指针域分别是【prev】前驱指针以及【next】后继指针,分别指向前面和后面一个结点
typedef int DLDataType; typedef struct DLinkList { DLDataType data; struct DLinkList* prev; struct DLinkList* next; }DList;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 可以看到,其结构体是比单链表来得复杂,但是你要这么想,给你的条件多了,多了一个【prev】指针,从代码实现的角度来看何尝不是一件好事呢?你就可以很轻易地找到当前结点的前一个结点了,不需要再从头开始遍历
🌳接口算法实现
接下去我们来看看双链表的接口算法实现。内容还是和单链表基本一致,只是内部实现的算法逻辑需要做一个改动
🍎动态开辟&初始化【Init】
- 好,首先我们来说一说如何去进行初始化,因为是带头,所以其初始化就需要去将这个头结点进行一个处理,然后又因为是双向的,所以我们需要去处理两个指针,也就是【prev】和【next】,那要怎么进行一个初始化呢,我们又可以观察到,这是一个循环的链表,那对于一个只有头结点的循环链表,其【prev】和【next】都是指向它自己的,然后对于【data】域的话我们直接置为【-1】就好了,表示这是开始,因为不可以将这个头置空。
- 所以一开始的头结点初始化应该是下面这样的
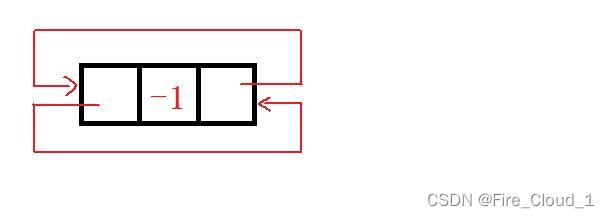
- 我们来看一下代码
- 可以看到,这里的初始化结点,我使用的是一级指针,没有像单链表里面那样使用二级指针,其实不使用二级指针传参的话是改变不了这个链表的结构的,只是函数内部做了一个修改,但是我们知道,想对头结点做一个改动有以下这三种方法
①传二级指针 ②C++引用【&】传参 ③设置返回值 - 由于我的数据结构是使用纯C实现的,所以我没有使用C++中的引用,而是使用的第三种方法,也就是【设置返回值】,将我修改后的头结点做一个返回,然后外部使用一个结构体指针做一个接收,便可以获取到内部函数所修改的结点
/*初始化结点*/ DList* DlistInit() { DList* phead = DListBugNode(-1); phead->prev = phead; phead->next = phead; return phead; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
DList* phead = DlistInit();- 1
- 然后是这个申请结点的代码,这个我在单链表中做过详细介绍,就不多讲了
/*开辟一个结点空间*/ DList* DListBugNode(DLDataType x) { DList* newnode = (DList*)malloc(sizeof(DList)); if (newnode == NULL) { perror("fail malloc"); exit(-1); } newnode->data = x; newnode->prev = NULL; newnode->next = NULL; return newnode; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
🍎尾插【PushBack】
- 好,我们来说说尾插,不要紧张,没有你想得那么复杂
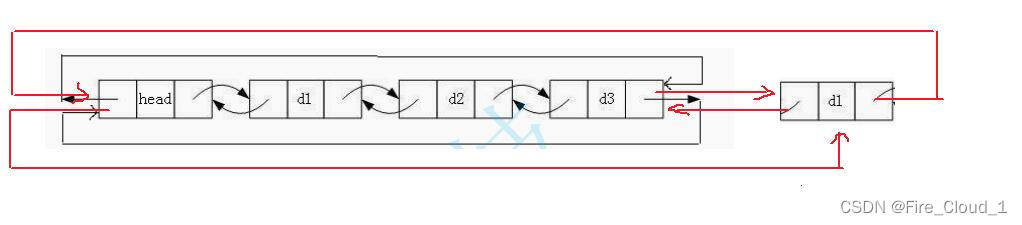
- 可以看到,我们在后面增加一个结点,此时我们只需要修改一下【prev】和【next】这两个指针即可
- 但是在这之前呢,因为你是要在最后一个结点之后新增一个结点,所以你要找到最后一个结点的地址才可以,那我们怎么去找呢,始终要牢记,这是一个双向循环链表,是循环的!!!最后一个结点指向头结点,那么头结点也就是保存着尾结点的地址,因此第一步我们就需要通过头来找到这个尾结点
//1、首先需要找到尾指针 DList* tail = phead->prev;- 1
- 2
- 有了指向这个尾结点的结构体指针,就可以去修改其指针域了,
//2、修改指针域进行插入 tail->next = newnode; newnode->prev = tail; newnode->next = phead; phead->prev = newnode;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
那有同学说,真的就是这么简单吗?是的,真的就是这样。为什么不禁锢你的思维,我们再来看一种特殊的
- 可以看到,也就是下面这个直接在头结点之后进行的尾插,对照上面的代码你可以发现,一样适用,不需要做额外的判断
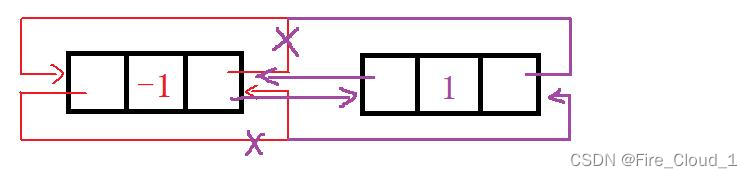
- 很清晰,很简略,很震撼
- 没错,这个链表的操作就是这么容易,其实这些指针的修改时很容易出错的,但是你在经历过【单链表】的地狱训练🎃后,就会觉得这个双链表也就那样。好,我么继续看下去,难点后面还是有的👇
🍎尾删【PopBack】
