-
【手写一个SpringBoot简易版框架】
提示:不多废话,直接上代码,看代码,看演示效果
文章目录
- 一、项目框架
- 二、创建simple-springboot父模块
- 三、创建springboot-module子模块
- 1.修改pom.xml
- 2.创建META-INF/services/com.example.springboot.AutoConfiguration
- 3.创建AutoConfiguration
- 4.创建WebServerAutoConfiguration
- 5.创建AutoConfigurationImportSelector
- 6.创建ExampleCondition
- 7.创建ExampleConditionalOnClass
- 8.创建ExampleSpringApplication
- 9.创建ExampleSpringBootApplication
- 10.创建JettyWebServer
- 11.创建TomcatWebServer
- 12.创建WebServer
- 四、创建user-module子模块
- 五、测试效果
- 六、总结
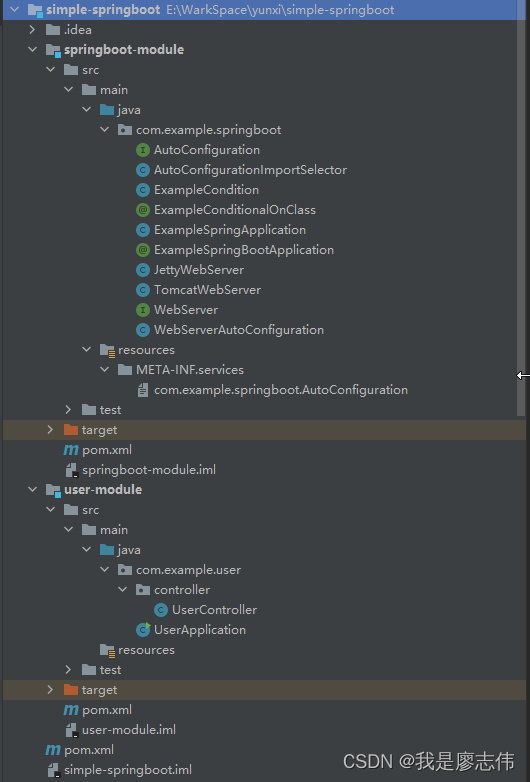
一、项目框架
如下图(示例):
二、创建simple-springboot父模块
1.修改pom.xml
代码如下(示例):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>org.example</groupId> <artifactId>simple-springboot</artifactId> <packaging>pom</packaging> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <modules> <module>springboot-module</module> <module>user-module</module> </modules> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target> </properties> </project>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
三、创建springboot-module子模块
1.修改pom.xml
代码如下(示例):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <parent> <artifactId>simple-springboot</artifactId> <groupId>org.example</groupId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </parent> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <artifactId>springboot-module</artifactId> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId> <version>5.3.18</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.3.18</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> <version>5.3.18</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId> <version>5.3.18</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.3.18</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>4.0.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId> <artifactId>tomcat-embed-core</artifactId> <version>9.0.60</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.eclipse.jetty</groupId> <artifactId>jetty-server</artifactId> <version>9.4.48.v20220622</version> <optional>true</optional><!--<optional>true</optional>表示不传递给调用服务,也就是user-module服务--> <!--由于springboot-module是要给其他服务调用的,所以必须支持多种web容器服务(tomcat/jetty),调用端只能使用其中一种,否则就会报错--> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
2.创建META-INF/services/com.example.springboot.AutoConfiguration
代码如下(示例):
com.example.springboot.WebServerAutoConfiguration- 1
3.创建AutoConfiguration
代码如下(示例):
package com.example.springboot; /** * @Author: zhiwei Liao * @Date: 2022/11/14 23:08 * @Description: 自动装配接口 */ public interface AutoConfiguration { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
4.创建WebServerAutoConfiguration
代码如下(示例):
package com.example.springboot; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; /** * web服务配置实现类 由于ExampleSpringBootApplication扫描的包是(com.example.user.*),WebServerAutoConfiguration配置类无法被扫描到,所以需要@Import注解,将当前类导入进来让它被扫描到 */ @Configuration public class WebServerAutoConfiguration implements AutoConfiguration{ @Bean @ExampleConditionalOnClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat") public TomcatWebServer tomcatWebServer(){ return new TomcatWebServer(); } @Bean @ExampleConditionalOnClass("org.eclipse.jetty.server.Server") public JettyWebServer jettyWebServer(){ return new JettyWebServer(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
