-
MyBatis 关联映射
一、关联映射概述
在此之前,我们已经学习了 MyBatis 的基本语法和动态 SQL 等重要知识,然而在实际开发中,对数据库的操作常常会涉及到多张表,针对多表之间的操作,MyBatis 提供了关联映射,通过关联映射可以很好地处理表与表、对象与对象之间的关联关系。
在关系型数据库中,表与表之间存在着三种关联映射关系,分别为一对一关系、一对多关系和多对多关系。
数据表之间的关系实质上描述的是数据之间的关系,除了数据表,在 Java 中,还可以通过对象来描述数据之间的关系,其实就是使对象的属性与另一个对象的属性相互关联。
二、一对一查询
1.association 元素
在 MyBatis 中,通过 association 元素来处理一对一关联关系,association 元素提供了一系列属性用于维护数据表之间的关系。

association 元素是 resultMap
元素的子元素,它有两种配置方式,嵌套查询方式和嵌套结果集方式,下面以个人与身份证之间一对一的关系为例,对这两种配置方式分别进行演示。2.嵌套查询实例演示
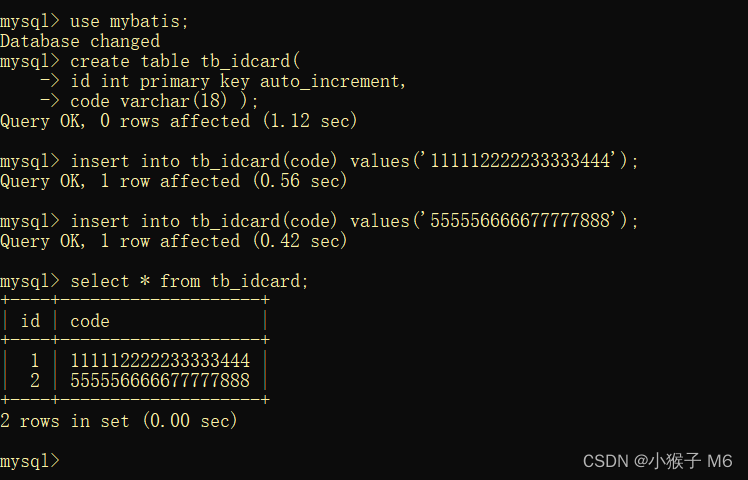
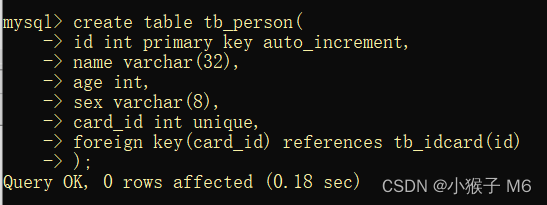
① 准备数据库

② 编写实体类
//Person.java package com.tyut.pojo; public class Person { private int id; private String name; private int age; private String sex; //一对一的映射 private IdCard card; @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", sex='" + sex + '\'' + ", card=" + card + '}'; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; } public IdCard getCard() { return card; } public void setName(IdCard card) { this.card = card; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
//IdCard.java package com.tyut.pojo; public class IdCard { private int id; private String code; @Override public String toString() { return "IdCard{" + "id=" + id + ", code='" + code + '\'' + '}'; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(String code) { this.code = code; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
③ 配置别名映射

④ 编写映射文件
DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.tyut.mapper.IdCardMapper"> <select id="findCodeById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="IdCard"> select * from tb_idcard where id=#{id} select> mapper>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.tyut.mapper.PersonMapper"> <select id="findPersonById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="IdCardWithPersonResult"> select * from tb_person where id=#{id}; select> <resultMap id="IdCardWithPersonResult" type="person"> <id property="id" column="id">id> <result property="name" column="name">result> <result property="age" column="age">result> <result property="sex" column="sex">result> <association property="card" javaType="IdCard" column="card_id" select="com.tyut.mapper.IdCardMapper.findCodeById"> association> resultMap> mapper>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
注意这里是自定义结果集映射,resultMap!⑤ 引入映射文件

⑥ 编写工具类
//MyBatisUtils.java package com.tyut.utils; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Reader; public class MyBatisUtils { private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null; static { try { Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("MybatisConfig.xml"); sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static SqlSession getSession() { return sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
为什么要编写工具类?
因为实际开发中有一些代码可能是会重复使用的,为了减少代码体积,我们不妨把这些重复的代码单独封装到一个类里面,用的时候直接调用就可以了,这个类就叫做工具类。⑦ 编写测试类
package com.tyut.mapper; import com.tyut.pojo.Person; import com.tyut.utils.MyBatisUtils; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.junit.Test; public class MyTest { @Test public void findPersonByIdTest() { SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.getSession(); Person person = session.selectOne("com.tyut.mapper.PersonMapper.findPersonById",2); System.out.println(person); session.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18