- 来看看尾删,对于尾删,也是一样,修改一下其指针域的指向接即可
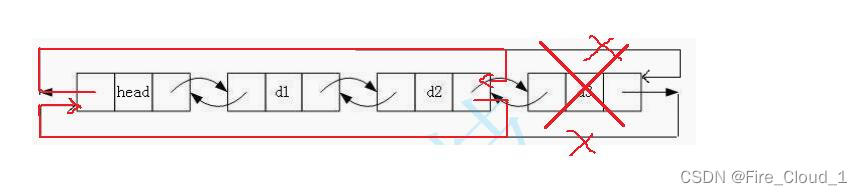
- 首先,我们一样需要去找到这个尾结点,通过头结点去找
//1.先找到尾指针 DList* tail = phead->prev;- 1
- 2
- 通过链表的学习我们可以知道,要删除一个结点,那就要找到它的前驱结点,因为只有这个前驱结点才是指向这个当前要删除结点的,需要删除当前这个结点,就是要修改其前驱结点的【next】指向。这个时候双向链表的优势就来了,只需要一个【prev】指针,便可以很轻易找到这个结点
//2.保存待删结点的上一个结点 DList* pre = tail->prev;- 1
- 2
- 然后的话就是修改指针域即可
//3.修改指针域进行删除 pre->next = phead; phead->prev = pre; free(tail);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 一样,我们再通过特殊情况做一个分析✍
- 找到当前待删的尾结点的上一个结点,也就是头结点,然后使头结点的【next】域指向头结点就是它自己,让头结点【prev】指向待删结点的上一个结点,也就是头结点自己,那就可以看出,还原成我们初始化的那个样子了
- 其实善于观察的小伙伴已经可以得出结论了,这个【带头双向循环链表】是一个很完美的结构,无论是对于现在的尾插和尾删,对于头插和头删以及后续的操作,其实都依赖于这个结构的完整性
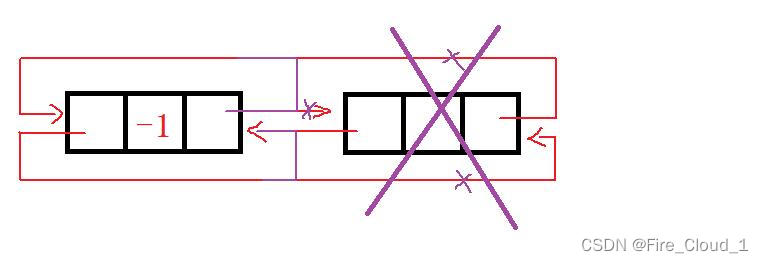
- 看我画的图是不是很工整呢😄

🍎头插【PushFront】
- 接下去我们继续看看头插,一样是通过普通示例和特殊示例来观察👀
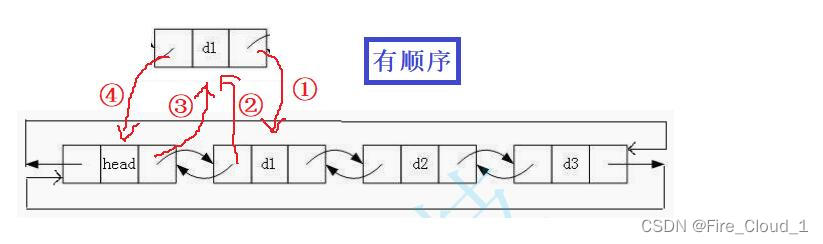
- 刚才有忽略的一个点,就是插入结点的时候需要动态开辟,也就是我们的【BuyNode】,这个大家不要忘了
DList* newnode = DListBugNode(x);- 1
- 从图中可以看出,对于这个即将插入的结点,我很明确地画出了这个指针域的修改过程,是存在顺序的;你要
先去修改待插入结点和首结点的指针指向,若是你直接去修改头结点和待插入结点的指针指向,因为头结点的【next】域存放的是首结点的地址,若是随意修改,就找不到首结点了 - 所以应该按照这个顺序来🐟
//需要考虑顺序 newnode->next = phead->next; phead->next->prev = newnode; phead->next = newnode; newnode->prev = phead;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 当然,你也可以选择不考虑顺序,这样的话就需要先去保存一下头结点的下一个结点也就是首结点
DList* first = phead->next; //无需考虑顺序 phead->next = newnode; newnode->prev = phead; newnode->next = first; first->prev = newnode;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 可以看到,以上这种是完全不需要考虑顺序的,直接修改即可
接下来看看特殊的插入
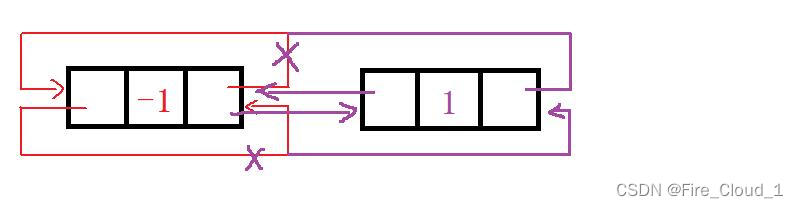
- 可以看到,对于头插和尾插,都是一样的,就是在头结点之后插入,而对于单链表而言则是不同
- 对照上面的代码可以发现,又是可以进行复用的,完全不需要进行特殊情况的判断
🍎头删【PopFront】
- 接着继续看头删
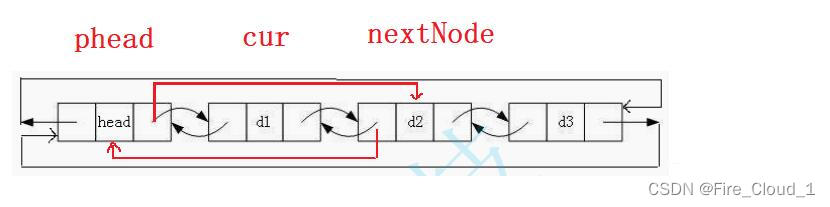
- 为了增加代码的可读性,我不会出现【
cur->next->next】这样的代码,所以会定义一些变量来帮助大家理解 - 首先,为了进行头删,我需要先行保存待删结点的下一个结点,因为待删结点中就存有它的地址,之后修改一下指向,让首结点指向它即可
DList* cur = phead->next; DList* nextNode = cur->next; phead->next = nextNode; nextNode->prev = phead; free(cur);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
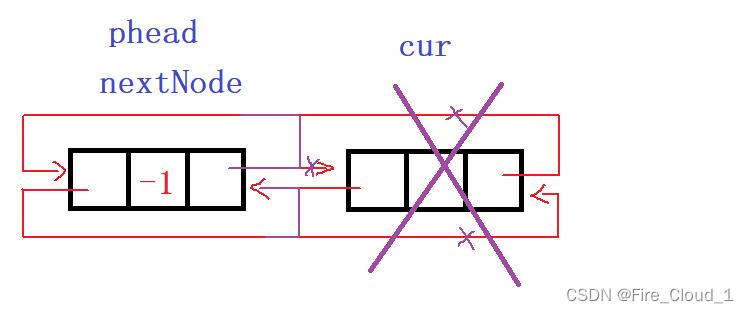
- 主要再来看特殊情况。我们依旧可以使用尾插的图示来复用
- 对照代码,我们来看【cur】即为首结点,【nextNode】为cur的next,也及时头结点,然后执行【phead->next = nextNode】和【nextNode->prev = phead】,离奇般的又可以链接上了🔗
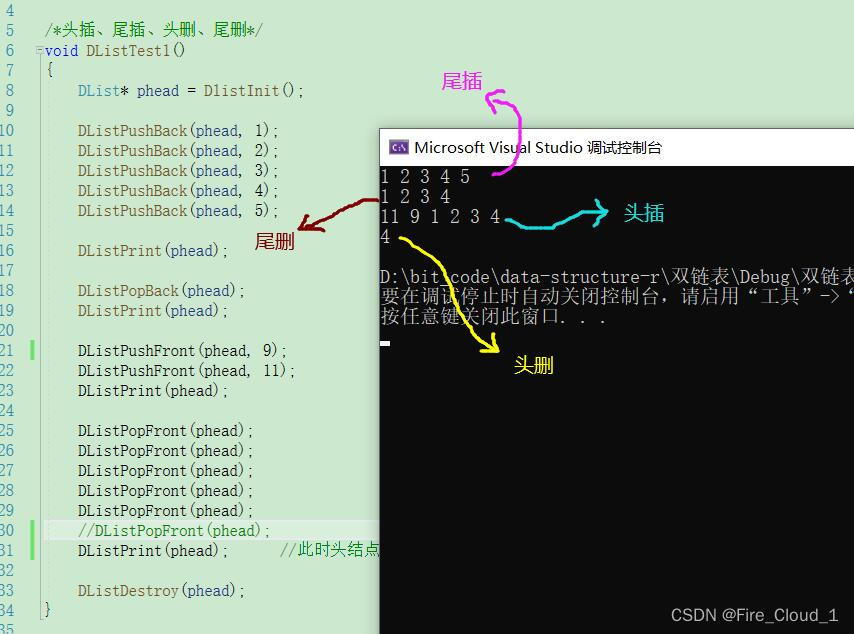
💻阶段测试一
