-
【序列比对】Needleman-Wunsch(全局)和Smith-Waterman(局部)算法py实现(多条回溯路径,三叉树思路,超详细注释)
Needleman-Wunsch和Smith-Waterman算法py实现(多条回溯路径)
话不多说,直接上结果图,多条回溯路径。

原理


代码详解(以NW为例)
导入包以及参数设置
import numpy as np sequence_1 = "AACGTACTCAAGTCT" sequence_2 = "TCGTACTCTAACGAT" match = 9 mismatch = -6 gap = -2- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
创建得分矩阵
- 创建得分矩阵,行数为第一条序列长度加一,列数为第二条序列长度加二
- 创建是否匹配的矩阵,这个矩阵的长宽就分别是两条序列的长度了。如果匹配了,对应的格子就是匹配的得分,反之就是不匹配的得分
- 动态规划的思想算每个格子的得分,每个格子需要考虑其左、上、左上的值,也可以说是考虑序列一、序列二引入空缺或直接匹配的最大值
# 创建得分矩阵,行数为第一条序列长度加一,列数为第二条序列长度加二 Score = np.zeros((len(sequence_1) + 1, len(sequence_2) + 1)) # 创建是否匹配的矩阵,这个矩阵的长宽就分别是两条序列的长度了。如果匹配了,对应的格子就是匹配的得分,反之就是不匹配的得分 Match_or_not = np.zeros((len(sequence_1), len(sequence_2))) for i in range(len(sequence_1)): for j in range(len(sequence_2)): if sequence_1[i] == sequence_2[j]: Match_or_not[i][j] = match else: Match_or_not[i][j] = mismatch # 填得分矩阵 # 第一步:初始化第一行和第一列 for i in range(len(sequence_1) + 1): Score[i][0] = i * gap for j in range(len(sequence_2) + 1): Score[0][j] = j * gap # 第二步:动态规划的思想算每个格子的得分,每个格子需要考虑其左、上、左上的值,也可以说是考虑序列一、序列二引入空缺或直接匹配的最大值 for i in range(1, len(sequence_1) + 1): for j in range(1, len(sequence_2) + 1): Score[i][j] = max(Score[i - 1][j - 1] + Match_or_not[i - 1][j - 1], Score[i - 1][j] + gap, Score[i][j - 1] + gap)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
看看得分矩阵长啥样吧


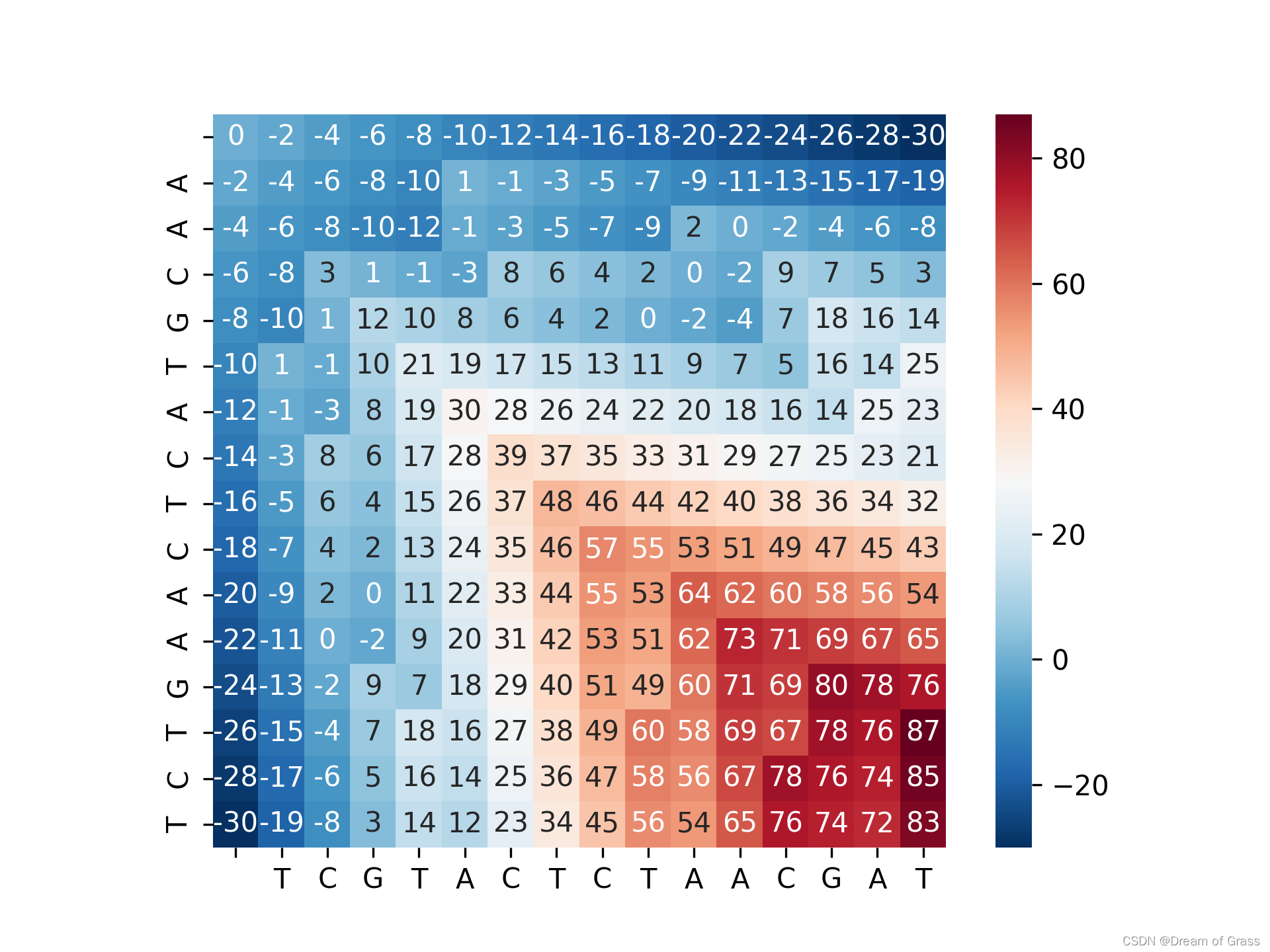
回溯
我们需要考虑的是可能会有多条回溯路径。全局比对的回溯是从右下角开始,左上角结束,其中可能会有分叉点。我们可以把右下角看成是一个树的根,矩阵中的每个值看成是一个节点。每个节点都可能会有三个子节点:左,上,对角线。分别对应了回溯的方向。而整个回溯的过程也就是遍历这颗三叉树的过程,严谨的说是从根节点遍历每个叶子节点的过程。
# 开始回溯 ''' 我们需要考虑的是可能会有多条回溯路径。 全局比对的回溯是从右下角开始,左上角结束,其中可能会有分叉点。 我们可以把右下角看成是一个树的根,矩阵中的每个值看成是一个节点。 每个节点都可能会有三个子节点:左,上,对角线。分别对应了回溯的方向。 而整个回溯的过程也就是遍历这颗三叉树的过程,严谨的说是从根节点遍历每个叶子节点的过程。 ''' class Node: # 用类来建立三叉树节点,属性包括了行、列、得分、左子树、上子树、对角线子树 def __init__(self, row=None, col=None, score=None): self.row = row self.col = col self.score = score self.left = None self.up = None self.diag = None def isLeaf(self): # 判断是否是叶子节点 return self.left is None and self.up is None and self.diag is None # 递归的函数查找从根节点到每个叶节点的路径 # 回溯路径的个数、回溯路径中的行号和列号 traceback_pathway_number = 0 traceback_pathway_row = [[]] traceback_pathway_col = [[]] def SaveRootToLeafPaths(Node, path_row, path_col): # 如果没有子树了 if Node is None: return # 包含当前节点的路径 path_row.append(Node.row) path_col.append(Node.col) global traceback_pathway_number global traceback_pathway_row global traceback_pathway_col # 如果找到叶节点,保存路径 if isLeaf(Node): if traceback_pathway_number == 0: traceback_pathway_row[traceback_pathway_number] = list(path_row) traceback_pathway_col[traceback_pathway_number] = list(path_col) else: traceback_pathway_row += [list(path_row)] traceback_pathway_col += [list(path_col)] traceback_pathway_number += 1 # 递归左、上、对角子树 SaveRootToLeafPaths(Node.left, path_row, path_col) SaveRootToLeafPaths(Node.up, path_row, path_col) SaveRootToLeafPaths(Node.diag, path_row, path_col) # 