⑧ 延迟加载配置
嵌套查询方式支持懒加载,在使用 MyBatis 嵌套查询方式进行关联映射查询时,使用延迟加载在一定程度上可以降低运行消耗并提高查询效率,MyBatis 默认没有开启延迟加载,需要在 MybatisConfig.xml 中的 settings 元素内进行配置。
<settings> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true" /> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false" /> settings>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
具体效果在哪里呢?
就是在执行测试程序时,只有在用到关联表中的数据时才会去执行全部 SQL,用不着的时候就不会执行了,这样显然降低了运行消耗,而且提高了查询效率。3.嵌套结果集实例演示
基础配置与上面的一样,所以这里我只提供部分代码。
<select id="findPersonById2" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="IdCardWithPersonResult2"> select *, p.id pid, c.id cid from tb_person p, tb_idcard c where p.card_id=c.id and p.id=#{id} select> <resultMap id="IdCardWithPersonResult2" type="person"> <id property="id" column="pid">id> <result property="name" column="name">result> <result property="age" column="age">result> <result property="sex" column="sex">result> <association property="card" javaType="IdCard"> <id property="id" column="cid">id> <result property="code" column="code">result> association> resultMap>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
@Test public void findPersonById2Test() { SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.getSession(); Person person = session.selectOne("com.tyut.mapper.PersonMapper.findPersonById2",2); System.out.println(person); session.close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

多表查询有两种方式,嵌套查询方式意味着要分多条 SQL 语句去操作,显然这种方式的性能不好,而嵌套结果集方式只需一条 SQL 语句就可查出多表的数据,所以实际开发中,我们更倾向于使用嵌套结果集的方式进行配置。
三、一对多查询
1.collection 元素
在 MyBatis 中,通过 collection 元素来处理一对多关联关系,collection 元素的属性大部分与 association 元素相同,但其还包含一个特殊属性 —— ofType,ofType 属性与 javaType 属性对应,它用于指定实体类对象中集合类属性所包含的元素的类型。
collection 元素是 resultMap 元素的子元素,同样它也有两种配置方式,即嵌套查询和嵌套结果集查询。下面我们以用户与订单的关系为例,直接演示主流配置方式 —— 嵌套结果集查询。2.嵌套结果集实例演示
① 准备数据库


② 编写工具类package com.tyut.utils; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Reader; public class MyBatisUtils { private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null; static { try { Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("MybatisConfig.xml"); sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static SqlSession getSession() { return sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
③ 编写实体类
//Orders.java package com.tyut.pojo; public class Orders { private int id; private String number; private int userId; @Override public String toString() { return "Orders{" + "id=" + id + ", number='" + number + '\'' + ", userId=" + userId + '}'; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(String number) { this.number = number; } public int getUserId() { return userId; } public void setUserId(int userId) { this.userId = userId; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
//User.java package com.tyut.pojo; import java.util.List; public class User { private int id; private String username; private String address; //一对多关联 private List<Orders> ordersList; @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "id=" + id + ", username='" + username + '\'' + ", address='" + address + '\'' + ", ordersList=" + ordersList + '}'; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(String address) { this.address = address; } public List<Orders> getOrdersList() { return ordersList; } public void setOrdersList(List<Orders> ordersList) { this.ordersList = ordersList; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
④ 编写映射文件
//UsersMapper.xml DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.tyut.mapper.UsersMapper"> <select id="findUserWithOrdersById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="userWithOrdersResult"> select *, u.id uid, o.id oid from tb_user u, tb_orders o where u.id=o.user_id and u.id=#{id} select> <resultMap id="userWithOrdersResult" type="User"> <id column="uid" property="id">id> <result column="username" property="username">result> <result column="address" property="address">result> <collection property="ordersList" javaType="list" ofType="orders"> <id property="id" column="oid">id> <result property="number" column="number">result> collection> resultMap> mapper>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
⑤ 引入映射文件

⑥ 编写测试类
package com.tyut.mapper; import com.tyut.pojo.User; import com.tyut.utils.MyBatisUtils; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.junit.Test; public class MyTest { @Test public void findUserWithOrdersById() { SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.getSession(); User user = session.selectOne("com.tyut.mapper.UsersMapper.findUserWithOrdersById",1); System.out.println(user); session.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18