5.创建AutoConfigurationImportSelector
代码如下(示例):
package com.example.springboot; import org.springframework.context.annotation.DeferredImportSelector; import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.ServiceLoader; /** * 自定义批量导入 */ public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector { @Override public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) { //String[]返回的是 SpringBoot默认的+第三方的jar 自动配置类的名字 // jars --》META-inf/spring.factories的value是springboot提供的各种配置类的名字 EnableAutoConfiguration 是springboot提供的各种配置类的名字 //例如需要加载springboot项目里面配置类,META-INF/services目录下创建spring.factories文件将配置类的路径名称写上去就可以了 ServiceLoader<AutoConfiguration> serviceLoader = ServiceLoader.load(AutoConfiguration.class);//获取到自动装配接口的实现类 List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (AutoConfiguration autoConfiguration : serviceLoader) { list.add(autoConfiguration.getClass().getName());//获取类名 } return list.toArray(new String[0]); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
6.创建ExampleCondition
代码如下(示例):
package com.example.springboot; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext; import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata; import java.util.Map; /** * 条件判断 */ public class ExampleCondition implements Condition { @Override public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { // 条件 判断有ExampleConditionalOnClass注解修饰的值(org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat/org.eclipse.jetty.server.Server的类)才会加载 Map<String, Object> annotationAttributes = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(ExampleConditionalOnClass.class.getName()); String className = (String) annotationAttributes.get("value"); try { context.getClassLoader().loadClass(className); return true; } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { return false; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
7.创建ExampleConditionalOnClass
代码如下(示例):
package com.example.springboot; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; /** * 自定义注解:条件判断注解 */ @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Conditional(ExampleCondition.class) public @interface ExampleConditionalOnClass { String value(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
8.创建ExampleSpringApplication
代码如下(示例):
package com.example.springboot; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext; import org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext; import java.util.Map; /** * 自定义启动类 */ public class ExampleSpringApplication { public static void run(Class clazz){ // 创建一个Spring容器 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext支持springmvc AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(); applicationContext.register(clazz);//注册一个类进来 applicationContext.refresh(); // 启动web服务器(tomcat、jetty) WebServer webServer = getWebServer(applicationContext); webServer.start(applicationContext); } /** * 获取web服务:tomcat或者jetter * @param applicationContext * @return */ private static WebServer getWebServer(WebApplicationContext applicationContext) { Map<String, WebServer> beansOfType = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(WebServer.class); //二个都没有定义 @ExampleSpringBootApplication修饰的类中没有定义TomcatWebServer或者JettyWebServer if (beansOfType.size() == 0) { throw new NullPointerException(); } //定义了二个 @ExampleSpringBootApplication修饰的类中没有定义TomcatWebServer和JettyWebServer if (beansOfType.size() > 1) { throw new IllegalStateException(); } //拿第一个 @ExampleSpringBootApplication修饰的类中没有定义TomcatWebServer或者JettyWebServer其中一个 return beansOfType.values().stream().findFirst().get(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