回溯,出栈 path_row.pop() path_col.pop() # 建立三叉树,为 Score 矩阵里所有值都找到它的左、上、对角子树,用一个二位列表来存储节点 NodeTree = [[Node() for _ in range(len(sequence_2) + 1)] for _ in range(len(sequence_1) + 1)] # 先把节点们的行号列号和得分记录下来 for i in range(len(sequence_1) + 1): for j in range(len(sequence_2) + 1): NodeTree[i][j].row = i NodeTree[i][j].col = j NodeTree[i][j].score = Score[i][j] # 设置第一列和第一行的节点的上子树和左子树(其实也能在下面这个大循环里设置,但是这样可读性更高) for i in range(1, len(sequence_1) + 1): NodeTree[i][0].up = NodeTree[i - 1][0] for j in range(1, len(sequence_2) + 1): NodeTree[0][j].left = NodeTree[0][j - 1] # 设置剩下的节点 for i in range(1, len(sequence_1) + 1): for j in range(1, len(sequence_2) + 1): if (Score[i][j] == Score[i - 1][j - 1] + Match_or_not[i - 1][j - 1]): NodeTree[i][j].diag = NodeTree[i - 1][j - 1] if (Score[i][j] == Score[i - 1][j] + gap): NodeTree[i][j].up = NodeTree[i - 1][j] if (Score[i][j] == Score[i][j - 1] + gap): NodeTree[i][j].left = NodeTree[i][j - 1] # 遍历树并保存路径 SaveRootToLeafPaths(NodeTree[len(sequence_1)][len(sequence_2)], [], []) # 改成numpy的ndarray类型,更加方便! traceback_pathway_row = np.array(traceback_pathway_row) traceback_pathway_col = np.array(traceback_pathway_col) # 记录一下回溯时走不走左边或上边,如果走就记为1,不走就记为0 Go_left = traceback_pathway_col[:, range(traceback_pathway_col.shape[1] - 1)] - traceback_pathway_col[:, range(1, traceback_pathway_col.shape[ 1])] Go_up = traceback_pathway_row[:, range(traceback_pathway_row.shape[1] - 1)] - traceback_pathway_row[:, range(1, traceback_pathway_row.shape[1])] # 用列表来存储序列一和序列二比对后的结果 seq1_align_set = [] seq2_align_set = [] print("总共有{}个比对结果".format(traceback_pathway_number)) for tpn in range(traceback_pathway_number): ''' 下面其实就是经典的nw回溯的代码了,这部分的原理可以参考nw算法回溯的伪代码。 唯一不同的就是我们是多条回溯路径,所以有多少条路经就得循环多少次。 值得一提的是,回溯过去的序列是逆序的, 在python中字符串逆置十分方便,只需要合理利用切片,如:str[::-1]即可。 ''' seq1_align = '' seq2_align = '' i = len(sequence_1) j = len(sequence_2) k = 0 while i > 0 or j > 0: if i > 0 and j > 0 and Go_left[tpn][k] and Go_up[tpn][k]: seq1_align += sequence_1[i - 1] seq2_align += sequence_2[j - 1] i -= 1 j -= 1 elif i > 0 and not (Go_left[tpn][k]) and Go_up[tpn][k]: seq1_align += sequence_1[i - 1] seq2_align += '-' i -= 1 elif j > 0 and Go_left[tpn][k] and not (Go_up[tpn][k]): seq1_align += '-' seq2_align += sequence_2[j - 1] j -= 1 k += 1 seq1_align_set += [seq1_align[::-1]] seq2_align_set += [seq2_align[::-1]] print("下面是第{}个".format(tpn + 1)) print(seq1_align[::-1]) print(seq2_align[::-1]) print(' ')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
输出
总共有15个比对结果
下面是第1个
AA-CGTACTC-AA-G-TCT
–TCGTACTCTAACGAT–下面是第2个
A-ACGTACTC-AA-G-TCT
-T-CGTACTCTAACGAT–下面是第3个
-AACGTACTC-AA-G-TCT
T–CGTACTCTAACGAT–下面是第4个
AA-CGTACTC-AAGTC–T
–TCGTACTCTAA–CGAT下面是第5个
A-ACGTACTC-AAGTC–T
-T-CGTACTCTAA–CGAT下面是第6个
-AACGTACTC-AAGTC–T
T–CGTACTCTAA–CGAT下面是第7个
AA-CGTACTC-AA-GTC-T
–TCGTACTCTAACG–AT下面是第8个
