-
《数据结构》顺序表ArrayList
《数据结构》顺序表ArrayList
什么是顺序表:
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储,在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表通过控制数组中的有效数据个数,进而包装成一个连续存储数据元素的线性结构.
模拟实现顺序表(以int类型为例)
import java.util.*; class MyArraylist{ public int size; public int[] elem; MyArraylist(){ elem = new int[0]; } MyArraylist(int n){ elem = new int[n]; } private boolean isfull(){ return size==elem.length; } private boolean checkpos(int pos){ if(pos<0||pos>=size){ return false; } return true; } public boolean isempty(){ return size==0; } public void display(){ for(int i = 0;i < size;i++){ System.out.print(elem[i]+" "); } } public void add(int x){ if(isempty()){ elem = new int[10]; } if(isfull()){ elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,elem.length*2); } elem[size] = x; size++; } public void add(int x,int pos){ if(isempty()){ elem = new int[10]; } if(isfull()){ elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,elem.length*2); } if(checkpos(pos)){ for(int i = size;i>pos;i--){ elem[i] = elem[i-1]; } elem[pos] = x; size++; }else{ System.out.println("pos下标不合法"); } } public boolean contains(int tofind){ if(isempty()){ System.out.println("顺序表为空,查找失败"); } for(int i = 0;i < size;i++){ if(elem[i]==tofind){ return true; } } return false; } //返回数值k的下标 public int indexOf(int k){ if(isempty()){ System.out.println("顺序表为空,查找失败"); } for(int i = 0;i < size;i++){ if(elem[i]==k){ return i; } } return -1; } //得到pos下标的值 public int get(int pos){ if(!checkpos(pos)){ System.out.println("pos下标不合法"); } return elem[pos]; } public void set(int x,int pos){ if(!checkpos(pos)){ System.out.println("pos下标不合法"); }else{ elem[pos] = x; } } public void remove(int k){ if(!checkpos(k)){ System.out.println("pos下标不合法"); }else{ for(int i = k;i<size;i++){ elem[i] = elem[i+1]; } size--; } } public int size(){ return size; } public void clean(){ size = 0; } } public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ MyArraylist arraylist = new MyArraylist(); arraylist.add(1); arraylist.add(2); arraylist.add(1); arraylist.add(2); arraylist.add(1); arraylist.add(2); //arraylist.display(); arraylist.add(3,2); arraylist.display(); arraylist.remove(2); arraylist.display(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
值得注意的是:
在我们的remove和clean方法中,如果删除的元素是引用类型时,需要把这个要被删除的元素置为null,防止出现内存泄露的问题.一般而言,对于pos指针不合法,或者顺序表为空无法查询的情况,我们也可以通过抛出异常来终止本次操作并提醒程序员.
详解ArrayList:
ArrayList实现的接口:

-
ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,表明ArrayList支持随机访问
-
ArrayList实现了Cloneable接口,表明ArrayList是可以clone的
-
ArrayList实现了Serializable接口,表明ArrayList是支持序列化的
-
ArrayList不是线程安全的,可以在单线程使用.
ArrayList的构造方法:
-
ArrayList()
-
ArrayList(Collection c) 利用其他 Collection 构建 ArrayList
-
ArrayList(int initialCapacity) 指定顺序表初始容量
对源码的解析:
对于ArrayList():
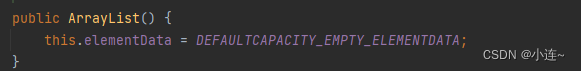

我们可以很明显的得出,使用ArrayList构造出来的顺序表,底层是一个空数组,没有容量.
对于ArrayList(Collection c):
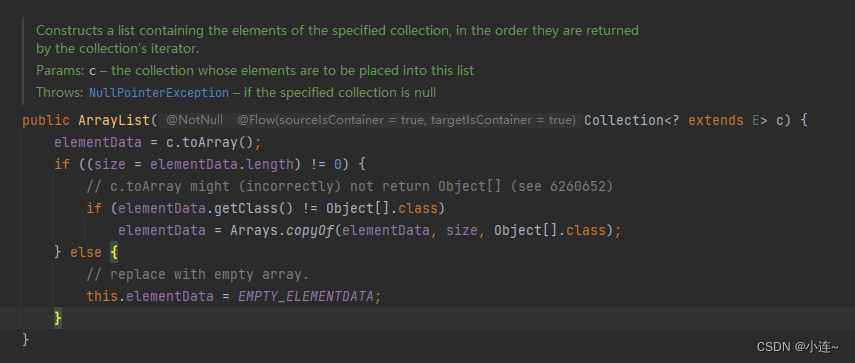
首先.这个构造方法会将接受的c转化为数组存入elem中,并且如果该数组的大小为空,则直接生成一个空数组来作为底层数组,如果不为空 这会判断这个数组是不是一个Object数组,如果是一个Object数组,则不需要进行拷贝了,已经赋值成功了,如果不是一个Object数组,则需要进行拷贝.