9.创建ExampleSpringBootApplication
代码如下(示例):
package com.example.springboot; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import; import java.lang.annotation.*; /** * 自定义注解:启动类注解 */ @Target(ElementType.TYPE)//作用于类上面 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited//@Inherited是一个标识,用来修饰注解。作用:如果一个类用上了@Inherited修饰的注解,那么其子类也会继承这个注解 @Configuration @ComponentScan//找到被修饰的类(UserApplication),扫描当前包下的所有类(com.example.user.*) //@Import(WebServerAutoConfiguration.class)//直接导入类,不够优雅,而且如果有很多个配置类,写在这里也不好,@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)是优化后的自动配置类 @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)//作为springboot框架提供给调用方使用,调用方可能会有很多很多的配置类,不在调用方扫描的包下(不在com.example.user.*下),例如:ElasticsearchRestClientAutoCofiguration、JacksonoAutoConfiguration等等,所以需要一个自动批量导入的类 public @interface ExampleSpringBootApplication { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
10.创建JettyWebServer
代码如下(示例):
package com.example.springboot; import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext; /** * web服务:启动jetty相关代码 */ public class JettyWebServer implements WebServer{ @Override public void start(WebApplicationContext applicationContext) { System.out.println("启动Jetty"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
11.创建TomcatWebServer
代码如下(示例):
package com.example.springboot; import org.apache.catalina.*; import org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector; import org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext; import org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine; import org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHost; import org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat; import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext; import org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet; /** * web服务:启动tomcat相关代码 */ public class TomcatWebServer implements WebServer{ @Override public void start(WebApplicationContext applicationContext) { System.out.println("============启动Tomcat============="); Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat(); Server server = tomcat.getServer(); Service service = server.findService("Tomcat"); Connector connector = new Connector(); connector.setPort(9081); Engine engine = new StandardEngine(); engine.setDefaultHost("localhost"); Host host = new StandardHost(); host.setName("localhost"); String contextPath = ""; Context context = new StandardContext(); context.setPath(contextPath); context.addLifecycleListener(new Tomcat.FixContextListener()); host.addChild(context); engine.addChild(host); service.setContainer(engine); service.addConnector(connector); tomcat.addServlet(contextPath, "dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(applicationContext)); context.addServletMappingDecoded("/*", "dispatcher"); try { tomcat.start(); } catch (LifecycleException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
12.创建WebServer
代码如下(示例):