A-ACGTACTC-AA-GTC-T
-T-CGTACTCTAACG–AT下面是第9个
-AACGTACTC-AA-GTC-T
T–CGTACTCTAACG–AT下面是第10个
AA-CGTACTC-AA-GT-CT
–TCGTACTCTAACG-A-T下面是第11个
A-ACGTACTC-AA-GT-CT
-T-CGTACTCTAACG-A-T下面是第12个
-AACGTACTC-AA-GT-CT
T–CGTACTCTAACG-A-T下面是第13个
AA-CGTACTC-AA-G-TCT
–TCGTACTCTAACGA–T下面是第14个
A-ACGTACTC-AA-G-TCT
-T-CGTACTCTAACGA–T下面是第15个
-AACGTACTC-AA-G-TCT
T–CGTACTCTAACGA–T画一下回溯的路径


可视化代码
''' 下面就是得分矩阵的热图以及回溯路径(格子)画出来了 ''' import pandas as pd import seaborn as sns from matplotlib import pyplot as plt Score = pd.DataFrame(Score) row_name = list(sequence_1) row_name.insert(0, ' ') col_name = list(sequence_2) col_name.insert(0, ' ') Score.index = row_name Score.columns = col_name traceback_way_mat = np.ones([len(sequence_1) + 1, len(sequence_2) + 1]) for i in range(traceback_pathway_row.shape[0]): traceback_way_mat[traceback_pathway_row[i][:], traceback_pathway_col[i][:]] = 0 ax1 = sns.heatmap(Score, linecolor='white', linewidth=0, square=True, cmap="RdBu_r", annot=True) plt.savefig('nw_Heatmap with annotation.png',dpi=300) plt.show() ax2 = sns.heatmap(Score, linecolor='white', linewidth=0, square=True, cmap="RdBu_r") plt.savefig('nw_Heatmap.png',dpi=300) plt.show() ax3 = sns.heatmap(Score, linecolor='white', linewidth=0, square=True, cmap="RdBu_r", mask=traceback_way_mat) plt.savefig('nw_Heatmap_traceback',dpi=300) plt.show() #%% # params={'font.family':'serif', # 'font.serif':'Times New Roman', # 'font.style':'normal',#'italic' # 'font.weight':'normal', #or 'blod' # 'font.size':12,#or large,small # 'figure.figsize':(6,6) # } plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (6, 6) # plt.rcParams.update(params) for j in range(traceback_pathway_col.shape[0]): fig = plt.figure() ax = plt.axes() plt.grid(zorder=0, linestyle='-.') for i in range(traceback_pathway_col.shape[1]-1): xs = traceback_pathway_col[j][i] ys = traceback_pathway_row[j][i] xe = traceback_pathway_col[j][i+1] ye = traceback_pathway_row[j][i+1] ax.arrow(xs, ys, xe-xs, ye-ys, length_includes_head=True,head_width=0.3, fc='crimson', ec='hotpink',zorder=10) ax.set_xlim(-0.5, len(col_name)-0.5) ax.set_ylim(-0.5, len(col_name)-0.5) plt.xticks(np.arange(0,len(col_name),1), col_name) plt.yticks(np.arange(0,len(row_name),1), row_name) ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('top') ax.invert_yaxis() ax.set_title('No.{}'.format(j+1),fontsize=12,color='k',loc='left',y=0.86,x=0.3,fontweight='bold') ax.set_title('{}{}{}'.format(seq1_align_set[j],'\n',seq2_align_set[j]),fontsize=16,fontfamily ='monospace',color='k',fontweight='bold',y=0.83,x=0.7) # plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (6, 6) plt.savefig('nw_No.{}'.format(j+1)+'.png',dpi=300) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
Smith Waterman算法
局部比对的和全局比对差不多,只需再几个小细节上改改就行,大家可以在两个代码之间找找茬~
完整代码
NW
