-
unix网络编程(四)epoll反应堆
原理
【epoll模型原来的流程】:
epoll_create(); // 创建监听红黑树
epoll_ctl(); // 向书上添加监听fd
epoll_wait(); // 监听
有监听fd事件发送—>返回监听满足数组—>判断返回数组元素—>
lfd满足accept—>返回cfd---->read()读数据—>write()给客户端回应。【epoll反应堆模型的流程】:
epoll_create(); // 创建监听红黑树
epoll_ctl(); // 向书上添加监听fd
epoll_wait(); // 监听
有客户端连接上来—>lfd调用acceptconn()—>将cfd挂载到红黑树上监听其读事件—>
epoll_wait()返回cfd—>cfd回调recvdata()—>将cfd摘下来监听写事件—>
epoll_wait()返回cfd—>cfd回调senddata()—>将cfd摘下来监听读事件—>…—>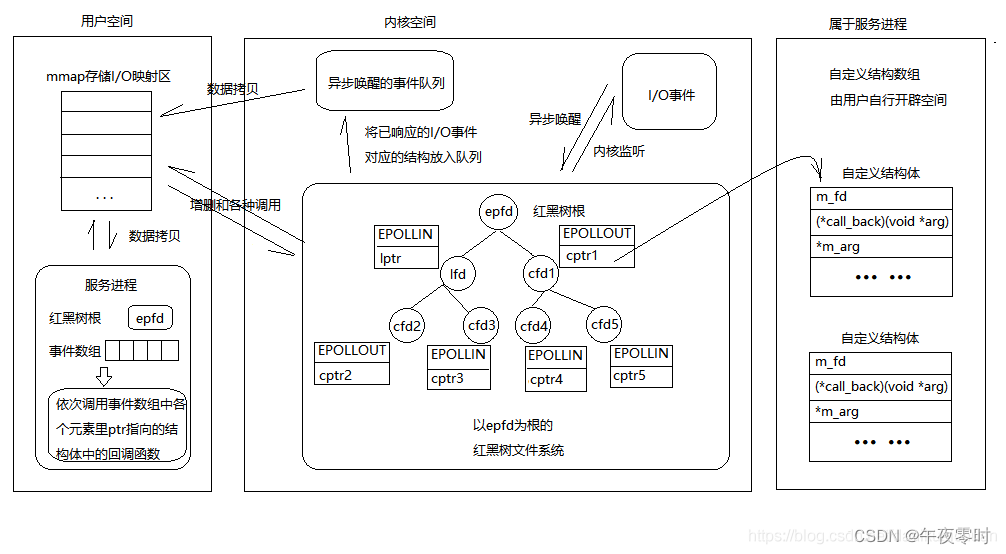
参考青萍之末的博客,其中有具体的epoll和epoll反应堆模型的分析。
参考B站学习视频,Linux系统编程和linux网络编程教程。代码
demo
实现一个epoll反应堆模型的反射服务器。
#include#include #include #include #include #include "pub.h" #define MAXSIZE 1024 #define MAXOPEN 1024 // 自定义事件驱动结构体,必包括fd、void *、call_back,按情况添加其他的数据 typedef struct _xevent { int fd; uint32_t events; int epfd; void *arg; void (*call_back)(void *arg1, void *arg2); // 第一个为xevent的项,第二个为xevent数组的地址 char buf[MAXSIZE]; int buflen; } xevent; void write_data(void *arg1, void *arg2); void read_data(void *arg1, void *arg2); // 注册事件 void eventadd(int epfd, int fd, uint32_t events, xevent *xev, void (*call_back)(void *, void *)) { // 初始化xevent xev->fd = fd; xev->events = events; xev->epfd = epfd; xev->call_back = call_back; // 初始化epoll_event , 上树监听 struct epoll_event ev; ev.events = events; ev.data.ptr = xev; epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &ev); } void eventmod(int epfd, int fd, uint32_t events, xevent *xev, void(*call_back)(void *, void *)) { // 修改xevent结构体 xev->fd = fd; xev->events = events; xev->epfd = epfd; xev->call_back = call_back; // 修改epoll_event struct epoll_event ev; ev.events= events; ev.data.ptr = xev; epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, fd, &ev); } // 删除事件 void eventdel(int epfd, int fd, xevent *xev) { // 修改xevent结构体 xev->fd = 0; xev->events = 0; xev->epfd = 0; xev->call_back = NULL; // 删除epoll_event epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, fd, NULL); } // 修改事件 /* 对本程序而言,功能为接受数据并将接受的数据发送回去,因此可以 * 在接收数据时将fd改为监听可写,在发送数据后改为监听可读。 * 通常在需要监听可写时,注册fd的可写事件,写完即注销fd的可写事件, * 需要来回上树下树十分浪费时间,本程序是取巧的行为 */ // 读数据 void read_data(void *arg1, void *arg2) { xevent *xev = arg1; xevent *my_xevents = arg2; xev->buflen = read(xev->fd, xev->buf, sizeof(xev->buf)); if(xev->buflen > 0) { // 读到数据,设置可写监听 eventmod(xev->epfd, xev->fd, EPOLLOUT, xev, write_data); } else if(0 == xev->buflen) { // 客户端关闭,关闭fd、删除fd监听事件 printf("client close\n"); close(xev->fd); eventdel(xev->epfd, xev->fd, xev); } else { perror("read"); exit(-1); } } //写数据 void write_data(void *arg1, void *arg2) { xevent *xev = arg1; xevent *my_xevents = arg2; // 写数据,并设置可读监听 write(xev->fd, xev->buf, xev->buflen); xev->buflen = 0; eventmod(xev->epfd, xev->fd, EPOLLIN, xev, read_data); } // 接受新连接 void init_accept(void *arg1, void *arg2) { xevent *xev = arg1; xevent *my_xevents = arg2; // 从my_xevents数组中找出一个未使用的xevent,accept新连接并上树监听 for(int i = 0; i < MAXOPEN; i++) { if(my_xevents[i].fd == 0) { int cfd = Accept_with_print(xev->fd); eventadd(xev->epfd, cfd, EPOLLIN, &my_xevents[i], read_data); break; } } } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if(argc < 3) { printf("usage: ./%s ip_address port_number\n", basename(argv[0])); return -1; } char *ip = argv[1]; int port = atoi(argv[2]); int lfd = socketBind(ip, port); // 创建内核事件表的描述符 int epfd = epoll_create(MAXOPEN); if(-1 == epfd) { perror("epoll_create"); return -1; } // 创建xevent数组并初始化 xevent my_xevents[MAXOPEN]; memset(my_xevents, 0, sizeof(my_xevents)); // 创建接受内核事件通知的epoll_event数组 struct epoll_event events[MAXOPEN]; // lfd注册监听,使用xevent数组的最后一个 eventadd(epfd, lfd, EPOLLIN, &my_xevents[MAXOPEN-1], init_accept); while(1) { int nready = epoll_wait(epfd, events, MAXOPEN, -1); if(nready < 0) { perror("epoll_wait"); break; } for(int i = 0; i<nready; i++) { xevent *xev = events[i].data.ptr; if(events[i].events == xev->events) { xev->call_back(xev, my_xevents); } } } } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
-
相关阅读:
设计模式——工厂模式
【Spring注解必知必会】深度解析@Configuration注解
静态HTML网页设计作品——仿京东-海贼王(1页) HTML+CSS+JavaScript 学生DW网页设计作业成品 wweb前端期末大作业
linux的dirty page回写磁盘过程中是否允许并发写入更新page?
华为云项目部署
idea 启动报错 Command line is too long
Spring之@Qualifier注解简介及示例
【英杰送书第三期】Spring 解决依赖版本不一致报错 | 文末送书
Flink SQL -- 反压
安全测试前置实践1-白盒&黑盒扫描
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_55796594/article/details/127960881