- 好,我们进行一个小结:看完了尾插、尾删、头插、头删,你应该觉得双链表虽然看起来很复杂,但是其接口的算法实现却一点也不复杂,只需要修改一下指针的指向即可
- 接下去我们使用上面的代码进行一个阶段性的测试【测试代码后面统一给出】
🍌查找指定结点【FindNode】
- 对于查找,很简单,我们在单链表中也讲到过,因此不做细讲【唯一要修改的就是遍历链表的结束条件】
/*查找*/ DList* DListFind(DList* phead, DLDataType x) { DList* cur = phead->next; while (cur != phead) { if (cur->data == x) return cur; cur = cur->next; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
🍌插入【Insert】
- 好,接下来我们再来说一说这个【insert】插入,这个值得是在给出的【pos】指针所指结点的前面插入一个结点
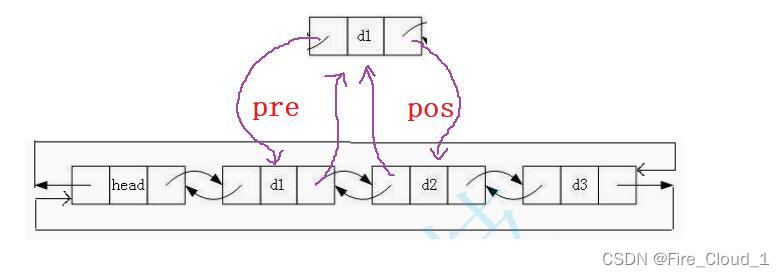
- 若是这个【pos】位置位于链表中间的某处,也是一样修改指针域的指向即可,但是要先找到【pos】所指结点的前一个结点
DList* pre = pos->prev;- 1
- 找到了之后还是一样,无需考虑顺序,直接做修改即可
pre->next = newnode; newnode->prev = pre; newnode->next = pos; pos->prev = newnode;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 好,接下去我们一样去考虑一下极端的位置。可以看到,当【pos】位于头结点的下一个结点时,在其前面插入就是一个头插。如果你去试着写一下也可以发现依旧是可以使用的
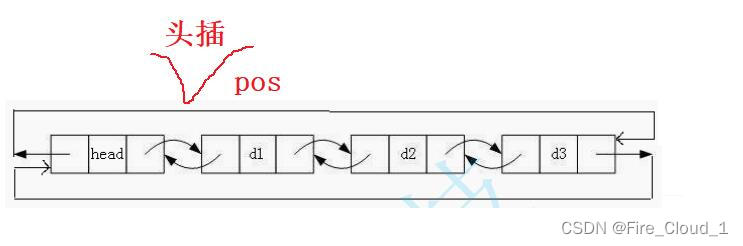
- 那可以实现头插,一定可以实现尾插,那若是要实现尾插,这个【pos】该在何处呢,因为是要在尾结点后插入一个结点,那其实就是在头结点的前面插入一个结点,就像下面这样。因为这是一个带头的循环链表,头结点和尾结点之间是相互关联的
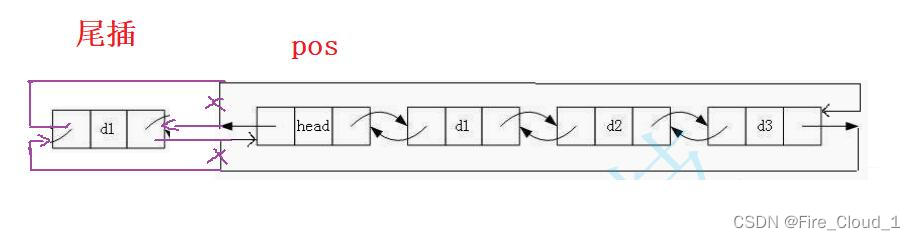
- 看完了上面的叙述,你应该明白了如何在【pos】所指结点的前一个位置插入结点了吧,我这里给出了两种形式,供你选择
直接万用版
- 这种是直接在这个【Insert】函数里做判断,就可以直接用,看清楚,参数是三个
/*插入 - 万能版*/ void DListInsert2(DList* phead, DList* pos, DLDataType x) { if (pos == phead->next) DListPushFront(phead, x); else if (pos == phead) DListPushBack(phead, x); else { DList* pre = pos->prev; DList* newnode = DListBugNode(x); pre->next = newnode; newnode->prev = pre; newnode->next = pos; pos->prev = newnode; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
直接复用版
- 这种是将头插和尾插的内核代码直接复用【Insert】,无需修改头结点,只需要插入的结点位置以及要插入的值,所以参数是两个
/*头插*/ DListInsert1(phead->next, x);- 1
- 2
/*尾插*/ DListInsert1(phead, x);- 1
- 2
/*插入 - 复用版*/ void DListInsert1(DList* pos, DLDataType x) { assert(pos); DList* pre = pos->prev; DList* newnode = DListBugNode(x); pre->next = newnode; newnode->prev = pre; newnode->next = pos; pos->prev = newnode; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
🍌删除【Erase】
- 有插入(
Insert),一定有删除(Erase) - 但是对于删除,我们是删除当前【pos】位置所指结点,而不是上一个
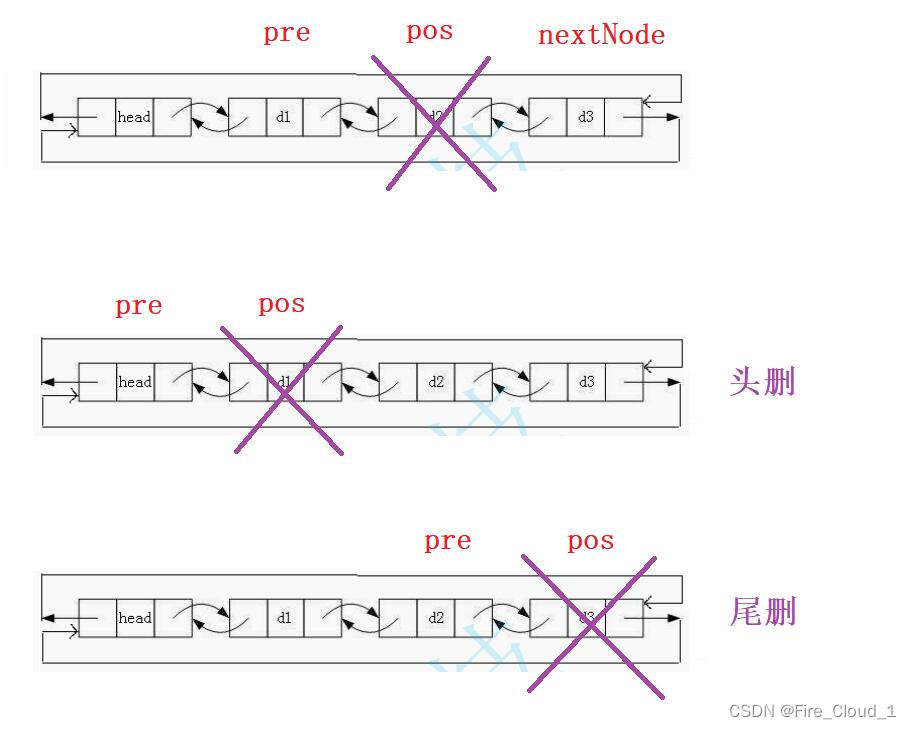
- 想必,不用我说你都可以分析出来这也是可以复用的吧【你他喵就是懒得讲好吧o(=•ェ•=)m】
直接万用版