import numpy as np sequence_1 = "AACGTACTCAAGTCT" sequence_2 = "TCGTACTCTAACGAT" match = 9 mismatch = -6 gap = -2 # 创建得分矩阵,行数为第一条序列长度加一,列数为第二条序列长度加二 Score = np.zeros((len(sequence_1) + 1, len(sequence_2) + 1)) # 创建是否匹配的矩阵,这个矩阵的长宽就分别是两条序列的长度了。如果匹配了,对应的格子就是匹配的得分,反之就是不匹配的得分 Match_or_not = np.zeros((len(sequence_1), len(sequence_2))) for i in range(len(sequence_1)): for j in range(len(sequence_2)): if sequence_1[i] == sequence_2[j]: Match_or_not[i][j] = match else: Match_or_not[i][j] = mismatch # 填得分矩阵 # 第一步:初始化第一行和第一列 for i in range(len(sequence_1) + 1): Score[i][0] = i * gap for j in range(len(sequence_2) + 1): Score[0][j] = j * gap # 第二步:动态规划的思想算每个格子的得分,每个格子需要考虑其左、上、左上的值,也可以说是考虑序列一、序列二引入空缺或直接匹配的最大值 for i in range(1, len(sequence_1) + 1): for j in range(1, len(sequence_2) + 1): Score[i][j] = max(Score[i - 1][j - 1] + Match_or_not[i - 1][j - 1], Score[i - 1][j] + gap, Score[i][j - 1] + gap) # 开始回溯 ''' 我们需要考虑的是可能会有多条回溯路径。 全局比对的回溯是从右下角开始,左上角结束,其中可能会有分叉点。 我们可以把右下角看成是一个树的根,矩阵中的每个值看成是一个节点。 每个节点都可能会有三个子节点:左,上,对角线。分别对应了回溯的方向。 而整个回溯的过程也就是遍历这颗三叉树的过程,严谨的说是从根节点遍历每个叶子节点的过程。 ''' class Node: # 用类来建立三叉树节点,属性包括了行、列、得分、左子树、上子树、对角线子树 def __init__(self, row=None, col=None, score=None): self.row = row self.col = col self.score = score self.left = None self.up = None self.diag = None def isLeaf(self): # 判断是否是叶子节点 return self.left is None and self.up is None and self.diag is None # 递归的函数查找从根节点到每个叶节点的路径 # 回溯路径的个数、回溯路径中的行号和列号 traceback_pathway_number = 0 traceback_pathway_row = [[]] traceback_pathway_col = [[]] def SaveRootToLeafPaths(Node, path_row, path_col): # 如果没有子树了 if Node is None: return # 包含当前节点的路径 path_row.append(Node.row) path_col.append(Node.col) global traceback_pathway_number global traceback_pathway_row global traceback_pathway_col # 如果找到叶节点,保存路径 if isLeaf(Node): if traceback_pathway_number == 0: traceback_pathway_row[traceback_pathway_number] = list(path_row) traceback_pathway_col[traceback_pathway_number] = list(path_col) else: traceback_pathway_row += [list(path_row)] traceback_pathway_col += [list(path_col)] traceback_pathway_number += 1 # 递归左、上、对角子树 SaveRootToLeafPaths(Node.left, path_row, path_col) SaveRootToLeafPaths(Node.up, path_row, path_col) SaveRootToLeafPaths(Node.diag, path_row, path_col) # 回溯,出栈 path_row.pop() path_col.pop() # 建立三叉树,为 Score 矩阵里所有值都找到它的左、上、对角子树,用一个二位列表来存储节点 NodeTree = [[Node() for _ in range(len(sequence_2) + 1)] for _ in range(len(sequence_1) + 1)] # 先把节点们的行号列号和得分记录下来 for i in range(len(sequence_1) + 1): for j in range(len(sequence_2) + 1): NodeTree[i][j].row = i NodeTree[i][j].col = j NodeTree[i][j].score = Score[i][j] # 设置第一列和第一行的节点的上子树和左子树(其实也能在下面这个大循环里设置,但是这样可读性更高) for i in range(1, len(sequence_1) + 1): NodeTree[i][0].up = NodeTree[i - 1][0] for j in range(1, len(sequence_2) + 1): NodeTree[0][j].left = NodeTree[0][j - 1] # 设置剩下的节点 for i in range(1, len(sequence_1) + 1): for j in range(1, len(sequence_2) + 1): if (Score[i][j] == Score[i - 1][j - 1] + Match_or_not[i - 1][j - 1]): NodeTree[i][j].diag = NodeTree[i - 1][j - 1] if (Score[i][j] == Score[i - 1][j] + gap): NodeTree[i][j].up = NodeTree[i - 1][j] if (Score[i][j] == Score[i][j - 1] + gap): NodeTree[i][j].left = NodeTree[i][j - 1] # 遍历树并保存路径 SaveRootToLeafPaths(NodeTree[len(sequence_1)][len(sequence_2)], [], []) # 改成numpy的ndarray类型,更加方便! traceback_pathway_row = np.array(traceback_pathway_row) traceback_pathway_col = np.array(traceback_pathway_col) # 记录一下回溯时走不走左边或上边,如果走就记为1,不走就记为0 Go_left = traceback_pathway_col[:, range(traceback_pathway_col.shape[1] - 1)] - traceback_pathway_col[:, range(1, traceback_pathway_col.shape[ 1])] Go_up = traceback_pathway_row[:, range(traceback_pathway_row.shape[1] - 1)] - traceback_pathway_row[:, range(1, traceback_pathway_row.shape[1])] # 用列表来存储序列一和序列二比对后的结果 seq1_align_set = [] seq2_align_set = [] print("总共有{}个比对结果".format(traceback_pathway_number)) for tpn in range(traceback_pathway_number): ''' 下面其实就是经典的nw回溯的代码了,这部分的原理可以参考nw算法回溯的伪代码。 唯一不同的就是我们是多条回溯路径,所以有多少条路经就得循环多少次。 值得一提的是,回溯过去的序列是逆序的, 在python中字符串逆置十分方便,只需要合理利用切片,如:str[::-1]即可。 ''' seq1_align = '' seq2_align = '' i = len(sequence_1) j = len(sequence_2) k = 0 while i > 0 or j > 0: if i > 0 and j > 0 and Go_left[tpn][k] and Go_up[tpn][k]: seq1_align += sequence_1[i - 1] seq2_align += sequence_2[j - 1] i -= 1 j -= 1 elif i > 0 and not (Go_left[tpn][k]) and Go_up[tpn][k]: seq1_align += sequence_1[i - 1] seq2_align += '-' i -= 1 elif j > 0 and Go_left[tpn][k] and not (Go_up[tpn][k]): seq1_align += '-' seq2_align += sequence_2[j - 1] j -= 1 k += 1 seq1_align_set += [seq1_align[::-1]] seq2_align_set += [seq2_align[::-1]] print("下面是第{}个".format(tpn + 1)) print(seq1_align[::-1]) print(seq2_align[::-1]) print(' ') #%% ''' 下面就是得分矩阵的热图以及回溯路径(格子)画出来了 ''' import pandas as pd import seaborn as sns from matplotlib import pyplot as plt Score = pd.DataFrame(Score) row_name = list(sequence_1) row_name.insert(0, ' ') col_name = list(sequence_2) col_name.insert(0, ' ') Score.index = row_name Score.columns = col_name traceback_way_mat = np.ones([len(sequence_1) + 1, len(sequence_2) + 1]) for i in range(traceback_pathway_row.shape[0]): traceback_way_mat[traceback_pathway_row[i][:], traceback_pathway_col[i][:]] = 0 ax1 = sns.heatmap(Score, linecolor='white', linewidth=0, square=True, cmap="RdBu_r", annot=True) plt.savefig('nw_Heatmap with annotation.png',dpi=300) plt.show() ax2 = sns.heatmap(Score, linecolor='white', linewidth=0, square=True, cmap="RdBu_r") plt.savefig('nw_Heatmap.png',dpi=300) plt.show() ax3 = sns.heatmap(Score, linecolor='white', linewidth=0, square=True, cmap="RdBu_r", mask=traceback_way_mat) plt.savefig('nw_Heatmap_traceback',dpi=300) plt.show() #%% # params={'font.family':'serif', # 'font.serif':'Times New Roman', # 'font.style':'normal',#'italic' # 'font.weight':'normal', #or 