对于ArrayList(int initialCapacity)
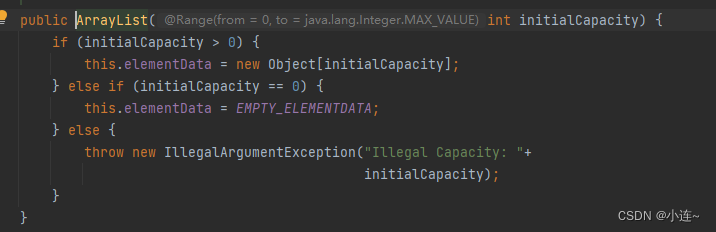
作用比较单一 ,传入的int是多大,那么底层数组的容量就是多大.
ArrayList的方法
方法 解释 boolean add(E e) 尾插 e void add(int index, E element) 将 e 插入到 index 位置 boolean addAll(Collection c) 尾插 c 中的元素 E remove(int index) 删除 index 位置元素 boolean remove(Object o) 删除遇到的第一个 o E get(int index) 获取下标 index 位置元素 E set(int index, E element) 将下标 index 位置元素设置为 element void clear() 清空 boolean contains(Object o) 判断 o 是否在线性表中 int indexOf(Object o) 返回第一个 o 所在下标 int lastIndexOf(Object o) 返回最后一个 o 的下标 List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) 截取部分 list ArrayList的扩容机制
为了ArrayList的动态存储,对于数组的长度采用的动态扩容的机制.
源码
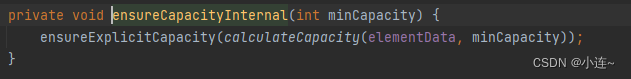
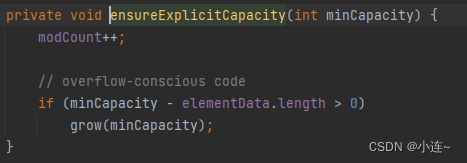
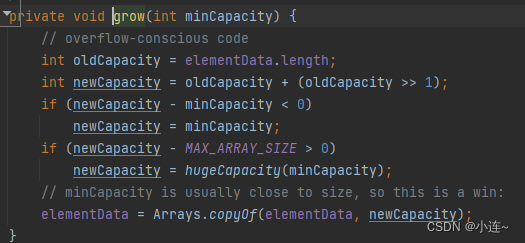
重点关注grow()
private void grow(int minCapacity) { // 获取旧空间大小 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 预计按照1.5倍方式扩容 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 如果用户需要扩容大小 超过 原空间1.5倍,按照用户所需大小扩容 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; // 如果需要扩容大小超过MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,重新计算容量大小 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // 调用copyOf扩容 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { // 如果minCapacity小于0,抛出OutOfMemoryError异常 if (minCapacity < 0) throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
在确保数组已经无法存下元素之后,并且用户需要扩容的数值没有问题的情况下,grow保证了ArrayList的动态扩容机制
-
初步预估按照1.5倍大小扩容
-
如果用户所需大小超过预估1.5倍大小,则按照用户所需大小扩容
-
真正扩容之前检测是否能扩容成功,防止太大导致扩容失败
实现了ArrayList 的1.5倍扩容
ArrayList的缺陷
-
顺序表中间/头部的插入删除,时间复杂度为O(N)
-
增容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间。会有不小的消耗
-
相关阅读:
Unity 获取桌面路径的方法
java80-GULqq界面
如何实现一个K8S DevicePlugin?
【仿牛客网笔记】 Spring Boot进阶,开发社区核心功能-显示评论
算法每日一题(python,2024.05.27) day.9
TIOBE 5 月榜单揭晓:哪些编程语言正在上升?
Java虚拟机面试问题
95后大厂程序员删库被判刑,只因项目被接手对领导心生不满
服务端Skynet(一)——源码浅析
NOIP 模拟赛 长寿花 题解
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/simple_person/article/details/127914180