/*删除 - 万能版*/ void DListErase2(DList* phead, DList* pos) { assert(pos); if (pos == phead->next) DListPopFront(phead); //传入的是phead,不传pos,否则会出错【用的还是同一个头】 else if (pos == phead->prev) DListPopBack(phead); //传入的是phead,不传pos,否则会出错 else { DList* pre = pos->prev; DList* nextNode = pos->next; free(pos); pre->next = nextNode; nextNode->prev = pre; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
直接复用版
/*头删*/ DListErase1(phead->next);- 1
- 2
/*尾删*/ DListErase1(phead->prev);- 1
- 2
/*删除 - 复用版*/ void DListErase1(DList* pos) { assert(pos); DList* pre = pos->prev; DList* nextNode = pos->next; free(pos); pre->next = nextNode; nextNode->prev = pre; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
💻阶段测试二
- 好,我们对上面所写的【Insert】和【Erase】做一个测试
- 首先先看下查找结点吧
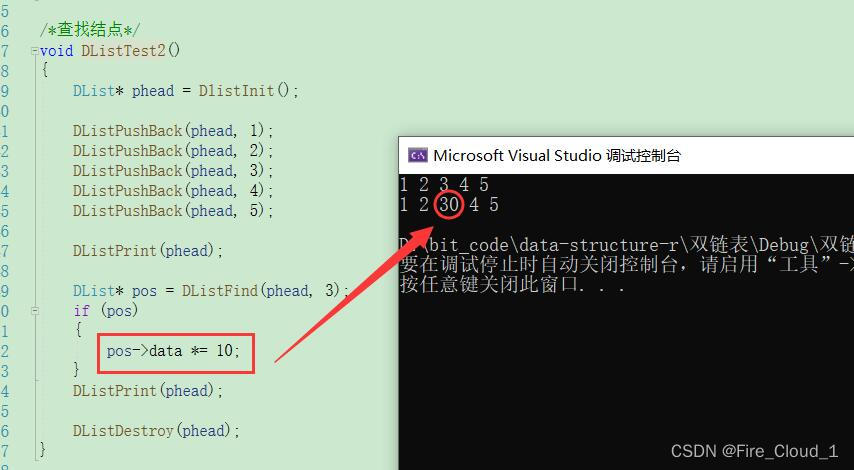
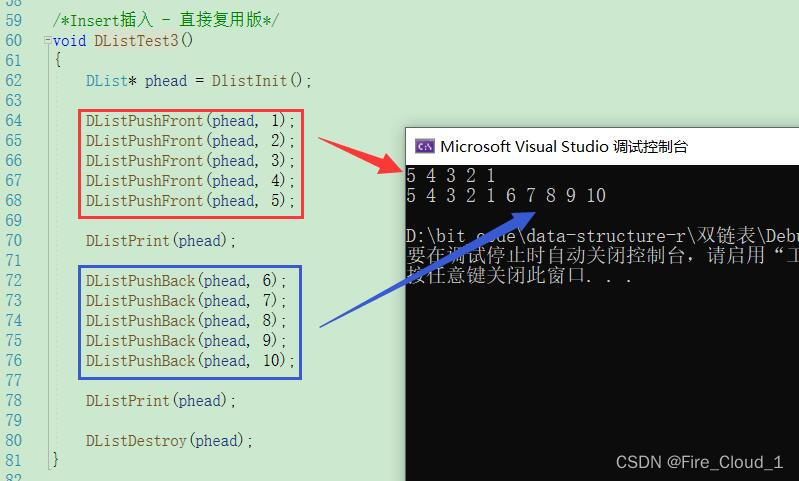
- 首先是插入的复用版,将【Insert】放到尾插和头插中复用
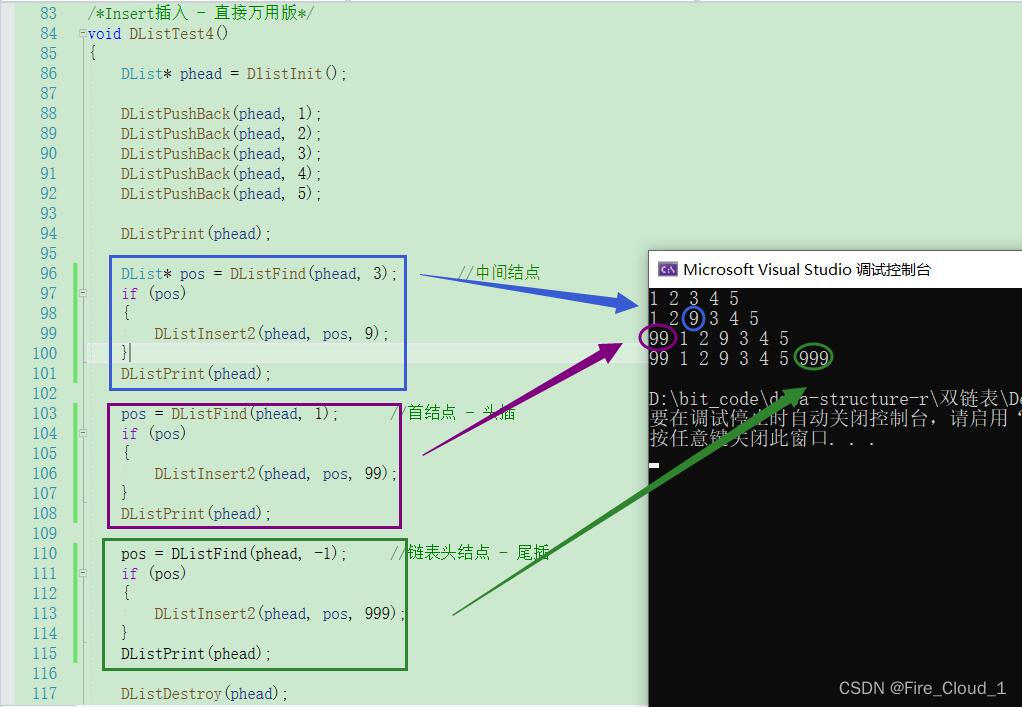
- 接着就是【直接万用板】,直接使用【Insert】
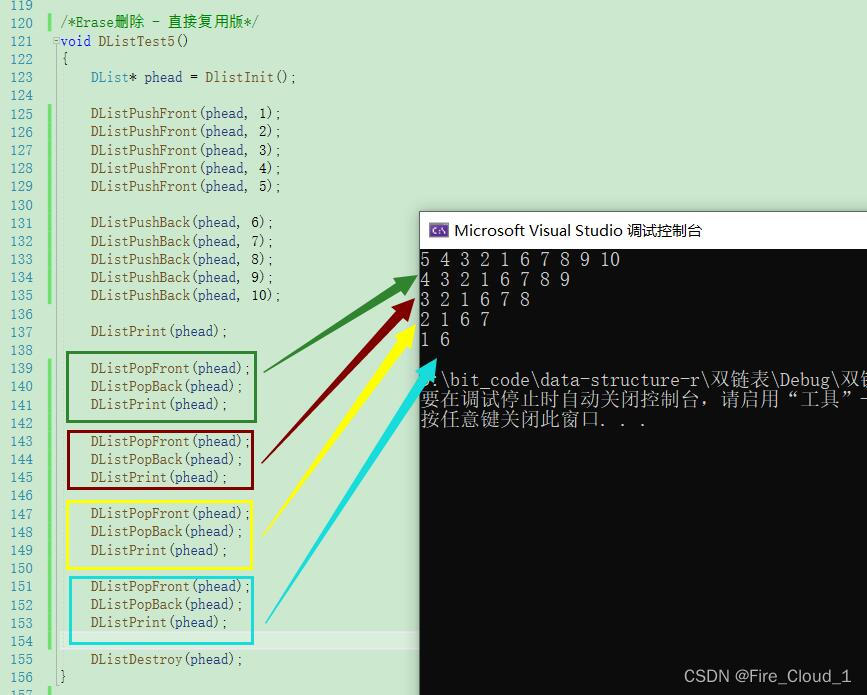
- 然后来看一下删除【Erase】
- 首先是【直接复用版】
- 然后是【直接万用版】,想删哪个删哪个
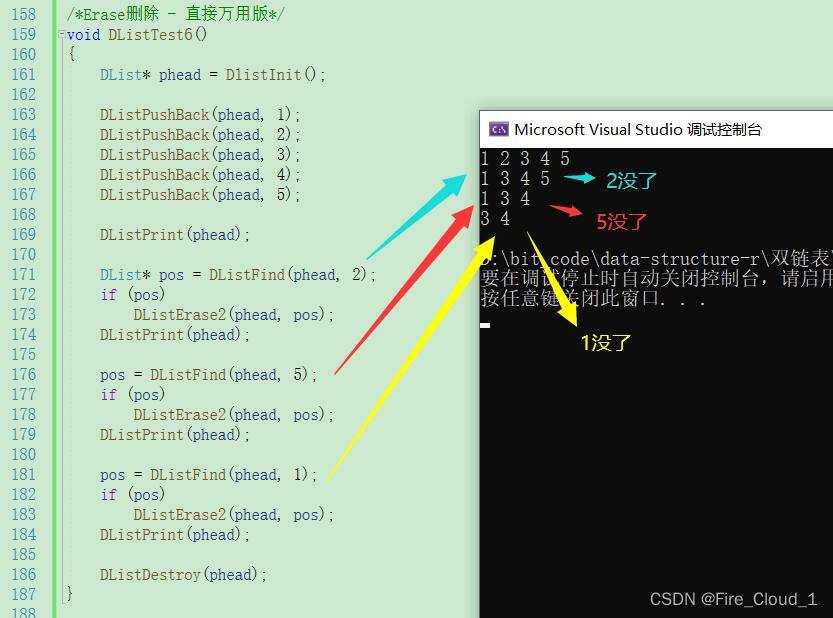
可以看出,直接万用版比较灵活,就是需要去查找位置,直接复用版只能进行头插和尾插,比较方便,无需查找位置。看自己喜好使用
🍒打印【Print】
- 可以看到,我上面在测试的的时候使用到了很多Print()语句,接下来我们来看看Print该如何去实现
- 很简单,和单链表一样的思路,【cur】指针代替遍历即可
/*打印*/ void DListPrint(DList* phead) { DList* cur = phead->next; while (cur != phead) { printf("%d ", cur->data); cur = cur->next; } printf("\n"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
🍒判空【Empty】
- 再来看一下如何判空,也就是一个结点都没有的时候,即只有头结点,那也就是我们初始化时的逻辑,头结点的【next】指向它自己
bool DListEmpty(DList* phead) { return phead->next == phead; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
🍒求解链表大小【Size】
- 对于求解链表的大小,其实是求内部有多少个结点,那此时有同学就选择直接return【phead->data】,大家觉得这个对吗,其实是不对的,直接去用头结点的【data】值表示的话,除非题目说明这个数据的类型就是整型,否则的话其实是不准确的,因为这个链表中的每一个数据结构不一样时一个数,放到很多现实中的场景中它就有可能是一个人、一条信息了,所以这个data的类型,也就是
typedef int DLDataType;- 1
- 可能是【char】【double】之类的,我们根本不能确定,所以应该去一个个地遍历这些结点,才能去求出这个链表长度
/*求解链表的大小*/ size_t DListSize(DList* phead) { size_t sz = 0; DList* cur = phead->next; while (cur != phead) { sz++; cur = cur->next; } return sz; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
🍒释放【Destroy】
- 最后的舞台📷,当然是留给【Destroy】了,有初始化,怎么能没有销毁呢,要做到有始有终
/*释放链表*/ void DListDestroy(DList* phead) { DList* cur = phead->next; while (cur != phead) { DList* nextNode = cur->next; free(cur); cur = nextNode; //迭代 } free(phead); //链表释放完后释放头结点 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