'blod' # 'font.size':12,#or large,small # 'figure.figsize':(6,6) # } plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (6, 6) # plt.rcParams.update(params) for j in range(traceback_pathway_col.shape[0]): fig = plt.figure() ax = plt.axes() plt.grid(zorder=0, linestyle='-.') for i in range(traceback_pathway_col.shape[1]-1): xs = traceback_pathway_col[j][i] ys = traceback_pathway_row[j][i] xe = traceback_pathway_col[j][i+1] ye = traceback_pathway_row[j][i+1] ax.arrow(xs, ys, xe-xs, ye-ys, length_includes_head=True,head_width=0.3, fc='crimson', ec='hotpink',zorder=10) ax.set_xlim(-0.5, len(col_name)-0.5) ax.set_ylim(-0.5, len(col_name)-0.5) plt.xticks(np.arange(0,len(col_name),1), col_name) plt.yticks(np.arange(0,len(row_name),1), row_name) ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('top') ax.invert_yaxis() ax.set_title('No.{}'.format(j+1),fontsize=12,color='k',loc='left',y=0.86,x=0.3,fontweight='bold') ax.set_title('{}{}{}'.format(seq1_align_set[j],'\n',seq2_align_set[j]),fontsize=16,fontfamily ='monospace',color='k',fontweight='bold',y=0.83,x=0.7) # plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (6, 6) plt.savefig('nw_No.{}'.format(j+1)+'.png',dpi=300) plt.show() import datetime print("这是代码执行时间: ",datetime.datetime.now())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
SW
import numpy as np sequence_1 = "AACGTACTCAAGTCT" sequence_2 = "TCGTACTCTAACGAT" match = 9 mismatch = -6 gap = -2 # 创建得分矩阵,行数为第一条序列长度加一,列数为第二条序列长度加二 Score = np.zeros((len(sequence_1) + 1, len(sequence_2) + 1)) # 创建是否匹配的矩阵,这个矩阵的长宽就分别是两条序列的长度了。如果匹配了,对应的格子就是匹配的得分,反之就是不匹配的得分 Match_or_not = np.zeros((len(sequence_1), len(sequence_2))) for i in range(len(sequence_1)): for j in range(len(sequence_2)): if sequence_1[i] == sequence_2[j]: Match_or_not[i][j] = match else: Match_or_not[i][j] = mismatch # 填得分矩阵 # 第一步:初始化第一行和第一列 for i in range(len(sequence_1) + 1): Score[i][0] = 0 for j in range(len(sequence_2) + 1): Score[0][j] = 0 # 第二步:动态规划的思想算每个格子的得分,每个格子需要考虑其左、上、左上的值,也可以说是考虑序列一、序列二引入空缺或直接匹配的最大值 for i in range(1, len(sequence_1) + 1): for j in range(1, len(sequence_2) + 1): Score[i][j] = max(Score[i - 1][j - 1] + Match_or_not[i - 1][j - 1], Score[i - 1][j] + gap, Score[i][j - 1] + gap, 0) # 开始回溯 ''' 我们需要考虑的是可能会有多条回溯路径。 全局比对的回溯是从右下角开始,左上角结束,其中可能会有分叉点。 我们可以把右下角看成是一个树的根,矩阵中的每个值看成是一个节点。 每个节点都可能会有三个子节点:左,上,对角线。分别对应了回溯的方向。 而整个回溯的过程也就是遍历这颗三叉树的过程,严谨的说是从根节点遍历每个叶子节点的过程。 ''' class Node: # 用类来建立三叉树节点,属性包括了行、列、得分、左子树、上子树、对角线子树 def __init__(self, row=None, col=None, score=None): self.row = row self.col = col self.score = score self.left = None self.up = None self.diag = None def isLeaf(self): # 判断是否是叶子节点 return self.left is None and self.up is None and self.diag is None # 递归的函数查找从根节点到每个叶节点的路径 # 回溯路径的个数、回溯路径中的行号和列号 traceback_pathway_number = 0 traceback_pathway_row = [[]] traceback_pathway_col = [[]] def