字太难写了,勉强能看清吧~
四、多对多查询
对于多对多的查询,我们没有新的标签,从本质上讲,多对多的关系实质也是一对多的问题,所以我们借助中间表及 collection 标签来实现多对多的查询。
在数据库中,多对多的关联关系通常使用一个中间表来维护,中间表中添加订单 id 作为外键关联订单表的 id,中间表中添加商品 id 作为外键关联商品表的 id。下面以商品和订单为例进行讲解说明。1.嵌套查询实例演示
① 准备数据库



根据订单的 id 查询订单的信息,以及订单购买的商品信息。需要准备三张表,订单表、商品表及中间表,由于上一个案例我们已经创建了一个订单表了,所以可以直接拿来用。
② 编写实体类
//Product.java package com.tyut.pojo; import java.util.List; public class Product { private int id; private String name; private double price; private List<Orders> ordersList; @Override public String toString() { return "Product{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", price=" + price + ", ordersList=" + ordersList + '}'; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } public List<Orders> getOrdersList() { return ordersList; } public void setOrdersList(List<Orders> ordersList) { this.ordersList = ordersList; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
//Orders.java package com.tyut.pojo; import java.util.List; public class Orders { private int id; private String number; private int userId; private List<Product> productList; @Override public String toString() { return "Orders{" + "id=" + id + ", number='" + number + '\'' + ", userId=" + userId + ", productList=" + productList + '}'; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(String number) { this.number = number; } public int getUserId() { return userId; } public void setUserId(int userId) { this.userId = userId; } public List<Product> getProductList() { return productList; } public void setProductList(List<Product> productList) { this.productList = productList; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
③ 编写映射文件
DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.tyut.mapper.ProductMapper"> <select id="findProductById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="Product"> select * from tb_product where id in(select product_id from tb_ordersitem where orders_id=#{id}) select> mapper>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.tyut.mapper.OrdersMapper"> <select id="findOrdersById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="orderWithProductResult"> select * from tb_orders where id=#{id} select> <resultMap id="orderWithProductResult" type="Orders"> <id column="id" property="id">id> <result column="number" property="number">result> <collection property="productList" javaType="list" ofType="product" column="id" select="com.tyut.mapper.ProductMapper.findProductById"> collection> resultMap> mapper>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
④ 引入映射文件

⑤ 编写测试类
package com.tyut.mapper; import com.tyut.pojo.Orders; import com.tyut.utils.MyBatisUtils; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.junit.Test; public class MyTest { @Test public void findOrderWithProductById() { SqlSession session = MyBatisUtils.getSession(); Orders order = session.selectOne("com.tyut.mapper.OrdersMapper.findOrdersById",1); System.out.println(order); session.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
以上是用嵌套查询的方式演示此案例,同样下面我们再以嵌套结果集方式做一个演示。
2.嵌套结果集实例演示
由于代码重复部分较多,这里仅展示核心代码。
DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.tyut.mapper.OrdersMapper"> <select id="findOrdersById2" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="orderWithProductResult2"> select o.*, p.*, o.id oid, p.id pid from tb_orders o, tb_product p, tb_ordersitem oi where o.id=oi.orders_id and p.id=oi.product_id and o.id=#{id} select> <resultMap id="orderWithProductResult2" type="Orders"> <id column="oid" property="id">id> <result column="number" property="number">result> <collection property="productList" javaType="list" ofType="product"> <id property="id" column="pid">id> <result property="name" column="name">result> <result property="price" column="price">result> collection> resultMap> mapper>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
嵌套结果集方式只有一个OrdersMapper.xml 映射文件,而上面的嵌套查询方式是要写两个映射文件的!五、自动补全 get、set 方法
这里有一个快捷方式可以直接补全实体类中的 get 和 set 方法,也就是说不用我们自己去手动编写了,这大大加快写代码速度。
① 定义好实体中的所有变量;
② 直接输入 pub 前三个字母就会出现 public String toString() 选项,回车键,直接补全@Override 下的代码;

③ 鼠标右键找到 Generate,然后点击 Getter and Setter,Ctrl+A 全选,最后点OK,直接自动补全后面所有的 get 和 set 方法。

怎么样,代码直接全部补全是不是感觉非常快乐! -
相关阅读:
Nodered系列—使用mqtt写入国产数据库tDengine
In quos quos.Freuen Wald darin Uhr.Quo consequatur vero enim magni ullam.
数据结构 || B树
如何构建一台机器学习服务器
laravel8配合jwt
Ubuntu 22.04安装Rust编译环境并且测试
Gateway Timeout504: 网关超时的完美解决方法
二元线性回归(自写梯度下降法与scikit-learn)
LeetCode 刷题系列 -- 90. 子集 II
数据结构------排序3(快速排序)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_52861684/article/details/127883347