🌳OJ题目实训
【LeetCode】138 - 复制带随机指针的链表
🌳整体代码展示
- 这里给出源码,供需要的小伙伴使用
DList.h
#pragma once #include#include #include #include typedef int DLDataType; typedef struct DLinkList { DLDataType data; struct DLinkList* prev; struct DLinkList* next; }DList; DList* DListBugNode(DLDataType x); DList* DlistInit(); void DListPushBack(DList* phead, DLDataType x); void DListPopBack(DList* phead); void DListPushFront(DList* phead, DLDataType x); void DListPopFront(DList* phead); void DListInsert1(DList* pos, DLDataType x); void DListInsert2(DList* phead, DList* pos, DLDataType x); void DListErase1(DList* pos); void DListErase2(DList* phead, DList* pos); void DListPrint(DList* phead); DList* DListFind(DList* phead, DLDataType x); bool DListEmpty(DList* phead); size_t DListSize(DList* phead); void DListDestroy(DList* phead); - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
DList.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 /* * 带头双向循环链表 */ #include "DList.h"; /*开辟一个结点空间*/ DList* DListBugNode(DLDataType x) { DList* newnode = (DList*)malloc(sizeof(DList)); if (newnode == NULL) { perror("fail malloc"); exit(-1); } newnode->data = x; newnode->prev = NULL; newnode->next = NULL; return newnode; } /*初始化结点*/ DList* DlistInit() { DList* phead = DListBugNode(-1); phead->prev = phead; phead->next = phead; return phead; } /*尾插*/ void DListPushBack(DList* phead, DLDataType x) { //assert(phead); //DList* newnode = DListBugNode(x); 1、首先需要找到尾指针 //DList* tail = phead->prev; 2、修改指针域进行插入 //tail->next = newnode; //newnode->prev = tail; //newnode->next = phead; //phead->prev = newnode; DListInsert1(phead, x); } /*尾删*/ void DListPopBack(DList* phead) { //assert(phead); 1.先找到尾指针 //DList* tail = phead->prev; 2.保存待删结点的上一个结点 //DList* pre = tail->prev; 3.修改指针域进行删除 //pre->next = phead; //phead->prev = pre; //free(tail); DListErase1(phead->prev); } /*头插*/ void DListPushFront(DList* phead, DLDataType x) { //assert(phead); //DList* newnode = DListBugNode(x); //需要考虑顺序 //newnode->next = phead->next; //phead->next->prev = newnode; // //phead->next = newnode; //newnode->prev = phead; //可以先保存头结点的下一结点 //DList* first = phead->next; 无需考虑顺序 //phead->next = newnode; //newnode->prev = phead; //newnode->next = first; //first->prev = newnode; DListInsert1(phead->next, x); } /*头删*/ void DListPopFront(DList* phead) { //assert(phead); //DList* cur = phead->next; //DList* nextNode = cur->next; //phead->next = nextNode; //nextNode->prev = phead; //free(cur); DListErase1(phead->next); } /*查找*/ DList* DListFind(DList* phead, DLDataType x) { DList* cur = phead->next; while (cur != phead) { if (cur->data == x) return cur; cur = cur->next; } } /*插入 - 复用版*/ void DListInsert1(DList* pos, DLDataType x) { assert(pos); DList* pre = pos->prev; DList* newnode = DListBugNode(x); pre->next = newnode; newnode->prev = pre; newnode->next = pos; pos->prev = newnode; } /*插入 - 万能版*/ void DListInsert2(DList* phead, DList* pos, DLDataType x) { if (pos == phead->next) DListPushFront(phead, x); else if (pos == phead) DListPushBack(phead, x); else { DList* pre = pos->prev; DList* newnode = DListBugNode(x); pre->next = newnode; newnode->prev = pre; newnode->next = pos; pos->prev = newnode; } } /*删除 - 复用版*/ void DListErase1(DList* pos) { assert(pos); DList* pre = pos->prev; DList* nextNode = pos->next; free(pos); pre->next = nextNode; nextNode->prev = pre; } /*删除 - 万能版*/ void DListErase2(DList* phead, DList* pos) { assert(pos); if (pos == phead->next) DListPopFront(phead); else if (pos == phead->prev) DListPopBack(phead); else { DList* pre = pos->prev; DList* nextNode = pos->next; free(pos); pre->next = nextNode; nextNode->prev = pre; } } /*打印*/ void DListPrint(DList* phead) { DList* cur = phead->next; while (cur != phead) { printf("%d ", cur->data); cur = cur->next; } printf("\n"); } /*判空*/ bool DListEmpty(DList* phead) { return phead->next == phead; } /*求解链表的大小*/ size_t DListSize(DList* phead) { size_t sz = 0; DList* cur = phead->next; while (cur != phead) { sz++; cur = cur->next; } return sz; } /*释放链表*/ void DListDestroy(DList* phead) { DList* cur = phead->next; while (cur != phead) { DList* nextNode = cur->next; free(cur); cur = nextNode; //迭代 } free(phead); //链表释放完后释放头结点 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include "DList.h" /*头插、尾插、头删、尾删*/ void DListTest1() { DList* phead = DlistInit(); DListPushBack(phead, 1); DListPushBack(phead, 2); DListPushBack(phead, 