SaveRootToLeafPaths(Node, path_row, path_col): # 如果没有子树了 if Node is None: return # 包含当前节点的路径 path_row.append(Node.row) path_col.append(Node.col) global traceback_pathway_number global traceback_pathway_row global traceback_pathway_col # 如果找到叶节点,保存路径 if isLeaf(Node): if traceback_pathway_number == 0: traceback_pathway_row[traceback_pathway_number] = list(path_row) traceback_pathway_col[traceback_pathway_number] = list(path_col) else: traceback_pathway_row += [list(path_row)] traceback_pathway_col += [list(path_col)] traceback_pathway_number += 1 # 递归左、上、对角子树 SaveRootToLeafPaths(Node.left, path_row, path_col) SaveRootToLeafPaths(Node.up, path_row, path_col) SaveRootToLeafPaths(Node.diag, path_row, path_col) # 回溯,出栈 path_row.pop() path_col.pop() # 建立三叉树,为 Score 矩阵里所有值都找到它的左、上、对角子树,用一个二位列表来存储节点 NodeTree = [[Node() for _ in range(len(sequence_2) + 1)] for _ in range(len(sequence_1) + 1)] # 先把节点们的行号列号和得分记录下来 for i in range(len(sequence_1) + 1): for j in range(len(sequence_2) + 1): NodeTree[i][j].row = i NodeTree[i][j].col = j NodeTree[i][j].score = Score[i][j] # 设置第一列和第一行的节点的上子树和左子树(其实也能在下面这个大循环里设置,但是这样可读性更高) for i in range(1, len(sequence_1) + 1): NodeTree[i][0].up = NodeTree[i - 1][0] for j in range(1, len(sequence_2) + 1): NodeTree[0][j].left = NodeTree[0][j - 1] # 设置剩下的节点 for i in range(1, len(sequence_1) + 1): for j in range(1, len(sequence_2) + 1): if (Score[i][j] == Score[i - 1][j - 1] + Match_or_not[i - 1][j - 1]): NodeTree[i][j].diag = NodeTree[i - 1][j - 1] if (Score[i][j] == Score[i - 1][j] + gap): NodeTree[i][j].up = NodeTree[i - 1][j] if (Score[i][j] == Score[i][j - 1] + gap): NodeTree[i][j].left = NodeTree[i][j - 1] # 遍历树并保存路径 r, c = np.where(Score == np.max(Score)) SaveRootToLeafPaths(NodeTree[int(r)][int(c)], [], []) # 改成numpy的ndarray类型,更加方便! traceback_pathway_row = np.array(traceback_pathway_row) traceback_pathway_col = np.array(traceback_pathway_col) # 记录一下回溯时走不走左边或上边,如果走就记为1,不走就记为0 Go_left = traceback_pathway_col[:, range(traceback_pathway_col.shape[1] - 1)] - traceback_pathway_col[:, range(1, traceback_pathway_col.shape[ 1])] Go_up = traceback_pathway_row[:, range(traceback_pathway_row.shape[1] - 1)] - traceback_pathway_row[:, range(1, traceback_pathway_row.shape[1])] # 用列表来存储序列一和序列二比对后的结果 seq1_align_set = [] seq2_align_set = [] print("总共有{}个比对结果".format(traceback_pathway_number)) for tpn in range(traceback_pathway_number): ''' 下面其实就是经典的nw回溯的代码了,这部分的原理可以参考nw算法回溯的伪代码。 唯一不同的就是我们是多条回溯路径,所以有多少条路经就得循环多少次。 值得一提的是,回溯过去的序列是逆序的, 在python中字符串逆置十分方便,只需要合理利用切片,如:str[::-1]即可。 ''' seq1_align = '' seq2_align = '' i = int(r) j = int(c) k = 0 while Score[i][j] > 0: # waterman修改条件,到零结束 if k < traceback_pathway_col.shape[1] - 1: if Go_left[tpn][k] and Go_up[tpn][k]: seq1_align += sequence_1[i - 1] seq2_align += sequence_2[j - 1] i -= 1 j -= 1 elif not (Go_left[tpn][k]) and Go_up[tpn][k]: seq1_align += sequence_1[i - 1] seq2_align += '-' i -= 1 elif Go_left[tpn][k] and not (Go_up[tpn][k]): seq1_align += '-' seq2_align += sequence_2[j - 1] j -= 1 k += 1 seq1_align_set += [seq1_align[::-1]] seq2_align_set += [seq2_align[::-1]] print("下面是第{}个".format(tpn + 1)) print(seq1_align[::-1]) print(seq2_align[::-1]) print(' ') #%% ''' 下面就是得分矩阵的热图以及回溯路径(格子)画出来了 ''' import pandas as pd import seaborn as sns from matplotlib import pyplot as plt Score = pd.DataFrame(Score) row_name = list(sequence_1) row_name.insert(0, ' ') col_name = list(sequence_2) col_name.insert(0, ' ') Score.index = row_name Score.columns = col_name traceback_way_mat = np.ones([len(sequence_1) + 1, len(sequence_2) + 1]) for i in range(traceback_pathway_row.shape[0]): traceback_way_mat[traceback_pathway_row[i][:], traceback_pathway_col[i][:]] = 0 ax1 = sns.heatmap(Score, linecolor='white', linewidth=0, square=True, cmap="RdBu_r", annot=True) plt.savefig('sw_Heatmap with annotation.png',dpi=300) plt.show() ax2 = sns.heatmap(Score, linecolor='white', linewidth=0, square=True, cmap="RdBu_r") plt.savefig('sw_Heatmap.png',dpi=300) plt.show() ax3 = sns.heatmap(Score, linecolor='white', linewidth=0, square=True, cmap="RdBu_r", mask=traceback_way_mat) plt.savefig('sw_Heatmap_traceback',dpi=300) plt.show() #%% plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (6, 6) for j in range(traceback_pathway_col.shape[0]): fig = plt.figure() ax = plt.axes() plt.grid(zorder=0, linestyle='-.') for i in range(traceback_pathway_col.shape[1]-2): xs = traceback_pathway_col[j][i] ys = traceback_pathway_row[j][i] xe = traceback_pathway_col[j][i+1] ye = traceback_pathway_row[j][i+1] ax.arrow(xs, ys, xe-xs, ye-ys, length_includes_head=True,head_width=0.3, fc='crimson', ec='hotpink',zorder=10) ax.set_xlim(-0.5, len(col_name)-0.5) ax.set_ylim(-0.5, len(col_name)-0.5) plt.xticks(np.arange(0,len(col_name),1), col_name) plt.yticks(np.arange(0,len(row_name),1), row_name) ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('top') ax.invert_yaxis() # ax.set_title('No.{}'.format(j+1),fontsize=12,color='k',loc='left') ax.set_title('No.{}'.format(j + 1), fontsize=12, color='k', loc='left', y=0.86, x=0.38, fontweight='bold') ax.set_title('{}{}{}'.format(seq1_align_set[j], '\n', seq2_align_set[j]), fontsize=16, fontfamily='monospace', color='k', fontweight='bold', y=0.83, x=0.7) plt.savefig('sw_No.{}'.format(j+1)+'.png',dpi=300) plt.show() import datetime print("这是代码执行时间: ",datetime.datetime.now())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
-
相关阅读:
2024如何恢复旧版的Chrome的主题样式
期货开户保证金能极端行情保安全
k8s网络模型介绍:pod内/间通信
Linux内存管理——段页式访问
ffmpeg sdk 视频合成
大学生HTML作业节日网页 HTML作业节日文化网页期末作业 html+css+js节日网页 HTML学生节日介绍 HTML学生作业网页视频
142.如何个性化推荐系统设计-2
python语法糖-推导式
Ubuntu下搭建NFS
[EIS 2019]EzPOP
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/dream_of_grass/article/details/127931152