package com.example.springboot; import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext; /** * web服务接口 */ public interface WebServer { public void start(WebApplicationContext applicationContext); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
四、创建user-module子模块
1.修改pom.xml
代码如下(示例):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <parent> <artifactId>simple-springboot</artifactId> <groupId>org.example</groupId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </parent> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <artifactId>user-module</artifactId> <properties> <!-- 文件拷贝时的编码 --> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <!-- 编译时的编码 --> <maven.compiler.encoding>UTF-8</maven.compiler.encoding> <maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.example</groupId> <artifactId>springboot-module</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <!-- 排除tomcat依赖--> <!-- <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId> <artifactId>tomcat-embed-core</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions>--> </dependency> <!-- 引入jetty依赖--> <!-- <dependency> <groupId>org.eclipse.jetty</groupId> <artifactId>jetty-server</artifactId> <version>9.4.48.v20220622</version> </dependency>--> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId> <artifactId>exec-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>1.6.0</version> <executions> <execution> <goals> <goal>java</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> <configuration> <classpathScope>test</classpathScope> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
2.创建UserApplication
代码如下(示例):
package com.example.user; import com.example.springboot.ExampleSpringApplication; import com.example.springboot.ExampleSpringBootApplication; import com.example.springboot.JettyWebServer; import com.example.springboot.TomcatWebServer; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; @ExampleSpringBootApplication public class UserApplication { /** * TomcatWebServer 和 JettyWebServer 只能定义其中一个 弊端:比较麻烦,需要有一个自动的配置类识别我要用什么类型的web服务容器 解决方案:WebServerAutoConfiguration * @return */ // @Bean // public TomcatWebServer tomcatWebServer(){ // return new TomcatWebServer(); // } /** * TomcatWebServer 和 JettyWebServer 只能定义其中一个 弊端:比较麻烦,需要有一个自动的配置类识别我要用什么类型的web服务容器 解决方案:WebServerAutoConfiguration * @return */ // @Bean // public JettyWebServer jettyWebServer(){ // return new JettyWebServer(); // } public static void main(String[] args) { ExampleSpringApplication.run(UserApplication.class); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
3.创建UserController
代码如下(示例):
package com.example.user.controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class UserController { @GetMapping("/test") public String test(){ return "test"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
五、测试效果
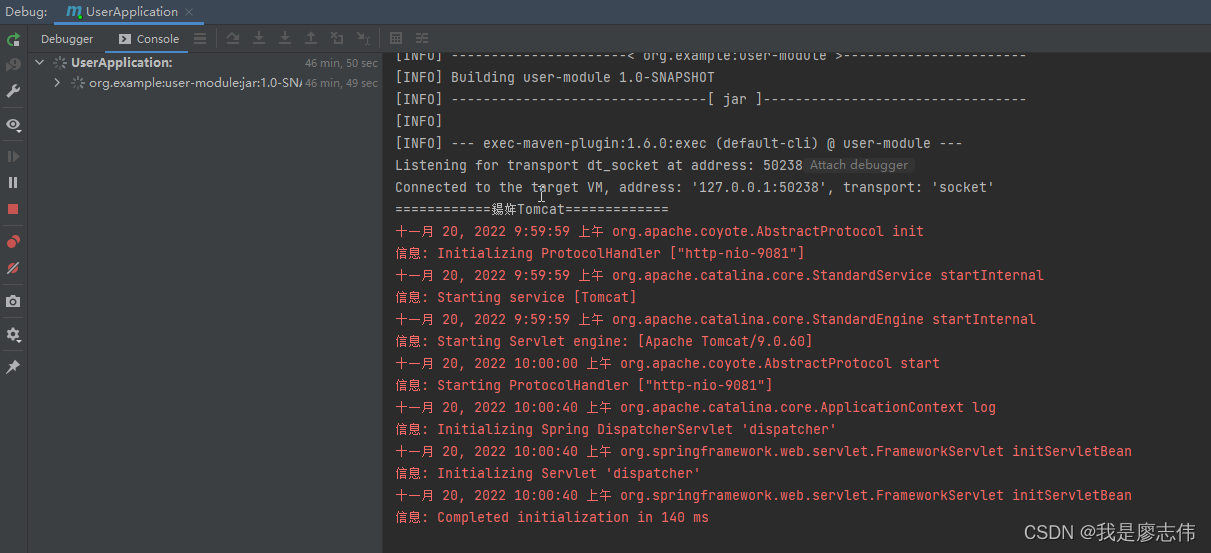
1.启动项目
如下图(示例):
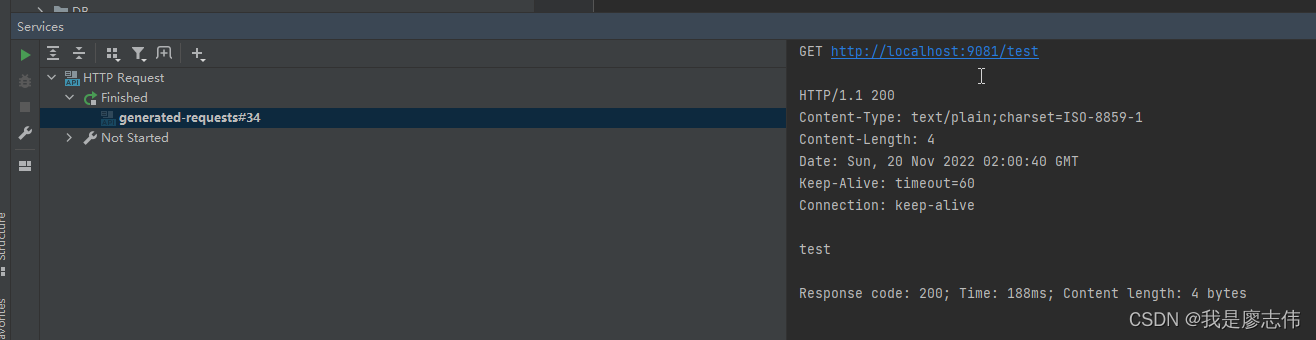
2.调用接口
如下图(示例):
六、总结
以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文仅仅简单的用代码介绍了springboot框架简易版的搭建,如需查看项目源码,请移步码云代码仓库:https://gitee.com/java_wxid/java_wxid/tree/master/demo/simple-springboot
-
相关阅读:
Pyhton 装饰器的作用
可视化大屏的应用(13):在能源环保领域的五大用武之地
DevExpress DxUpload实现大文件上传
最长公共子串LCS
第一章 数据可视化和matplotlib
如何知道Android SDK的安装路径
CMake语法结构说明
昨晚直播小鱼搞了个开源库之FishProtocol,目前已经两颗星
DC-2靶场渗透测试实验整理
Python-正则表达式使用
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/java_wxid/article/details/127946180