3); DListPushBack(phead, 4); DListPushBack(phead, 5); DListPrint(phead); DListPopBack(phead); DListPrint(phead); DListPushFront(phead, 9); DListPushFront(phead, 11); DListPrint(phead); DListPopFront(phead); DListPopFront(phead); DListPopFront(phead); DListPopFront(phead); DListPopFront(phead); //DListPopFront(phead); DListPrint(phead); //此时头结点的prev和next相同,都指向自己 DListDestroy(phead); } /*查找结点*/ void DListTest2() { DList* phead = DlistInit(); DListPushBack(phead, 1); DListPushBack(phead, 2); DListPushBack(phead, 3); DListPushBack(phead, 4); DListPushBack(phead, 5); DListPrint(phead); DList* pos = DListFind(phead, 3); if (pos) { pos->data *= 10; } DListPrint(phead); DListDestroy(phead); } /*Insert插入 - 直接复用版*/ void DListTest3() { DList* phead = DlistInit(); DListPushFront(phead, 1); DListPushFront(phead, 2); DListPushFront(phead, 3); DListPushFront(phead, 4); DListPushFront(phead, 5); DListPrint(phead); DListPushBack(phead, 6); DListPushBack(phead, 7); DListPushBack(phead, 8); DListPushBack(phead, 9); DListPushBack(phead, 10); DListPrint(phead); DListDestroy(phead); } /*Insert插入 - 直接万用版*/ void DListTest4() { DList* phead = DlistInit(); DListPushBack(phead, 1); DListPushBack(phead, 2); DListPushBack(phead, 3); DListPushBack(phead, 4); DListPushBack(phead, 5); DListPrint(phead); DList* pos = DListFind(phead, 3); //中间结点 if (pos) { DListInsert2(phead, pos, 9); } DListPrint(phead); pos = DListFind(phead, 1); //首结点 - 头插 if (pos) { DListInsert2(phead, pos, 99); } DListPrint(phead); pos = DListFind(phead, -1); //链表头结点 - 尾插 if (pos) { DListInsert2(phead, pos, 999); } DListPrint(phead); DListDestroy(phead); } /*Erase删除 - 直接复用版*/ void DListTest5() { DList* phead = DlistInit(); DListPushFront(phead, 1); DListPushFront(phead, 2); DListPushFront(phead, 3); DListPushFront(phead, 4); DListPushFront(phead, 5); DListPushBack(phead, 6); DListPushBack(phead, 7); DListPushBack(phead, 8); DListPushBack(phead, 9); DListPushBack(phead, 10); DListPrint(phead); DListPopFront(phead); DListPopBack(phead); DListPrint(phead); DListPopFront(phead); DListPopBack(phead); DListPrint(phead); DListPopFront(phead); DListPopBack(phead); DListPrint(phead); DListPopFront(phead); DListPopBack(phead); DListPrint(phead); DListDestroy(phead); } /*Erase删除 - 直接万用版*/ void DListTest6() { DList* phead = DlistInit(); DListPushBack(phead, 1); DListPushBack(phead, 2); DListPushBack(phead, 3); DListPushBack(phead, 4); DListPushBack(phead, 5); DListPrint(phead); DList* pos = DListFind(phead, 2); if (pos) DListErase2(phead, pos); DListPrint(phead); pos = DListFind(phead, 5); if (pos) DListErase2(phead, pos); DListPrint(phead); pos = DListFind(phead, 1); if (pos) DListErase2(phead, pos); DListPrint(phead); DListDestroy(phead); } /*头删复用Erase*/ void DListTest7() { DList* phead = DlistInit(); DListPushBack(phead, 1); DListPushBack(phead, 2); DListPushBack(phead, 3); DListPushBack(phead, 4); DListPushBack(phead, 5); DListPrint(phead); DListPopFront(phead); DListPrint(phead); DListPopFront(phead); DListPrint(phead); DListPopFront(phead); DListPrint(phead); DListPopFront(phead); DListPrint(phead); DListPopFront(phead); DListPrint(phead); DListDestroy(phead); } /*。。。*/ void DListTest8() { DList* phead = DlistInit(); bool ret = DListEmpty(phead); if (ret) printf("链表为空\n"); else printf("链表不为空\n"); DListPushBack(phead, 1); DListPushBack(phead, 2); DListPushBack(phead, 3); DListPushBack(phead, 4); DListPushBack(phead, 5); DListPrint(phead); ret = DListEmpty(phead); if (ret) printf("链表为空\n"); else printf("链表不为空\n"); size_t sz = DListSize(phead); printf("当前链表大小为:%d\n", sz); DListDestroy(phead); } int main(void) { //DListTest1(); //DListTest2(); //DListTest3(); //DListTest4(); //DListTest5(); //DListTest6(); //DListTest7(); DListTest8(); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
🌳总结与提炼
- 好,最后我们来总结一下本所讲解的内容,在本文中,我们认识了一个很复杂的结构,叫做【带头双向循环链表】,虽然这个结构看起来很复杂,但是在我们实现其接口算法的时候就可以感觉到虽然其结构复杂,但是具体的代码实现却并不复杂,只要画个图清楚了思路,那只需要修改一下指针的指向即可
- 其实这个就像是做题一样,题目给到我们的信息越多,那你所拥有的就越多,可以帮助你解出问题,但是当题目给给到你一句话的时候,让你去求一个未知的东西,那就需要你自己去想象然后去实现一些东西,就会感觉到很难,所以有点的时候不要被很长的题目给吓到了,要细心阅读,从中筛选出有用的信息,去解决问题
OK,以上就是本文所要介绍的所有内容,非常感谢您的观看,如有疑问请于评论区留言或者私信我都可以🍀
-
相关阅读:
QT连接mysql打包
Linux禁用退格键的响铃
Pytorch使用c++调用模型
ASP.NET Core 6 从入门到企业级实战开发应用技术汇总
Toronto Research Chemicals农药检测丨甲硫威
基于FPGA的PID控制器开发与实现
三维模型体积计算及其注意事项
Redis 性能问题&优化方案
linux 硬盘坏道检测
微信小程序弹框显示自定义内容(1)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Fire_Cloud_1/article/details/127902741
